11 Data Transmission
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Data Transmission
The process of sending and receiving data across a network.
The Internet
Global network of interconnected computers.
Infrastructure
Underlying physical and virtual systems that enable connectivity, transmission and communication.
Network Devices
Essential hardware components to manage data flow.
Protocols and standards
Rules and conventions that govern how data is transmitted.
Wireless systems
Cellular networks and Wi-Fi that allow for mobile and local access.
Internet Exchange Points (IXPs)
Locations where different networks connect and exchange traffic improving efficiency and connectivity.
HTTP
Hypertext transfer protocol.
IP
Internet protocol.
TCP
Transmission control protocol.
FTP
File transfer protocol.
VoIP
Voice over internet protocol.
POP3
Post office protocol 3.
SMTP
Simple message transfer protocol.
Data Packets
Essential units of data used in networking to facilitate efficient communication.
Contents of a Packet
Includes source address, destination address, sequence number, control signals, and error control bits.
Source Address
Address of the origin of the packets.
Destination Address
Device intended to receive the packet.
Sequence Number
Used to keep track of the order of the packets during transmission.
Control Signals
Indicate various types of information that manage the transmission process.
Error Control Bits
Used for error detection and correction.
Checksum
Used for error detection by adding together the binary values using a mathematical algorithm.
Parity Bits
Simple error checking that adds an extra bit to indicate the number of set bits is odd or even.
Serial Transmission
Data is sent one bit at a time over a single wire.
Synchronous Transmission
Data is sent in a continuous stream with both sender and receiver synchronized to a clock.
Asynchronous Transmission
Data is sent without a shared clock signal, framed with start/stop bits.
Parallel Transmission
Multiple bits are sent at the same time using multiple wires.
Duplexing
Methods of communication including simplex, half-duplex, and full-duplex.
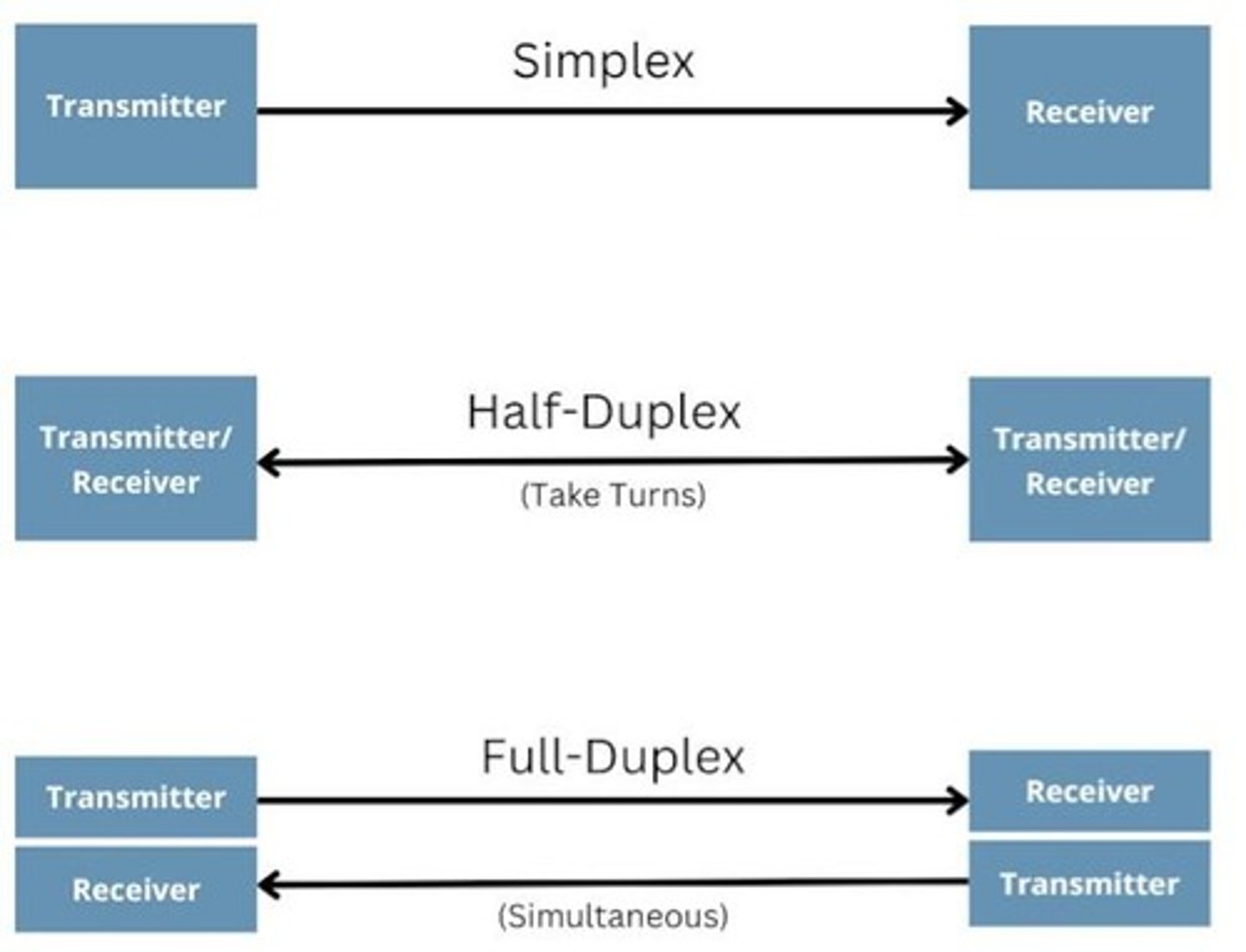
Simplex
Data can only be sent one way.
Half-Duplex
Data can be sent and received but only one at a time.
Full-Duplex
Data can be sent and received at the same time.
Multiplexing
Combines multiple signals or data into one over a shared medium.
Time-Division Multiplexing (TDM)
Each stream is assigned a time slot, which wastes bandwidth.
Circuit Switching
Establishes a dedicated communication path or circuit between two endpoints.
Packet Switching
Breaks down data into smaller packets sent over the network.
Routing Traffic
Determines the path data takes over a network using a route table.
Dijkstra's Algorithm
Calculates the lowest cost of the shortest path in a network.
CSMA/CD
Carrier Sense Multiple Access and Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) is the protocol to deal with collisions.
Collision Detection on Ethernet
On an ethernet network, collisions are detected by: A device transmits a signal when the medium is clear.
Collision Signal
If a collision occurs a collision signal is generated and is picked up by the sender.
Jam Signal
The sender transmits a jam signal which stops all transmissions of signal within affected areas.
Random Wait Time
The sender waits a random period of time before re-transmitting.
Bandwidth
Maximum amount of data that can be in a single cable.
Higher Bandwidth
Higher bandwidth allows for more data.
Bandwidth Measurement
Not a measure of speed.
Transmission Time
Transmission will always cross a cable in the same amount of time regardless of size.
Large Bandwidth Advantage
The advantage of having a larger bandwidth is that large files can be transferred without fragmentation.
Small Files Impact
Have no overall impact on the performance.
Bit Rate
Numerical expression of bandwidth.
High Bit Rate Requirement
High bit rate connections are required for large data to be sent in a short time.
Video Call Bit Rate
Video calls require high bit rate.
Low Bit Rate Impact
Low bit rate doesn't always impact the content delivery.
Network Connection
A device becomes a part of a vast network when connected.
Protocol Independence
Each network can decide its protocols.