All Advanced Higher Music Concepts
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Answer
In a fugue, after the subject is played, the same tune appears in another voice or part in the dominant (a 5th higher or a 4th lower) - this is called the answer
Anthem
Short sacred choral piece sung in English - sometimes sung by a choir unaccompanied and sometimes accompanied by organ, featuring solo parts
Antiphonal
Dialogue between voices or instruments - one group of voices or instruments answers the other

Appoggiatura
An ornament which sounds like a leaning note, takes half the value of the main note which follows it or two-thirds if the main note is dotted
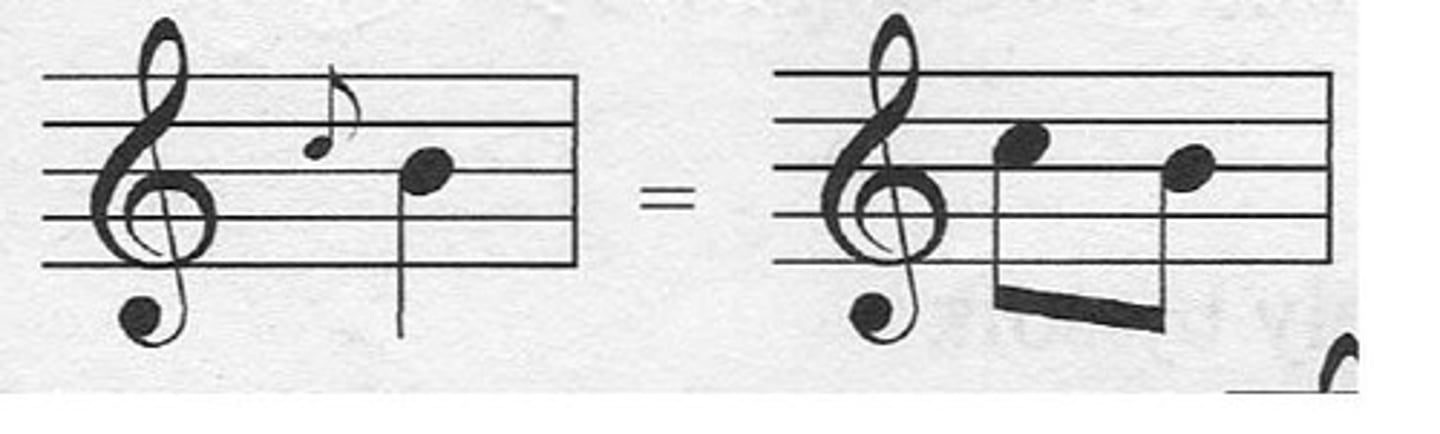

Augmented Triad
This chord is formed by a major triad in which the 5th degree is raised by a semitone
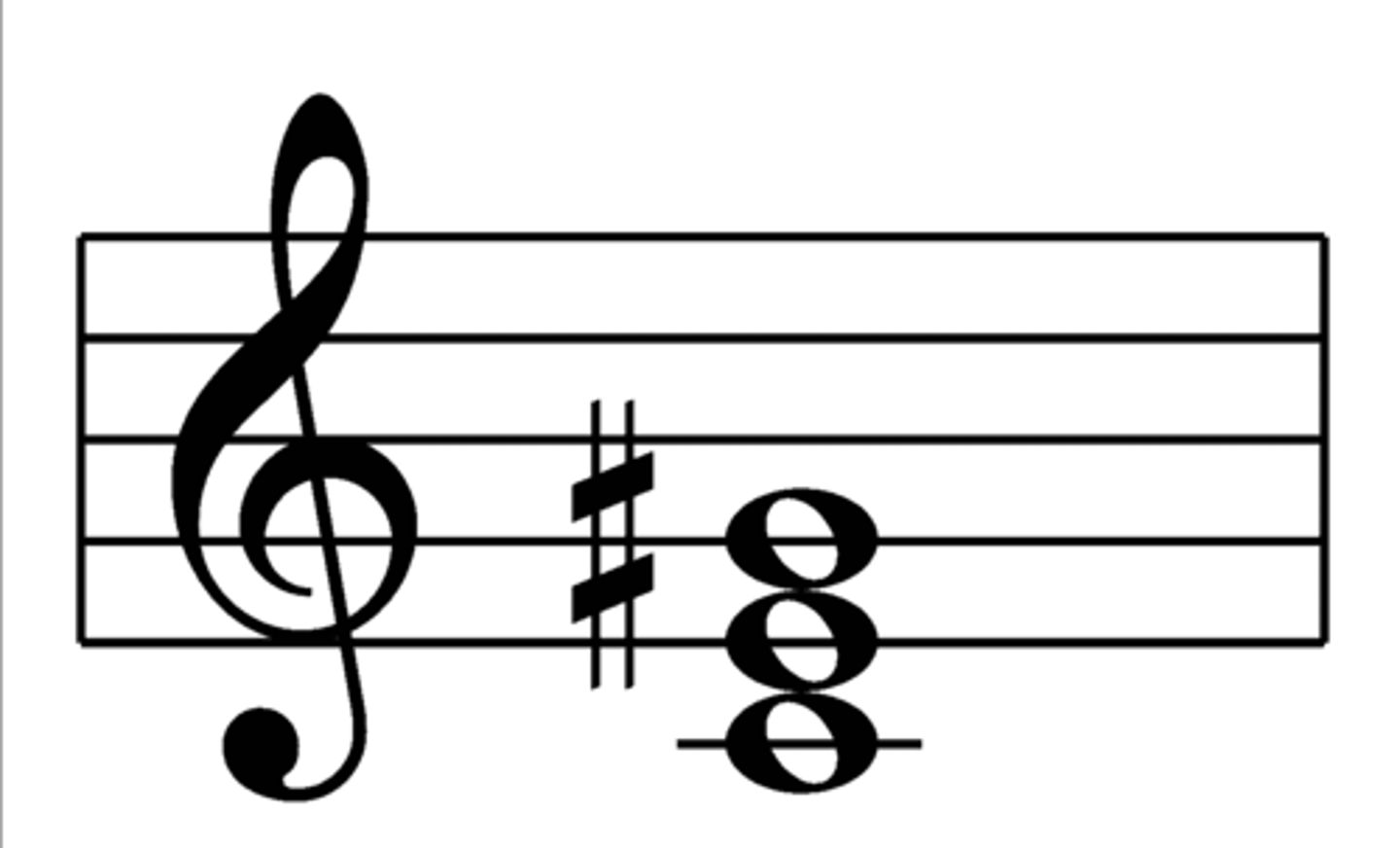
Ayre/Air
Song or simple melody, sometimes the title of a movement of a suite
Ballett
A type of madrigal in strophic form which was originally danced to - features a fa-la-la refrain at the end of each verse
Bridge
A link between two themes - in sonata form the bridge or transition links the first subject-group to the second subject-group and also modulates to the key of the second subject
Chorale
A German hymn tune, written in four parts for soprano, contralto (alto), tenor and bass
Chord II
In a major key, chord number two tends to be a minor chord
1st Inversion
When we alter the order of notes in a chord, we call it an inversion - C major chord I (CEG) if the bottom note (C) is moved to the top of the chord (EGC) we call this the first inversion
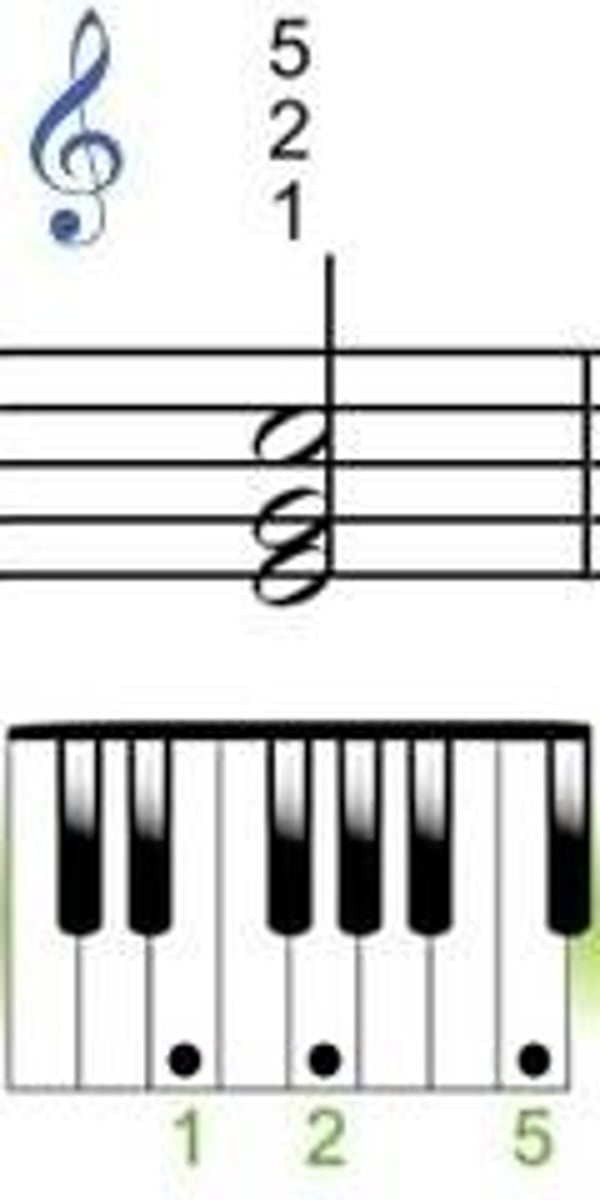

Chords I, IV, V and Vi in Major and Minor Keys
In a major key, it is normal for chords I, IV and V to be major chords - chord VI is normally a minor chord
Consort
Dance-like in style; this music could be played by solo instruments such a lutes, harpsichords or virginals, by small groups of instruments of the same family or a group of varied instruments from different families
Contemporary Jazz
Contemporary jazz is an umbrella term for all kinds of jazz music being played now - as well as jazz music of the 80s, 90s, 00s & 10s

Countersubject
In a fugue, after the subject or answer is played, the continuation of that same instrument or voice is called the countersubject
Countertenor
A male adult voice whose range is higher than a tenor's
Electronic Dance Music
Electronic dance music is normally heard in clubs where the DJ combines tracks electronically into one mix - it can encompass music of different genres including house music, dubstep, drum and bass

Fugue
A contrapuntal piece based on a theme (subject) announced in one voice part alone, then imitated by other voices in close succession
Galliard
A Renaissance court dance which follows the pavan - a galliard is quick and lively with three beats in a bar
Hemiola
A rhythmic device giving the impression of a piece of music changing from duple (2) to triple (3) time, or vice versa
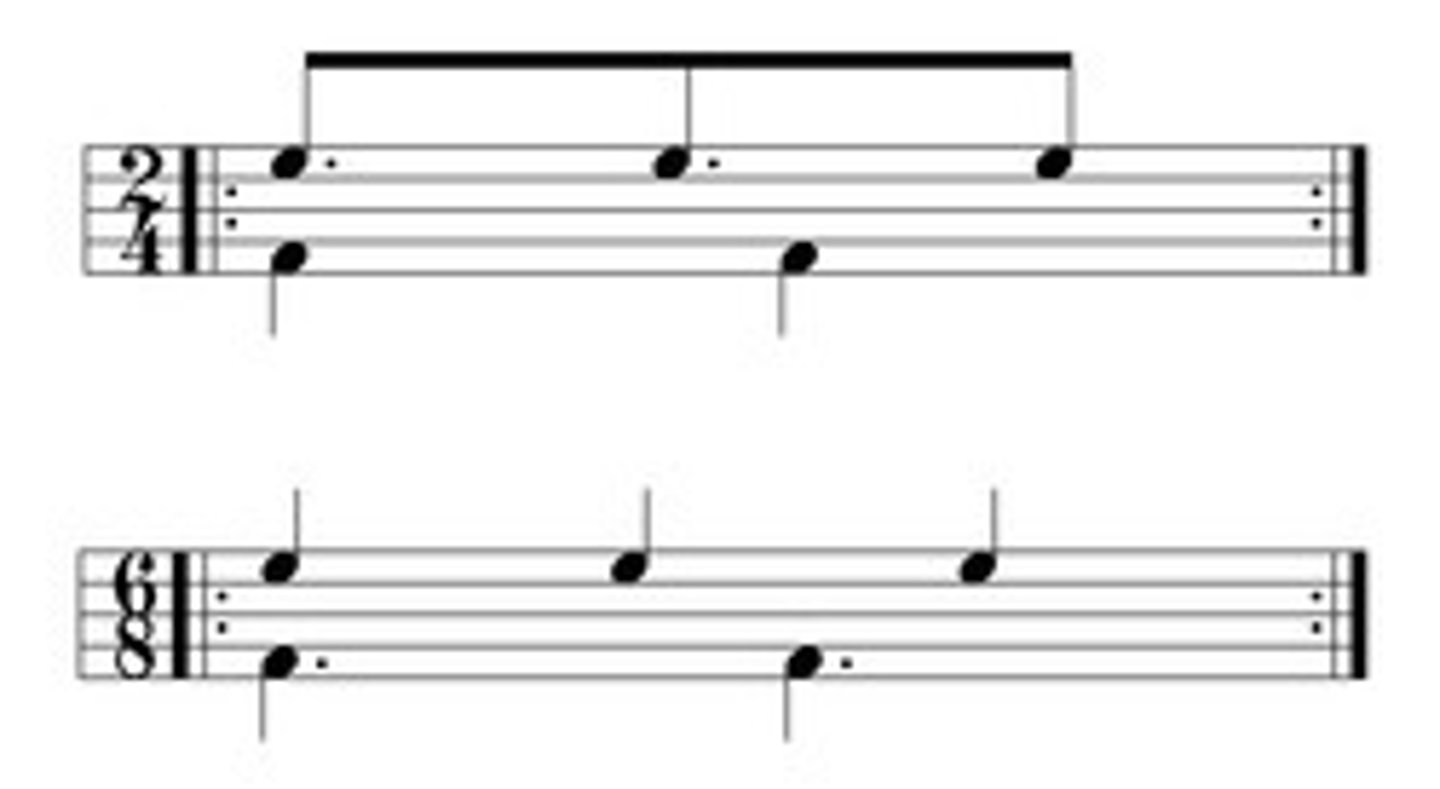

Inversion
An inverted chord is formed when a note other than the root is in the bass
Leitmotiv
A theme occurring throughout a work which represents a person, an event or an idea, etc
Madrigal
In the Renaissance era, this was a non-religious work, polyphonic in style, using imitation and sung a cappella in English

Motet
A sacred choral work with Latin text and polyphonic texture, usually sung a cappella
Nationalist
Music which incorporates elements of folk music of the composer's country - emerged about the second half of the 19th century and was a type of Romanticism
Neo-Classical
New classicism - from about 1929 onwards this style in music came about when composers reacted against Romanticism and wanted to return to the structures and styles of earlier periods but combined with dissonant, tonal and even atonal harmonies
Pavan
A Renaissance court dance linked with the galliard - the pavan is slow and stately with two beats in the bar
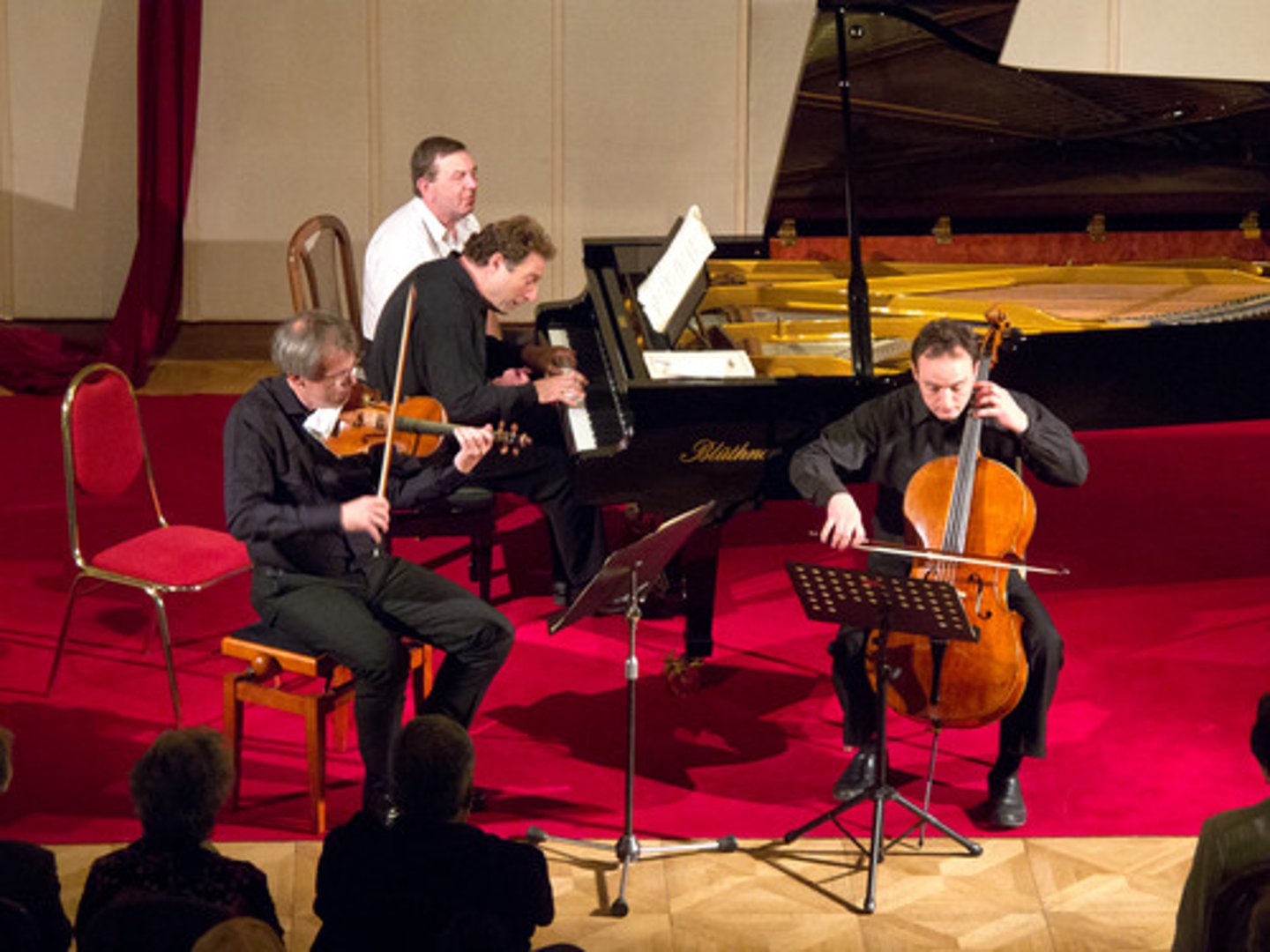
Piano Trio
A piano trio is a chamber music ensemble comprising of three instruments; the most common form comprises of a piano, violin and cello

Polytonality/Bitonality
The use of two (bitonality) or more keys (polytonality) played or sung at the same time
Renaissance
Period meaning 'rebirth', Renaissance (1400-1600 approx.) featured modes, plainchant and motets

Retrograde
To go backwards - a melody or a section of music can be written or performed from the end to the beginning
Serial
A 20th-century method of musical composition invented by Schoenberg in which the 12 notes of the Chromatic scale are organised into a series or tone row - this row can be transposed, inverted or played in retrograde, and forms the material basis for an entire work or movement
Song Cycle
A group of songs linked by a common theme or with a text written by the same author, usually accompanied by piano but sometimes by small ensembles or full orchestra

Sprechgesang
A technique used in vocal music where the singer is required to use the voice in an expressive manner half-way between singing and speaking
Stretto
Where voices or instruments enter very quickly one after the other, as in a fugue
Subject
The main theme in a composition, the main themes in sonata form, or the main theme on which a fugue is based
Suspension
This effect occurs when a note from one chord is held over to the next chord creating a discord, and is then resolved by moving one step to make a concord
Tone Row
An arrangement of the 12 notes of the octave which forms the basis of a composition
Tritone
Interval of an augmented 4th, e.g. C-F sharp or F-B - it is made up of three whole tones and sounds like 'The Simpsons'
Turn
Four notes which turn round the main note with the note above, the main note, the note below, and the main note again