CH 15: Eyes
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Subjective eye assessment (current symptoms)
Ask about:
Vision changes
Eye pain
Discharge
Light sensitivity or halos around lights
Function of eyelids & eyelashes
Protect the eye from debris and excessive light. Eyelids contain meibomian glands that produce oils to prevent tear evaporation
Conjunctiva function
Thin, transparent membrane covering the white part of the eye and inner eyelids. Produces mucus to lubricate the eye.
Produces, distributes, and drains tears. Includes lacrimal glands, puncta, canaliculi, and nasolacrimal duct.
Lacrimal System
Light Entry
Light passes through cornea, which bends light rays toward the pupil opening controlled by the iris.
Focusing (vision)
Lens adjusts shape to focus light precisely on the retina, with ciliary muscles controlling lens curvature.
Signal Conversion (vision)
Retinal photoreceptors convert light into electrical signals transmitted via optic nerve to visual cortex.
Subjective eye assessment (medical history)
Ask about:
Previous eye conditions or surgeries
Family history of eye disease
Systemic conditions (diabetes, hypertension)
Current medications affecting vision
Subjective eye assessment (lifestyle factors)
Ask about:
Occupational or recreational eye hazards
Use of protective eyewear
Screen time and digital eye strain
Last comprehensive eye examination
Objective eye assessment (general inspection)
Observe facial symmetry, eyebrow position, eyelid alignment, and overall eye appearance. Note any obvious abnormalities or asymmetry.
Eyelid Assessment (objective)
Check for ptosis, edema, lesions, or inflammation. Ensure complete eyelid closure and normal blinking reflex.
Drooping of upper eyelid due to muscle weakness or nerve damage. May be congenital or acquired. Can obstruct vision if severe
Ptosis
Conjunctival examination (objective
Inspect for redness, discharge, foreign bodies, or signs of infection. Gently evert lower lid if indicated.
Vision acuity testing
Snellen chart at 20 ft distance
Test each eye separately, than together
Record as fraction (20/20, 20/40, etc.)
Use pinhole test if vision is impaired
20/40
Top number = what patient can read at 20 ft
Bottom number = what average person can see at 40 ft
Eye tests
Snellen chart
Near vision using reading card
Peripheral vision (confrontation) test
Color vision screening
Depth perception assessment
Normal size of pupils
3-5 mm in normal light.
PERRLA
P – pupils:
3-5mm in normal light. Note size, shape (should be round), and equality between eyes.
E – Equal:
Both pupils should be the same size. Anisocoria (unequal pupils) may indicate neurological issues.
RR – Round/Reactive:
Pupils should be perfectly round and constrict (react) briskly when light is applied directly
L – Light:
Test direct and consensual light reflex. Both pupils should constrict when light hits either eye.
A – Accommodation:
Pupils constrict when focusing on near objects. Test by having patient focus from distant to near object.
Unequal pupils. May indicate neurological issues
Anisocoria
Lens loses flexibility, making near vision difficult. Reading glasses or bifocals often needed for close work
Presbyopia (occurs age 40s-50s)
Age-related eye changes
Presbyopia (40s-50s)
Common changes (60-70s)
Increased risk of (70s)
Higher incidence/increased risk of cataracts, glaucoma, macular degeneration, and diabetic retinopathy requiring regular monitoring. At what age does this occur?
70s+
Decreased tear production, reduced peripheral vision, increased sensitivity to glare, and slower dark adaptation
Common age-related eye changes
Clinical presentation for this disease is:
Red, tender bump on eyelid margin
Localized swelling and pain
May have purulent drainage
External (zeisian gland) or internal (meibomian gland)
Hordeolum (Stye)
Nursing interventions for Hordeolum (Stye)
Apply warm, moist compresses 10-15 minutes, 3-4 times daily
Educate about proper hand hygiene
Advise against squeezing or manipulating
Monitor for spreading infection
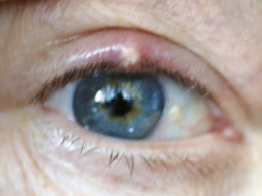
An acute localized staphylococcal infection of sebaceous gland in eyelid. It is painful, red, and swollen—a superficial, elevated lump or pustule at the lid margin. Rubbing the eyes can cause cross-contamination and development of another stye. Managed with warm compresses, topical antibiotic ointment, may be combined with steroid ointment
Hordeolum (Stye)
Silent Thief of Sight
Glaucoma
Increased intraocular pressure damages optic nerve, causing progressive vision loss. Often asymptomatic until advanced stages.
Pathophysiology of glaucoma
Risk factors for this disease include
Age > 40
Family history
African American
Diabetes
HTN
High myopia
Previous eye trauma
Glaucoma
Myopia
Near-sighted; can’t see far
Hyperopia
Far-sighted; can’t see close
Assessment findings for glaucoma
Peripheral vision loss, halos around lights, eye pain, N/V (acute angle-closure), elevated IOP >21 mmHg.
Patient education for glaucoma
Emphasize importance of regular eye exams, medication compliance, and recognizing symptoms requiring immediate attention.
Elevated IOP > 21 mm Hg indicates
Glaucoma
PHINVE (glaucoma assessment findings)
P – peripheral vision loss
H – Halos around lights
I – Intraocular pressure (IOP) > 21 mm Hg
NV – nausea/vomiting
E – Eye pain
Clinical manifestations of this disease includes
Gradual, painless vision loss
Increased glare sensitivity
Difficulty with night driving
Colors appear faded or yellowed
Frequent prescription (glasses/contacts) changes
Cloudy or milky appearance of lens
Cataracts (clouded vision)
Nursing care for cataracts
Educate about surgical options, pre/post-operative care (eye shield prevent rubbing), and safety measures. Emphasize that surgery is the only effective treatment
Risk factors for cataracts
Aging (most common)
UV light exposure
DM
Smoking and alcohol use
Steroid medications
Previous eye trauma
Thick, purulent discharge, usually yellow-green. Highly contagious. Treatment includes antibiotic drops and strict hygiene measures
Bacterial Conjunctivitis
Watery discharge, often associated with upper respiratory infection. Self- limiting but highly contagious. Supportive care only.
Viral Conjunctivitis
Bilateral itching, tearing, and redness. Not contagious. Treatment includes antihistamines and avoiding triggers.
Allergic Conjunctivitis
Abnormal protrusion of eyeballs, often associated with hyperthyroidism. May cause difficulty closing eyelids completely, leading to corneal dryness and damage
Exophthalmos
Eye safety & health promotion
Protective eyewear
UV Protection
Digital Eye Strain
Regular examinations
Protective eyewear (Eye Safety & Health Promotion)
Use appropriate safety glasses, goggles, or face shields during work, sports, and recreational activities with eye injury risk
UV protection (Eye Safety & Health Promotion)
Wear sunglasses with 100% UV protection outdoors. Choose wraparound styles for maximum coverage and reduce cataract risk
Digital Eye Strain (Eye Safety & Health Promotion)
Follow 20-20-20 rule: every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds. Adjust screen brightness and distance.
Regular Examinations ((Eye Safety & Health Promotion)
Annual comprehensive eye exams for adults >40, or as recommended based on risk factors and family history