Pharmacology: Module 1 (Nursing Process)
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
Nursing Process
Steps in the nursing process: Assessment, Analysis, Planning, Nursing interventions, Evaluation.
Clinical Judgment
The ability to recognize cues, analyze cues, prioritize hypotheses, generate solutions, take action, and evaluate outcomes.
Recognize cues
Identifying subjective and objective data.
Analyze cues and prioritize hypothesis
The process of analyzing cues and prioritizing patient problems.
Generate solutions
Identifying expected outcomes that are patient-centered, measurable, realistic, acceptable to both patient and nurse, and dependent on the patient's decision-making ability.
Take action
Involves patient teaching, addressing general information, side effects, self-administration, and assessing diet.
Evaluate outcomes
Determining if interventions and outcomes were met, if interventions were effective, ineffective, or made no difference, and documenting successful goal attainment.
ANA Code of Ethics
Developed as a guide for carrying out nursing responsibilities consistent with quality in nursing care and ethical obligations of the profession, adopted in 1950 and revised in 2015.
The Nurse's role in clinical research
Responsible for patient safety and integrity of research protocol.
Drug Standards
Includes the United States Pharmacopeia and the National Formulary, and is governed by federal legislation and Nurse Practice Acts.
U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA)
Responsible for drug scheduling and regulation.
Drug Names
Includes chemical names, generic names (required for NCLEX and exams), and brand/trade names.
Over-the-Counter Drugs
Drugs found to be safe and appropriate for use without direct supervision of a healthcare provider, available without a prescription.
FDA standardized OTC labeling
Implemented in 2002 to provide consumers with better information about benefits and risks of OTC drugs.
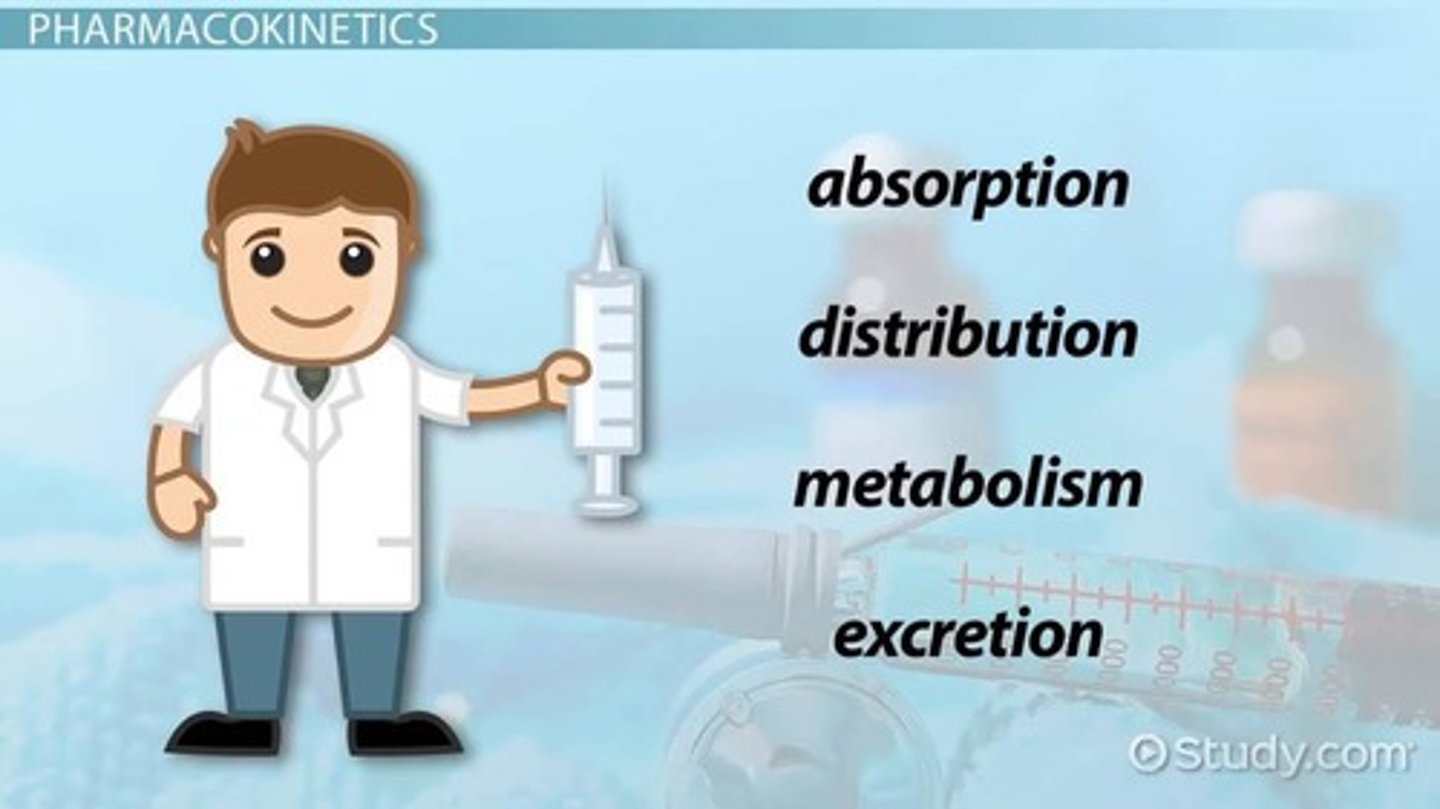
Pharmacokinetics
The study of drug movement through the body and what the body does to the drug, involving four processes: absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion.
Pharmacodynamics
What the drug does to the body as it moves throughout the body, involving receptor binding, postreceptor effects, and chemical reactions.
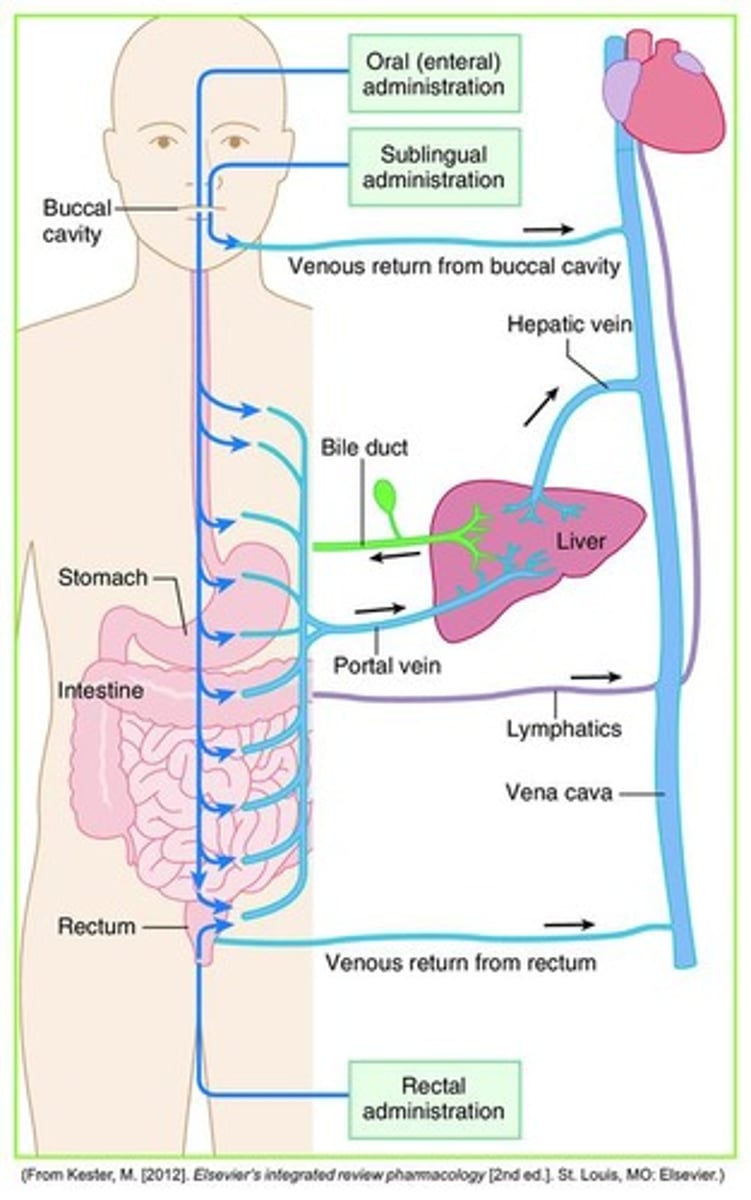
Drug absorption
The movement of the drug from the GI tract into the bloodstream, involving disintegration and dissolution.
First Pass Effect
The process of drug movement from the GI tract to the liver via the portal vein.
Drug response relationship
The body's physiologic response to changes in drug concentration at the site of action.
Potency
The amount of drug needed to produce a specific effect.
Maximal efficacy
The maximum effect that can be achieved with a drug.
Therapeutic index
The ratio of the toxic dose to the therapeutic dose of a drug.
Onset
The time it takes for a drug to reach minimum effective concentration.
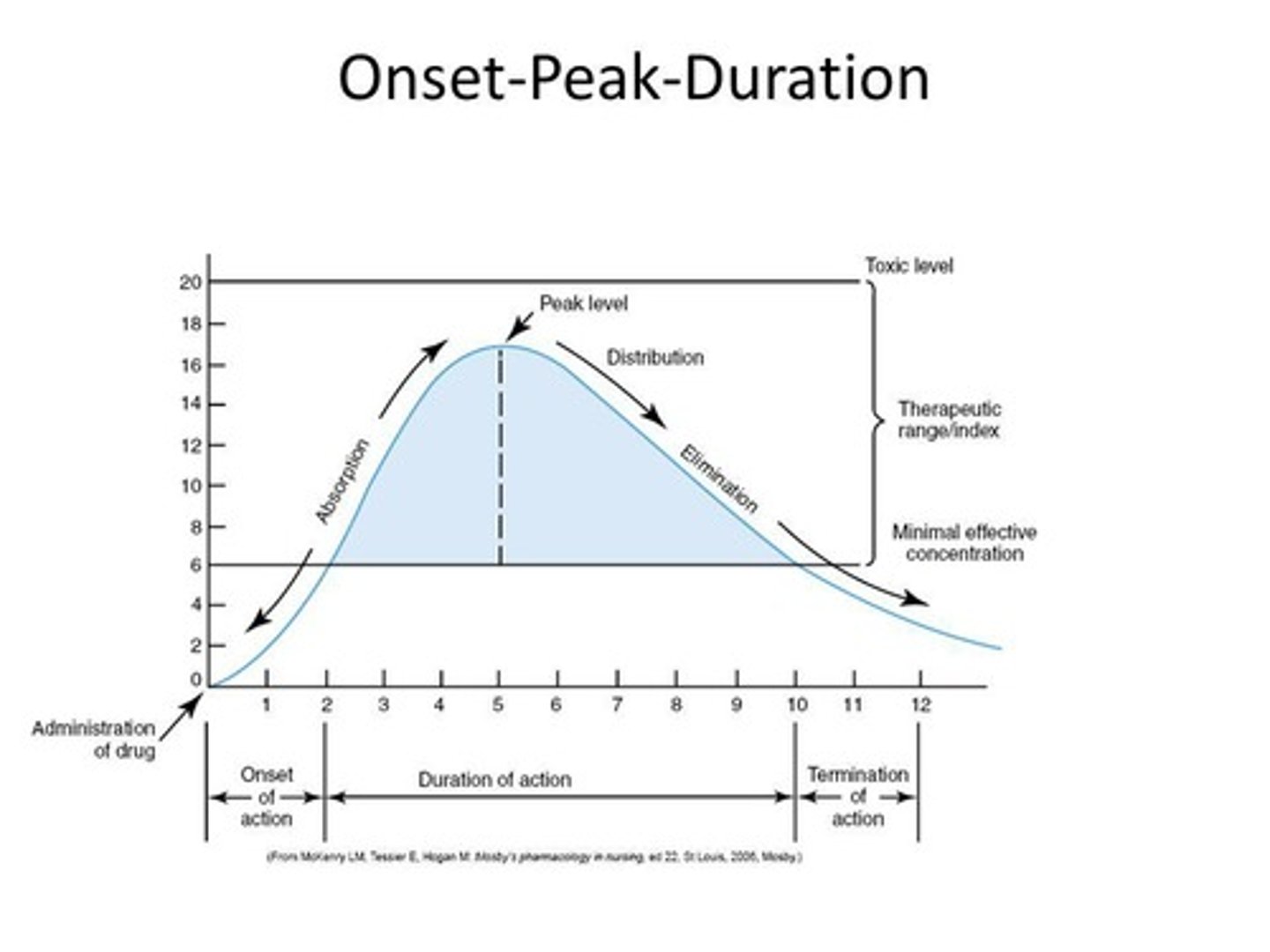
Peak
The highest concentration of a drug in the blood.
Duration
The length of time a drug exerts a therapeutic effect.
Peak drug level
highest plasma concentration of drug at a specific time
Trough drug level
lowest plasma concentration of drug
Agonists
Activate receptors and produce desired response
Partial Agonists
Elicit only moderate activity when binding to receptors and prevent receptor activation by other drugs
Antagonists
Prevent receptor activation and block response
Side effects
Secondary drug effects that can be mild to severe, unintentional, and unexpected
Adverse reactions
Undesirable effects that can range from mild to severe
Drug toxicity
Drug level exceeds therapeutic range
Tolerance
Decreased responsiveness to drug over course of therapy, requiring higher dose to achieve same therapeutic response
Tachyphlaxis
Acute, rapid decrease in response to a drug
Placebo effect
Drug response not attributed to drug's chemical properties
Additive drug effects
Sum of effects of two drugs
Synergistic drug effects
Effect of two drugs is much greater than effects of either drug alone
Antagonistic drug effects
One drug reduces or blocks effect of the other drug
Drug-nutrient interactions
Food may increase, decrease, or delay drug response
Drug-laboratory interactions
Drugs may cause misinterpretation of test results
Drug-induced photosensitivity
Drug induced skin reaction caused by sunlight exposure
Pharmacogenetics
Study of how a patient's genomes affect drug response, helping individualize optimal drug treatment regimens
Total body water (TBW)
60% of body weight in adults
Intracellular fluid
Fluid within cells
Extracellular fluid (ECF)
Fluid outside of cells, including interstitial fluid and intravascular fluid
Edema
Accumulation of fluid within the interstitial spaces caused by various factors
Sodium (Na+)
Primary ECF cation that regulates osmotic balance and nerve impulse conduction
Chloride (Cl-)
Primary ECF anion that regulates osmotic balance and plays a role in acid-base balance
Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
System that controls Na concentration through aldosterone
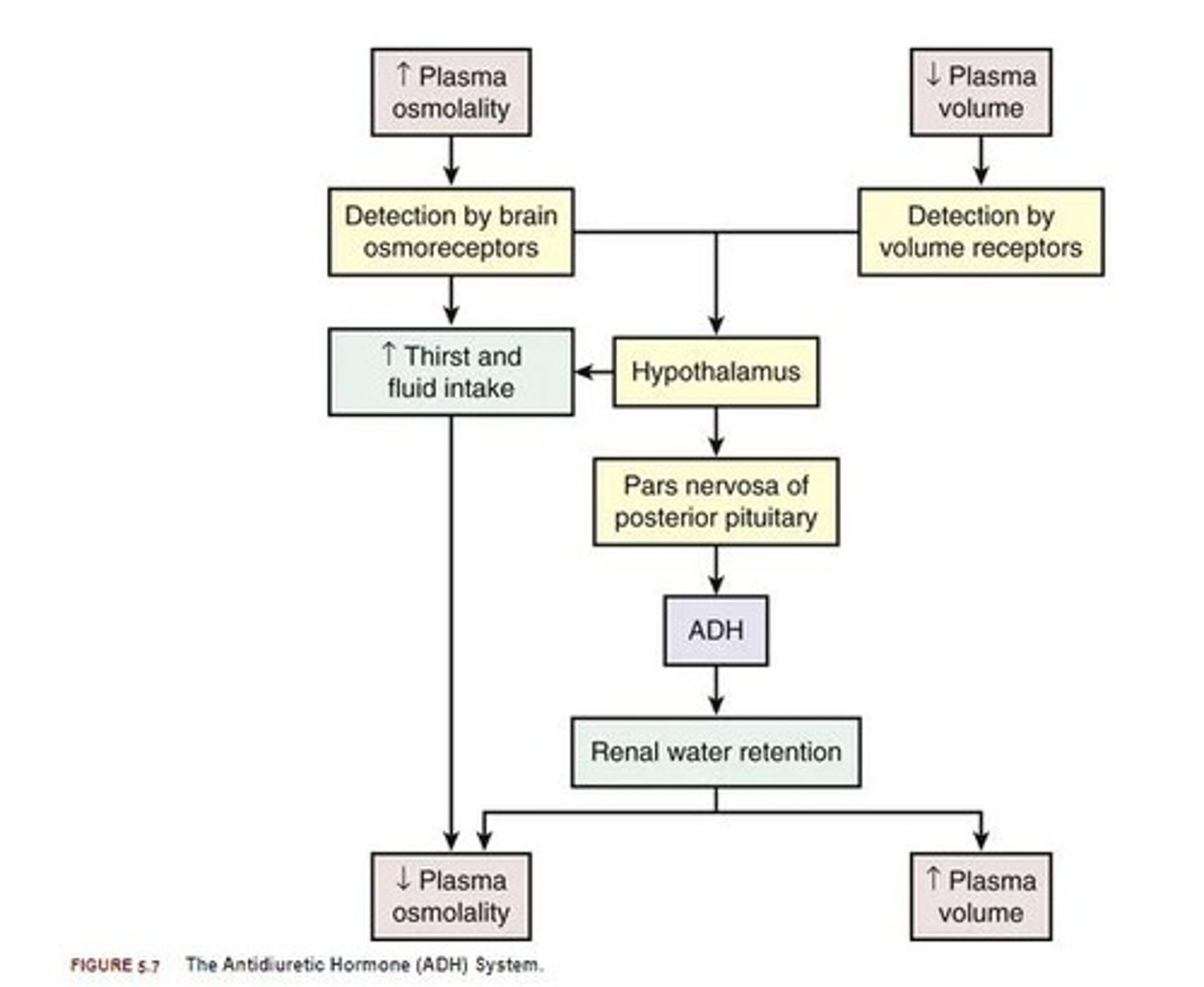
ADH (antidiuretic hormone)
Hormone that maintains water balance
Hypernatremia
H2O deficit in ECF (dehydration), most commonly caused by fluid loss or excess IV fluids
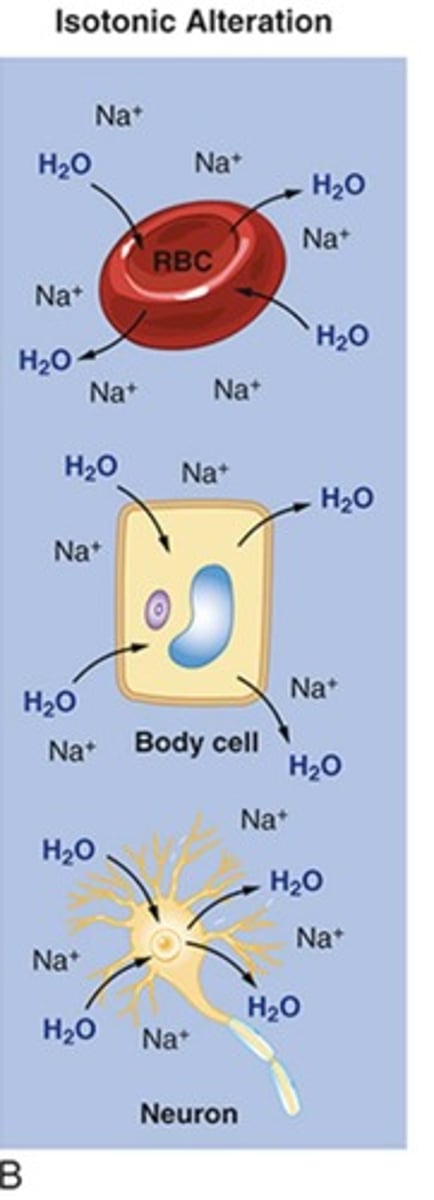
Hypotonic alterations
Alterations in osmolality leading to conditions such as Hyponatremia.
Hyponatremia
H2O excess in ECF resulting in cerebral edema.
Fluid Replacement
General considerations include all routes of fluid intake and loss.
Daily H2O Requirements
Fluid intake needs based on patient's weight and caloric needs.
Types of intravenous solutions
Includes crystalloids and colloids.
Crystalloids
Used for short-term maintenance therapy to treat dehydration and electrolyte imbalance.
Colloids
Plasma expanders that contain protein and large molecules to increase osmolarity.
Hypochloremia
Characterized by cues such as tremors and twitching.
Hyperchloremia
Characterized by cues such as weakness and lethargy.
Potassium (K+)
Normal range is 3.5 to 5.0 mEq/L; major intracellular cation that regulates electrical neutrality.
Hypokalemia
Potassium level <3.5 mEq/L with manifestations depending on heart rate and severity.
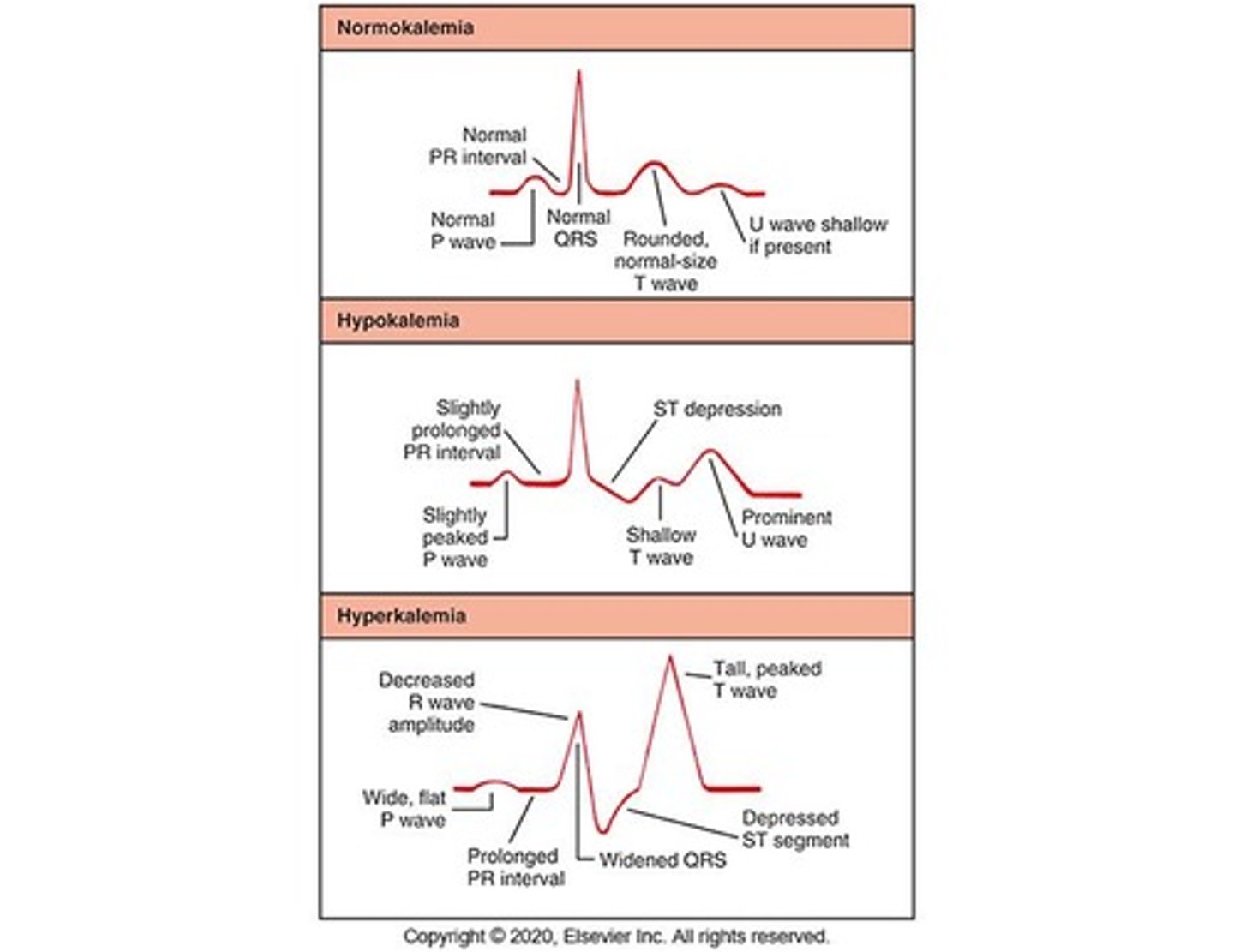
Hyperkalemia
Potassium level >5.0 mEq/L; rare due to efficient renal excretion.
Hyperkalemia Treatment
Includes potassium restriction, intravenous sodium bicarbonate, and calcium gluconate 10%.
Prototype Drug: Potassium Chloride (KCL)
Used for electrolyte replacement; must be diluted if given IV and monitored for ECG changes.
Calcium
Normal range is 8.6 to 10.2 mg/dl; most abundant mineral important for bone formation and nerve transmission.
Hypocalcemia
Ca level < 8.6 mg/dL caused by inadequate dietary intake or intestinal absorption.
Hypercalcemia
Calcium level > 10.2 mg/dL; Increased calcium concentration.
Causes of Hypercalcemia
Hyperparathyroidism, bone metastases, steroids, multiple fractures.
Effects of Hypercalcemia
Fatigue, muscle weakness, impaired renal function, kidney stones.
Prototype Drug: Calcium
Used for electrolyte replacement; caution for IV infiltration and enhanced digoxin effects.
Calcium Preparations
Calcium Gluconate, Calcium Chloride.
Side Effects of Calcium
Nausea/vomiting, constipation, pain.
Adverse Effects of Calcium
ECG changes, renal failure, cardiac arrest.
Clinical Judgment: Calcium - Concept
Fluid and electrolyte balance; check serum calcium levels and assess for signs of calcium imbalance.
Clinical Judgment: Calcium - Generate Solutions
Monitor serum total calcium & ionized calcium levels (4.5 - 5.6 mg/dL); monitor vital signs & report abnormal findings.
Phosphate
Normal levels 2.4 - 4.4 mg/dL; provides energy for muscle contraction and acid-base balance.
Hypophosphatemia
Phosphate concentration < 2.4 mg/dL; causes include intestinal malabsorption related to vitamin D.
Signs & Symptoms of Hypophosphatemia
Muscle weakness, tremors, paresthesia, bone pain.
Hyperphosphatemia
Phosphate concentration > 4.4 mg/dL; causes include acute & chronic renal failure.
Effects of Hyperphosphatemia
Symptoms related to low serum calcium levels; calcification of soft tissues with prolonged condition.
Magnesium
Normal levels 1.5 to 2.5 mEq/L; intracellular cation involved in neuromuscular excitability and cardiac contractions.
Hypomagnesemia
Magnesium concentration < 1.5 mEq/L; causes include malnutrition, malabsorption syndromes, alcoholism.
Effects of Hypomagnesemia
Behavioral changes, irritability, increased reflexes, tachycardia, digoxin toxicity.
Hypermagnesemia
Magnesium concentration > 2.5 mEq/L; causes include renal insufficiency or failure, antacids & laxatives.
Effects of Hypermagnesemia
Skeletal smooth muscle contraction, loss of deep tendon reflexes, nausea & vomiting.
Acid-Base Balance
Low concentration of H+ ions is 'basic'; high concentration of H+ ions is 'acidic'.
Buffer Systems
Chemicals that bind excessive H+ or OH- without a significant change in pH.
Bicarbonate-Carbonic Acid Buffering
CO2 + H2O = H2CO3; carbonic acid dissociates to form H+ and bicarbonate.
Acid-Base Imbalances
Acidosis: systemic increase in H+ concentration or decrease in bicarbonate; Alkalosis: systemic decrease in H+ concentration or increase in bicarbonate.
Metabolic Acidosis
Low pH & low HCO3; example: diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA).
Respiratory Acidosis
Low pH, high PaCO2; caused by alveolar hypoventilation.
Respiratory Alkalosis
High pH, low PaCO2; caused by alveolar hyperventilation.