Cellular Organelles
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
what are tissues?
groups of cells similar in structure and function
- specialized to perform specific tasks
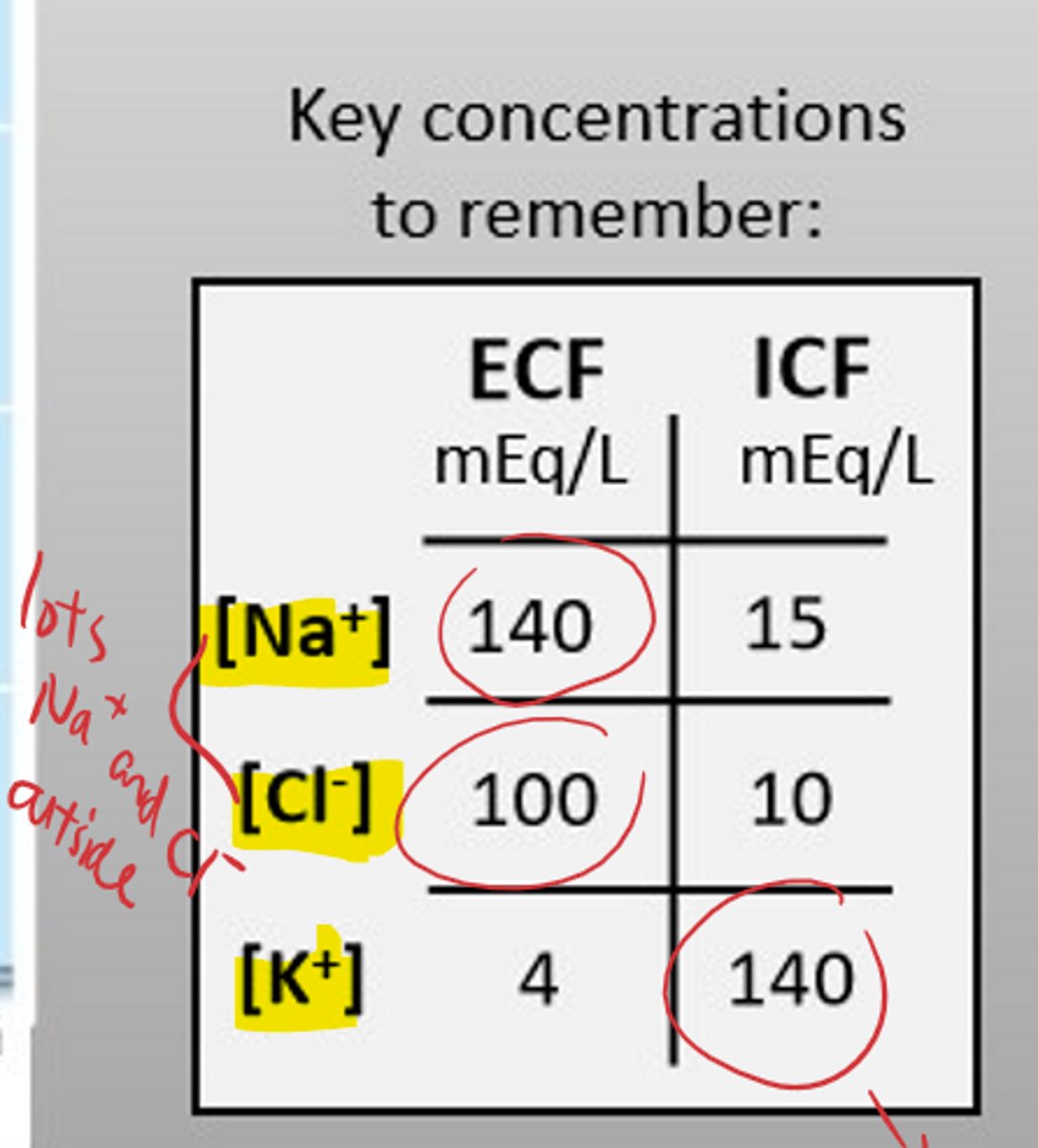
describe the differences in ion concentrations between intracellular fluid (ICF) and extracellular fluid (ECF)
- ICF is characterized by higher levels of K+ and other anions (A-) and lower levels of Ca²⁺, Na+, and Cl-
- ECF is characterized by higher levels of Ca²⁺, Na+, Mg²⁺, Cl-, PO4³⁻, HCO3-, and glucose
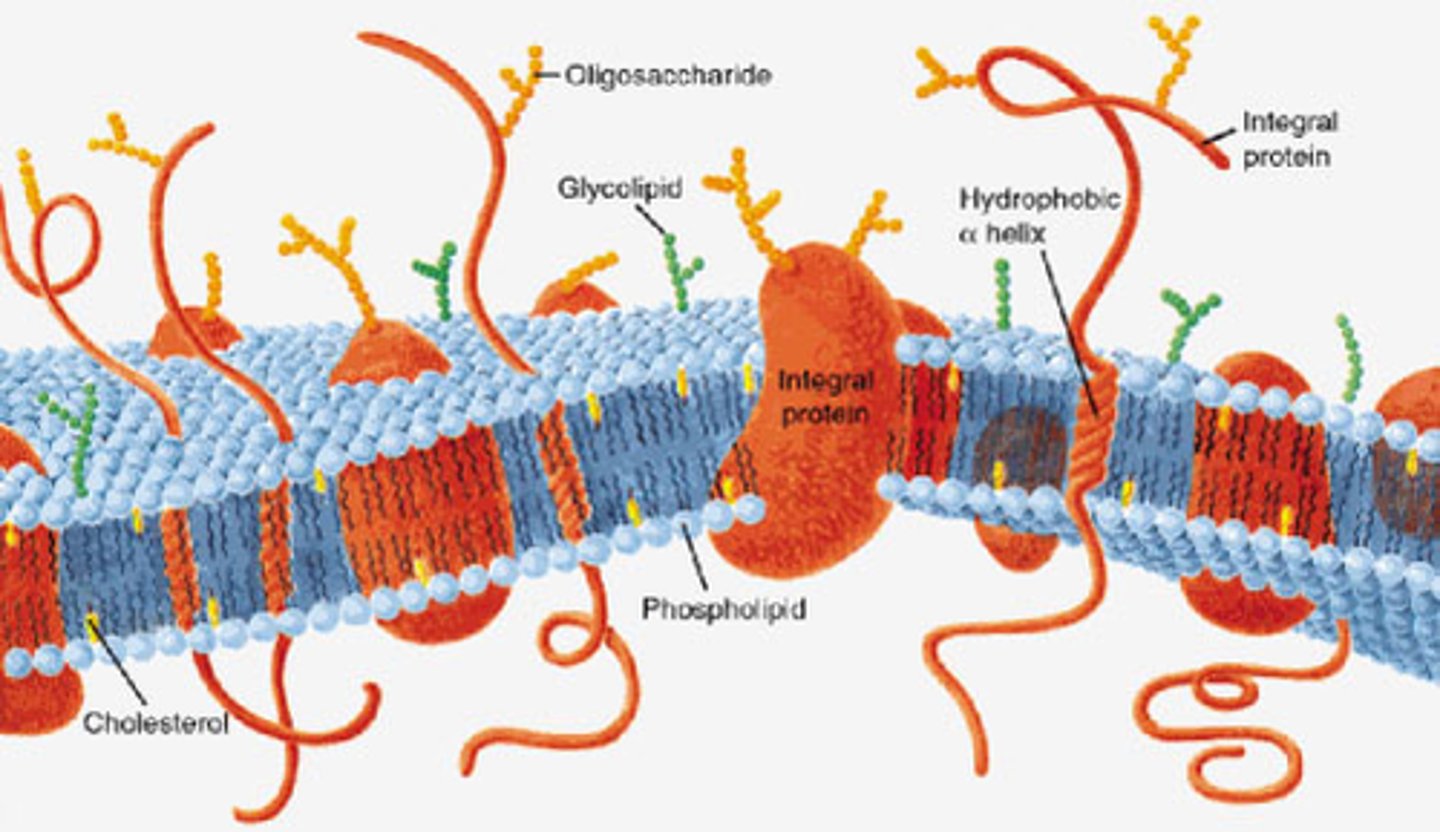
what are cell membranes composed of? what are the functions of the 2 main components?
phospholipids and proteins
- phospholipids serve as a barrier
- proteins allow cells to interact with and communicate with each other; also allow H2O and hydrophilic molecules to cross
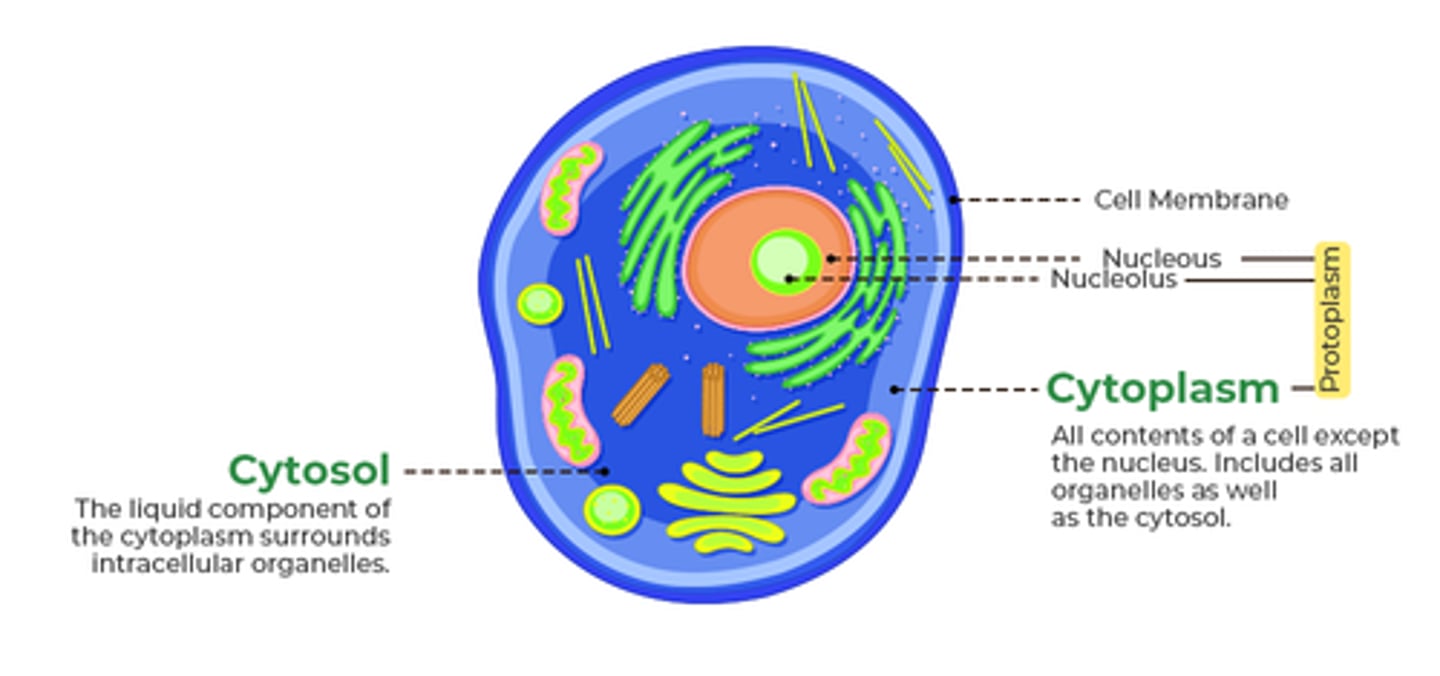
what's the difference between cytoplasm and cytosol?
- cytoplasm is the cell part entirely enveloped in the cell membrane and includes the organelles it surrounds
- cytosol denotes only the fluid part of the cytoplasm
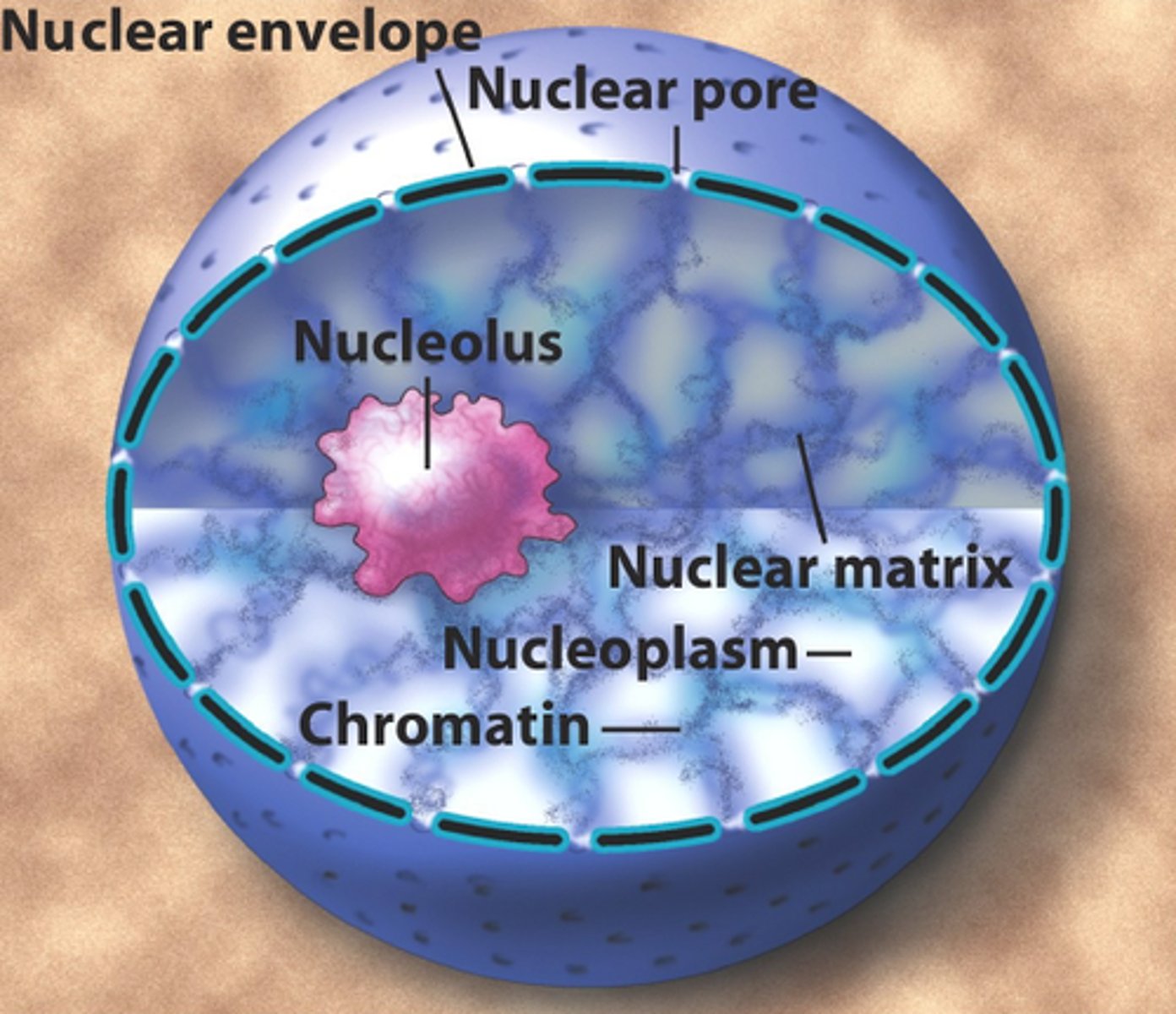
what is the nuclear envelope? how is material passed in and out of the nucleus?
double membrane that surrounds the nucleus
- nuclear pores in the membrane permit the passage of materials between the nucleus and cytosol
what is nucleoplasm?
The granular, jelly-like material that makes up the bulk of the nucleus (analogous to the cytosol)
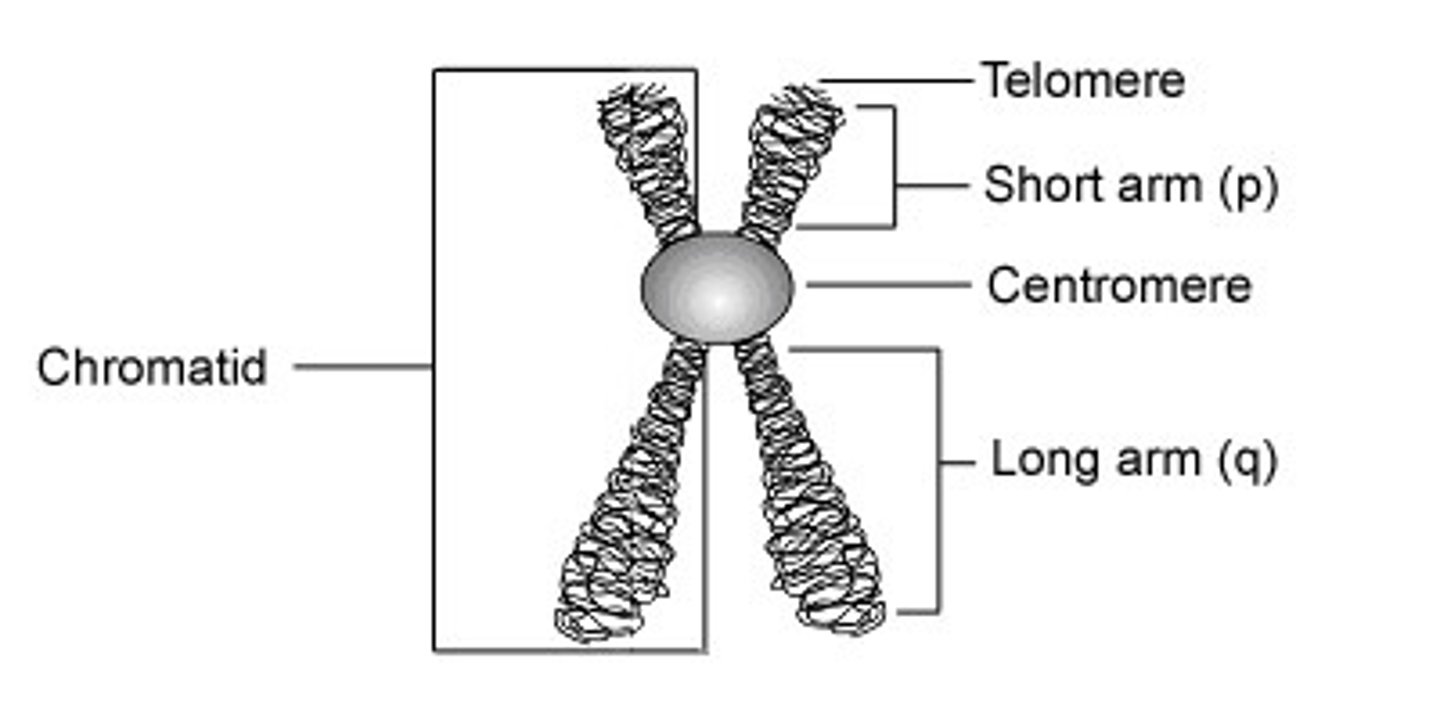
what are chromosomes, and what protein facilitates their condensing during cell division?
DNA molecules
- tightly wrapped around histones to establish their characteristic "X" shape
what are the centromere and telomeres of chromosomes?
- the centromere is the constriction point, where the 2 chromosomes meet
- telomeres are the tips of the chromosomes, which protect the DNA during replication
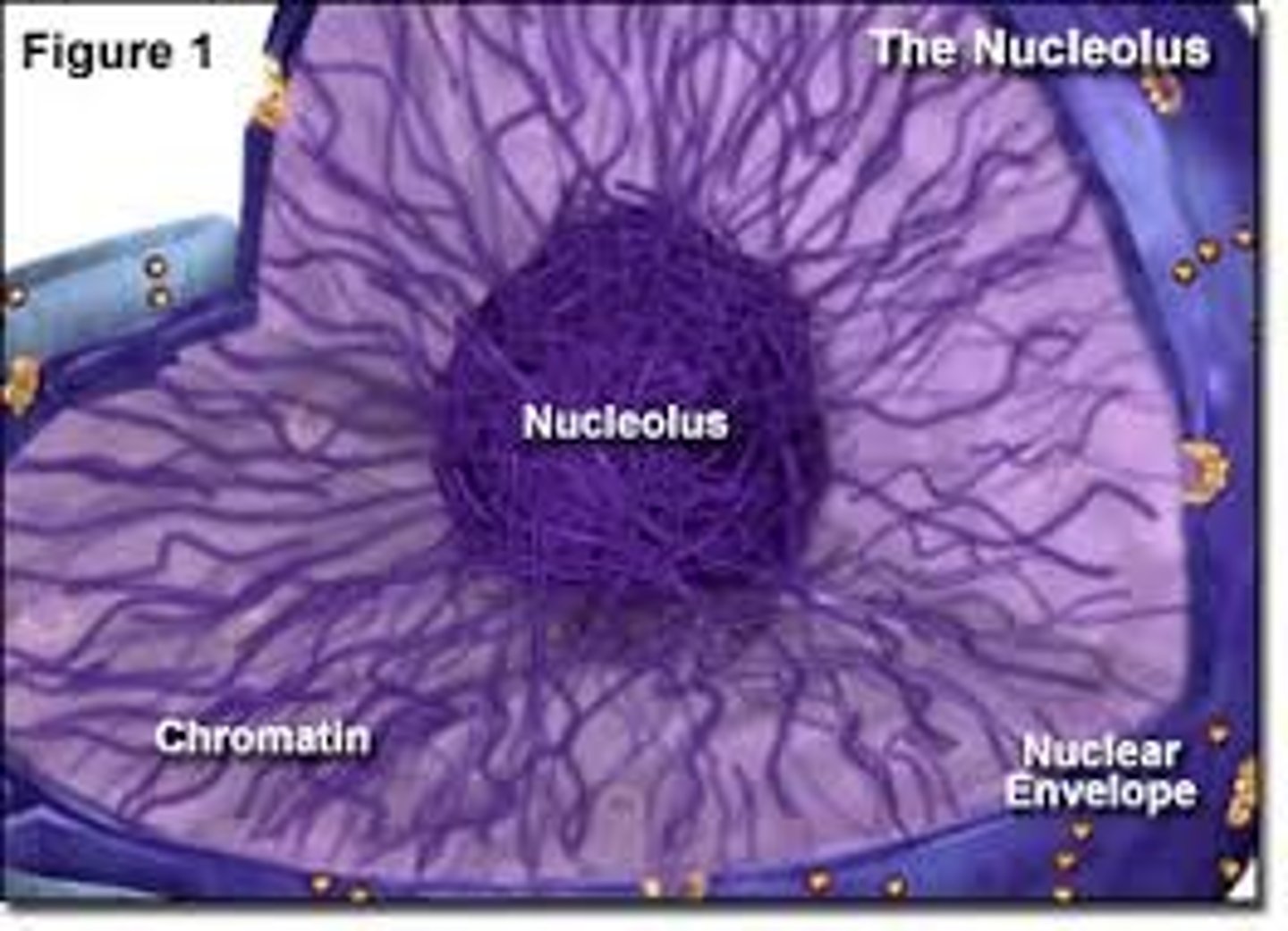
what is the nucleolus?
a small dense spherical structure in the nucleus of a cell
- primary function is to produce ribosomes; once produced, they are transported to the cell cytoplasm
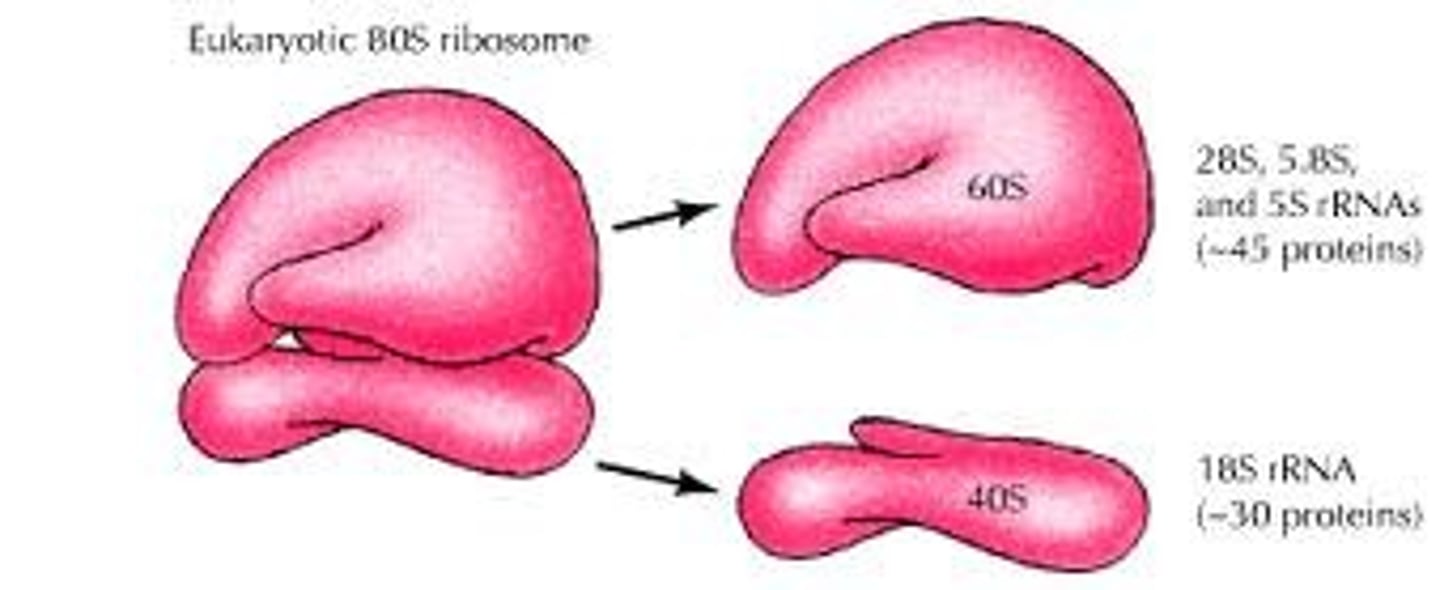
what are ribosomes? describe their structure
site of protein synthesis
- composed of proteins (40%) and rRNA (60%)
- 2 subunits, a small (40S) and a large (60S) → 40S is made of 1 rRNA and ~30 proteins, while 60S is made of 3 rRNA and ~50 proteins
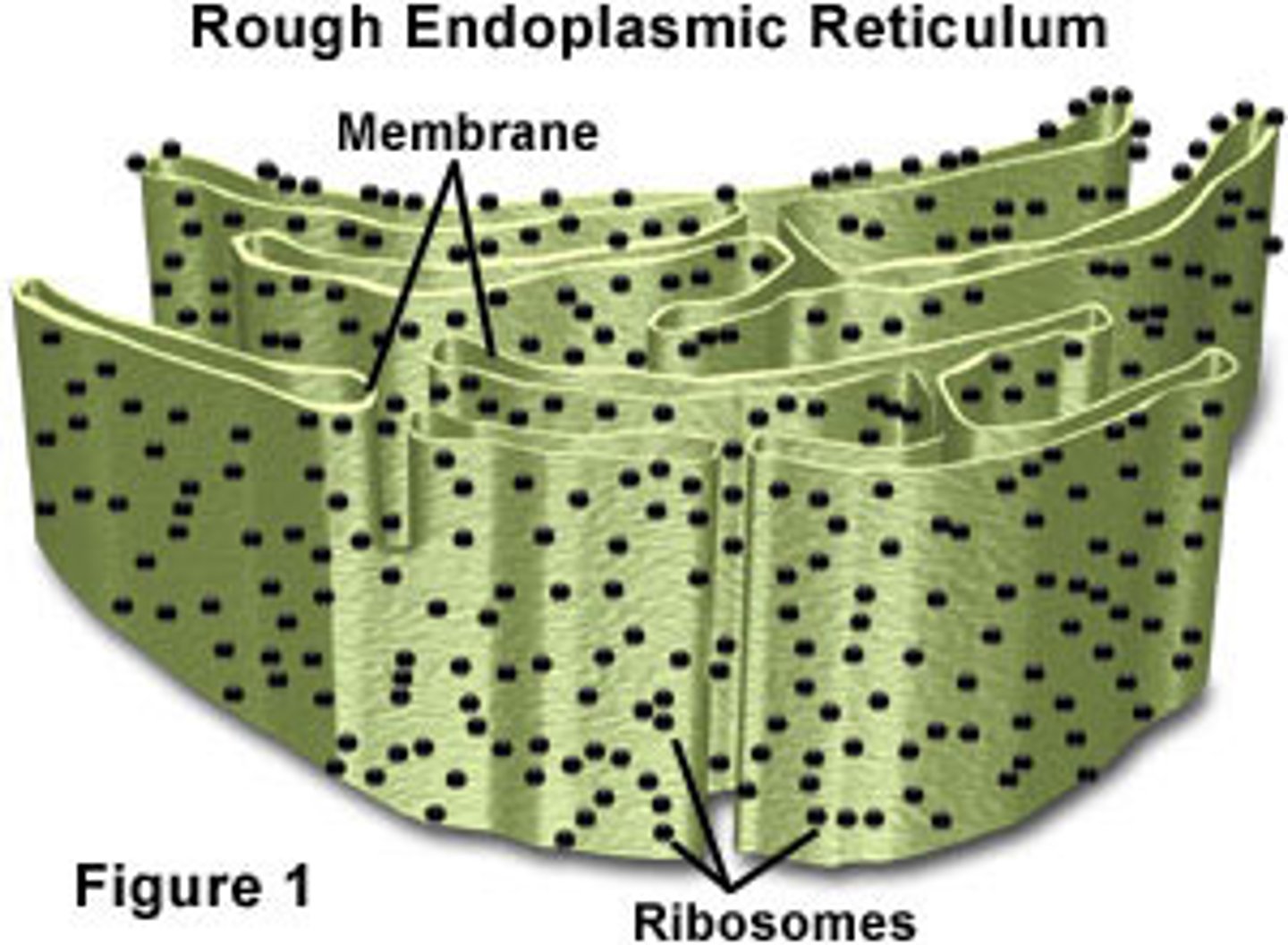
what is the rough endoplasmic reticulum (rER)? what is its function?
a system of membranes enclosing a fluid-filled space that is covered with ribosomes
- functions in the glycosylation of proteins (synthesis, folding, modification, and transport of proteins)
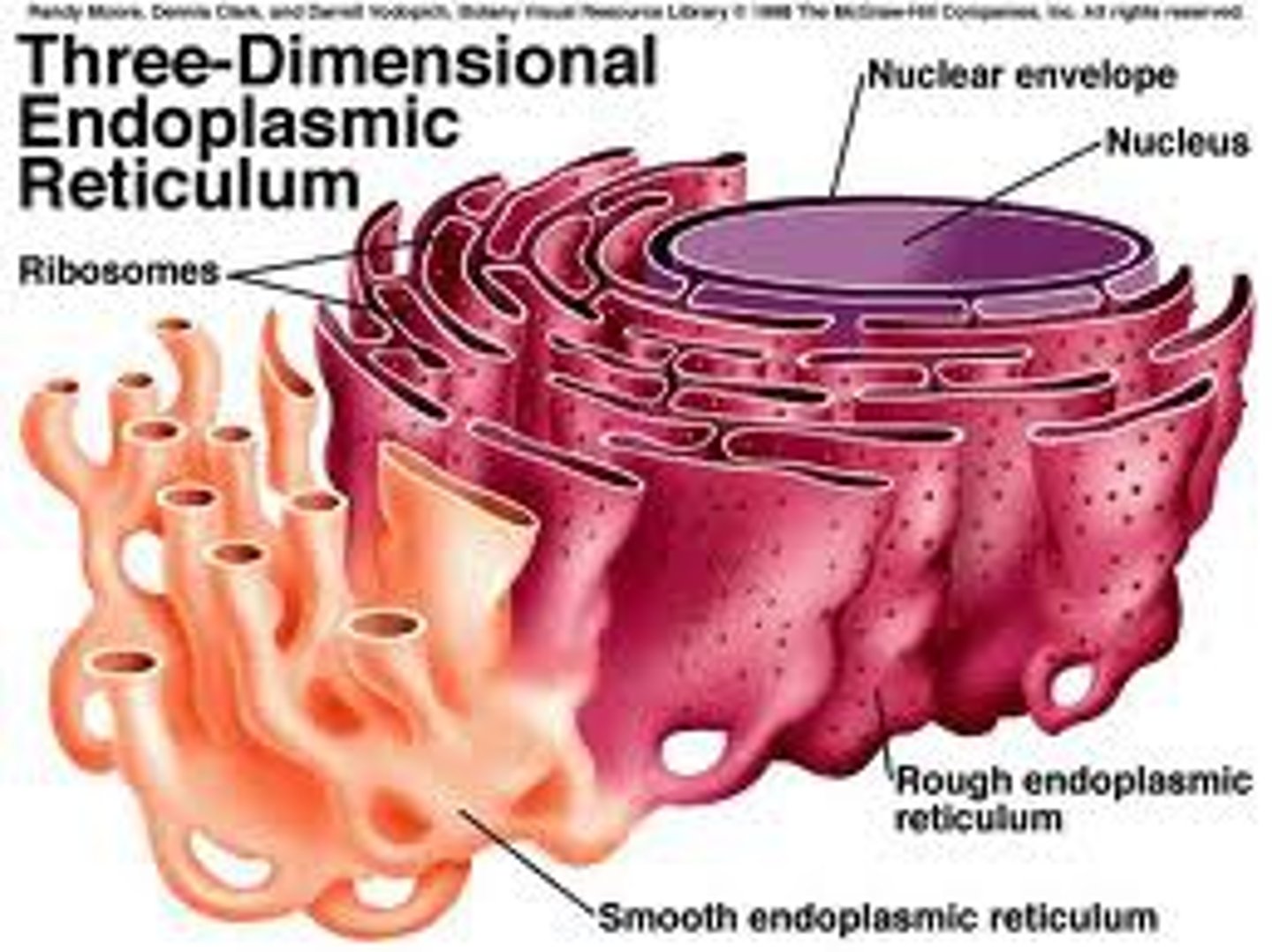
what is the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (sER)? what is its function?
a system of membranes enclosing a fluid-filled space that is NOT covered with ribosomes
- functions in lipid synthesis and detoxification
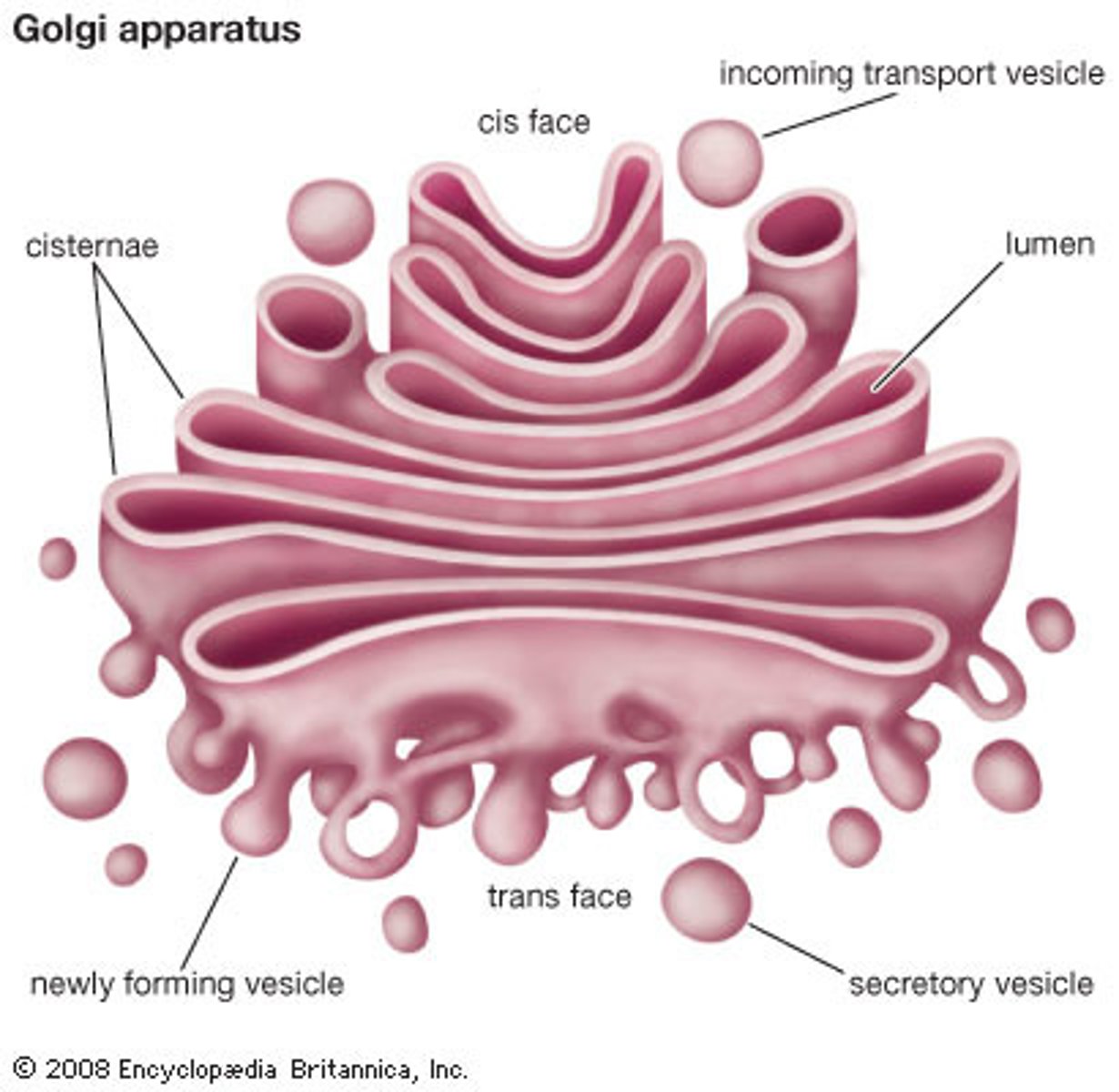
what is the Golgi apparatus? what are its 3 regions?
flattened membranous stacks that process, package, and deliver proteins and lipids from the ER; 3 regions:
- cis: closest to the ER; receives transport vesicles and packages the new proteins to be sent to the trans region
- medial: in the center
- trans: nearest the plasma membrane; sends out finished products
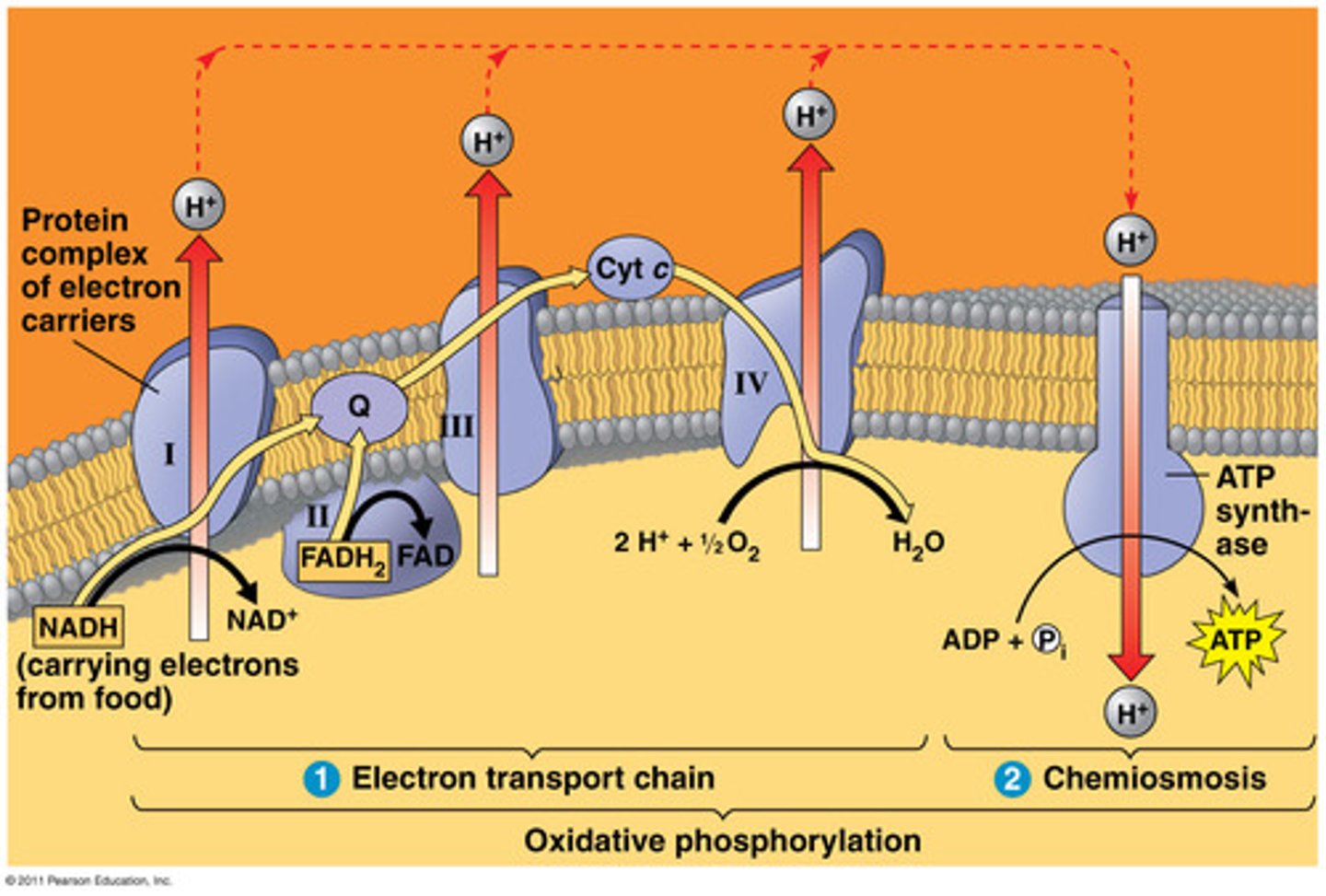
how do the mitochondria produce ATP?
use unique membranes to yield energy from the breakdown of carbs. and lipids via oxidative phosphorylation
- an electrochemical gradient is established by the pumping of H+ out of the matrix
- the flow of H+ back down their gradient drives energy production through ATP synthase
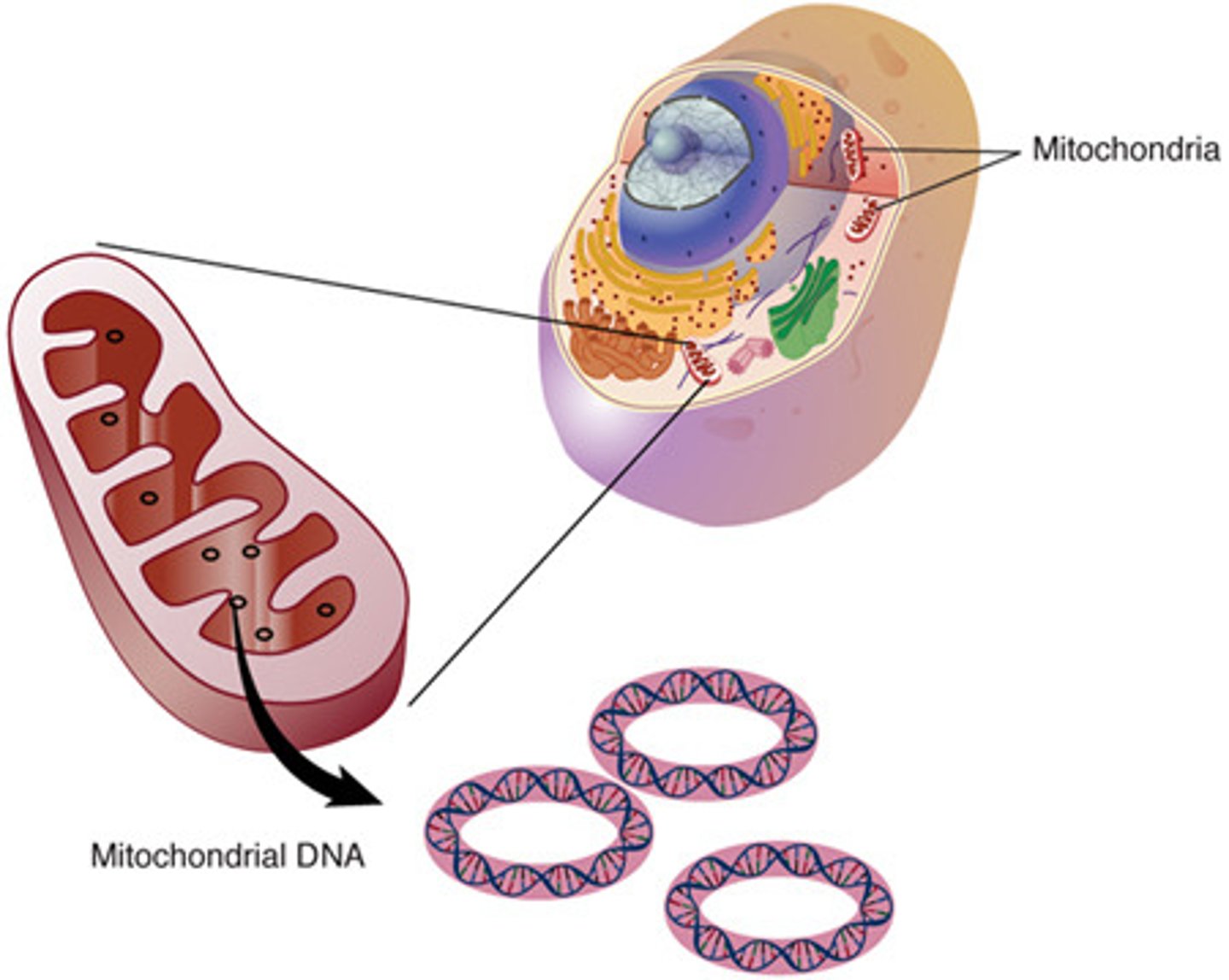
which organelle contains its own set of genetic material other than the nucleus?
mitochondria (mtDNA)
- also contain ribosomes for protein production
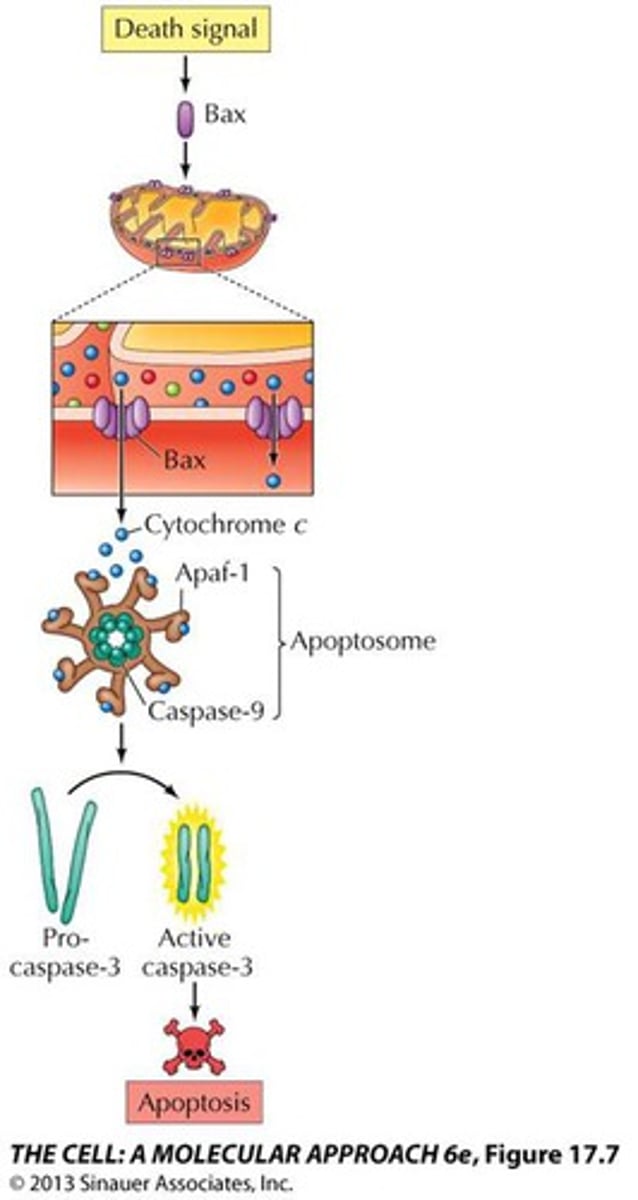
what is the mitochondria's role in organ formation during development?
during development, some cells must die to allow for proper tissue and organ formation
- mitochondria are responsible to regulating cell survival or initiating apoptosis as needed
- apoptosis is induced via cytochrome c, which stimulates a biochemical cascade that induces cell death
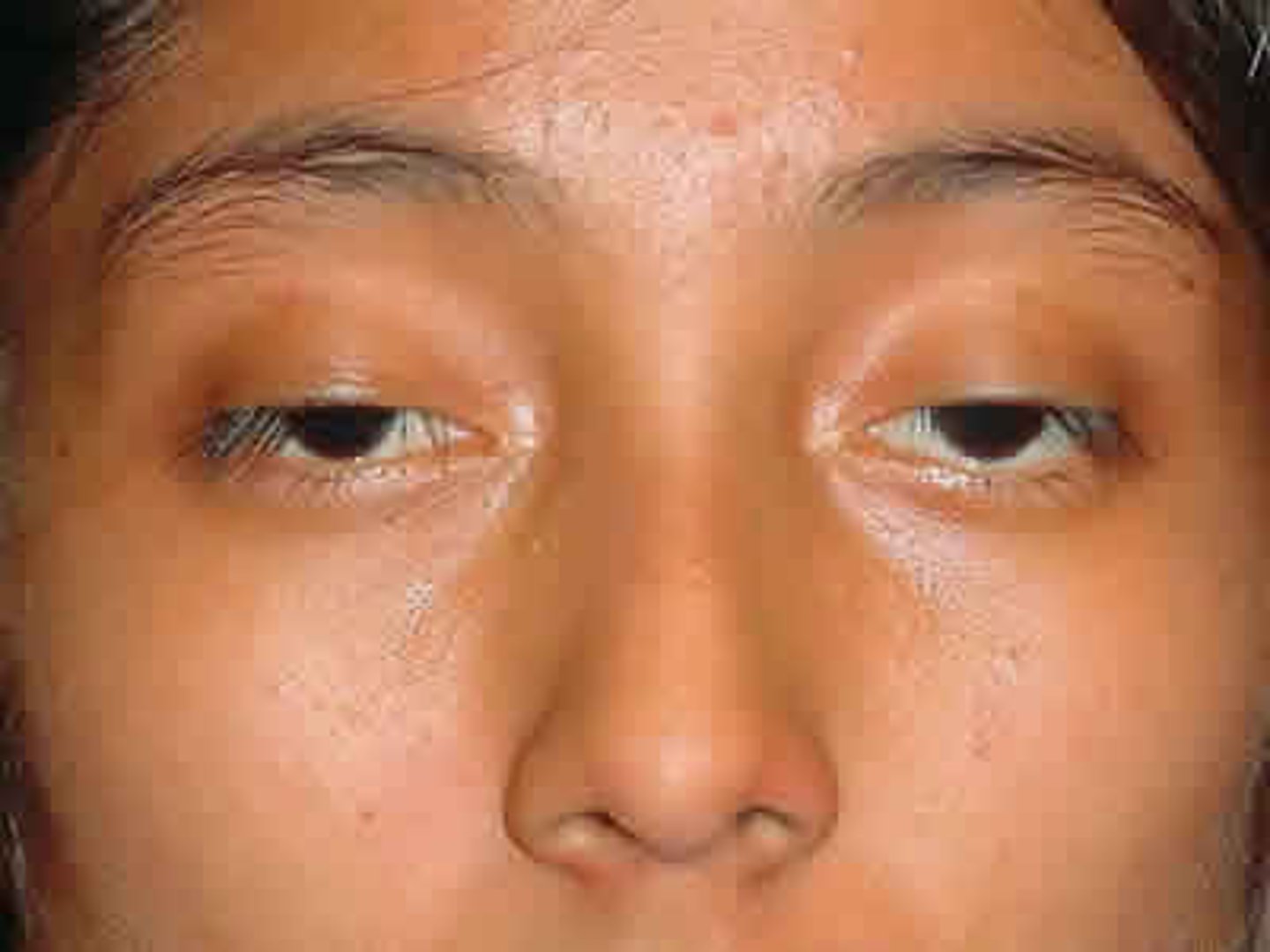
what is Kearns-Sayre syndrome, and what organelle is it linked to?
mitochondrial disorder (mtDNA deletion) that results in paralysis of eye muscles and degeneration of the retina
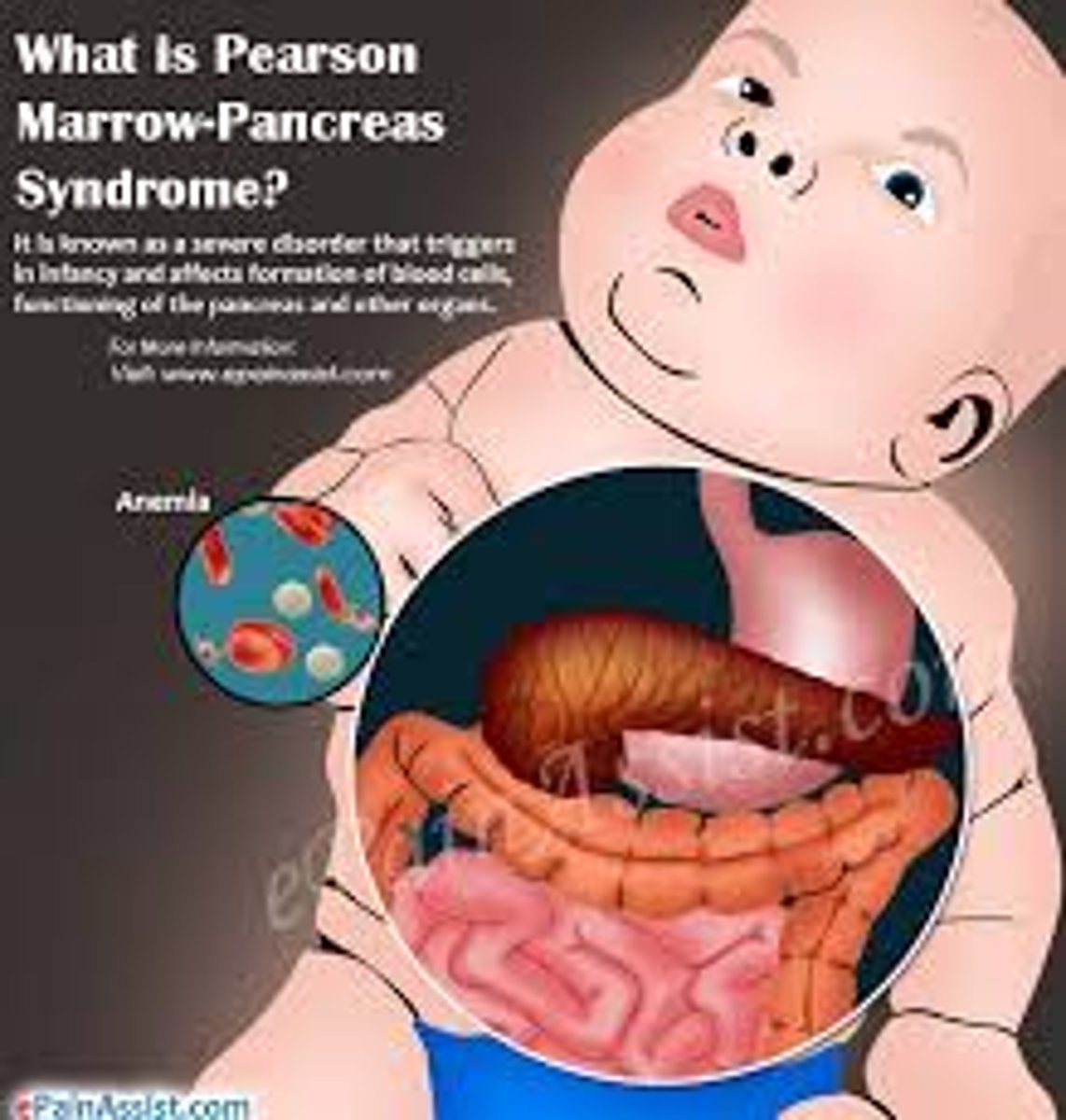
what is Pearson syndrome, and what organelle is it linked to?
mitochondrial disorder (mtDNA deletion) that causes bone marrow and pancreas dysfunction
what is Leber hereditary optic neuropathy, and what organelle is it linked to?
mitochondrial disorder (mtDNA mutation) that causes painless loss of central vision in 1 or both eyes
- inherited from the MOTHER

what enzymes are most prevalent in lysosomes?
acid hydrolases
- hydrolyze/break down macromolecules (protein, nucleic acids, carbs, lipids)
what are lysosomal storage diseases?
genetic disorders characterized by the accumulation of abnormal amounts of carbs or lipids, primarily due to their defective acid hydrolases
- categorized by the type of compound that accumulates to toxic levels within the lysosome
what is Tay-Sachs disease, and what organelle is it linked to?
an autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disease that causes nervous system breakdown and death, leading to mental and physical disabilities
- inability to swallow, blindness, deafness, paralysis, early death (by age 2-4)
- 3 types: infantile, juvenile, and adult/late-onset
- caused by mutations in the hexosaminidase (HEXA) on chromosome 15 and subsequent absence of β-HEXA A enzyme activity
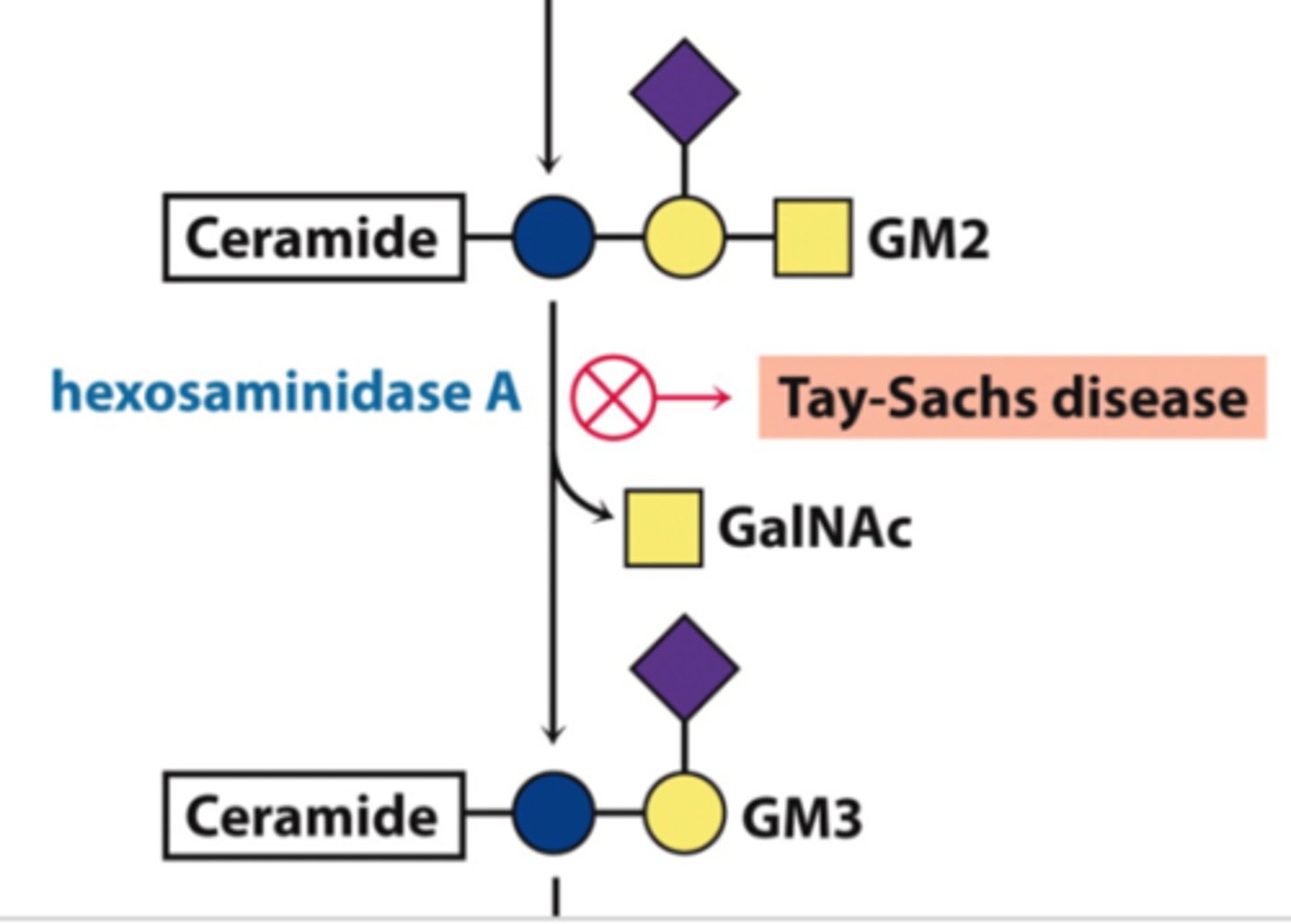
in Tay-Sachs disease, a certain enzyme is nonfunctional; what is the role of this enzyme under normal conditions?
HEXA A normally breaks down GM2 gangliosides
- mutation leads to accumulation of gangliosides in the brain, causing nerve cell damage
what are Hunter and Hurler syndrome, and what organelle are they linked to?
lysosomal storage diseases characterized by an accumulation of glycosaminoglycans