IB Bio Nervous System Part I
4.8(9)
4.8(9)
Card Sorting
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
1
New cards
neuron
nerve cell
2
New cards
nervous system
made of neurons
3
New cards
three parts of neuron
1. cell body
2. dendrites
3. axons
4
New cards
cell body function
does normal cellular functions
5
New cards
dendrites function
receive nerve impulses
6
New cards
axons function
deliver impulses to other neurons
7
New cards
sensory neurons
receive initial stimulus
8
New cards
are sensory neurons afferent, efferent, or interneurons?
afferent (carry messages toward central nervous system)
9
New cards
motor neurons
stimulate target cells (effectors) that produce some kind of response
10
New cards
are motor neurons afferent, efferent, or interneurons?
efferent (carry messages away from central nervous system)
11
New cards
associated neurons
receive impulses from sensory neurons or send impulses to motor neurons
12
New cards
are associated neurons afferent, efferent, or interneurons?
interneurons
13
New cards
associated neurons location
in spinal cord or brain
14
New cards
ion
single atom or group of atoms w/ positive or negative charge
15
New cards
two ions in nervous system
Na+ & K+
16
New cards
nerve impulses are a…
result of chemical changes across membrane
17
New cards
neuron membrane is…
polarized/non-firing b/c positive & negative charges = separated from each other
18
New cards
**ion** outside of neuron
Na+
19
New cards
**ion** inside of neuron
K+
20
New cards
**charge** outside of neuron
positive b/c only Na+
21
New cards
**charge** inside of neuron
negative b/c large negatively charged ions move in & contribute to overall level of charge (ex: Cl-, proteins-)
22
New cards
neuron membrane maintained by…
Na+/K+ pump
23
New cards
polarization
* outside: (+) charge, high Na+, low K+
* inside: (-) charge, high K+, low Na+, protein-
* inside: (-) charge, high K+, low Na+, protein-
24
New cards
depolarization
* Na+ channels open & Na+ rushes inside of membrane from outside
* outside: no charge, Na+ =, low K+
* inside: no charge, Na+ =, high K+, protein-
* outside: no charge, Na+ =, low K+
* inside: no charge, Na+ =, high K+, protein-
25
New cards
repolarization
* K+ channels open & K+ ions sent out of neuron from inside → polarized membrane is restored
* outside: (+) charge, Na+ =, K+ =
* inside: (-) charge, Na+ =, K+ =, protein-
* outside: (+) charge, Na+ =, K+ =
* inside: (-) charge, Na+ =, K+ =, protein-
26
New cards
channel proteins
allow ions to flow thru them from one side to the other of plasma membrane; allow neuron to be depolarized
27
New cards
nerve impulses are simply…
waves of depolarization
28
New cards
where do nerve impulses originate?
wherever plasma membrane is “disturbed” by stimulation
29
New cards
two causes of nerve impulses
external stimuli or neurotransmitters
30
New cards
what reverses membrane polarity?
Na+/K+ pumps stop; Na+ channels allow inflow of Na+ ions
31
New cards
the flow of Na+ ions through Na+ channels begins…
wave of depolarization (neighboring channels open & depolarize)
32
New cards
how long does it take for membrane to repolarize itself & be ready for another impulse?
1 msec
33
New cards
action potential graph
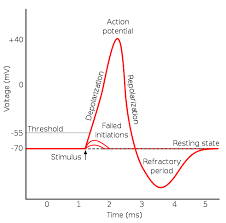
34
New cards
resting state is at ___ mV
\-70 mV
35
New cards
no polarization will occur & not spread to its neighbors at ___ mV
less than -55 mV
36
New cards
resting potential
unstimulated, polarized state of neuron
37
New cards
what happens if stimulus is strong enough?
neuron is above threshold level & causes action potential (complete depolarization)
38
New cards
threshold
* amount of depolarization that will cause a neuron to fire (@ -55 mV)
* prevents neurons from accidentally firing
* prevents neurons from accidentally firing
39
New cards
refractory period
* membrane cannot be stimulated (explains why nerve impulse only moves in one direction)
* neuron will not respond to new stimulus
* reestablishes original position of ions
* hyperpolarization
* neuron will not respond to new stimulus
* reestablishes original position of ions
* hyperpolarization
40
New cards
what does hyperpolarization prevent?
prevents nerve impulses moving in both directions
41
New cards
what does hyperpolarization allow?
allows nerve impulses to move in one direction
42
New cards
all-or-nothing principle
once threshold stimulus is achieved for neuron, impulse will begin & travel to end(s) of neuron
43
New cards
under the all-or-nothing principle, each neuron has its own ___ requirement
threshold
44
New cards
for both Na+ & K+…
there is no channel protein
45
New cards
pumps/transport proteins
active transport
46
New cards
channel protein
facilitated diffusion
47
New cards
how does a repolarized neuron go back to being polarized?
* by Na+/K+ pump (transport protein)
* out: 3Na+
* in: 2K+
* out: 3Na+
* in: 2K+
48
New cards
neuron diagram
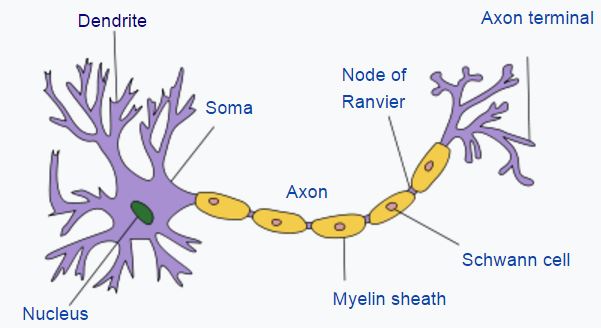
49
New cards
corpus callosum
communication btwn both brain hemispheres
50
New cards
pituitary gland
“master gland”, regulation of other glands & flow of hormones
51
New cards
cerebral cortex
controls high-level processes (ex: language, memory, reasoning, thought, learning, emotion)
52
New cards
thalamus
relays sensory & motor signals; sleep-wake regulation
53
New cards
hypothalamus
controls autonomic functions, body temperature, emotions, hunger, thirst, appetite, digestion, sleep
54
New cards
cerebellum
controls balance, equilibrium, posture, coordination, movement, fine motor skills
55
New cards
pons
“relay center”, transmits signals, controls unconscious movements, breathing, sleep & wake cycles
56
New cards
medulla oblongata
transmits signals, controls vital processes (heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure)
57
New cards
brain stem
controls automatic body functions (heart rate, breathing, sleep and wake cycles, swallowing)