28, 29 Neuro Exam and Intro to Principles of Neurosx, Physical therapy
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Working Up Suspected Neurologic Cases:
1. Signalment + Anamnesis
2. Complete general physical exam
3. Neuro exam
4. Localize the lesion
5. List of differential diagnosis
6. First rule out ddx outside of the nervous systme
In what scenarios is the neurologic exam inaccurate?
Shock, Post ictal, Severe pain, Fractures, Sedated/chemical influence
In what scenario should a neuro exam be performed in?
Quiet environment
Non slip-surface
Stabilized patient
6 Neuro Exam Components
1. Observation
2. Palpation
3. Cranial nerve evaluation
4. Postural reactions
5. Spinal reflexes
6. Pain localization and Sensory evaluation
Define Proprioception
ability to recognize location of the limbs relative to the rest of the body
Define Ataxia
Incoordination
-Cerebellar
-Spinal
-Vestibular
Paresis
weak voluntary motor function
Plegia
Absent voluntary motor function
Describing neuro status dictates ____ and ____
severity
urgency
If there is absent voluntary motor function, what should you describe next?
If patient can feel superficial or deep pain
What do you see with UMN signs?
↑ reflexes, ↑ muscle tone
- Rigidity: Increase in extensor AND flexor tone
- Spasticity: Increase in extensor tone
- Clonus: vibration of the limb during reflexes,
• Indicates chronicity
What do you see with LMN signs?
↓ reflexes, ↓ tone
- Flaccidity: Decrease in muscle tone, LMN
When you have ataxia, what anatomy may be affected?
cerebrum, cerebellum, vestibular system, spinal cord, nerves, receptors
When you have paresis, what anatomy may be affected?
voluntary motor pathways:
cerebrum, brainstem, spinal cord, peripheral
nerves
When you have plegia, what anatomy may be affected?
voluntary motor pathways: cerebrum, brainstem, spinal cord, peripheral nerves
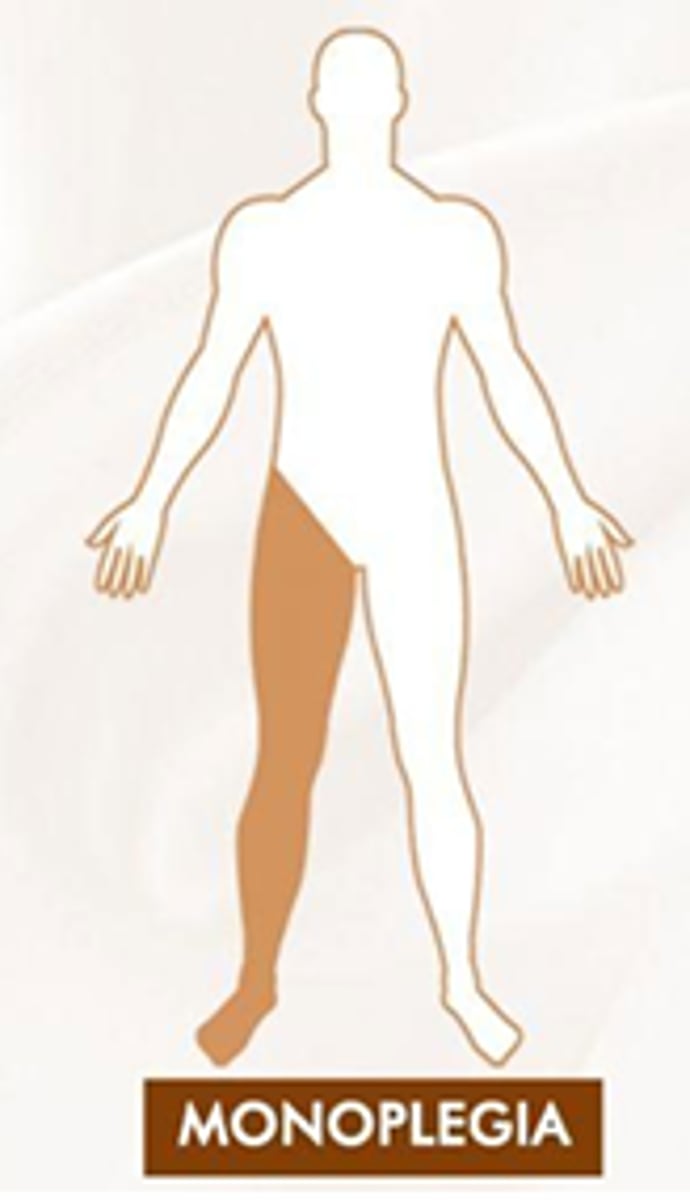
Define Mono- paresis/plegia and know most common cause
One limb
Trauma or tumor
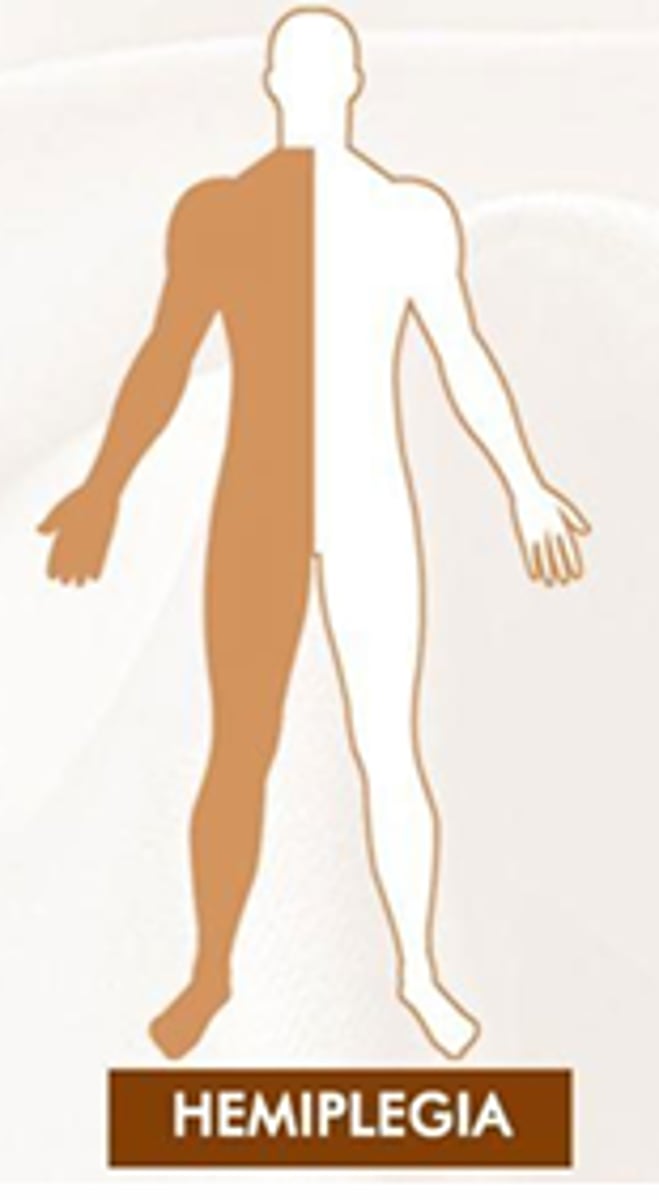
Define Hemi- paresis/plegia and know most common cause
Hemispheric weakness or paralysis
Disease/tumor/injury of the brain
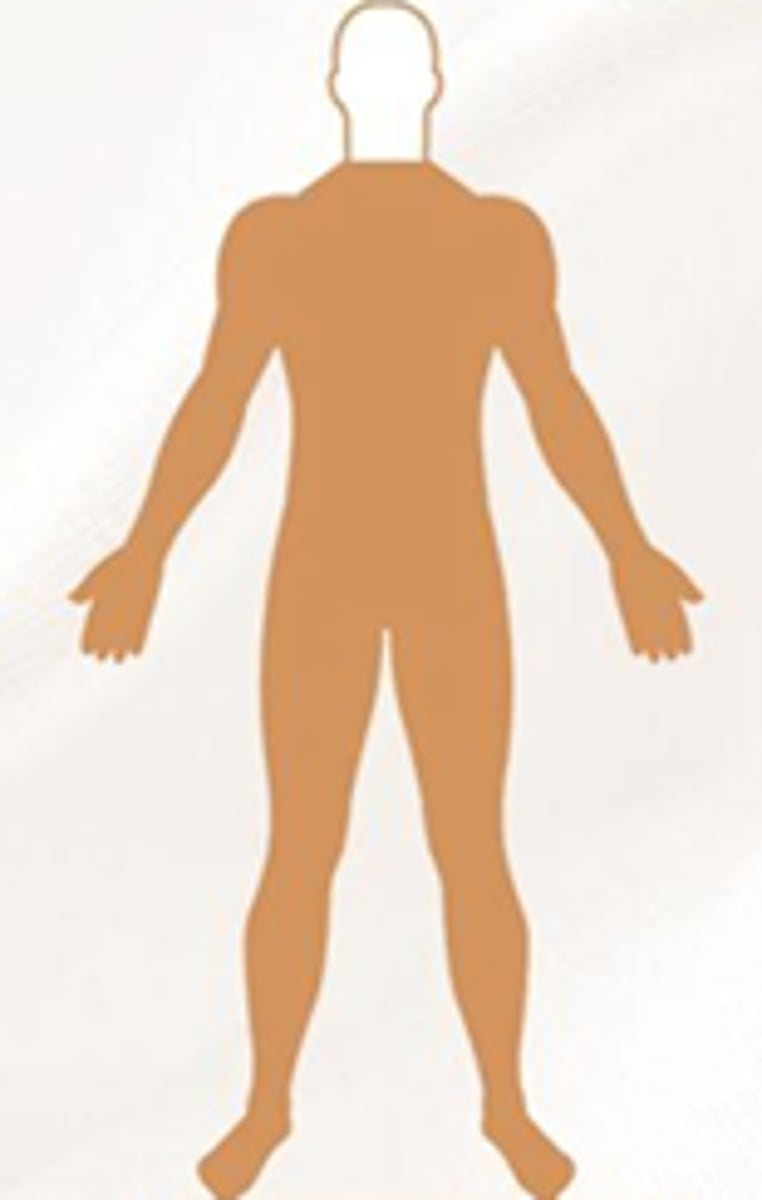
Define Tetra- paresis/plegia and know most common cause
all 4 limbs affected.
degenerative conditions (disk rupture) trauma, vascular, tumor
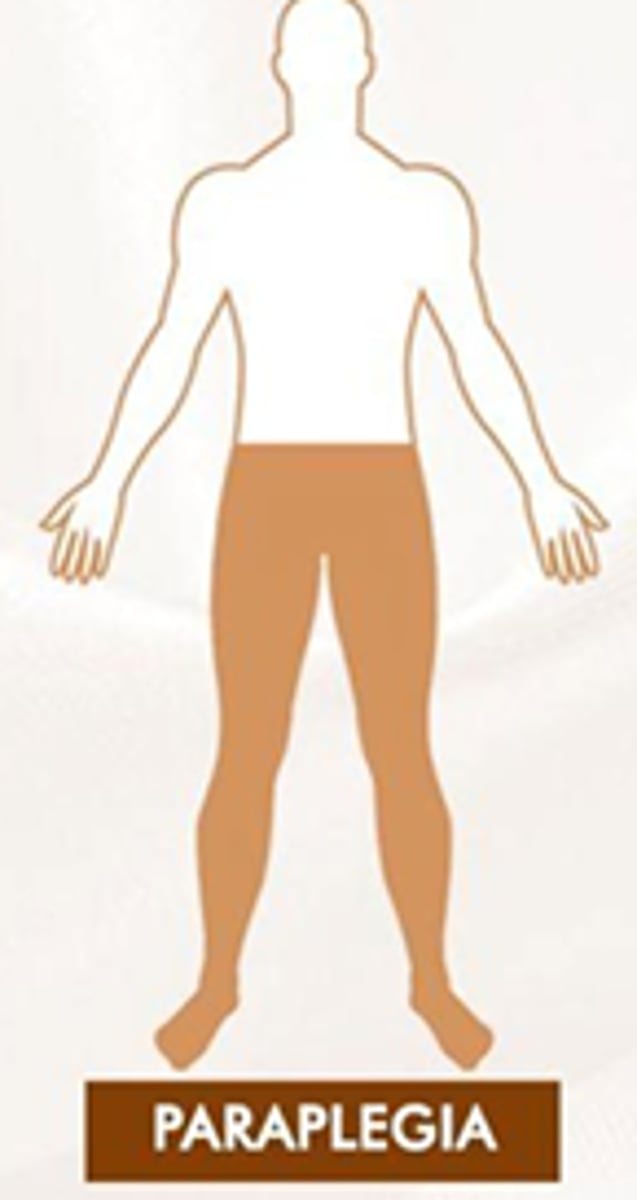
Define Para-paresis/plegia and know most common cause
Hind limbs are affected
denerative conditions (disk rupture) trauma, vascular, tumor
Wide circles indicated a problem in the ______
Tighter circles indicated a problem in the ________
Cerebrum
Vestibular
Which is more reliable: myotactic or withdrawal reflexes
withdrawal reflexes
What position do you test the myotactic and withdrawal reflexes?
Always perform with the patient in lateral recumbency on the "up" limb
C1-C5
Thoracic Limb reflex:
Pelvic limb reflex:
UMN
UMN
C6-T2
Thoracic Limb reflex:
Pelvic limb reflex:
LMN
UMN
T3-L3
Thoracic Limb reflex:
Pelvic limb reflex:
Normal
UMN
L4-S3
Thoracic Limb reflex:
Pelvic limb reflex:
Normal
LMN
When you tap the Triceps for myotactic reflexes, what nerve and spinal segments are you testing?
Radial n., C7-T1
When you tap the Biceps for myotactic reflexes, what nerve and spinal segments are you testing?
Musculocutaneous n. C6-C8
When you tap the Extensor Carpi Radialis for myotactic reflexes, what nerve and spinal segments are you testing?
Radial n C7-T1
When you tap the Patellar Tendon for myotactic reflexes, what nerve and spinal segments are you testing?
Femoral n L4-L6
When you tap the Gastrocnemius for myotactic reflexes, what nerve and spinal segments are you testing?
Sciatic n L7-S1
When you tap the Cranial Tibial for myotactic reflexes, what nerve and spinal segments are you testing?
Sciatic n L7-S1
What does paresthesia/dysesthesia look like?
Pins and needles
What is the order of loss of sensory function?
CP> Voluntary motor> Superficial Pain Sensation > Deep Pain sensation
If you pinch the bone and there is a flexor withdrawal but dog doesn't look at you, whatt does that mean?
Message not getting to the brain, no deep pain sensation, poor prognosis
What are the goals of neuro sx?
-Decompress CNS
- Maintain or return stability/ bony protection of the CNS
- Relieve pain
- Allow the CNS to heal if possible
Describe Hansen Type 1 IVDD
Nucleus pulposus (NP) dehydrates & accumulates mineral
For IVDD of the neck, what approach to we take?
Ventral slot (move trachea, esophagus etc out of the way)
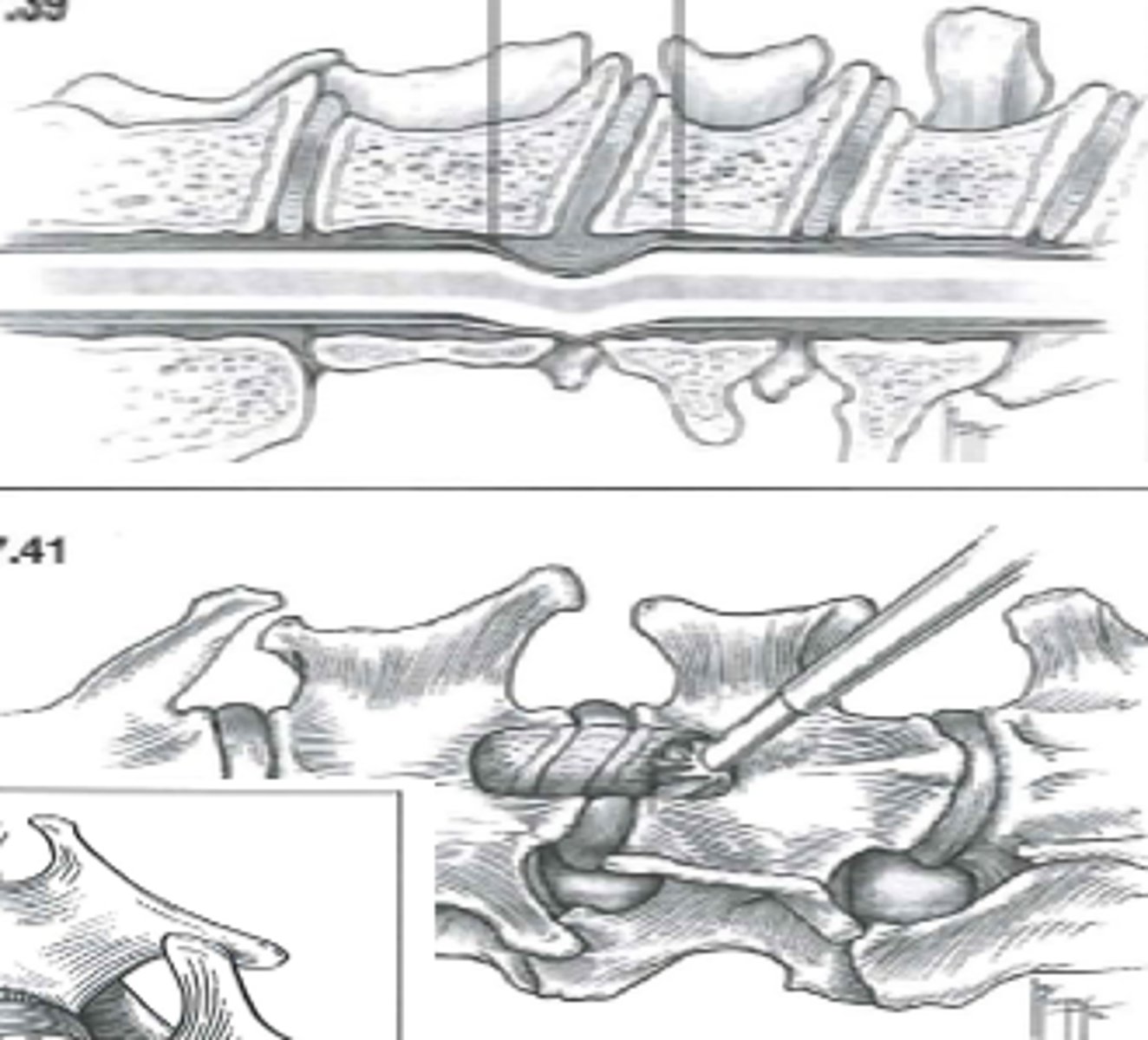
For IVDD of the Thoracolumbar region, what approach to we take?
Hemilaminectomy
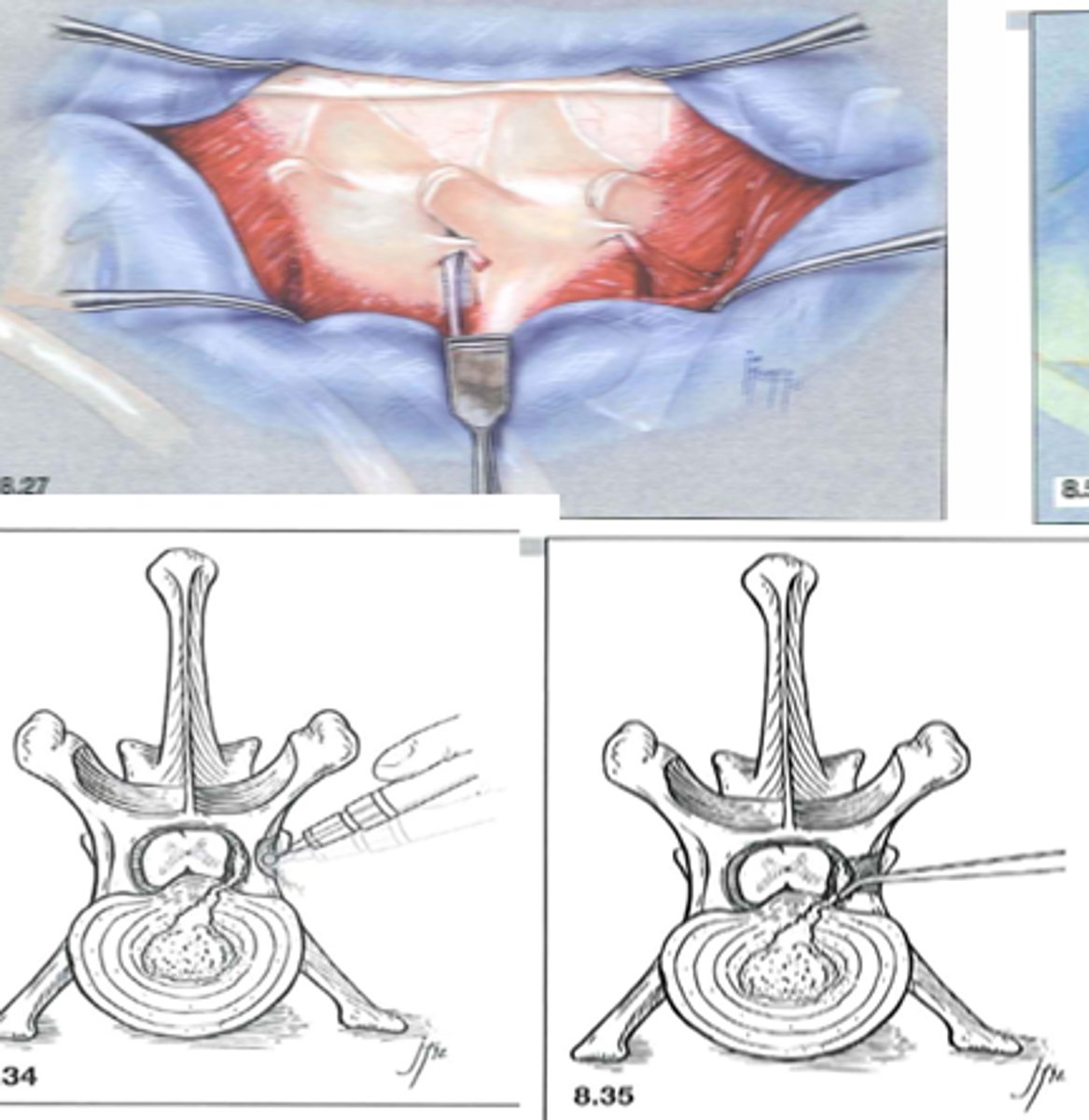
For IVDD of the caudal lumbar and lumbosacral region, what approach to we take?
Dorsal Laminectomy
Why Rehabilitation?
•Better healing of injuries
•Better recovery from surgery
•Improved management of pain
•Injury prevention
•Improving performance
•Weight loss/management
How does muscle and bone react to immobilization?
-Muscle atrophy and weakness
-Movement patterns are "forgotten"
-Bone resorption evident six weeks after screw placement for fracture
-Greater resorption with plate application
-Weight bearing to load fracture and encourage bone healing is crucial
What is the term of physical therapy legally reserved for?
In many states for rehabilitation of humans
What is the difference in an assessment by a regular vet vs a physical therapist?
–Veterinarians assess animals with the aim to obtain an anatomic/pathologic diagnosis
–Physical Therapists assess patients with the additional aim to determine functional diagnoses
What are problems with NOT doing rehab?
Pain
Stiffness (fibrosis/adhesions can be stretched)
Proprioception
Strength
Endurance
Tissue Healing
What are benefits of Cold Therapy or Cryotherapy?
•Provides anti-inflammatory effects
-Decreases swelling
-Decreases pain
-Decreases muscle spasms
What is the minimum time for cold therapy to be therapeutic?
Minimum of 10-20 min
(want to prevent hunting phenomenon aka reactive hyperemia which would cause inflammation)
What are side effects of Cold Therapy/Cryotherapy?
Can cause frostbites
•Inspect skin frequently
•Use insulating layer between ice and skin
-Hair coat, cloth
What are contraindications to cold therapy/cryotherapy?
Open wounds
Ischemic tissue damage
What can you do in combination with cryotherapy to make it a superior therapy?
Intermittent compression (intermittent is superior to static compression- mimics lymphatics)
Hot packs, heat lamps and warm water should be applied for ___-___ min.
Increases surface temperature (up to 1 cm depth) for up to ____ minutes
15-30 min
10ming
How does Heat therapy help?
-Local blood flow
-Enzyme activity/metabolism
-Muscle relaxation
-Tissue extensibility
-MAY decrease edema (depends on cause of edema)
What are indications of Heat Therapy?
-Older soft tissue injuries (>>72h) without signs of inflammation
-Muscle spasms
-Contractures/Adhesions
-Fibrosis (joint capsule)
Perform stretching after heating!
What is therapeutic ultrasound?
•High-frequency acoustic waves above our hearing range
-A type of heat therapy
What we use therapeutic ultrasound as a means for?
Means for deep tissue heating
1-5 cm depth
temperature inc more superficially and less deeper
What are other possible effects on tissue healing/repair from therapeutic ultrasound?
-Decreased lameness, fewer adhesions, faster healing in transected canine achilles tendons
What affect does therapeutic ultrasound on blood flow/pain/muscle spasms/ collagne extensibility/ range of motion?
–Increased blood flow
–Decreased pain
–Decreased muscle spasms
–Increased collagen extensibility
–Increased range of motion
What tissue are poorly ultrasounded?
•Tissues high in H2O and low in protein absorb ultrasound poorly (blood, fat)
What tissue absorb ultrasounds better?
•Tissues higher in protein absorb ultrasound energy better (nerve, muscle, skin, scar tissue, tendon, ligament, fascia)
Contraindications of Therapeutic Ultrasound
-Directly over the heart
-Over ischemic or necrotic tissue
-Over areas without sensation
-Over the pregnant uterus
-Directly over implants
-Over growing physes
-Directly over thrombophlebitis (risk of embolus)