AP Psych Sensation and Perception
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
parallel processing
The ability of the brain to simultaneously process incoming stimuli of differing quality. Parallel processing is associated with the visual system in that the brain divides what it sees into four components: color, motion, shape, and depth
sensation
what occurs when a stimulus activates a receptor
perception
the organization of sensory information into meaningful experiences
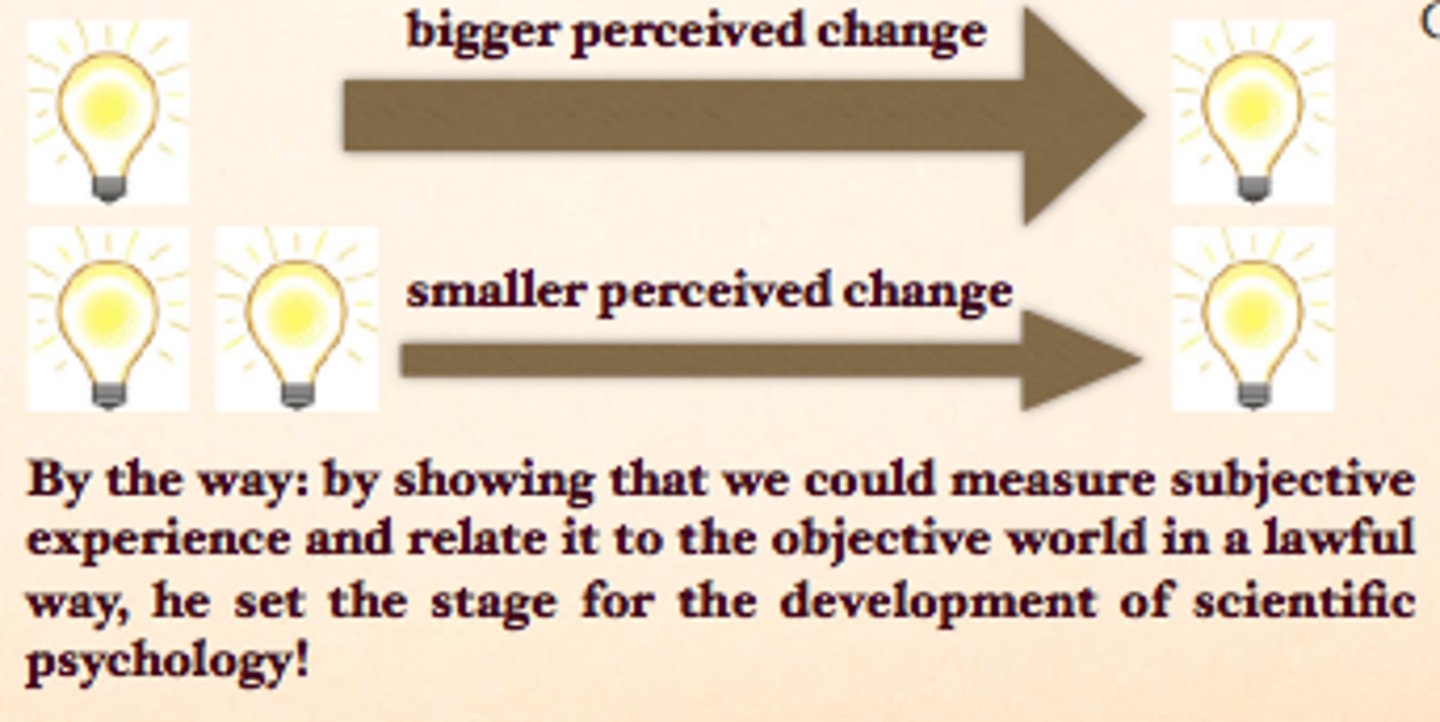
psychophysics
the study of the relationships between sensory experiences and the physical stimuli that causes them
absolute threshold
the weakest amount of a stimulus that a person can detect half the time
difference threshold
the smallest change in a physical stimulus that can be detected between two stimulus
Weber's law
the principle that the layer or stronger a stimulus, the larger the change required for an observer to notice a difference
signal-detection theory
the study of people's tendencies to make correct judgments in detecting the presence of stimuli
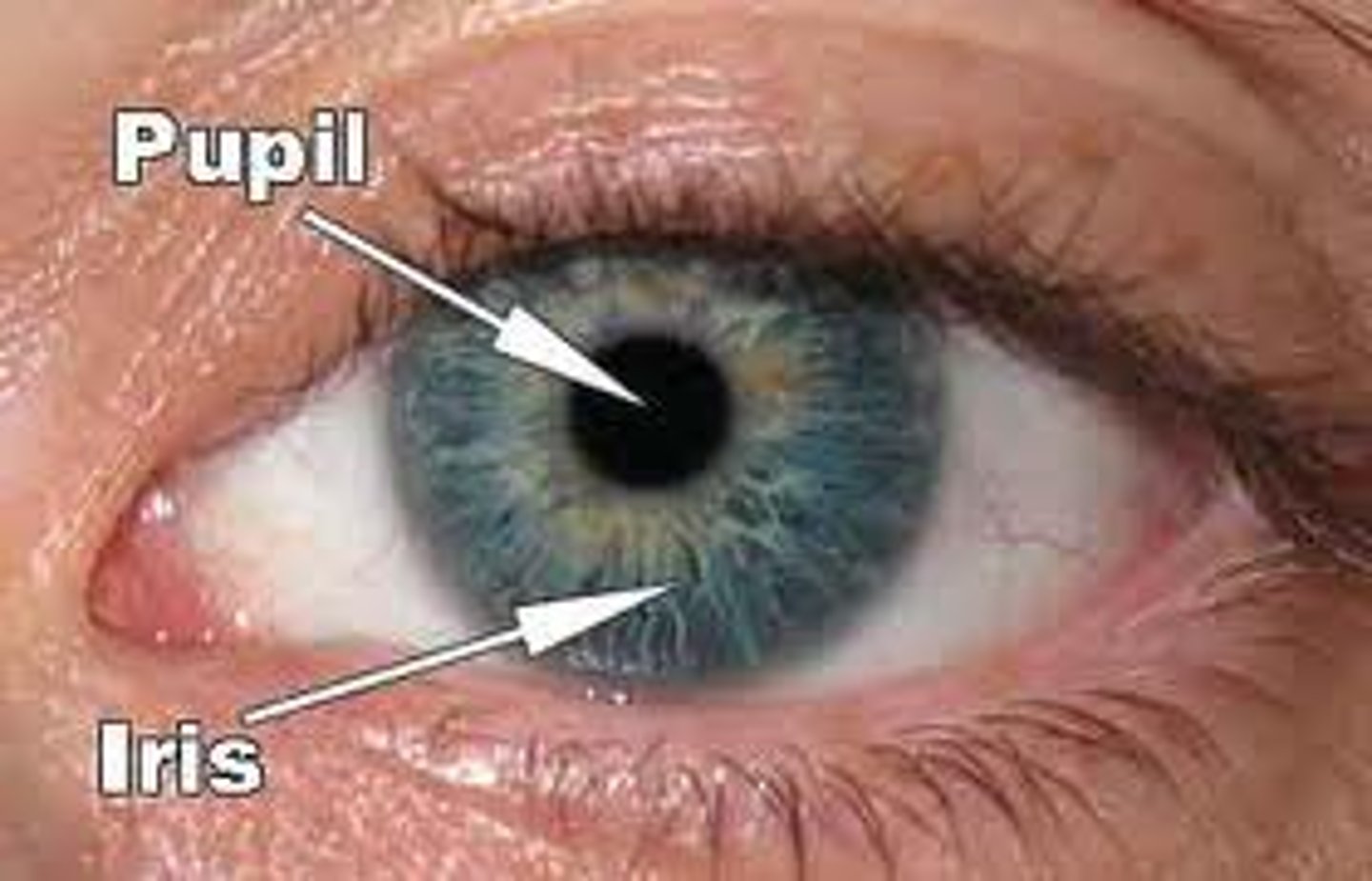
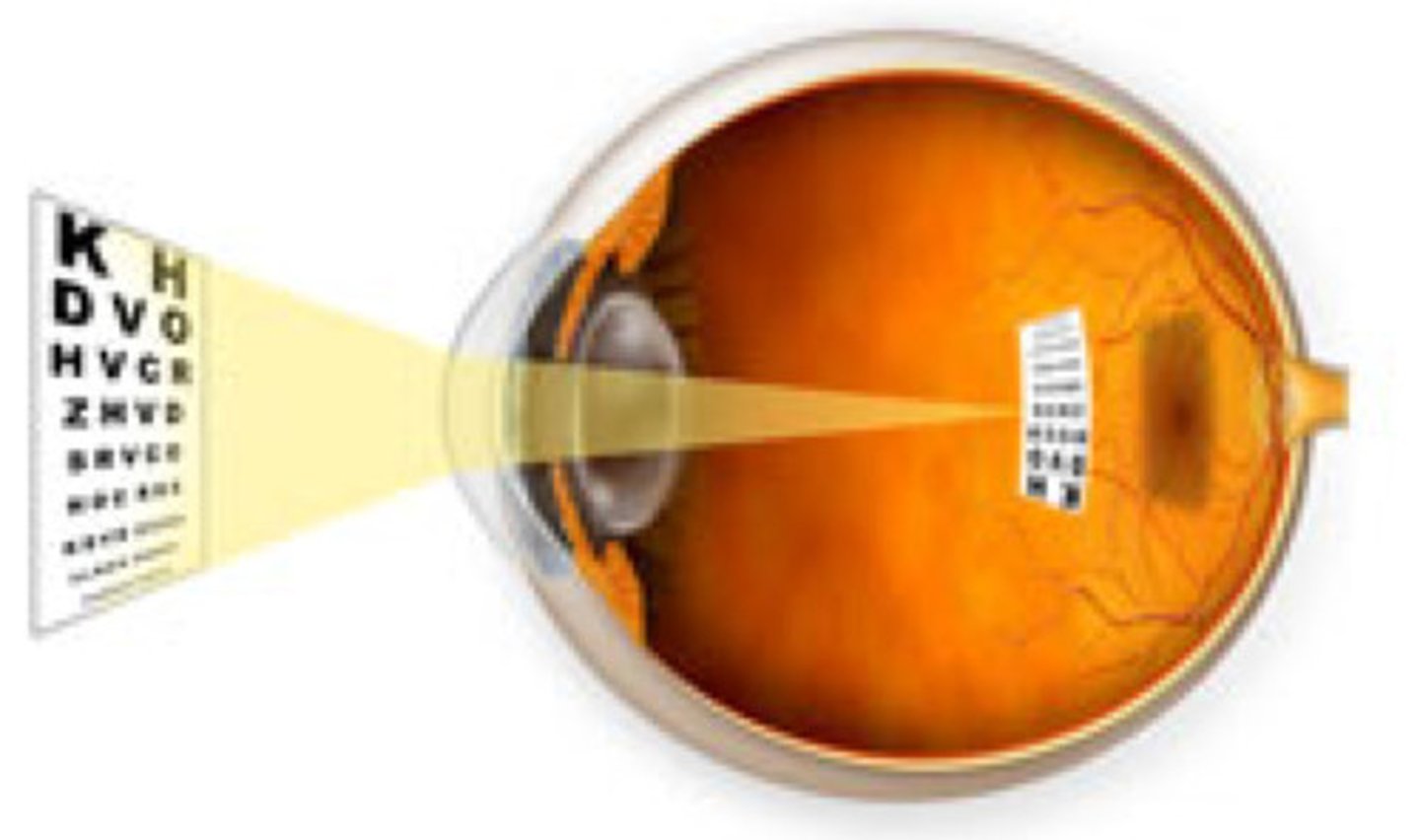
pupil
the opening in the iris that regulates the amount of light entering the eye
lens
a flexible, transparent structure in the eye that changes its shape to focus light on the retina
retina
the innermost coating of the back of the eye, containing the light sensitive receptor cells
optic nerve
the nerve that carries impulses from the retina to the brain
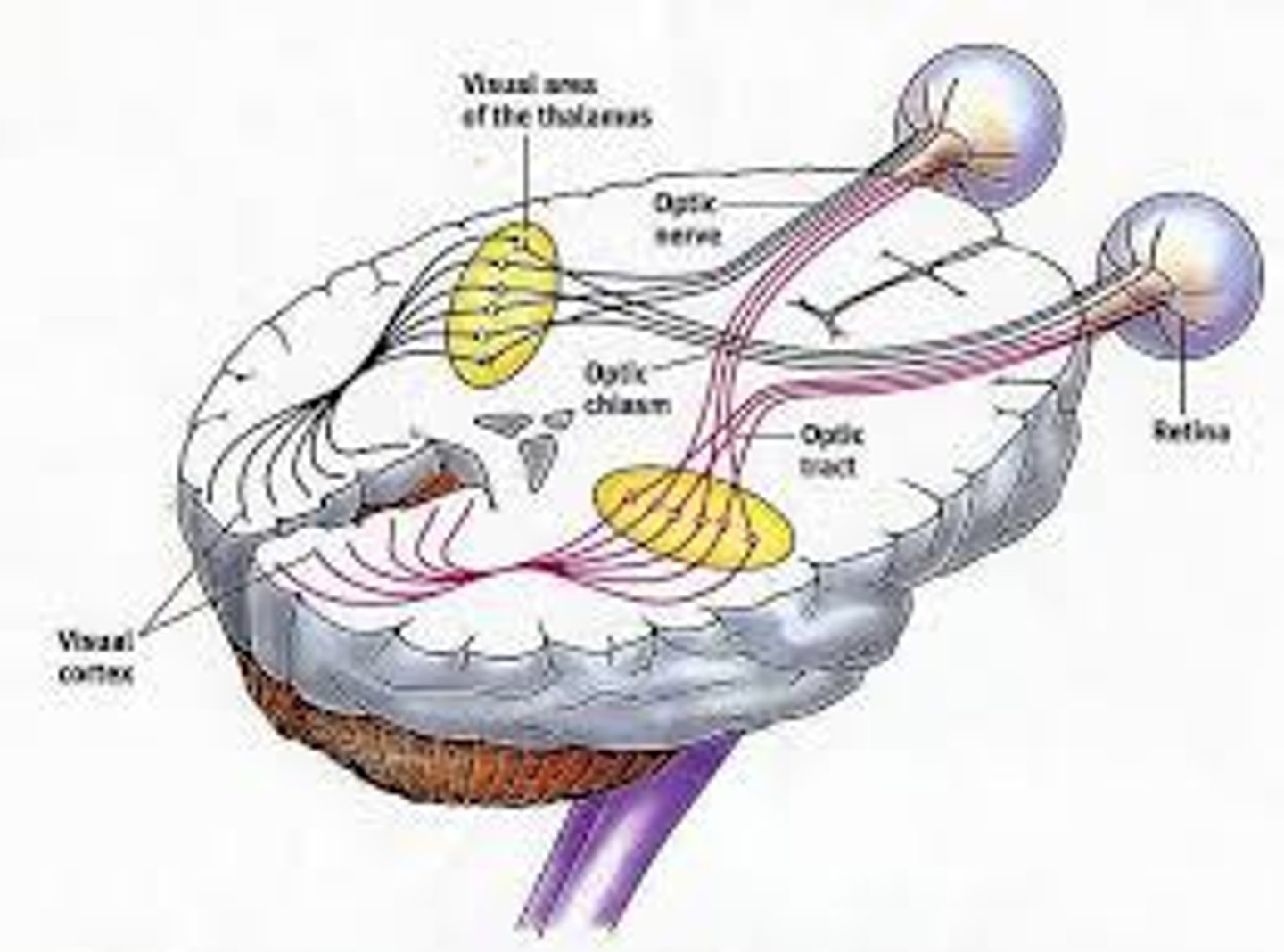
binocular fusion
the processes of combining the images received from the two eyes into a single fused image
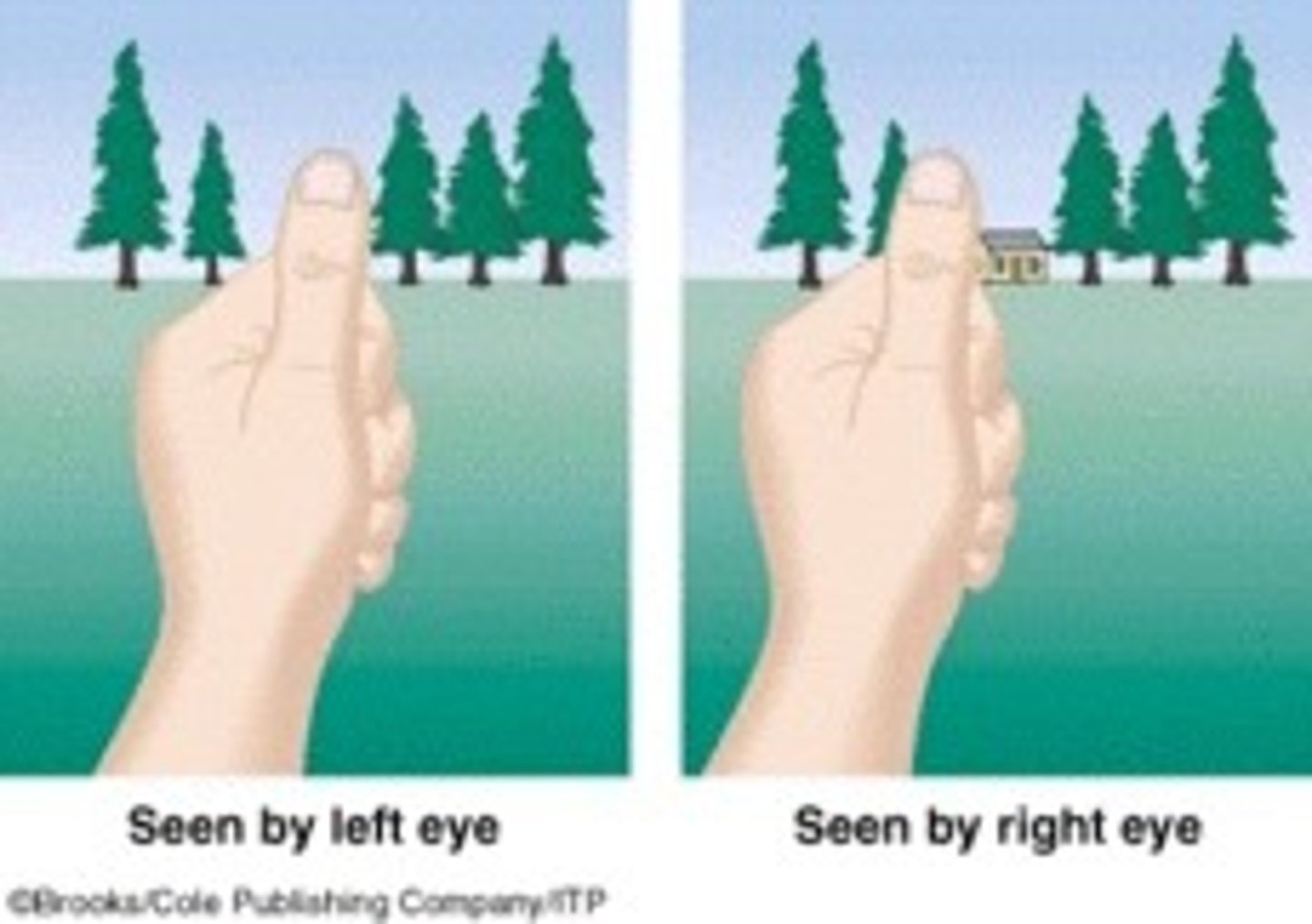
retinal disparity
the differences between the images stimulating each eye
auditory nerve
the nerve that carries impulses from the inner ear to the brain, resulting in the sensation of sound
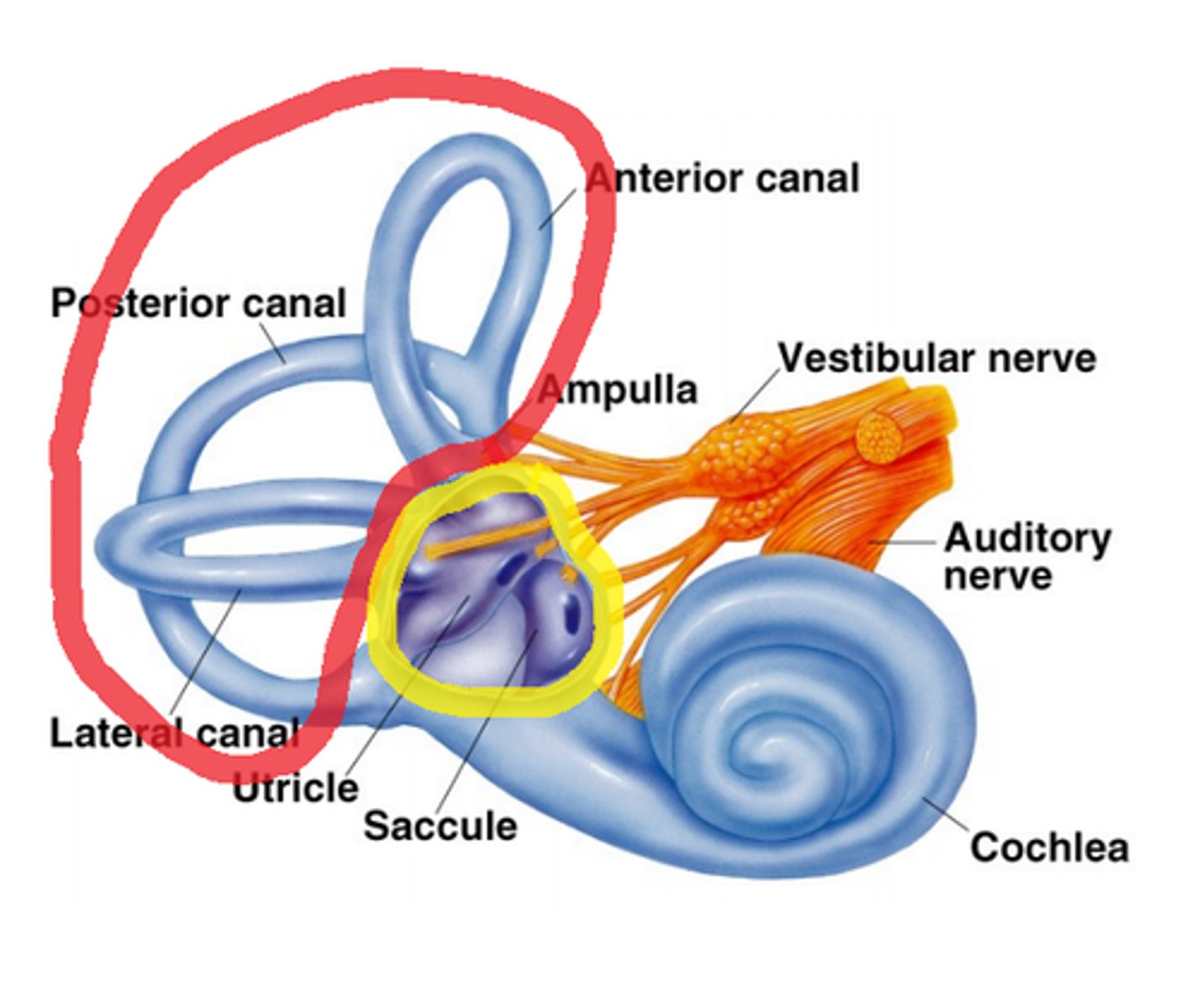
vestibular system
three semicircular canals that provide the sense of balance, located in the inner ear and connected to the brain by a nerve
olfactory nerve
the nerve that carries smell impulses from the nose to the brain
kinesthesis
the sense of movement and body postition
gestalt
the experience that comes from organizing bits and pieces of information into meaningful wholes
subliminal messages
brief auditory or visual messages that are presented below the absolute threshold

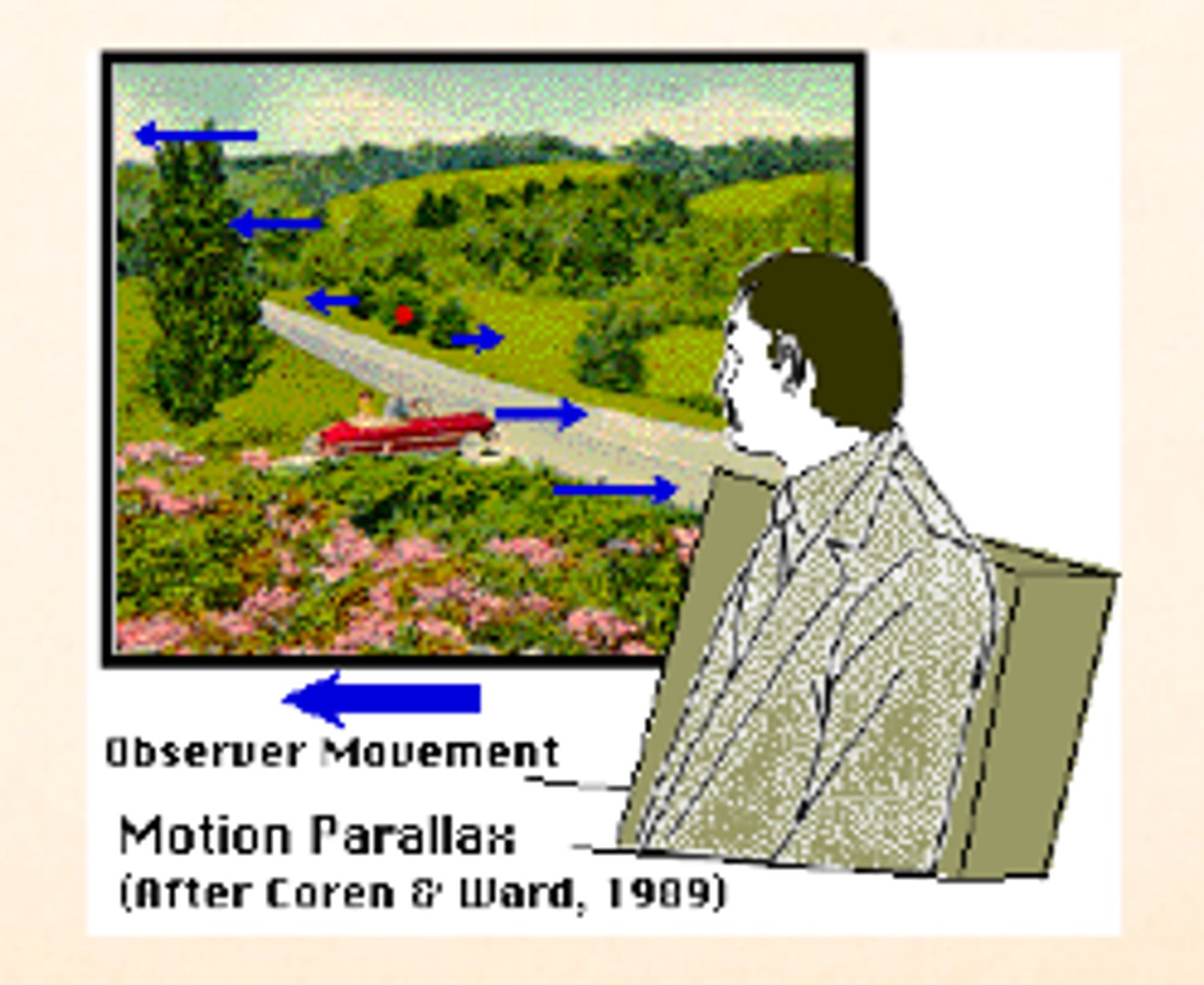
motion parallax
the apparent movement of stationary objects relative to one another that occurs when the observer changes postition

constancy
the tendency to perceive certain objects in the same way regardless of changing angle, distance or lighting
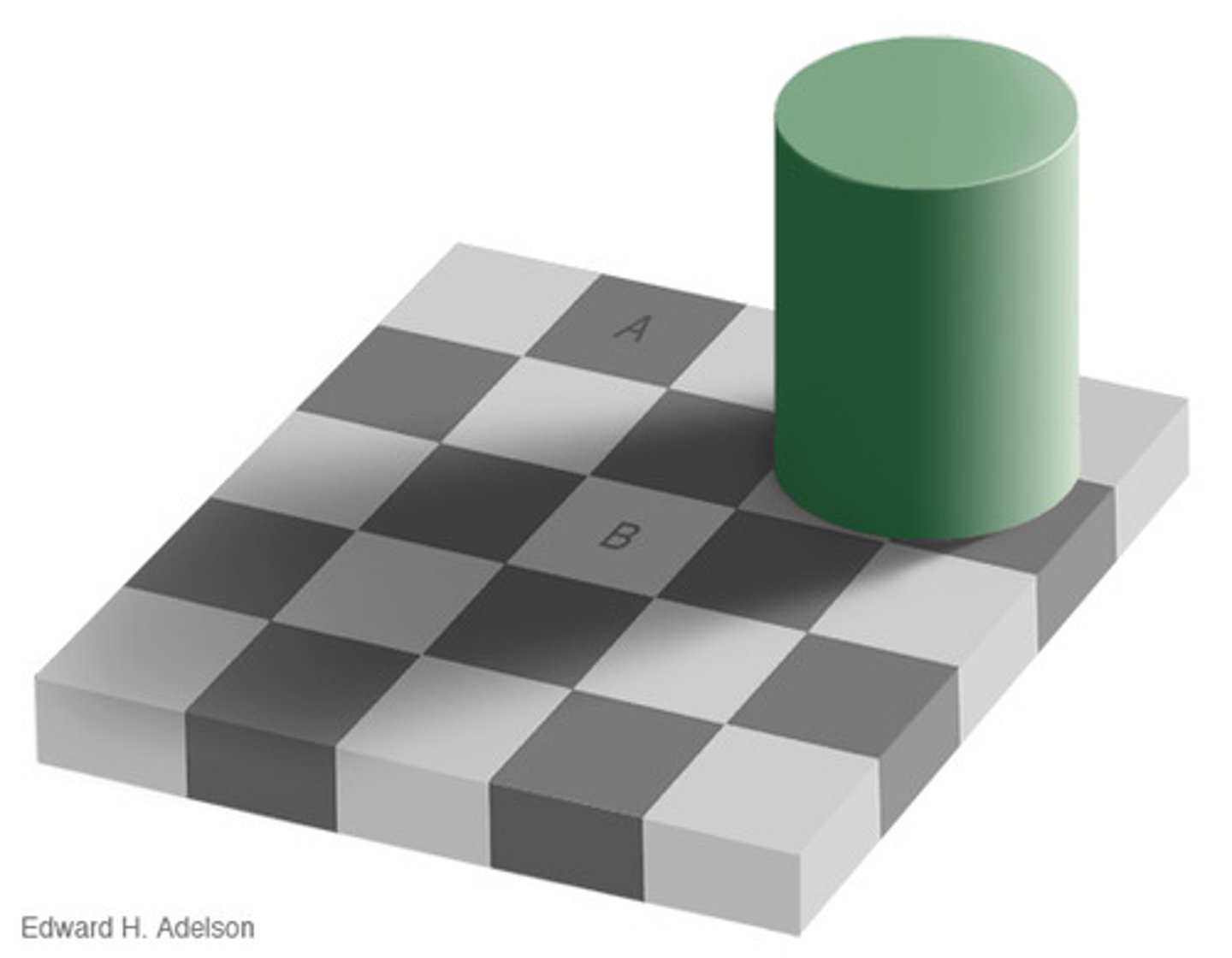
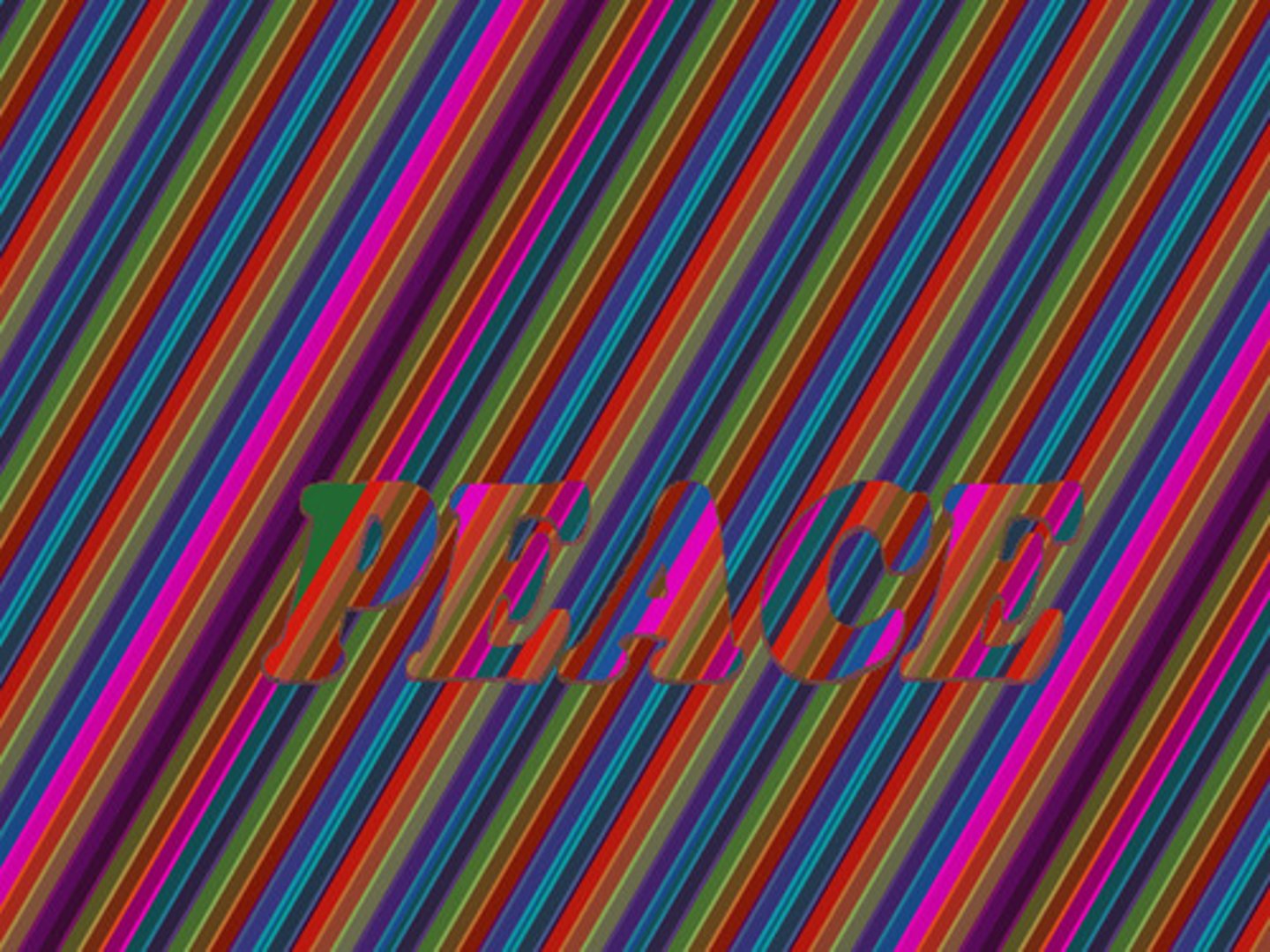
illusions
perceptions that misrepresent physical stimuli
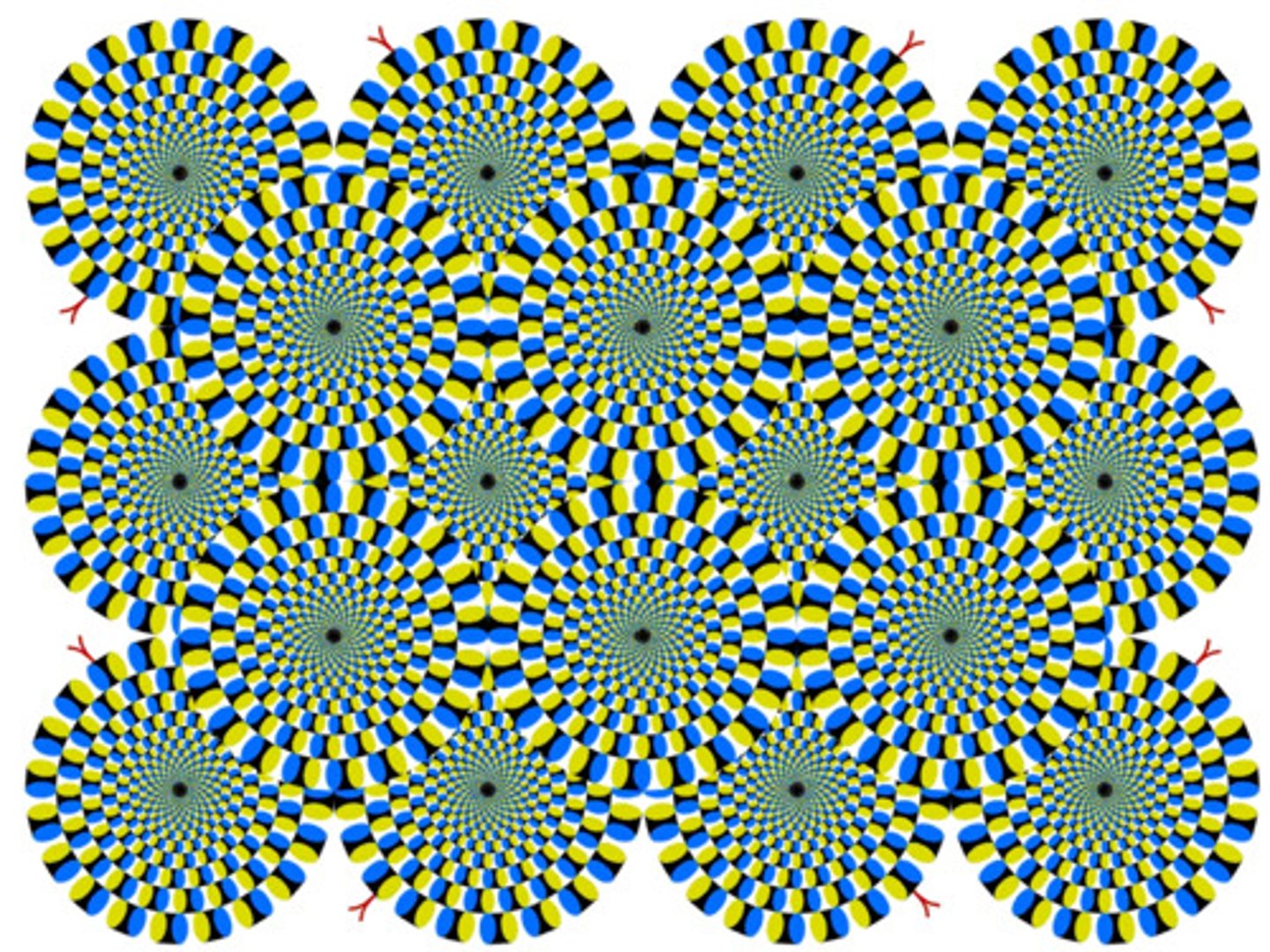
extrasensory perception
(ESP) an ability to gain information by some means other than the ordinary senses

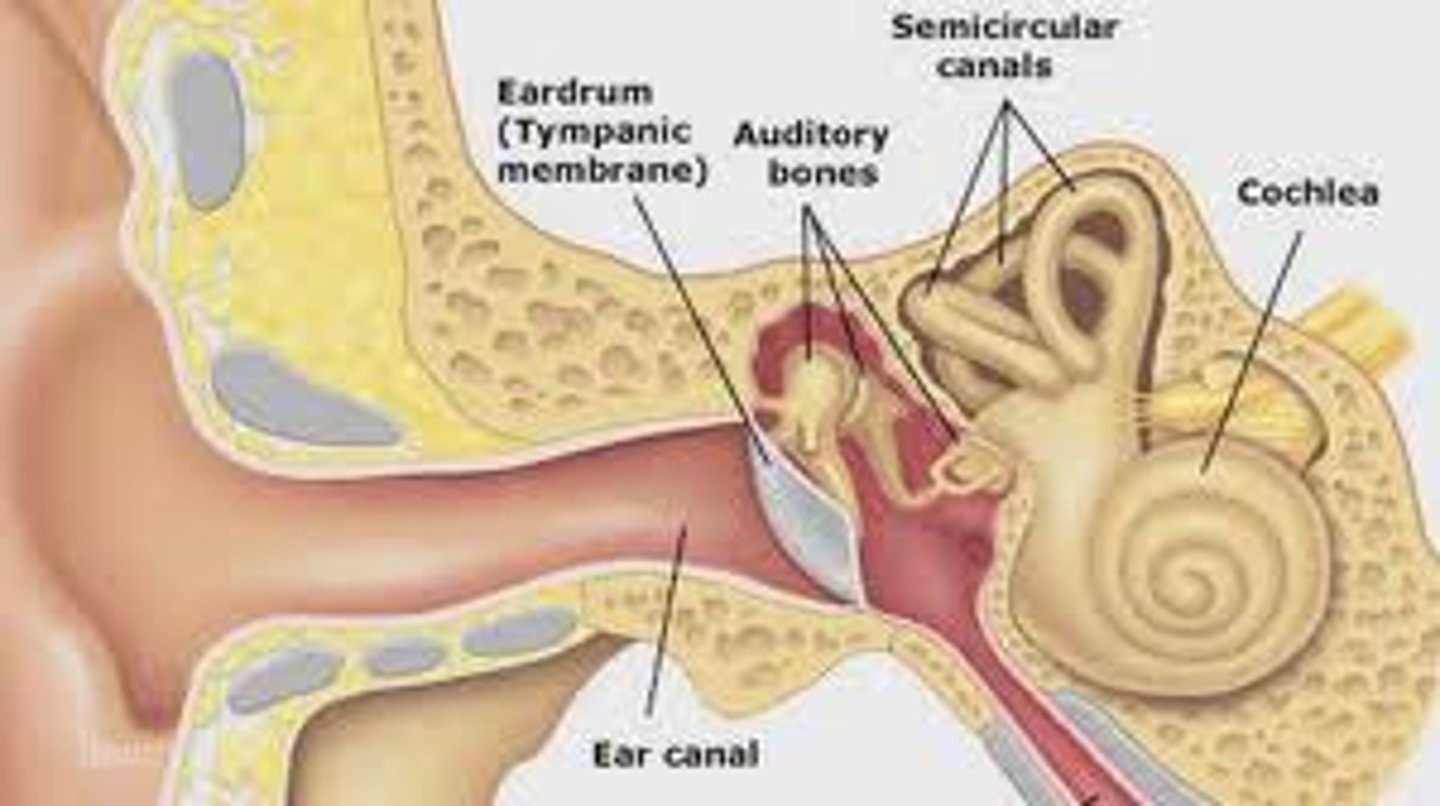
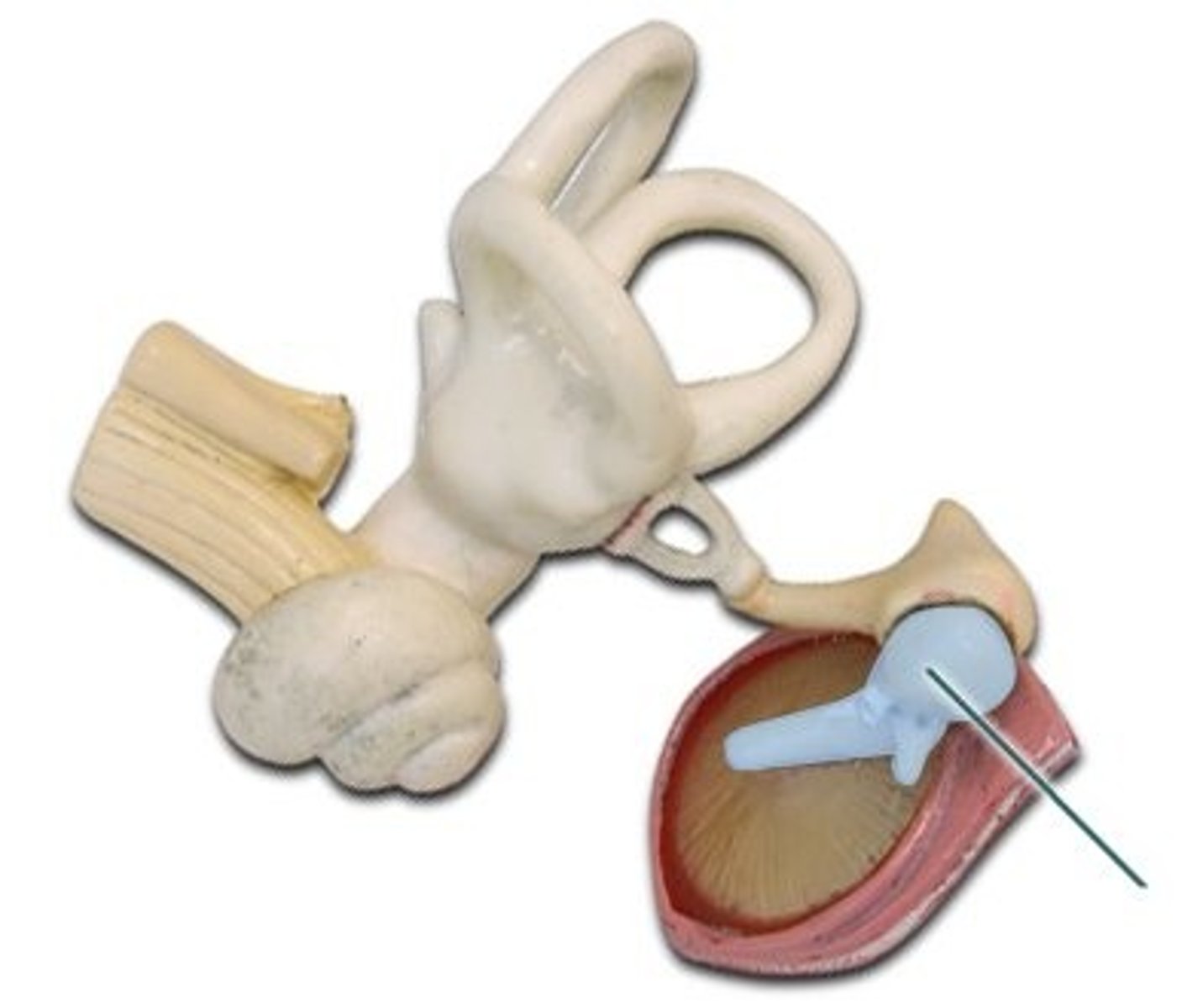
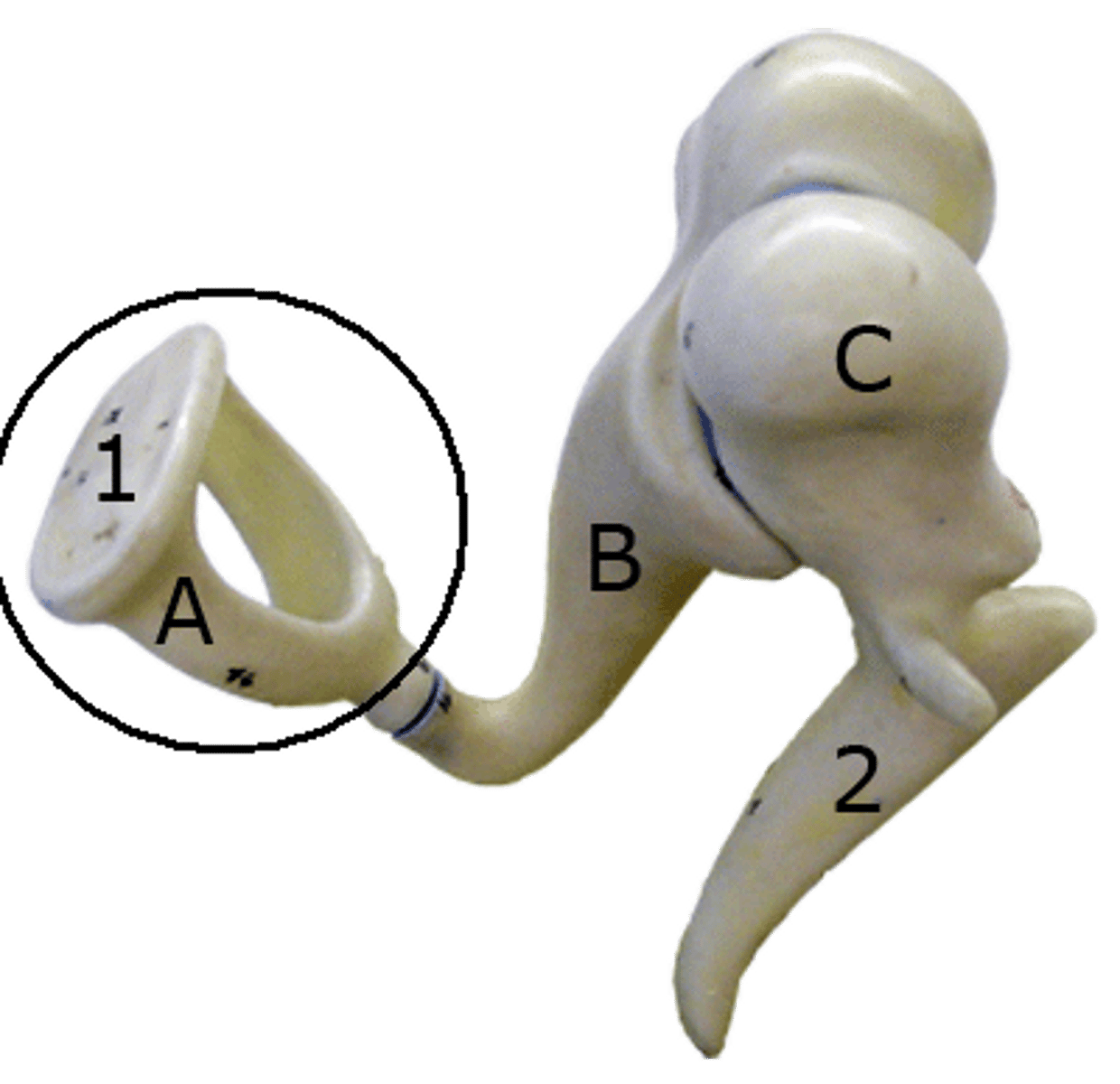
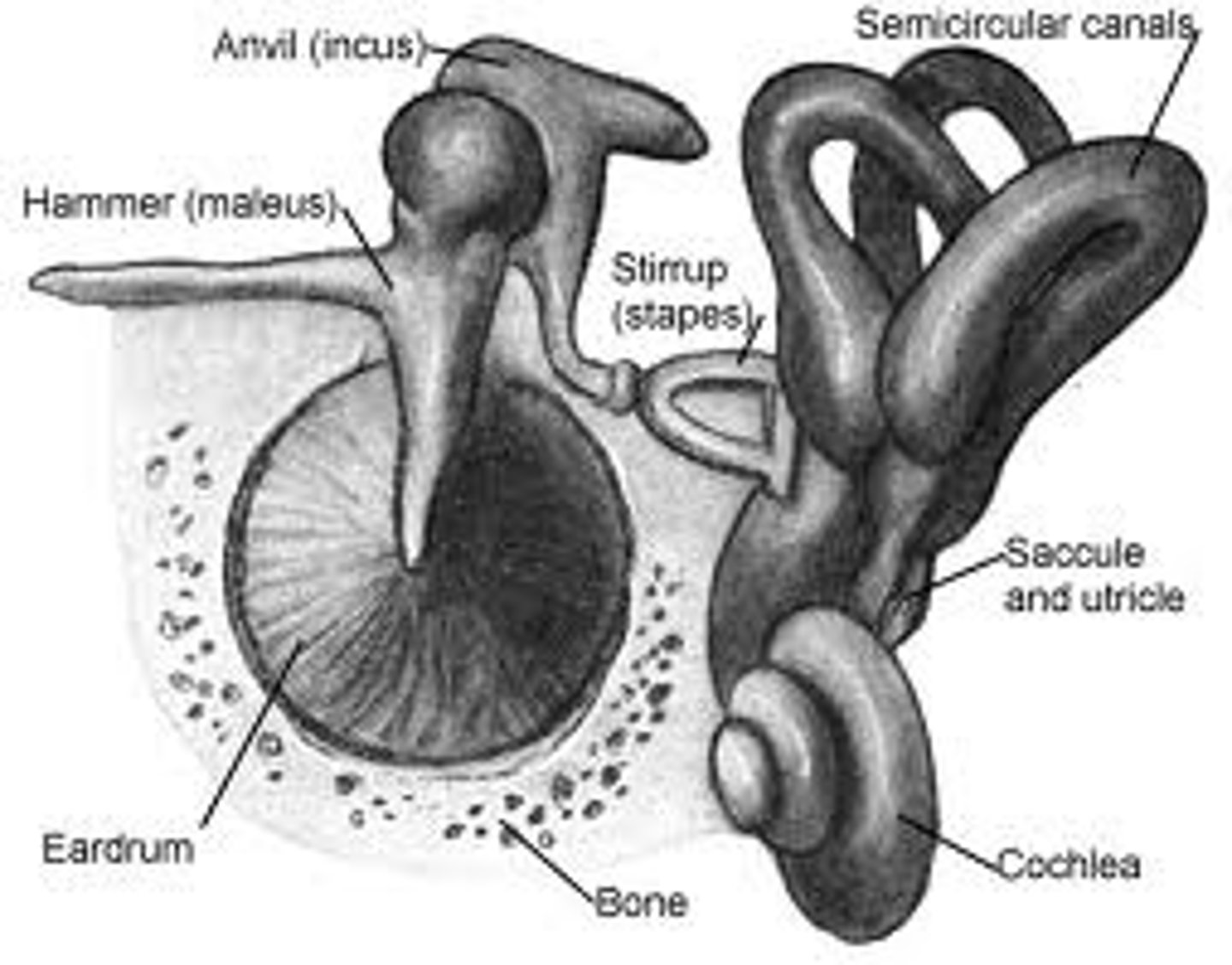
anvil
one of the three tiny bones in the ear. Also one of the main structures of the middle ear. (linked to cochlea & eardrum)
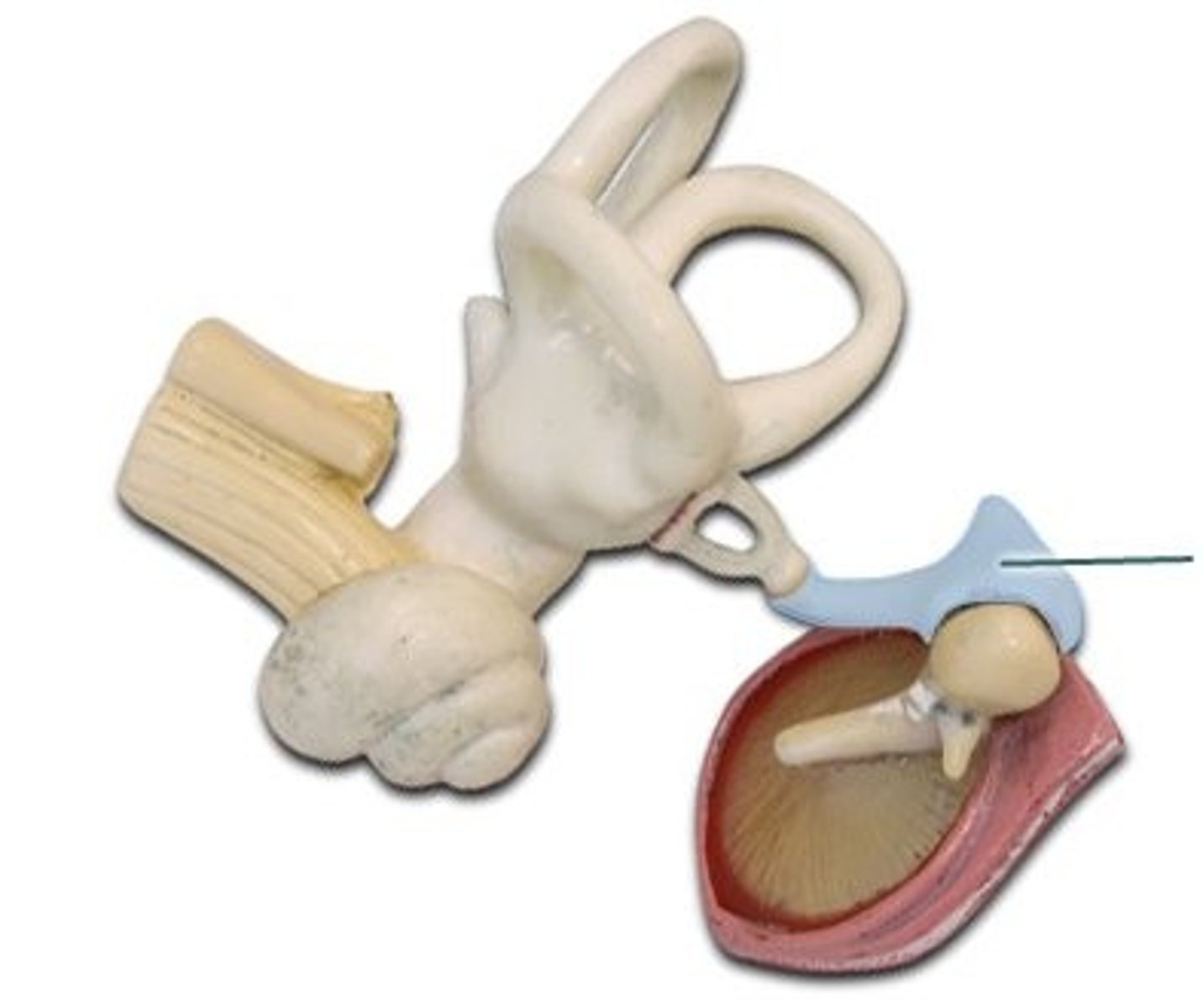
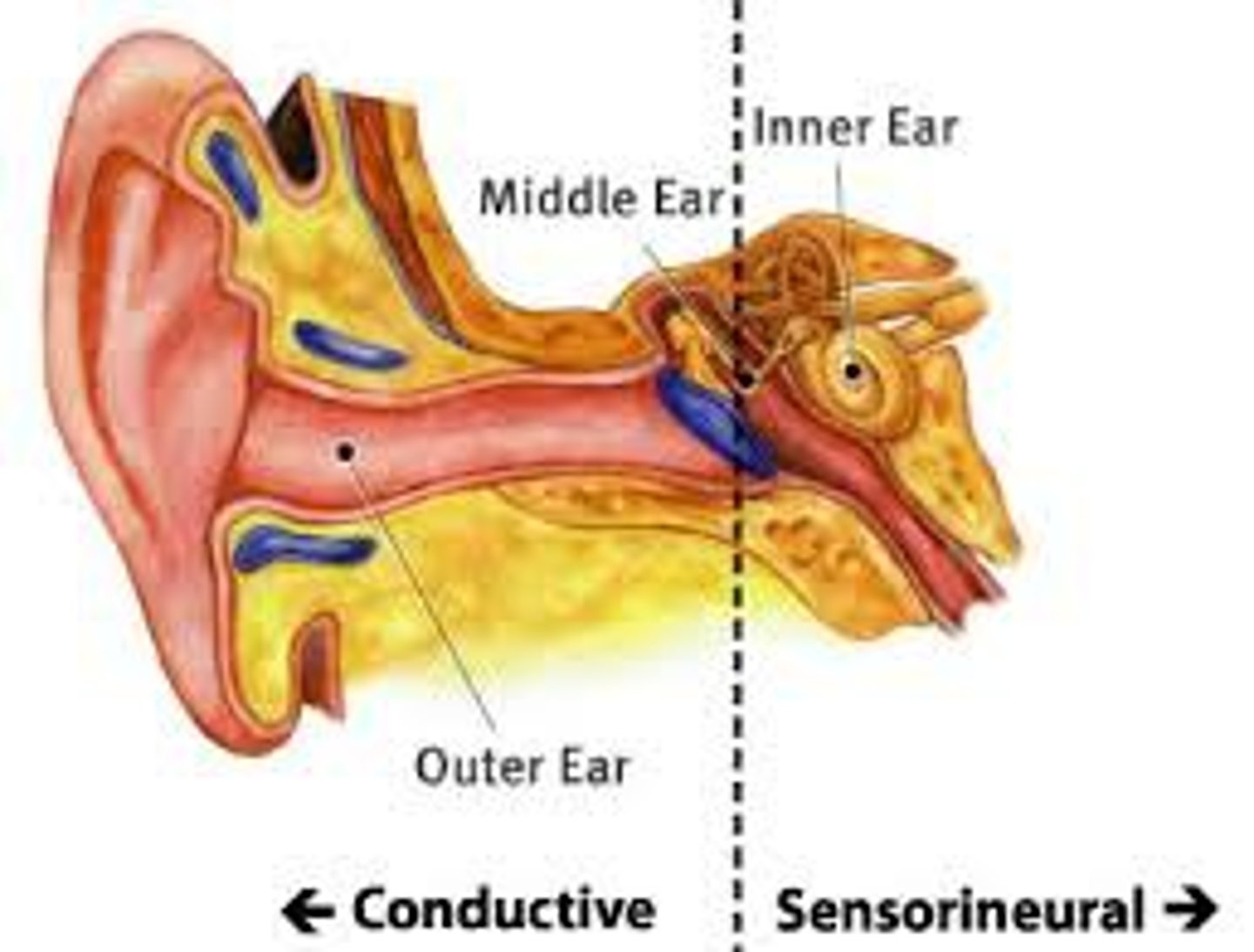
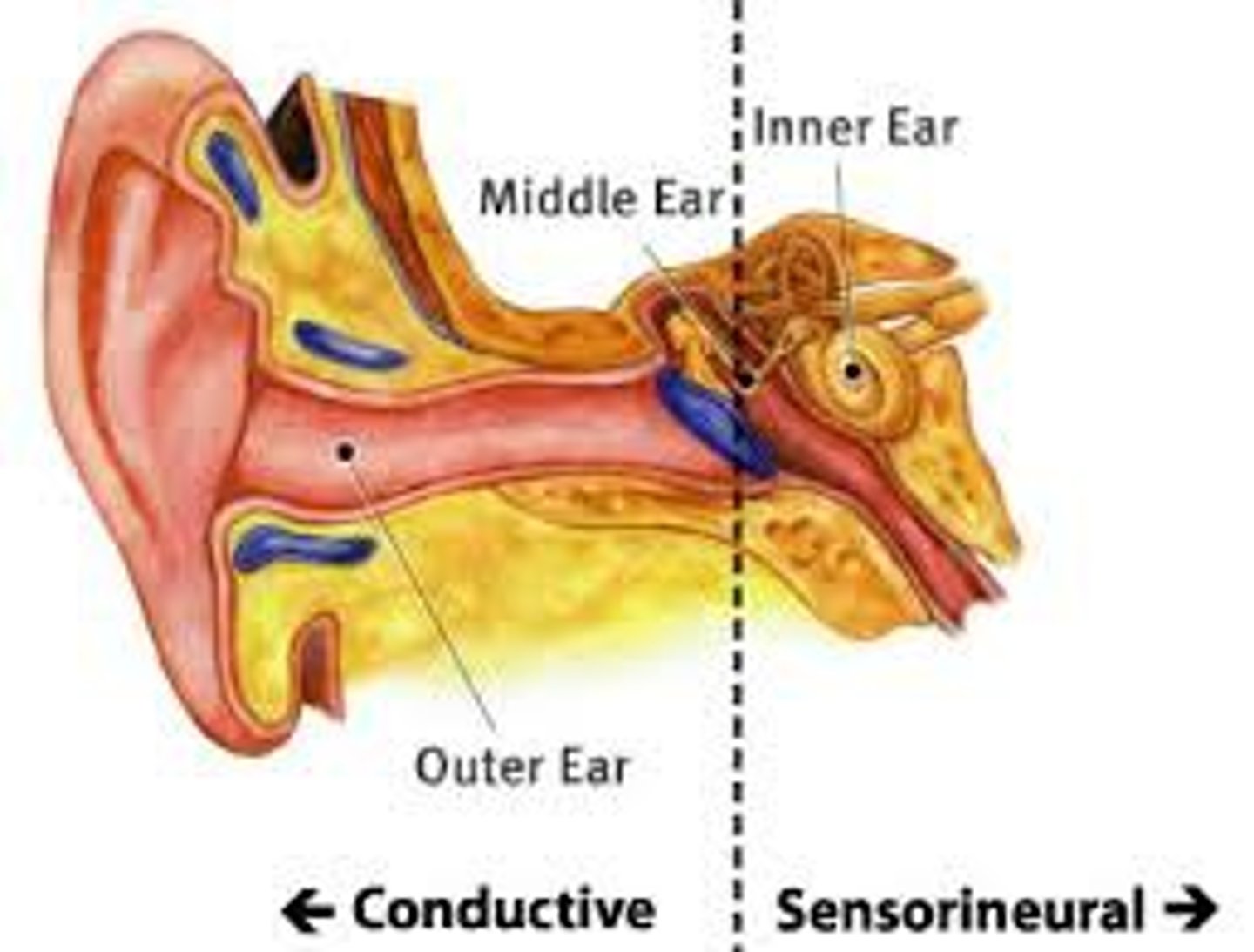
conduction deafness
occurs when anything hinders physical motion through the outer or middle ear or when the bones of the middle ear become rigid and cannot carry sounds inward
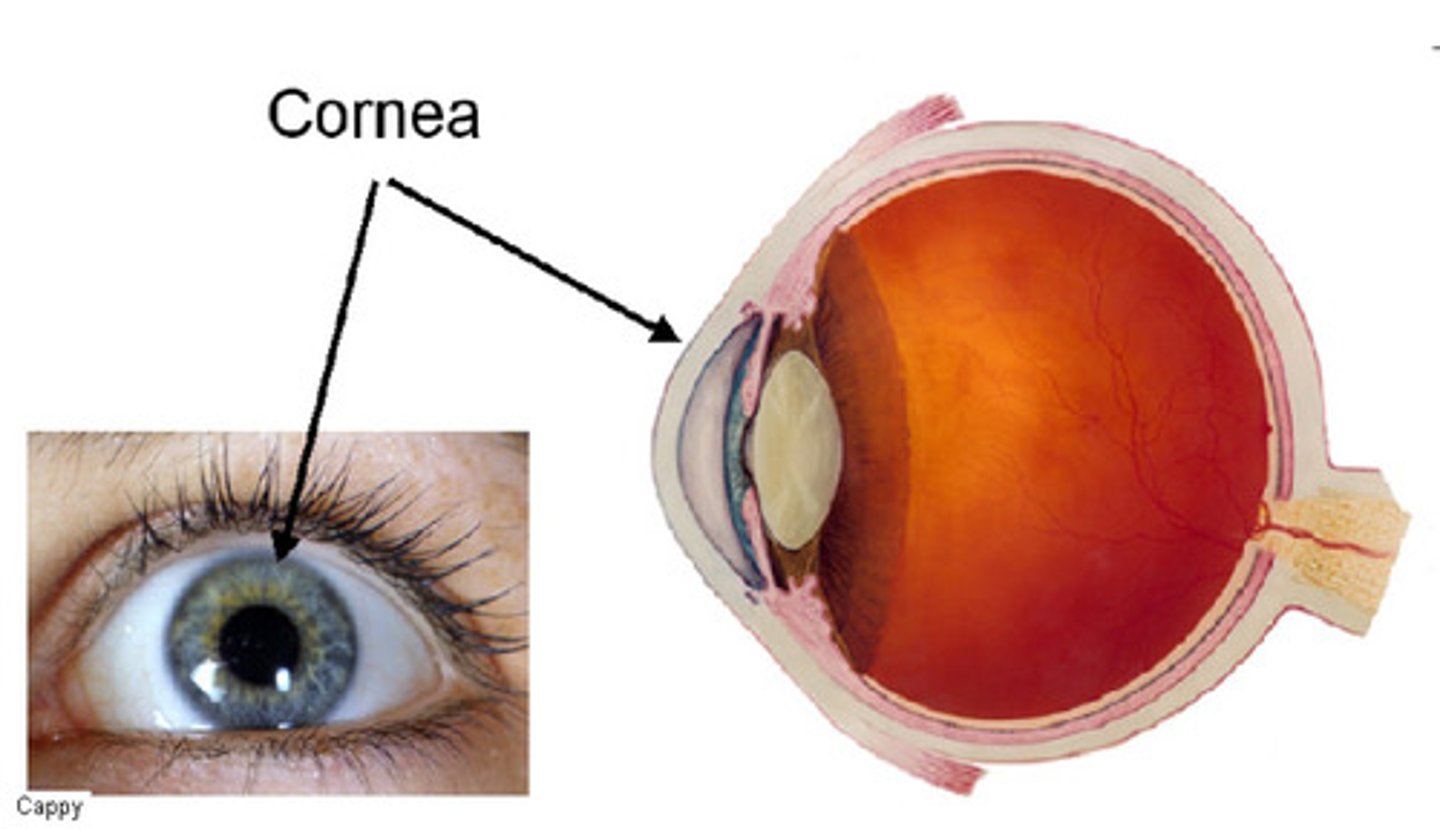
cornea
this cover that is in the front of the human eye
eardrum
where sound waves vibrate to start the hearing processes and is located at the end of the ear canal
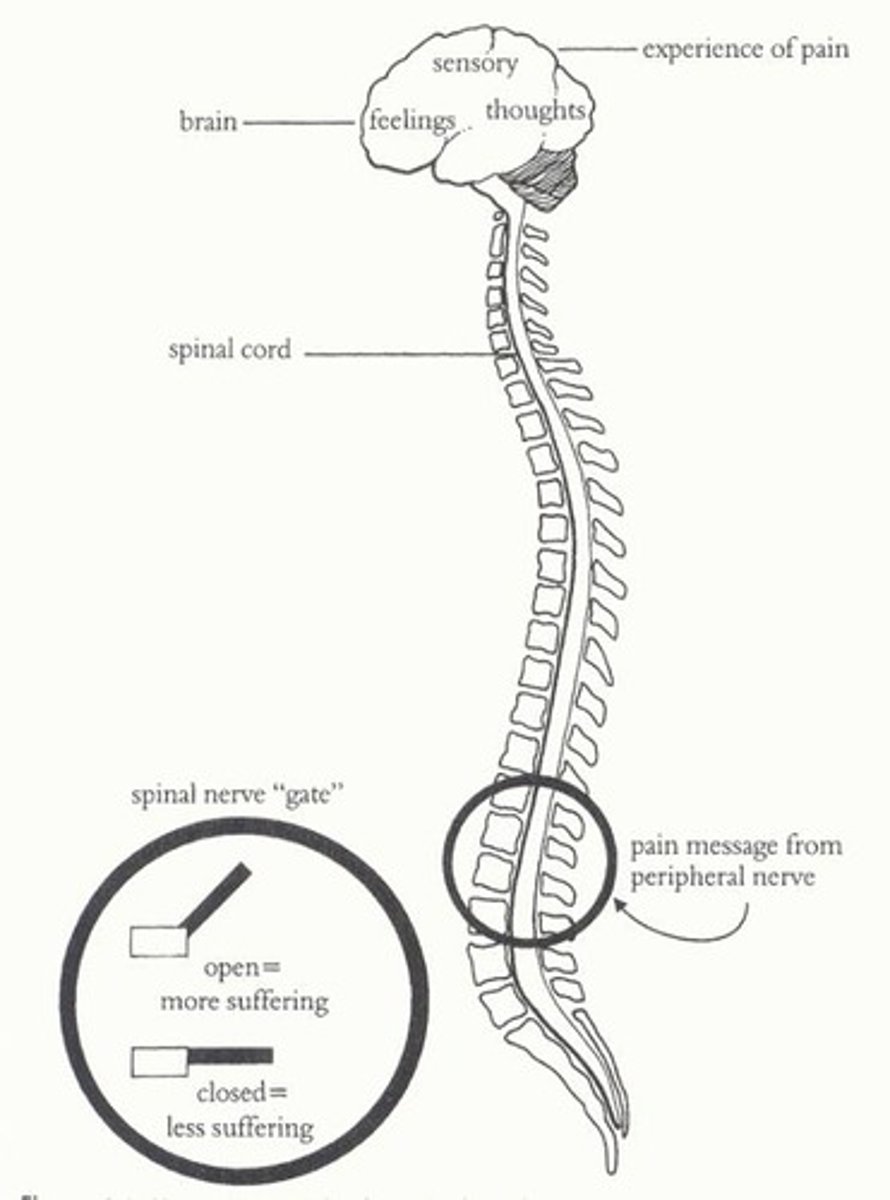
gate control theory
the theory that we can lessen some pains by shifting our attention away from the pain impulses or by sending other signals to compete withe the pain signals
motion sickness
where there is a lack of a sense of balance making it hard to walk and maybe cause you to stumble or fall

semicircular canals
prominent features of the vestibular system
sensorineural deafness
occurs from damage to the cochlea, the hair cells or the auditory neurons.
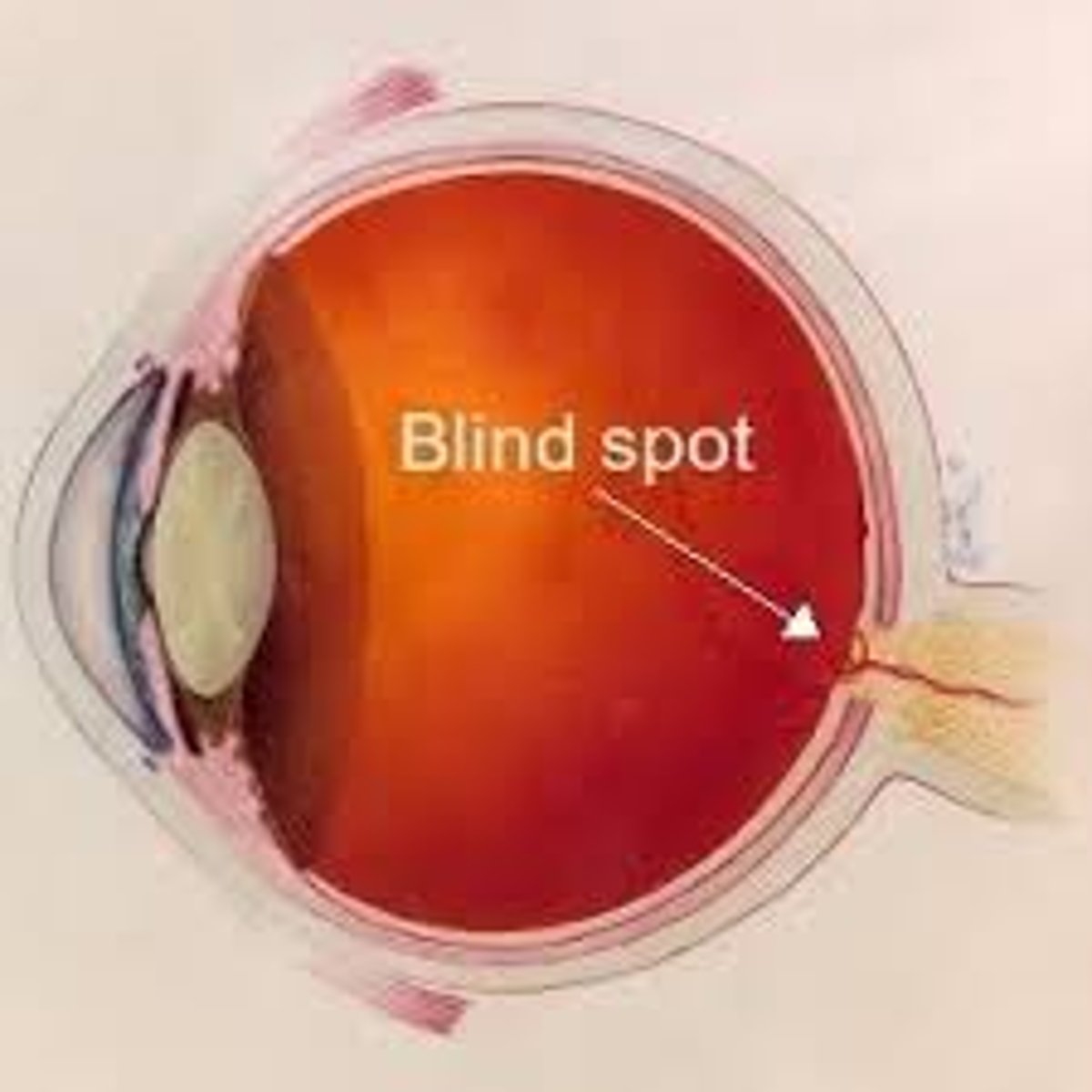
blind spot
the small are, insensitive to light, in the retina of the eye where the optic nerve enters
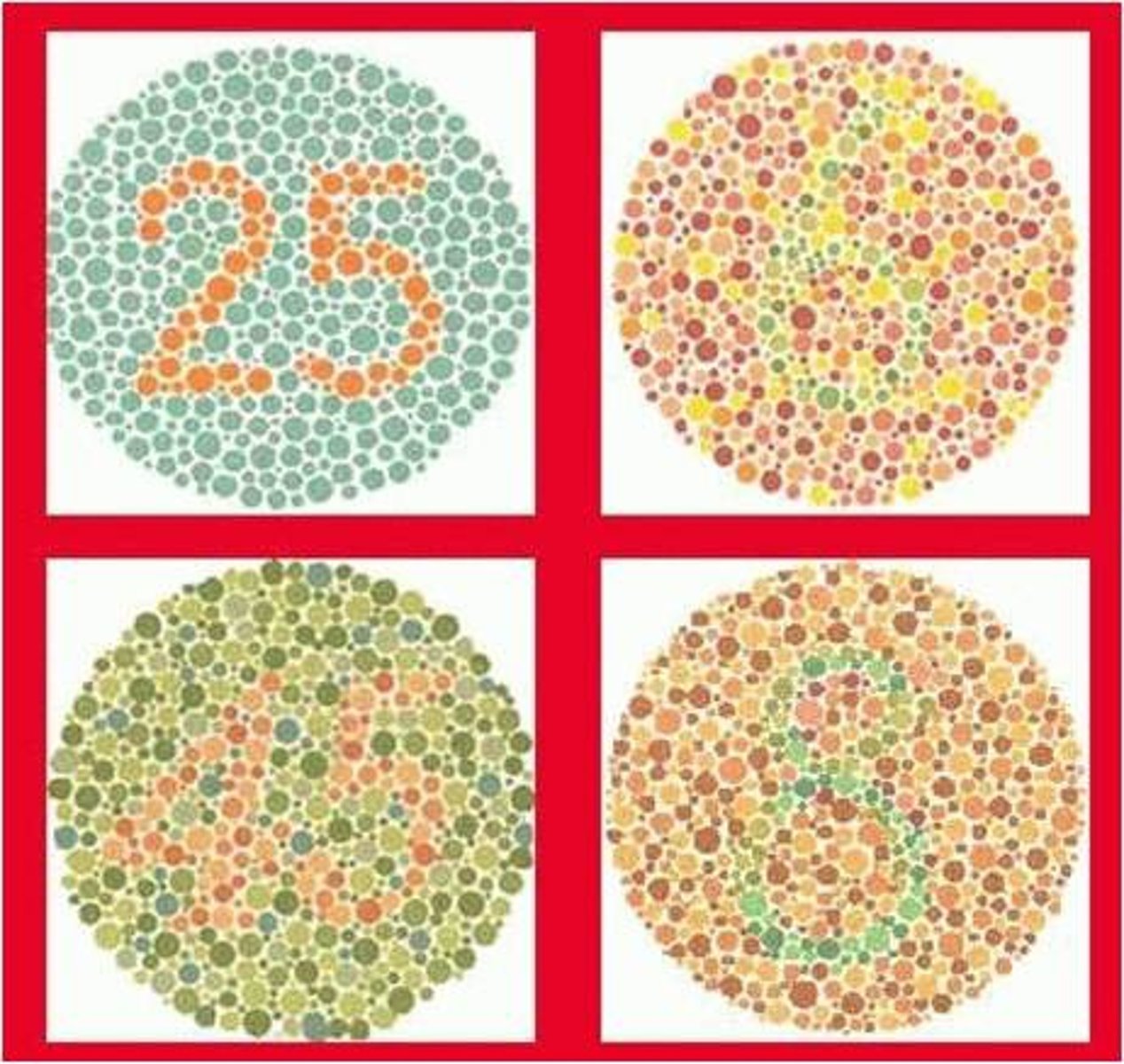
color deficiency
when a person can see some colors (not all)
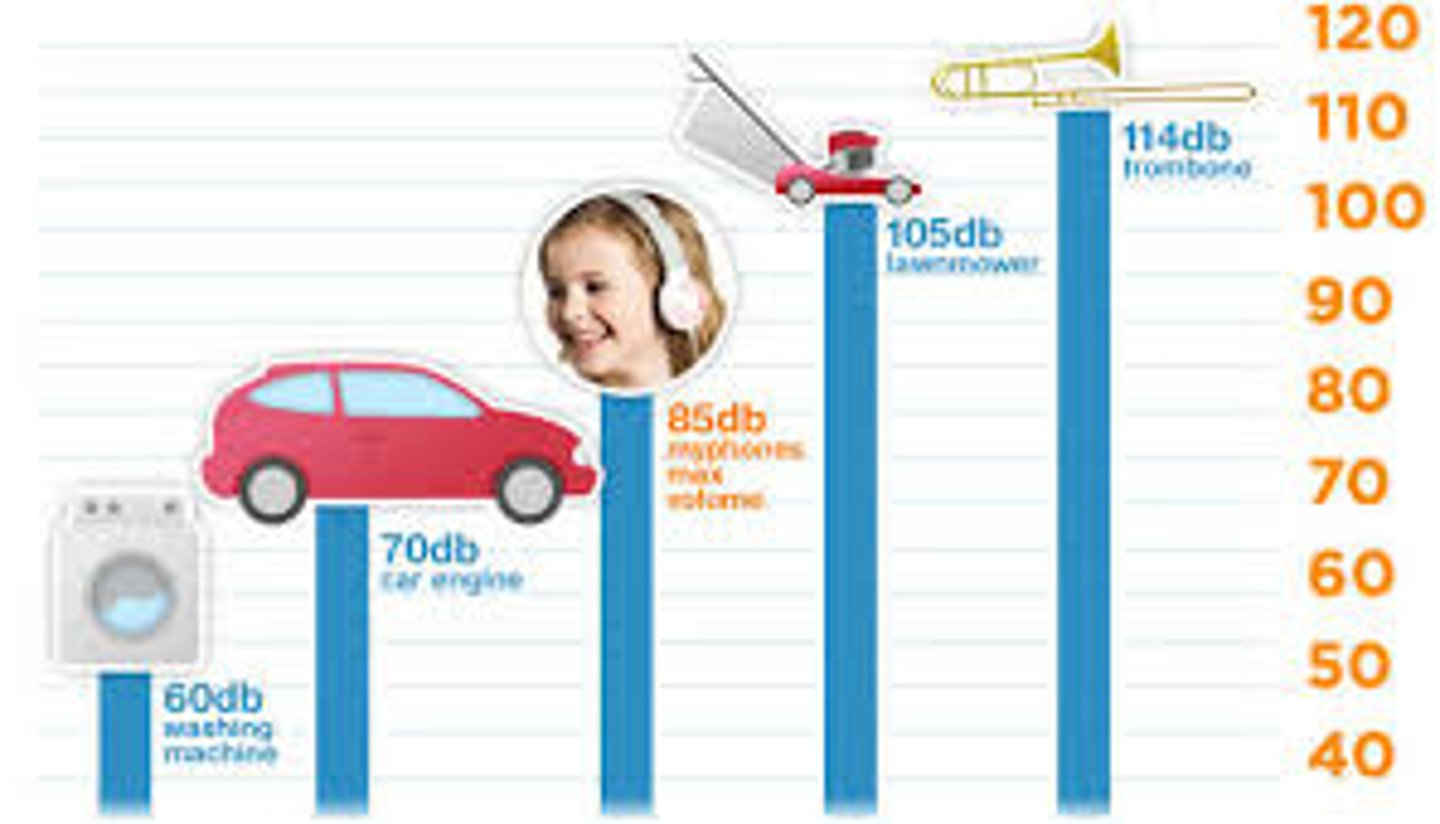
decibels
the softest sound humans can detect
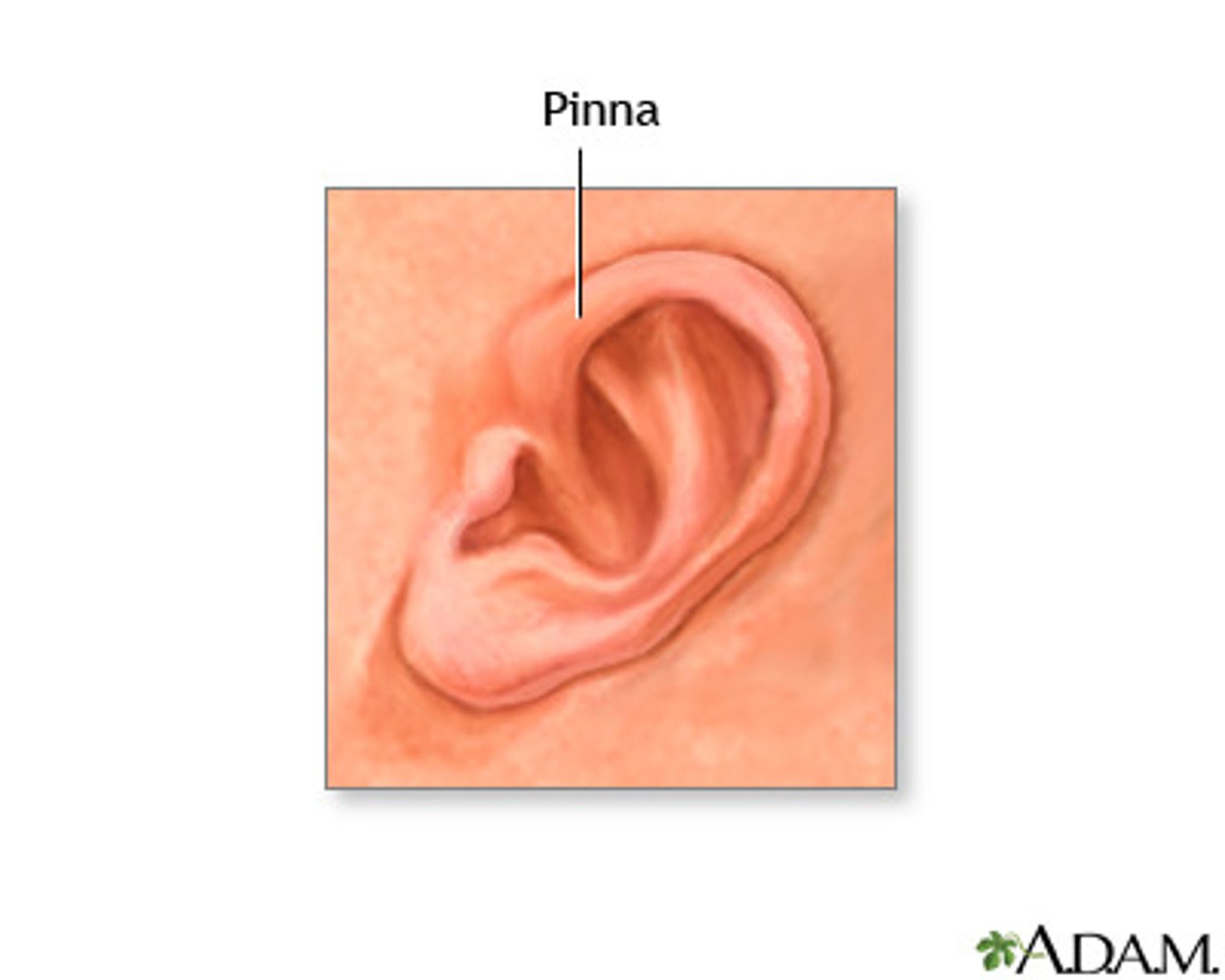
ear flap
outer part of the ear where sound to be directed into the auditory canal
hammer
one of the three bones in the middle ear (also the name of a tool)
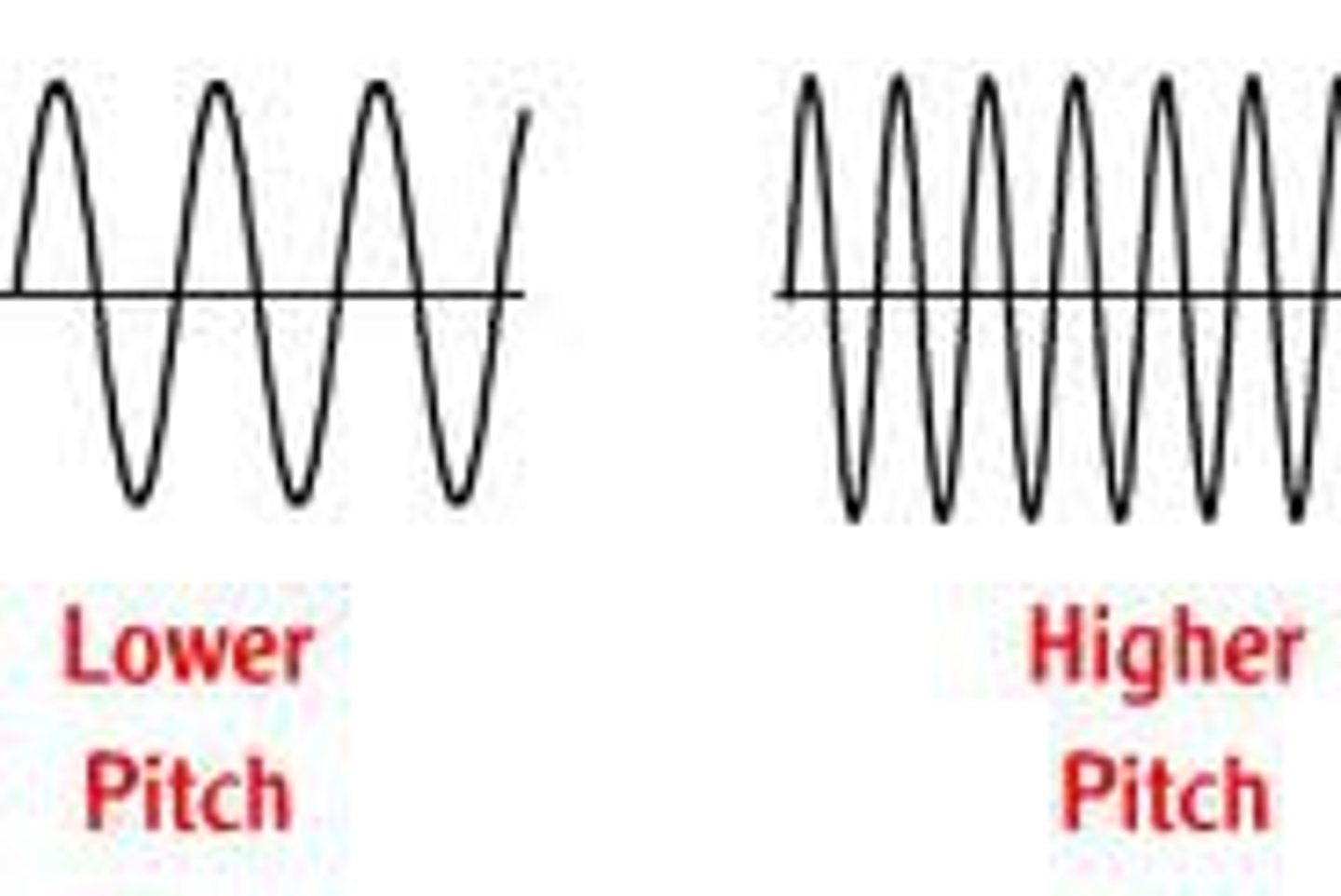
pitch
depends on sound-wave frequency or the rate of the vibration of the medium through which the sound wave is transmitted
sensory adaptiation
the sense of adapting to an environment
stirrup
one of the three bones in the middle ear (also the name of something on a horse)
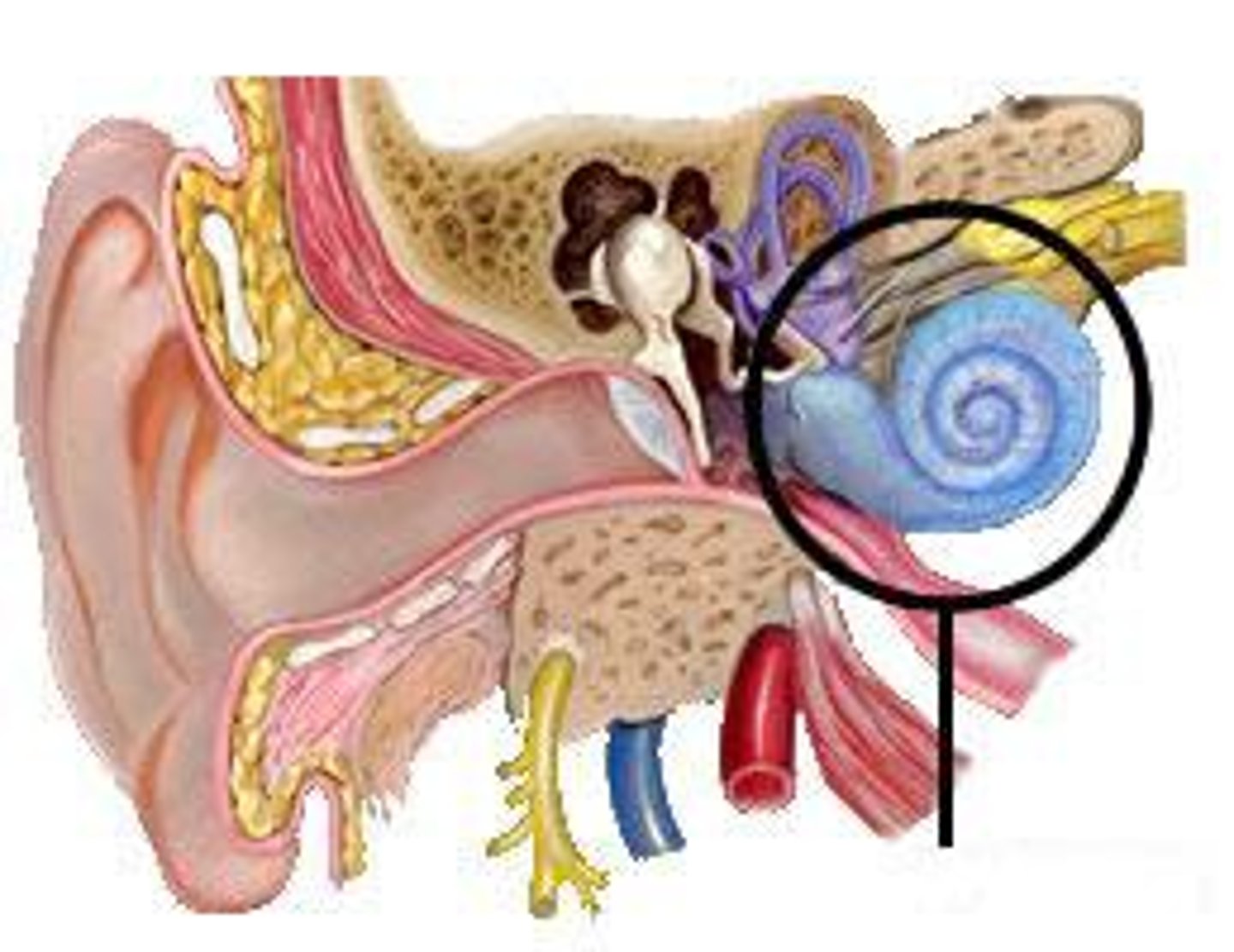
cochlea
makes up the inner ear. a bony tube that contains fluids and neurons
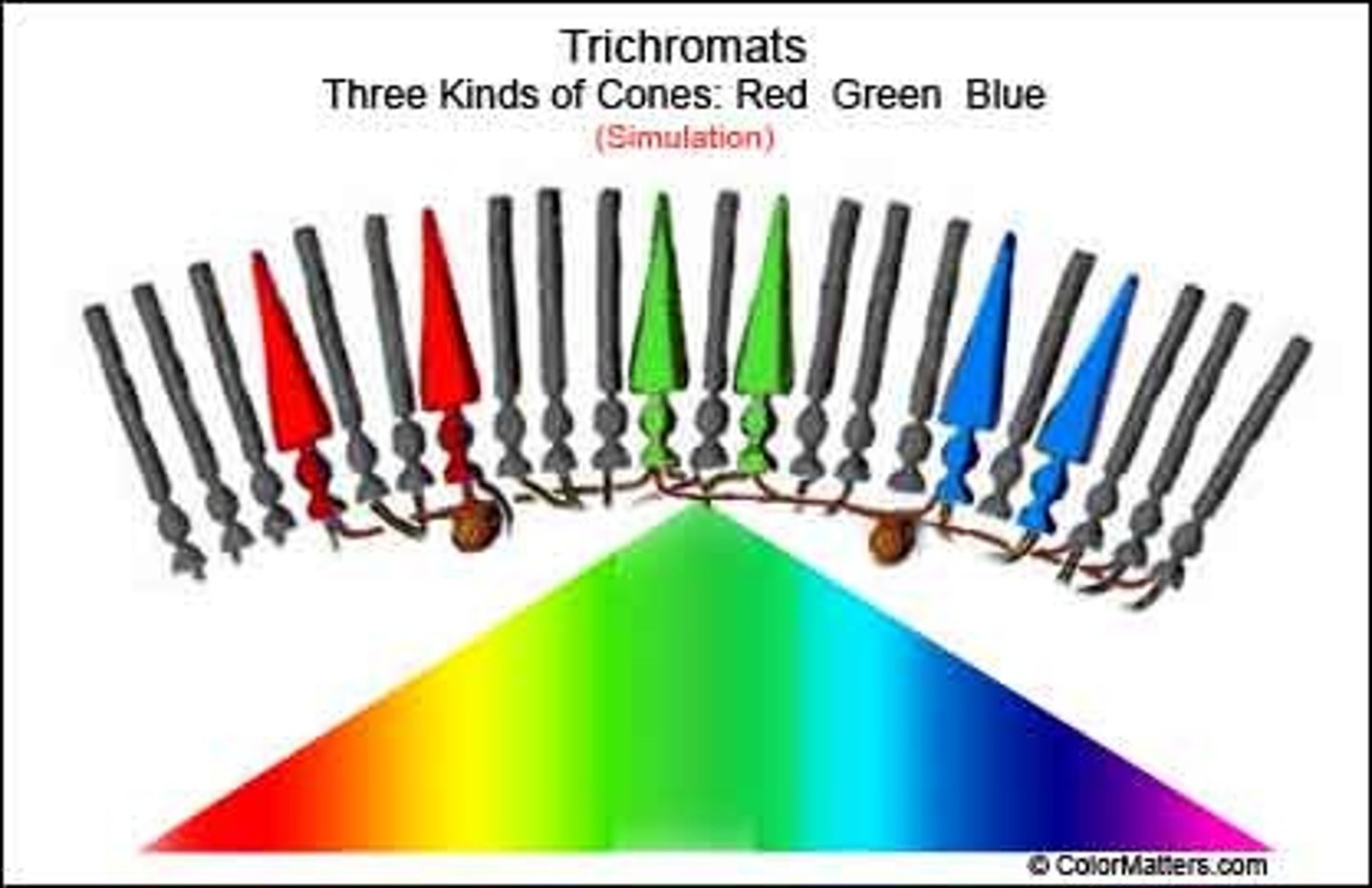
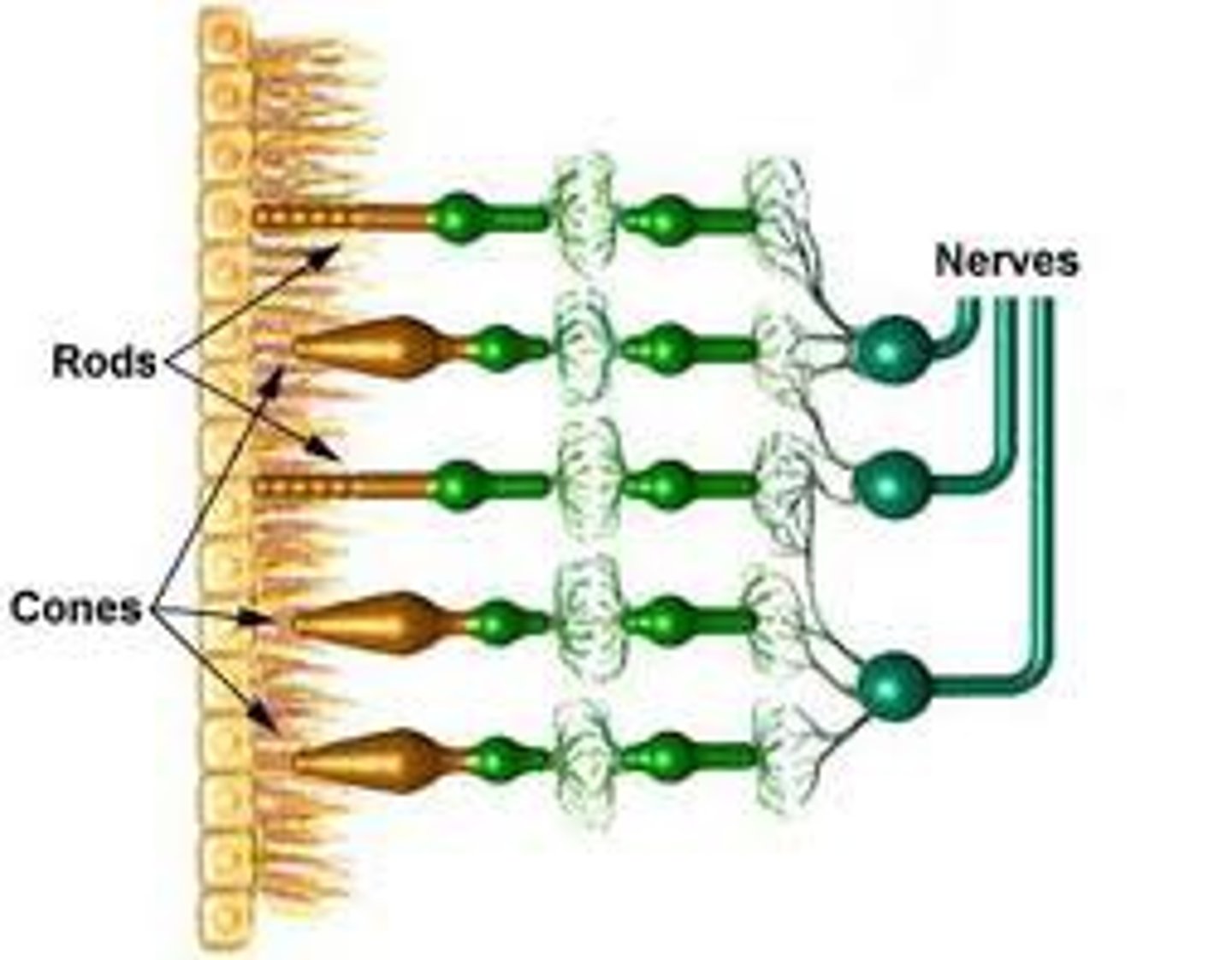
cones
a light sensitive receptor cell or photoreceptor
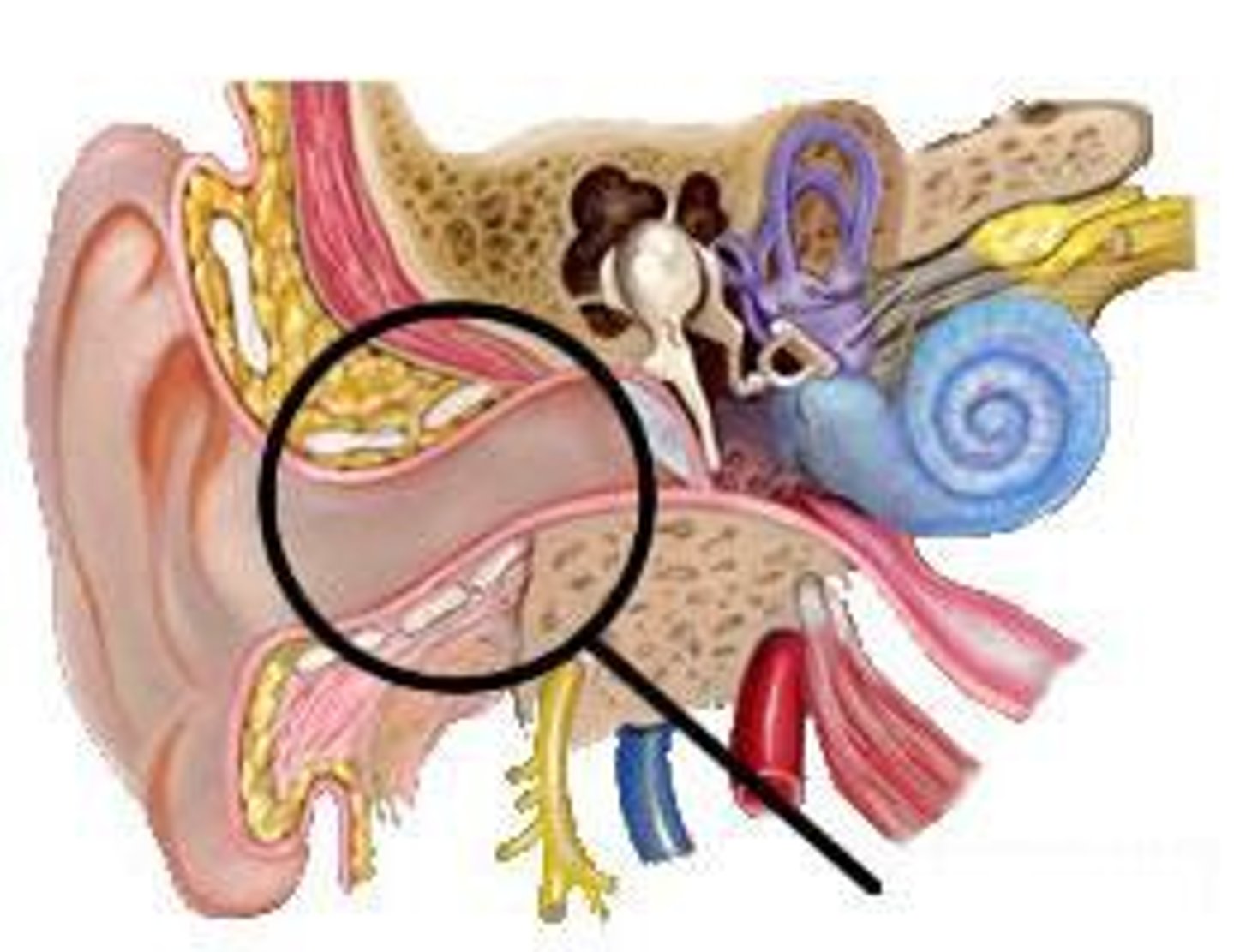
ear canal
tube that sound enters into to reach the eardrum
flavor
the combination of taste, smell and tactile sensations.

iris
part of the eye, regulates the amount of light entering the eye
rods
sensitive to low levels of light
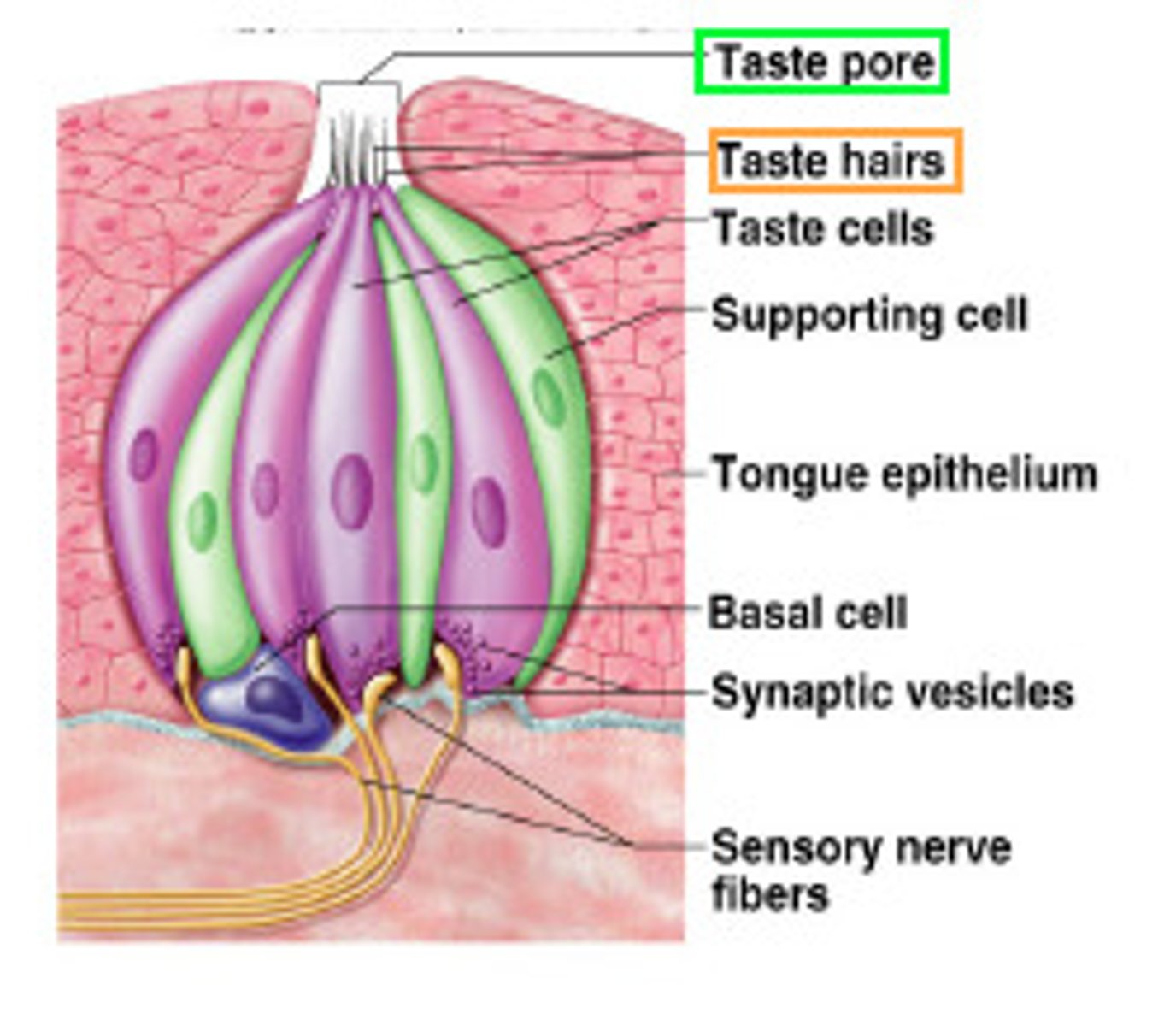
taste buds
on the tongue, sense organs
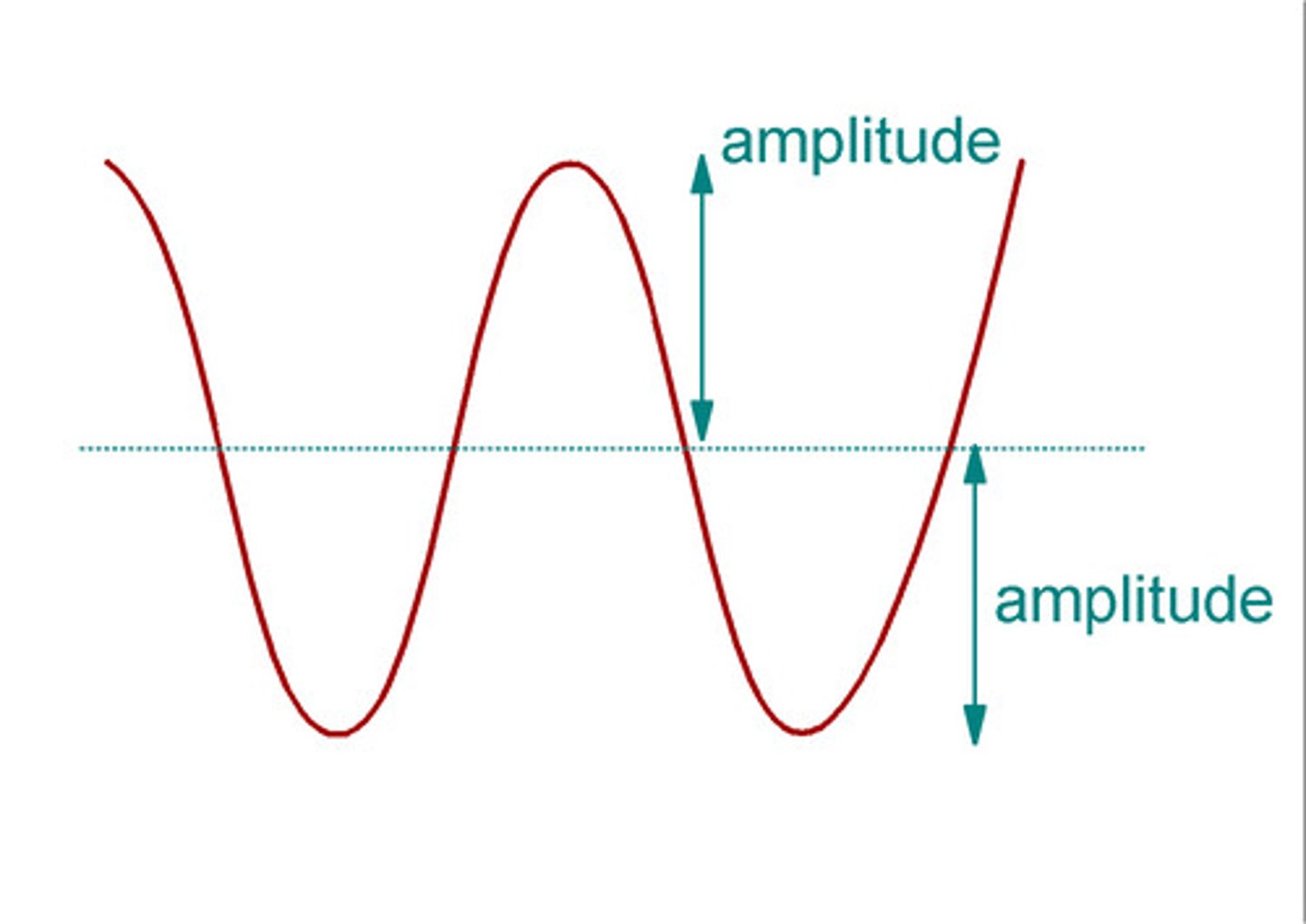
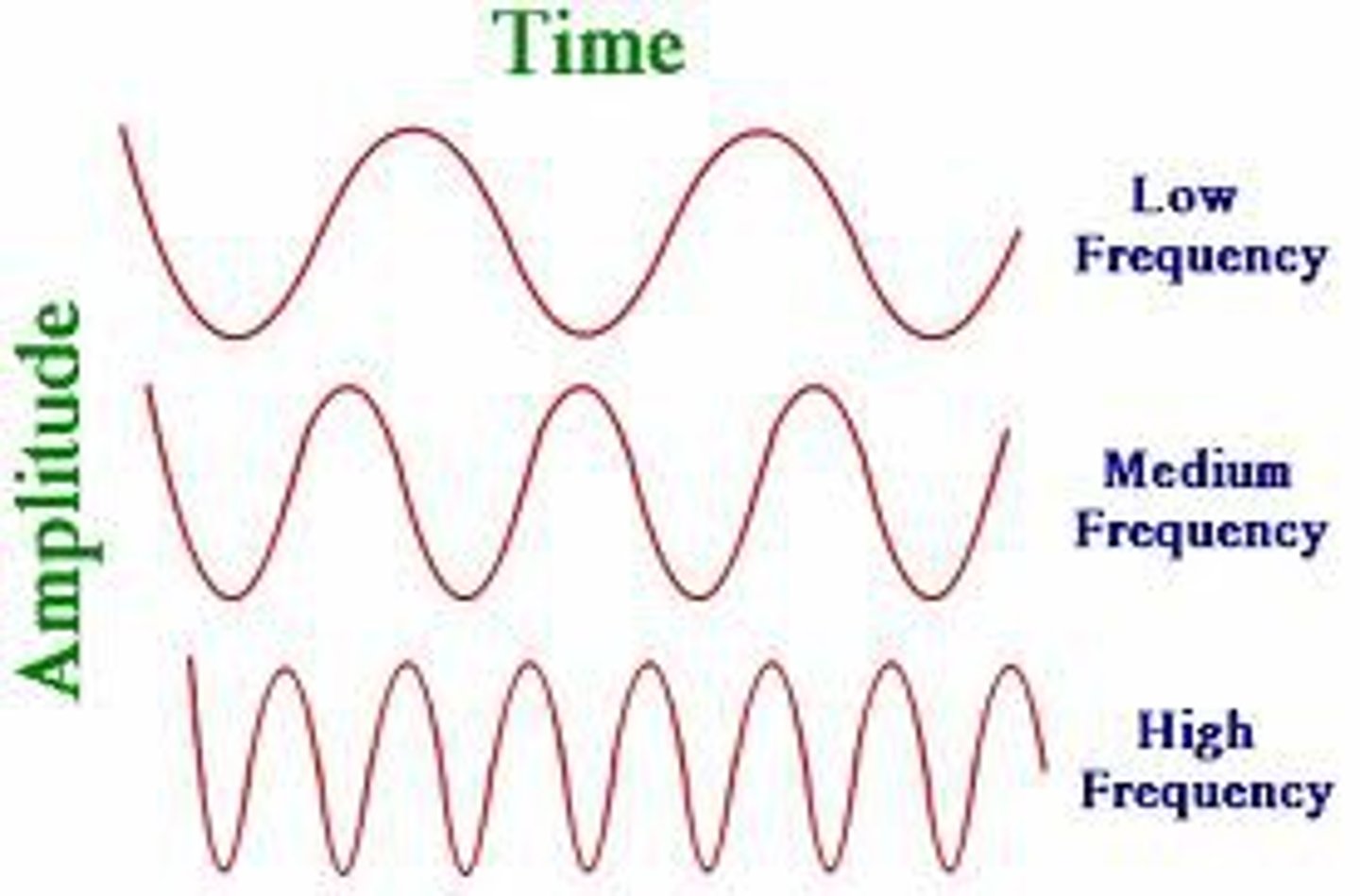
amplitude
height of a specific (sound or light) wave
bipolar cells
send messages from rods and cones to the ganglion cells
concentrations of skin receptors
on hands, lips or feet
farsightedness
medically known as hyperopia or hypermetropia, is a condition that is the result of the eye's physical inability to focus an image correctly on the retina at the back of the eye. Farsightedness is the result of the eyeball being too short, and/or the lens of the eye not being flexible enough, for proper focus to occur.
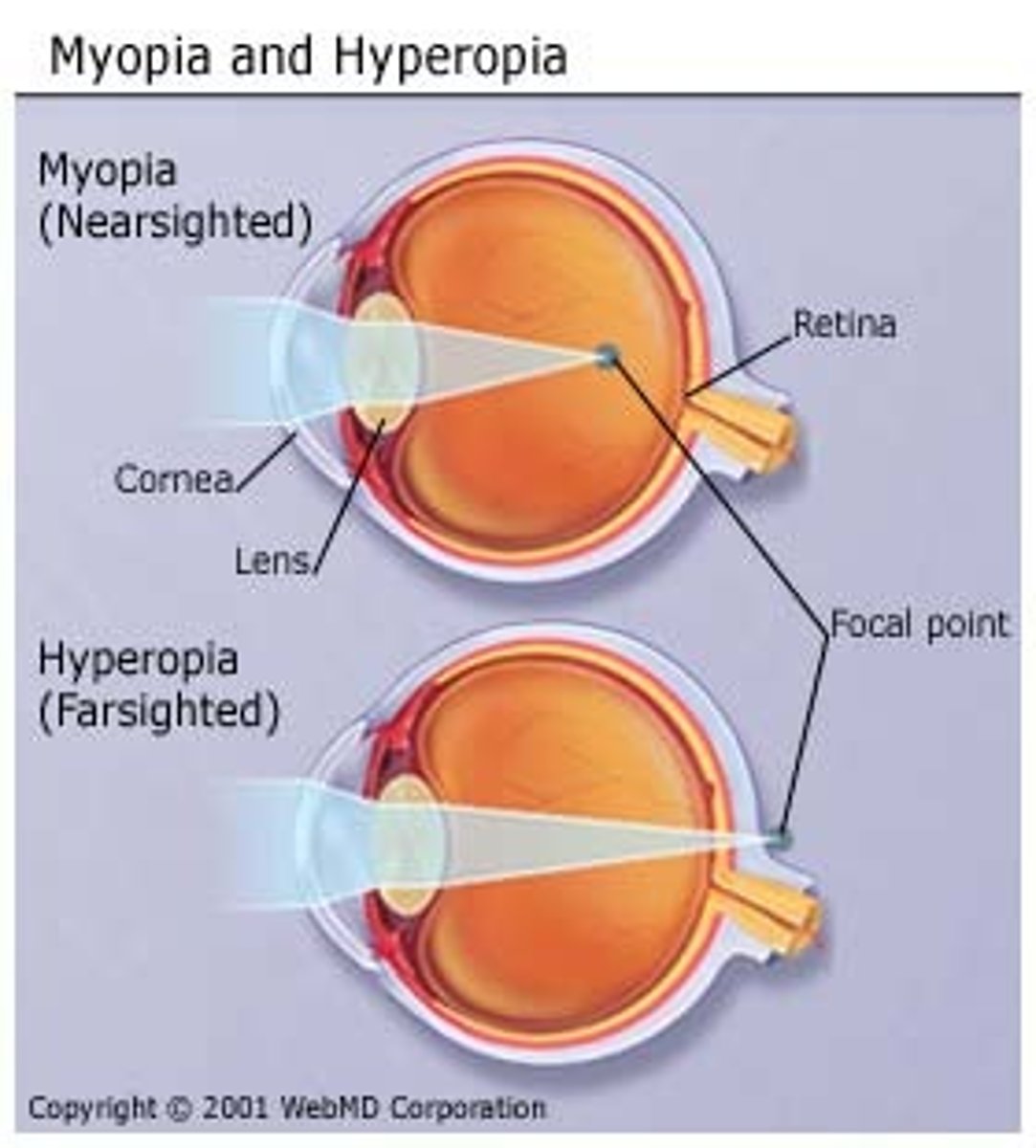
figure-ground perception
our visual system organizes images into figures that we see and a ground or background

lights, electricity and magnetism
forms of electromagnetic radiation
frequency
length of each wave (pitch)
ganglion cells
cells whose axons converge to form optic nerves which send neural signals to the brain
interposition
depth cue involves one object partially covering up another object
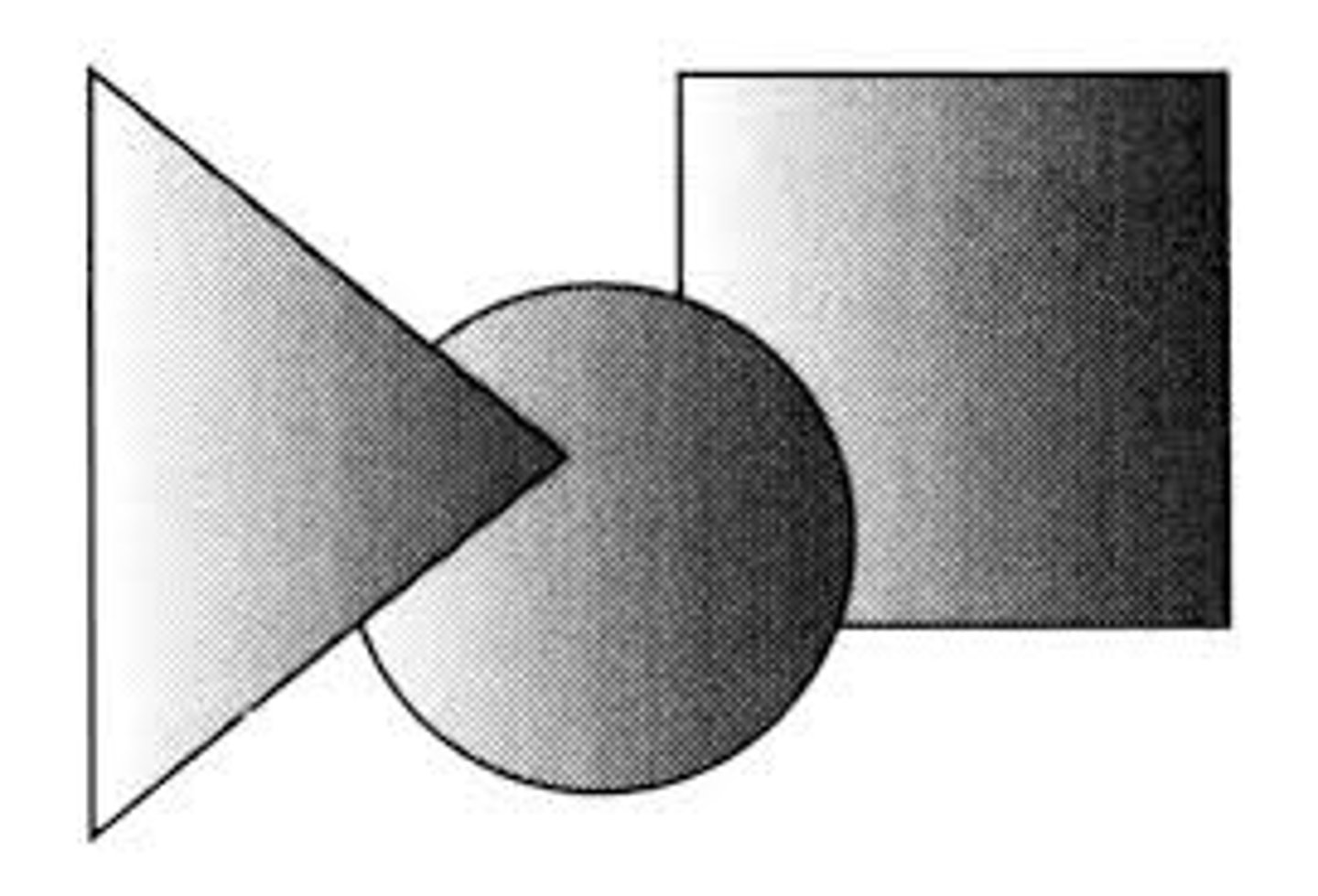
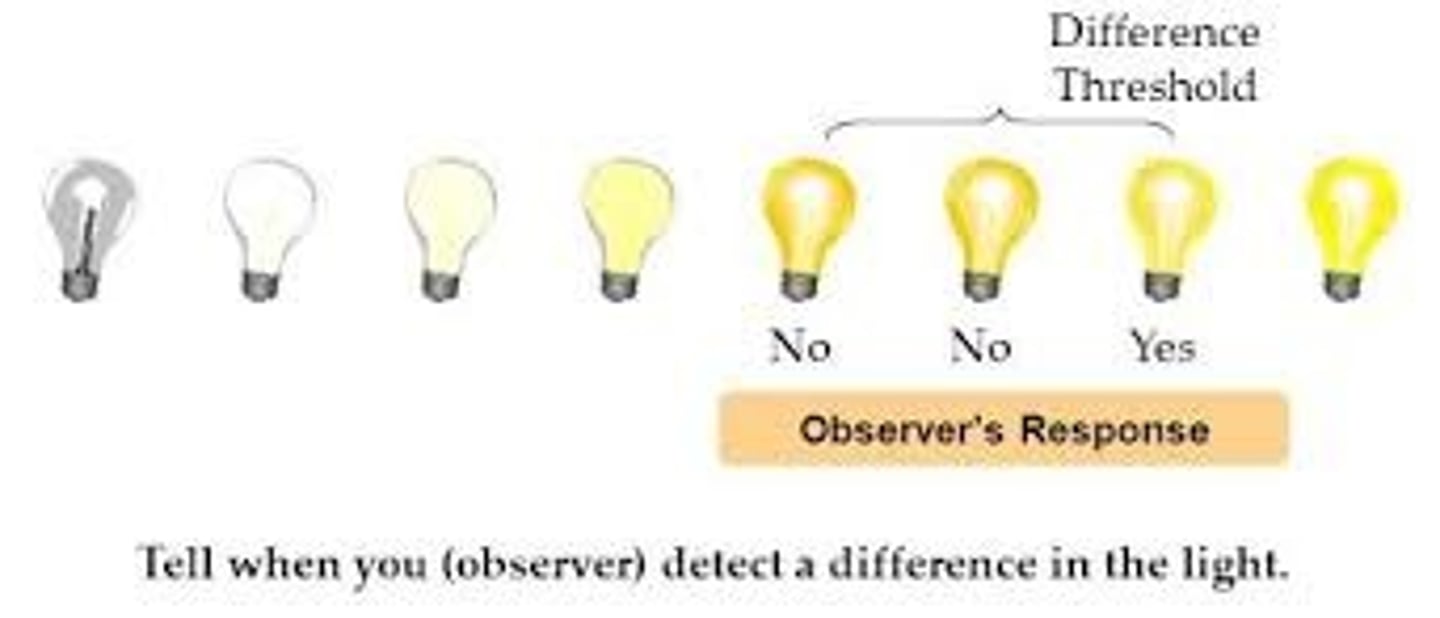
just noticeable difference
(JND) the smallest amount of change that you can notice
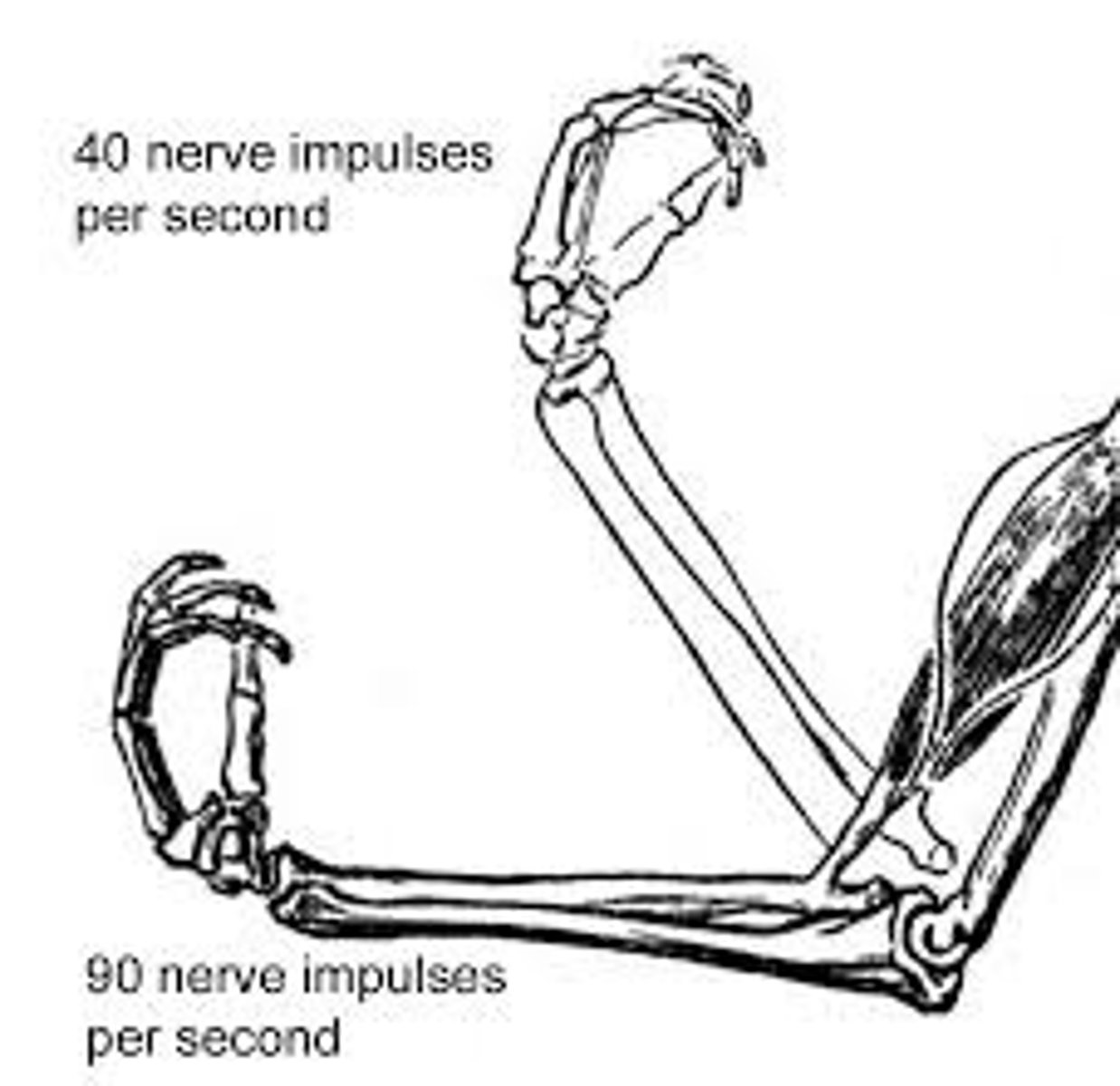
kinesthetic system
one of two parts of sensory system, helps a person stay balanced and coordinate his/her movements
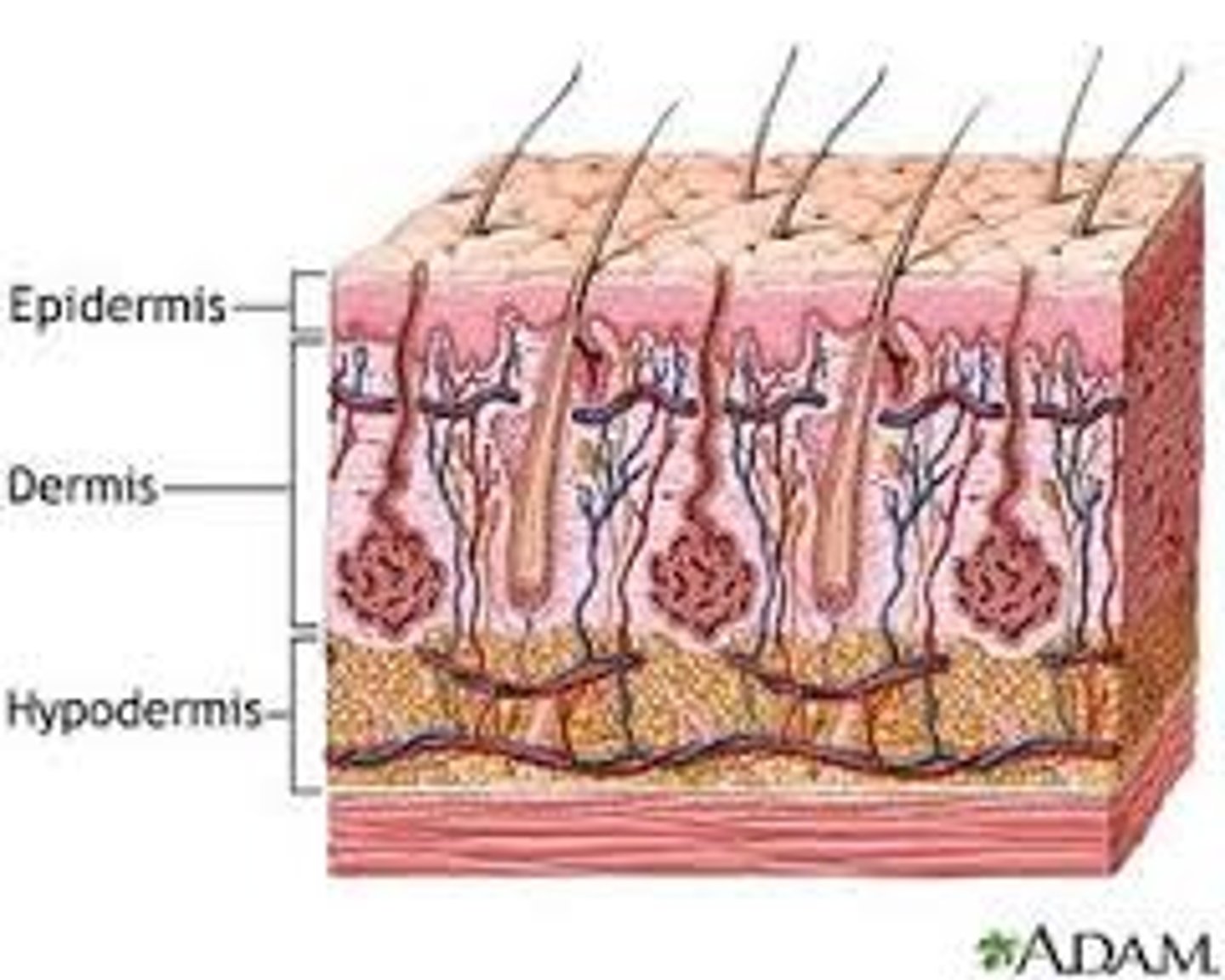
three layers of the skin
epidermis, dermis and hypodermis
nearsightedness
light rays from each eye meet before they hit the retina
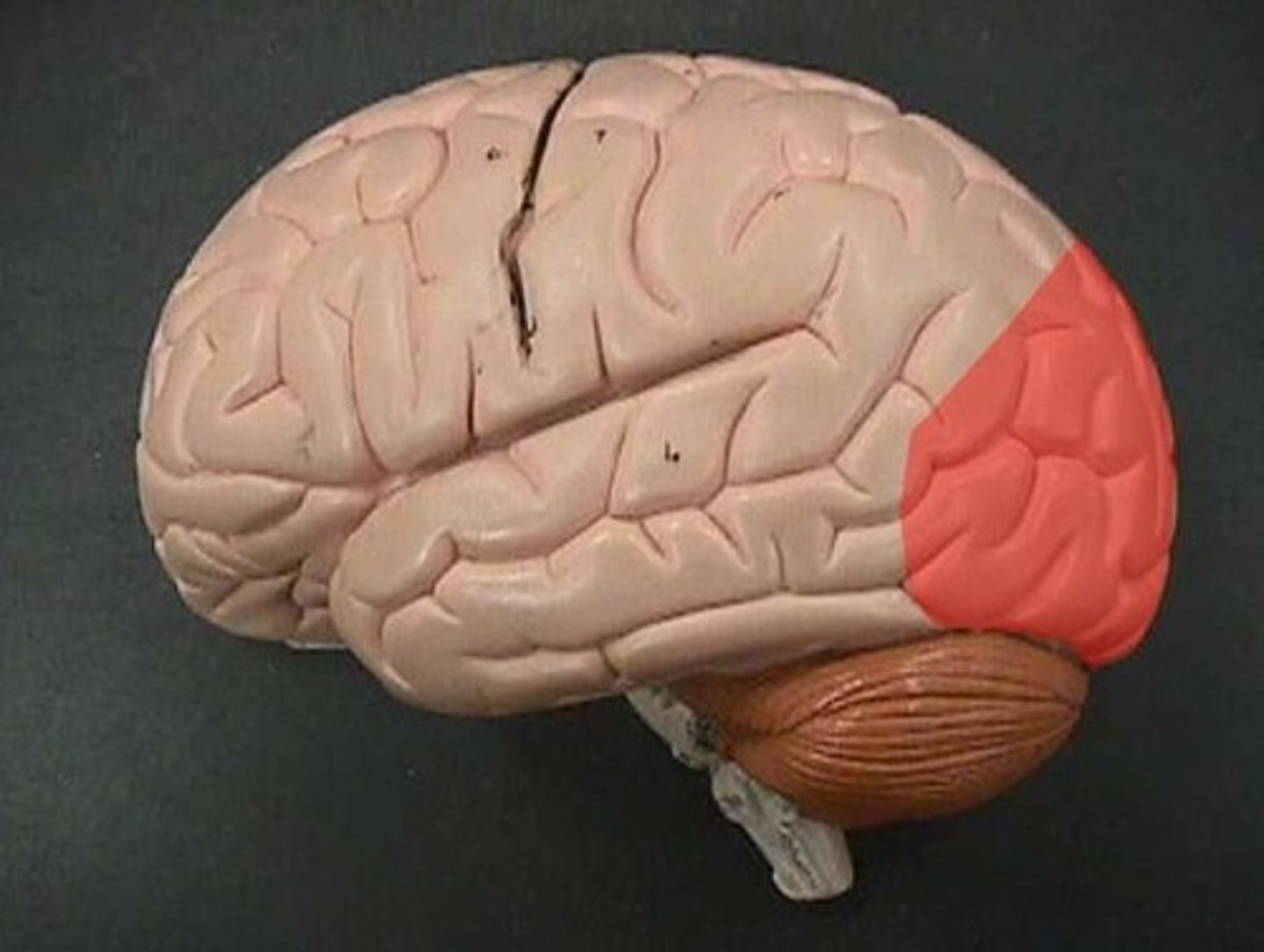
occipital lobe
where visual signals are processed
perceptual inference
same perceptions aren't based entirely on current sensory information, so we need to "fill in the gaps"
psychoanalysis
comprises of several interlocking theories concerning the functioning of the mind, unconscious basis for systems/ problems

psychokinesis
the purported ability to move or deform inanimate objects, as metal spoons, through mental processes.

relative motion
When you are riding in a car, (for example), and look at distant mountains, the objects in a nearby field seem to be moving in the opposite direction to your movement, Yet, when you look at distant mountains, the objects in a nearby or land beyond the animal seem to be moving in the same direction that you are
stroop effect
your right brain tries to say the color but your left brain insists on reading the work

afterimage
after staring at an image for a while, when you close your eyes or look away you see the negative image.

proximity
when we see a number of similar objects, we tend to perceive them as groups or sets of those that are close to each other
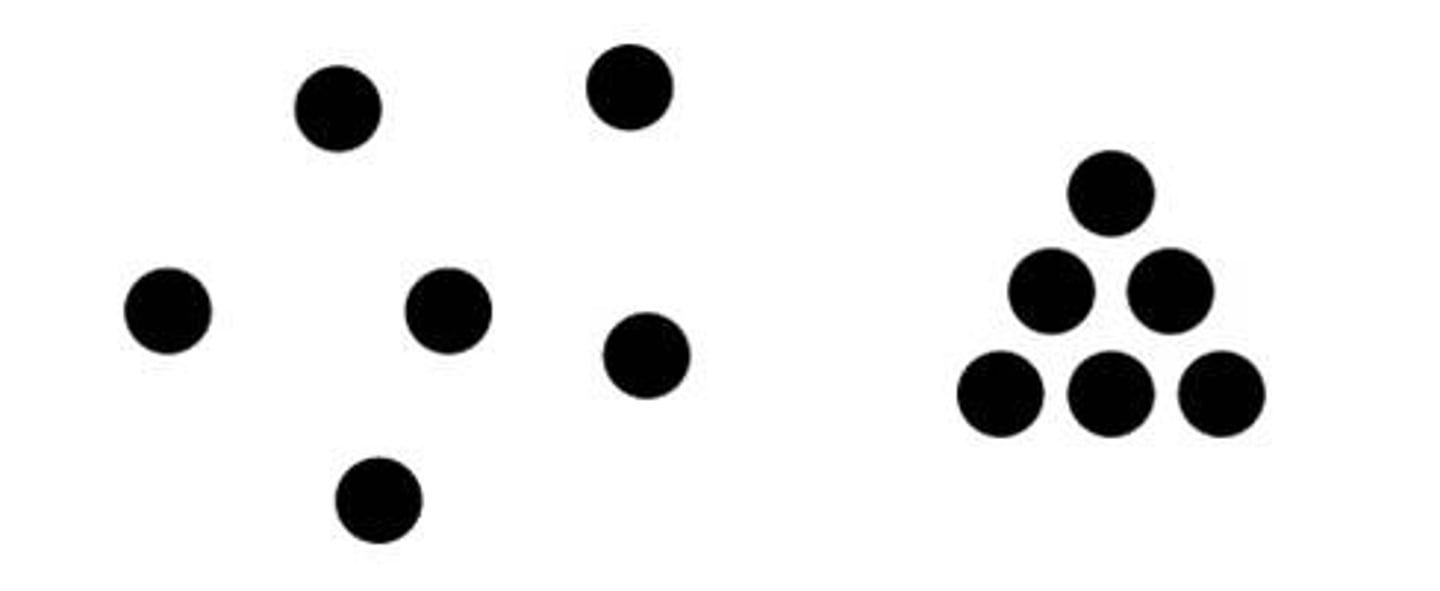
similarity
when similar and dissimilar objects are mingled, we see the similar objects as groups
closure
when we see a familiar pattern or shape with some missing parts, we fill in the gaps
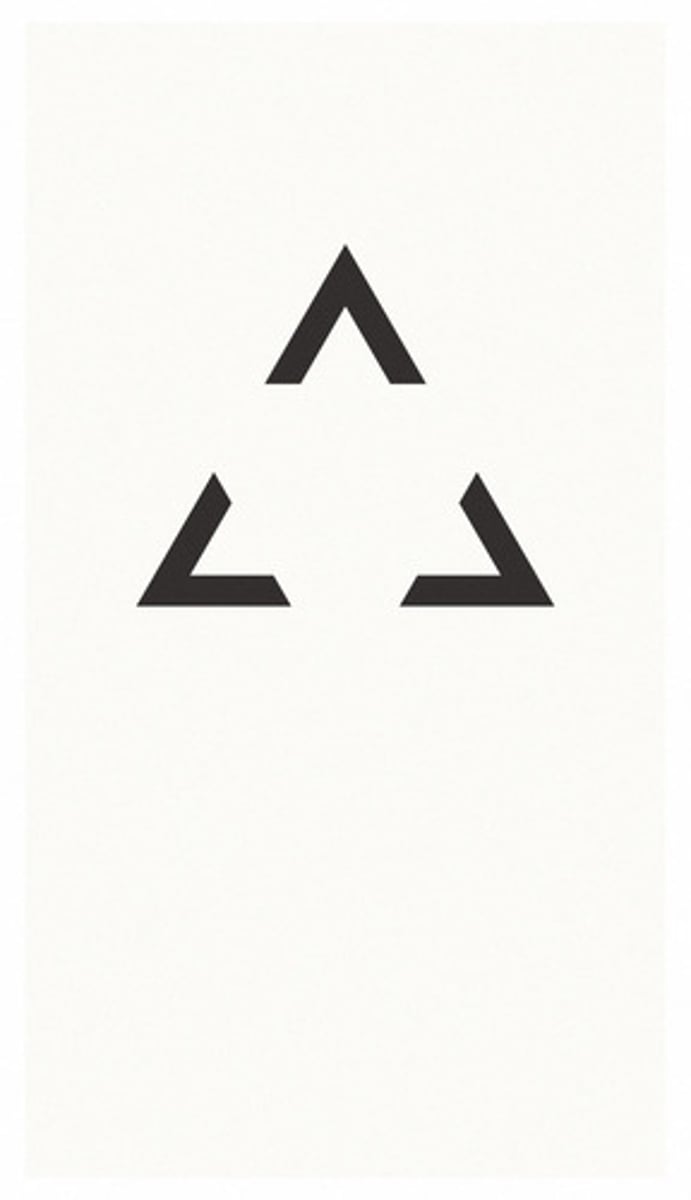

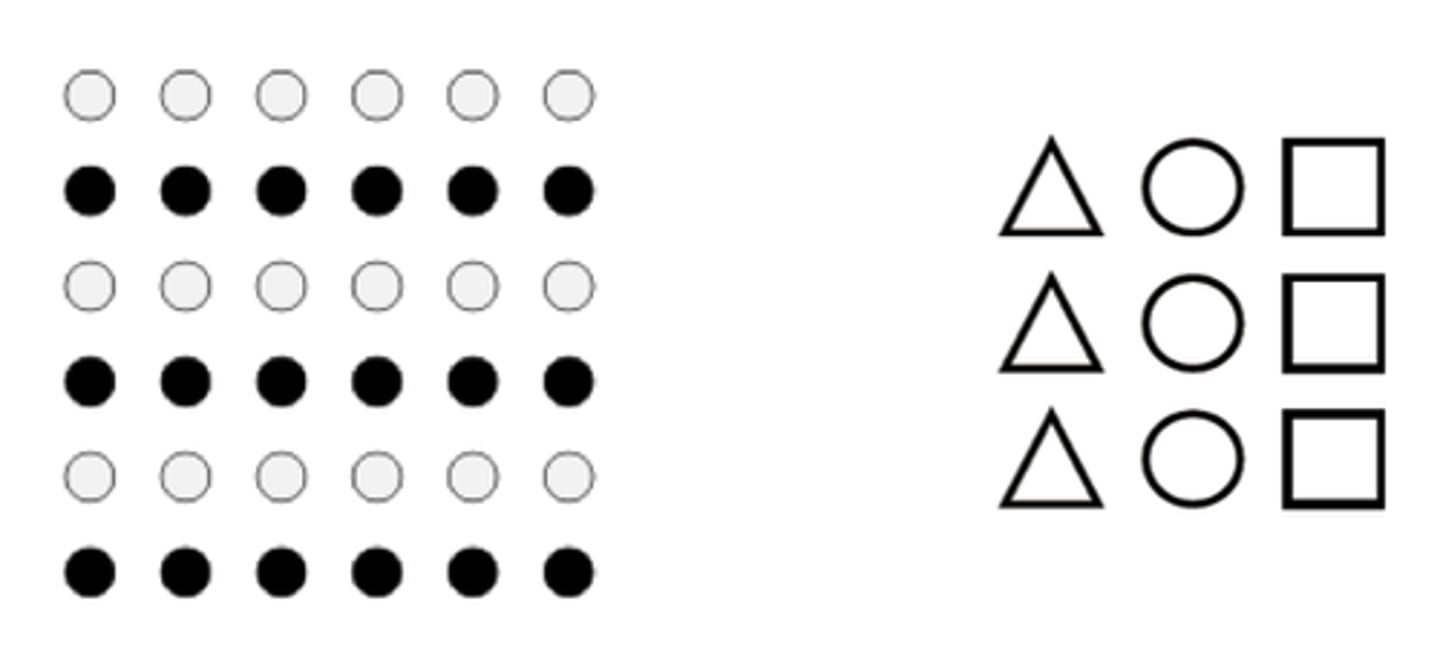
continuity
we tend to see continuous patterns, not disrupted ones
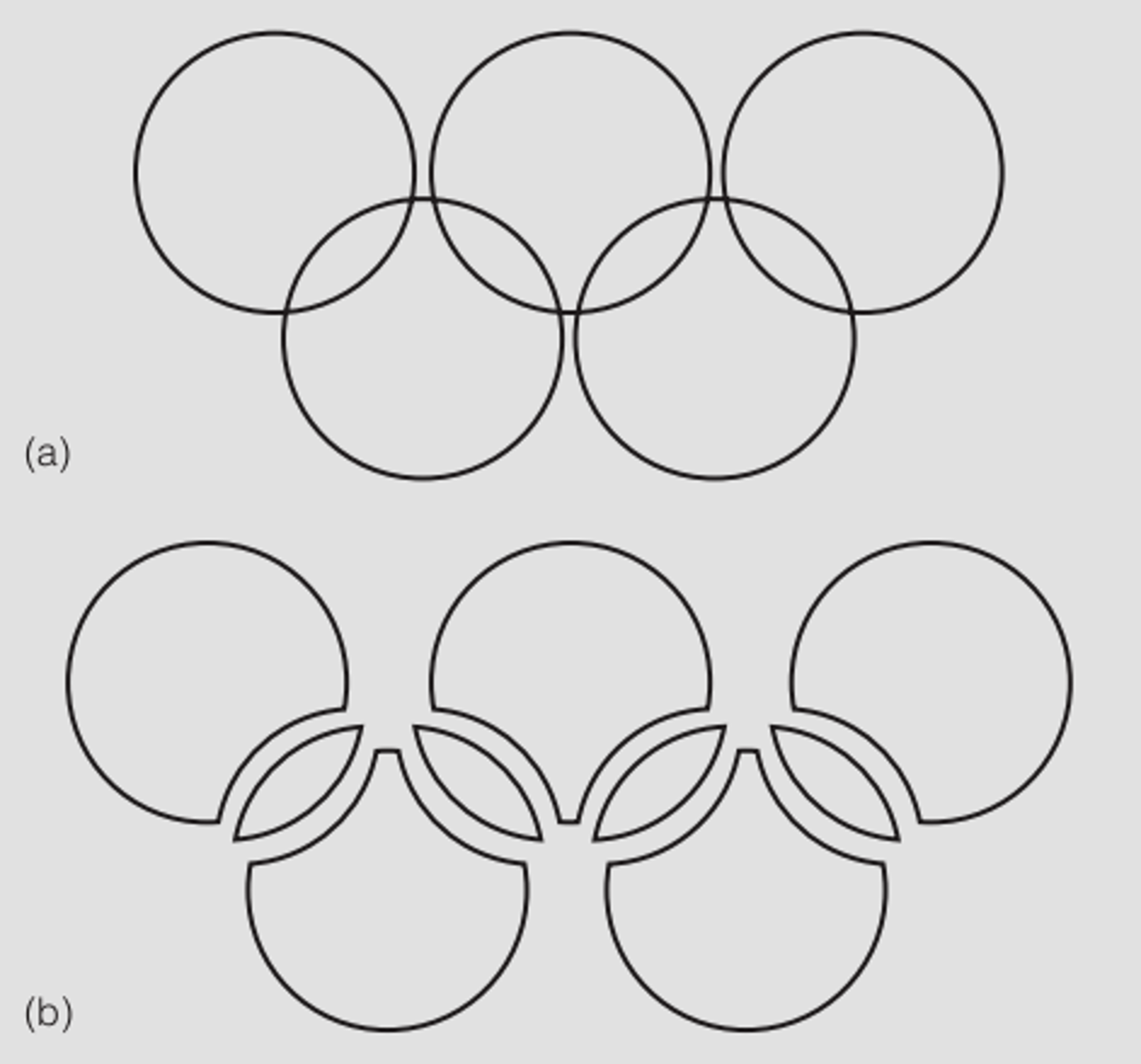
simplicity
our mind perceives everything in its simplest form. The image below, for example, when studied in depth is made up of individual components that have no meaning when viewed separately
texture-density/gradient
The farther removed an object is, the less detail we can identify. It is one of your monocular depth cues.

depth perception
the ability to see objects in three dimensions although the images that strike the retina are two-dimensional; allows us to judge distance
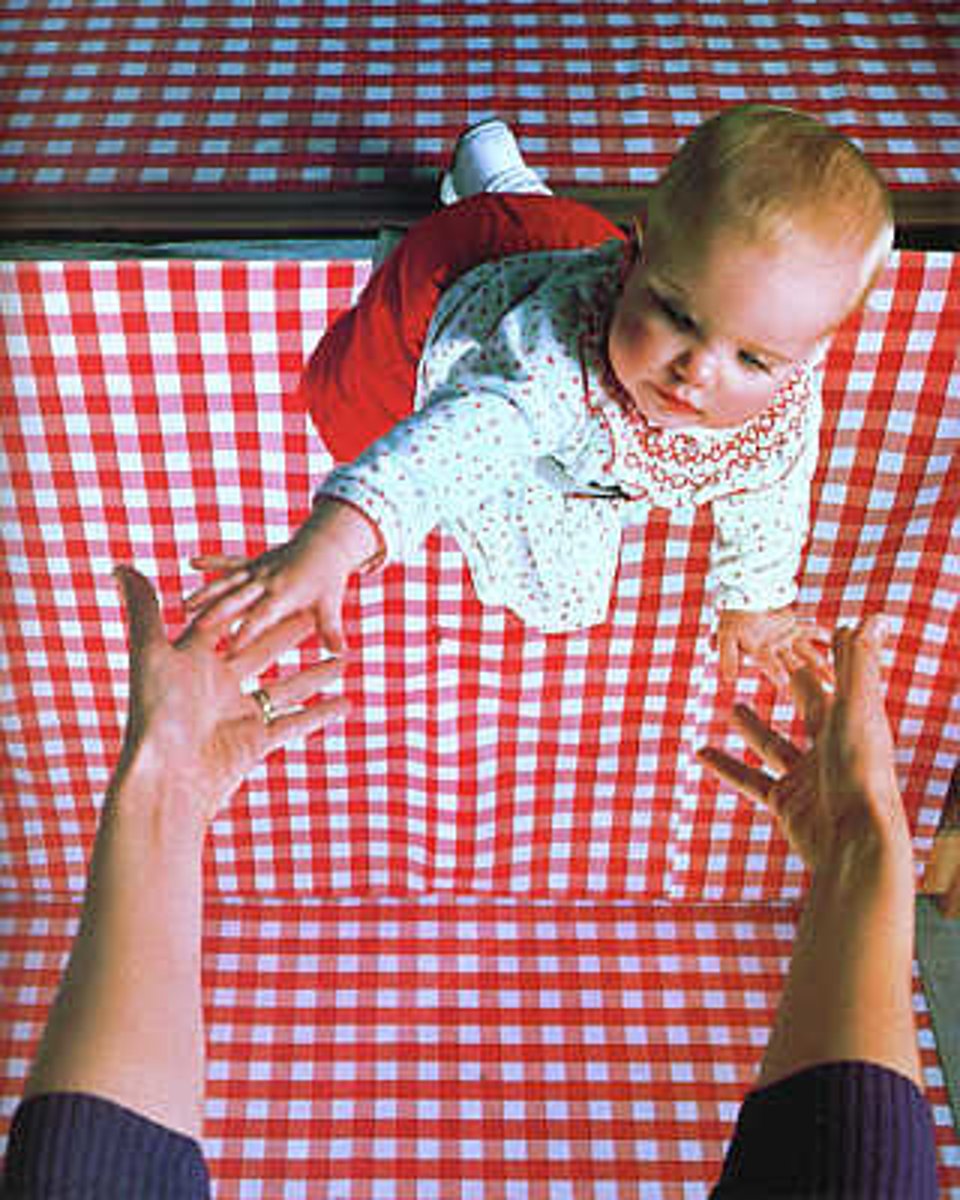

monocular cues
depth cues, such as interposition and linear perspective, available to either eye alone
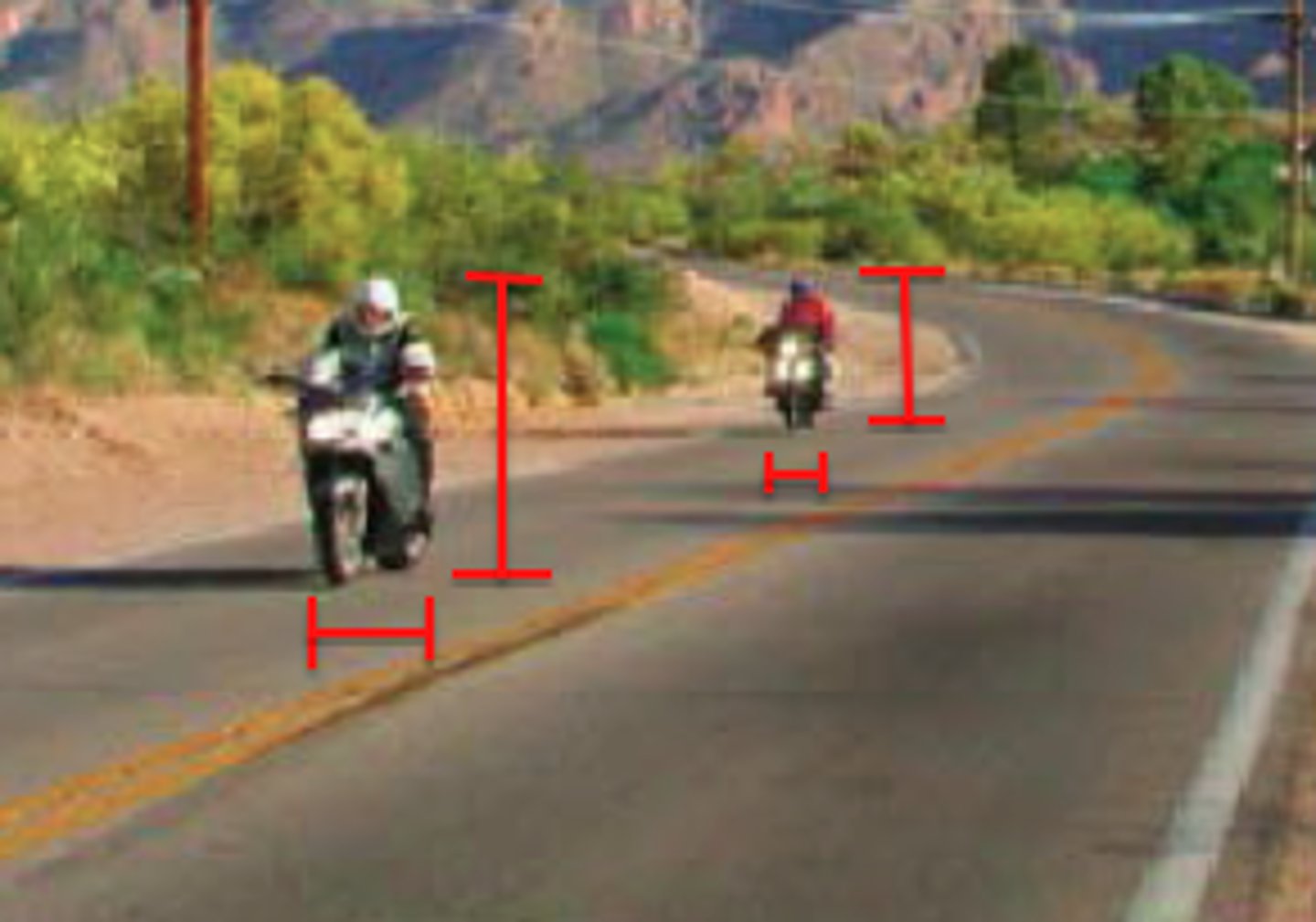

top-down processing
information processing guided by higher-level mental processes, as when we construct perceptions drawing on our experience and expectations
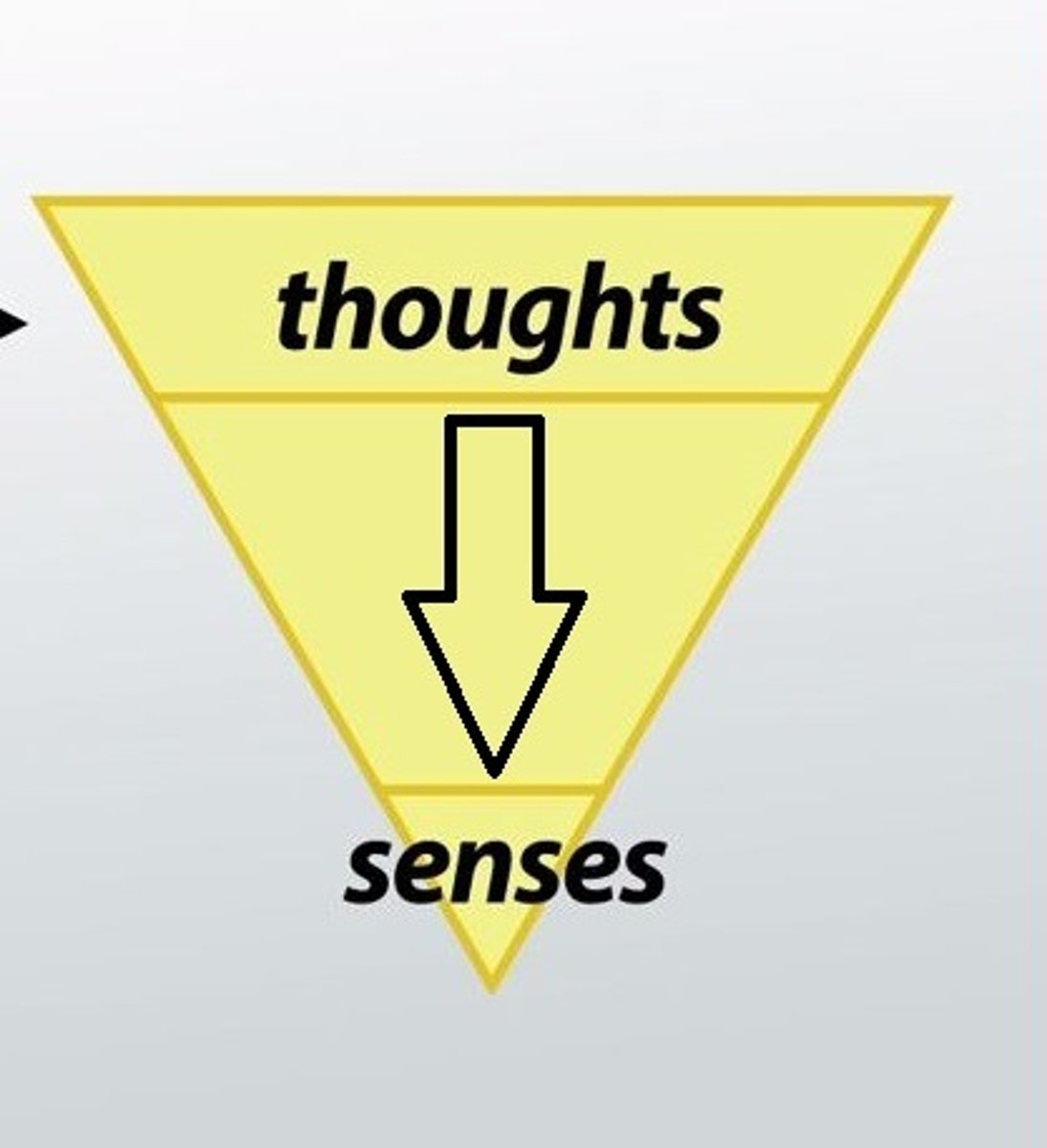
bottom-up processing
the analysis of the smaller features to build up to a complete perception
Gustav Fechner
early German psychologist credited with founding psychophysics
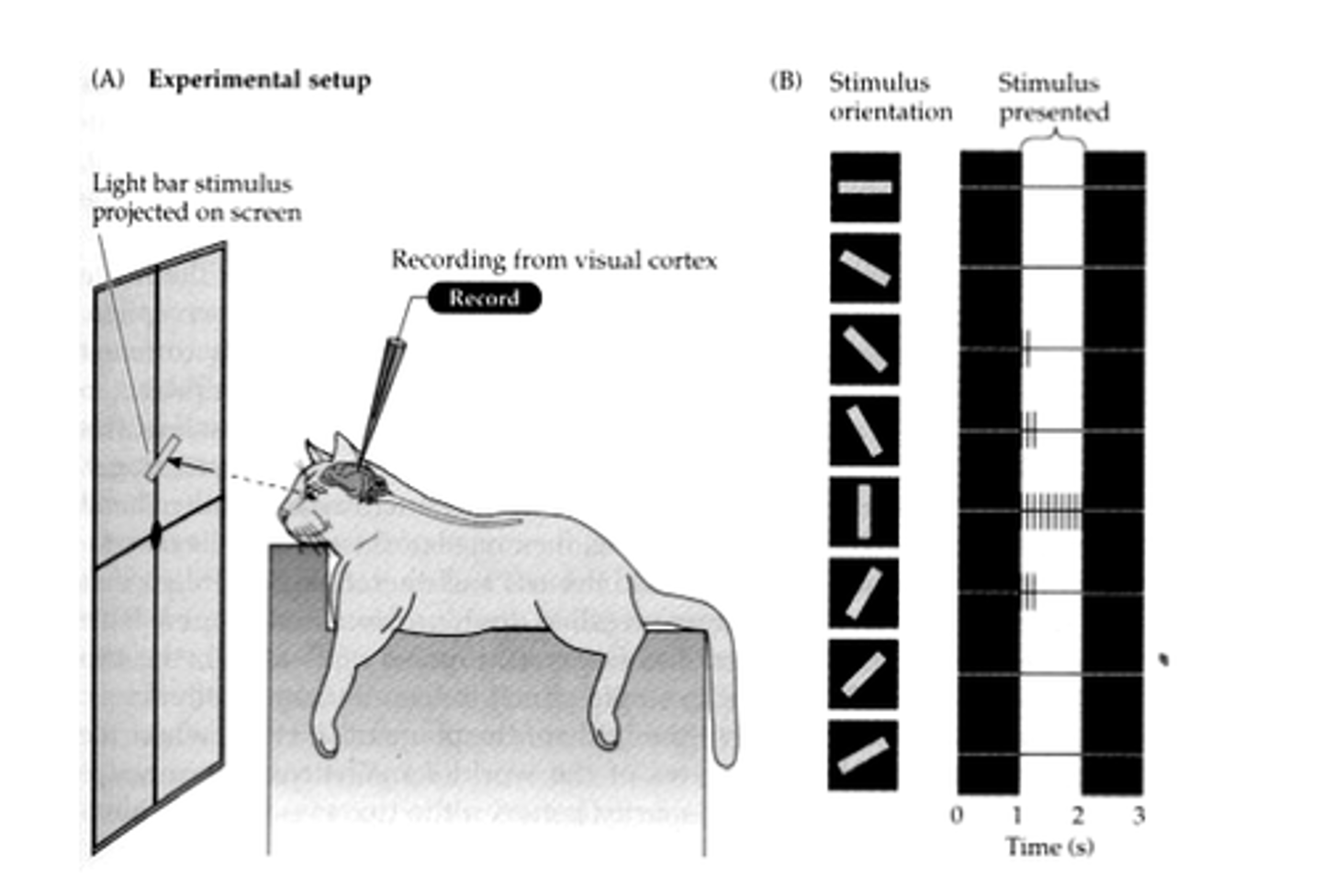
David Hubel and Torsten Wiesel
Nobel-prize-winning researchers who discovered "feature detectors" within the brain
Ernst Weber
1795-1878; Field: perception; Contributions: just-noticeable-difference (JND) that eventually becomes Weber's law; Studies: 1st study on JND
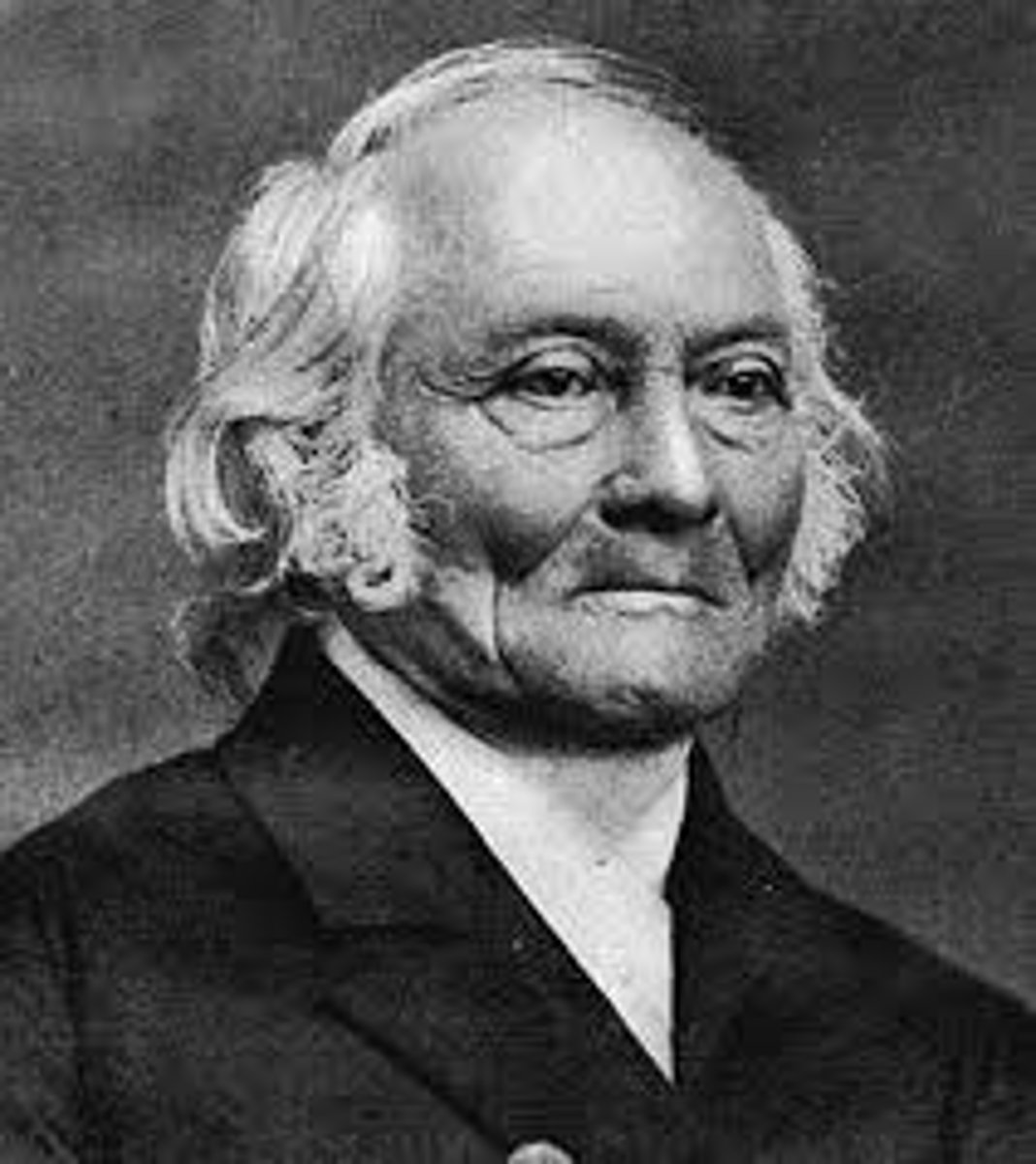

perceptual set
a mental predisposition to perceive one thing and not another
context effects
memory is aided by being in the physical location where encoding took place
Schema
a concept or framework that organizes and interprets information
Tri-Color Theory
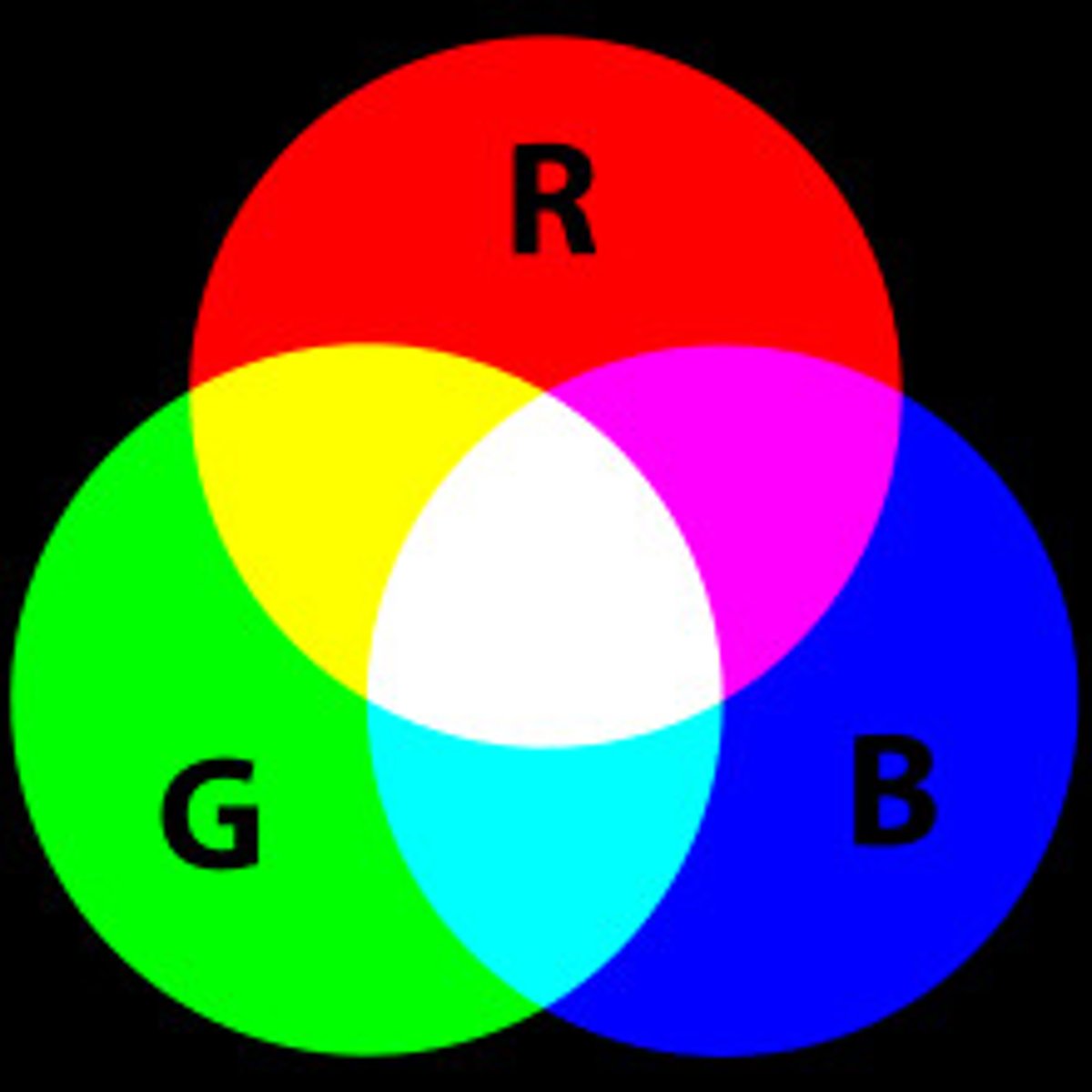
also known as the component theory; proposed by Thomas Young and Hermann van Helmholtz suggests that there are three types of receptors in the retina: cones that respond to red, blue or green
Synesthesia
describing one kind of sensation in terms of another ("a loud color", "a sweet sound")

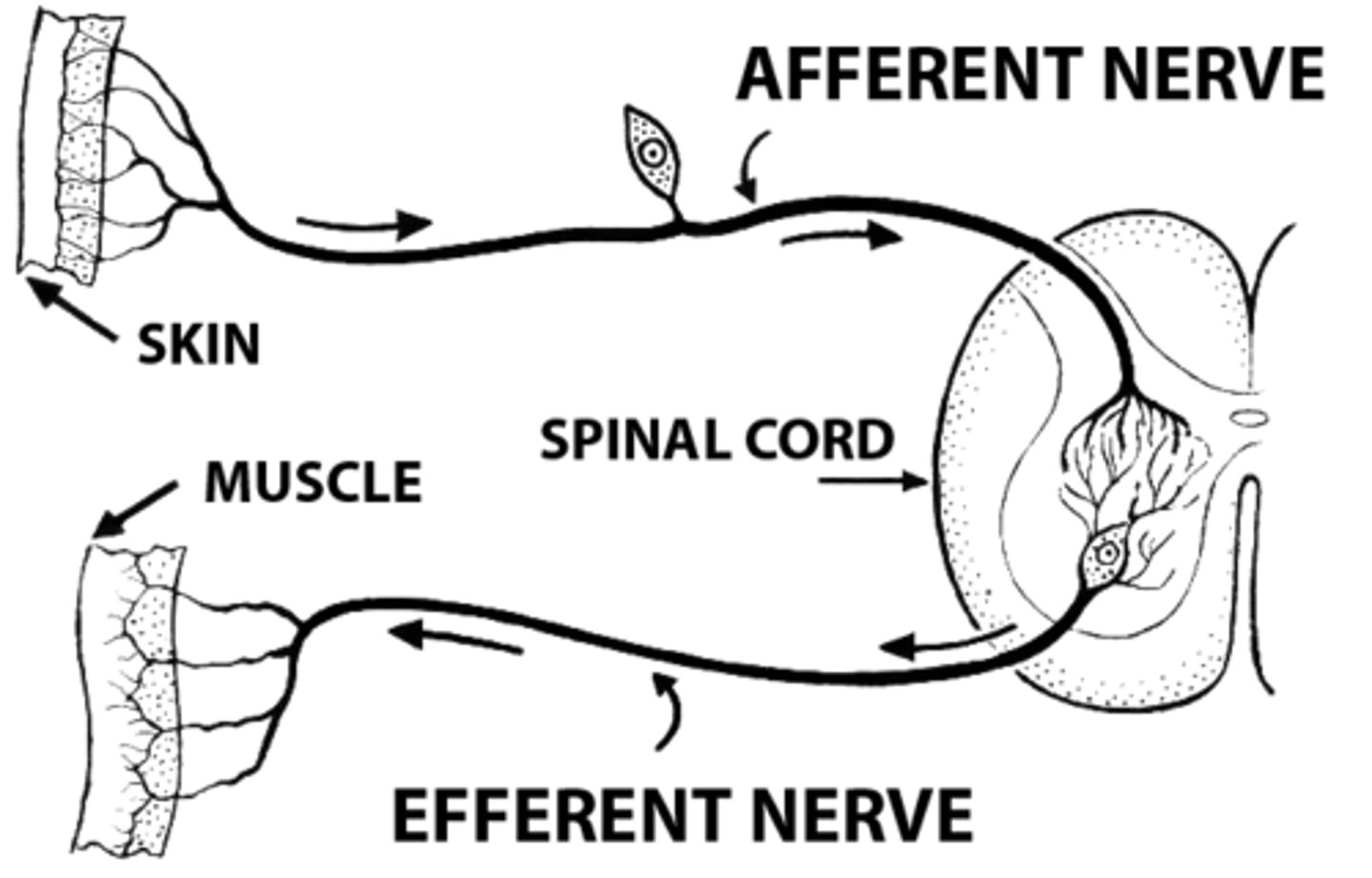
motor neurons
neurons that carry outgoing information from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands
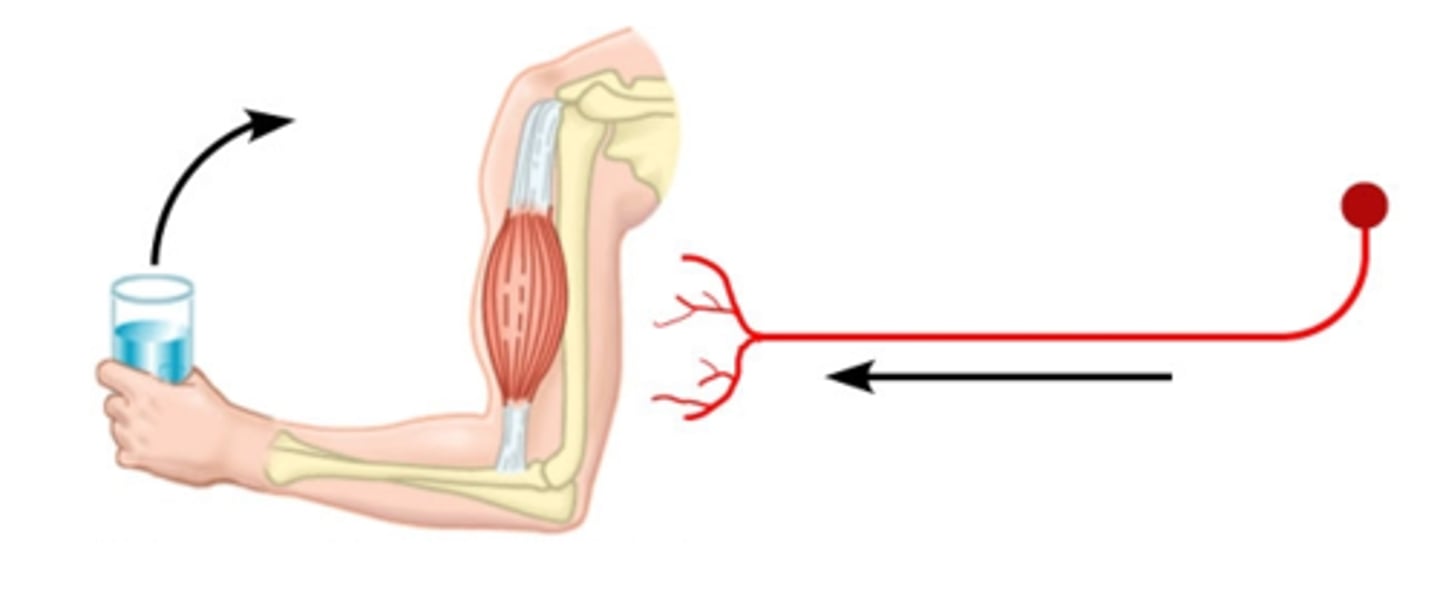
sensory neurons
neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord
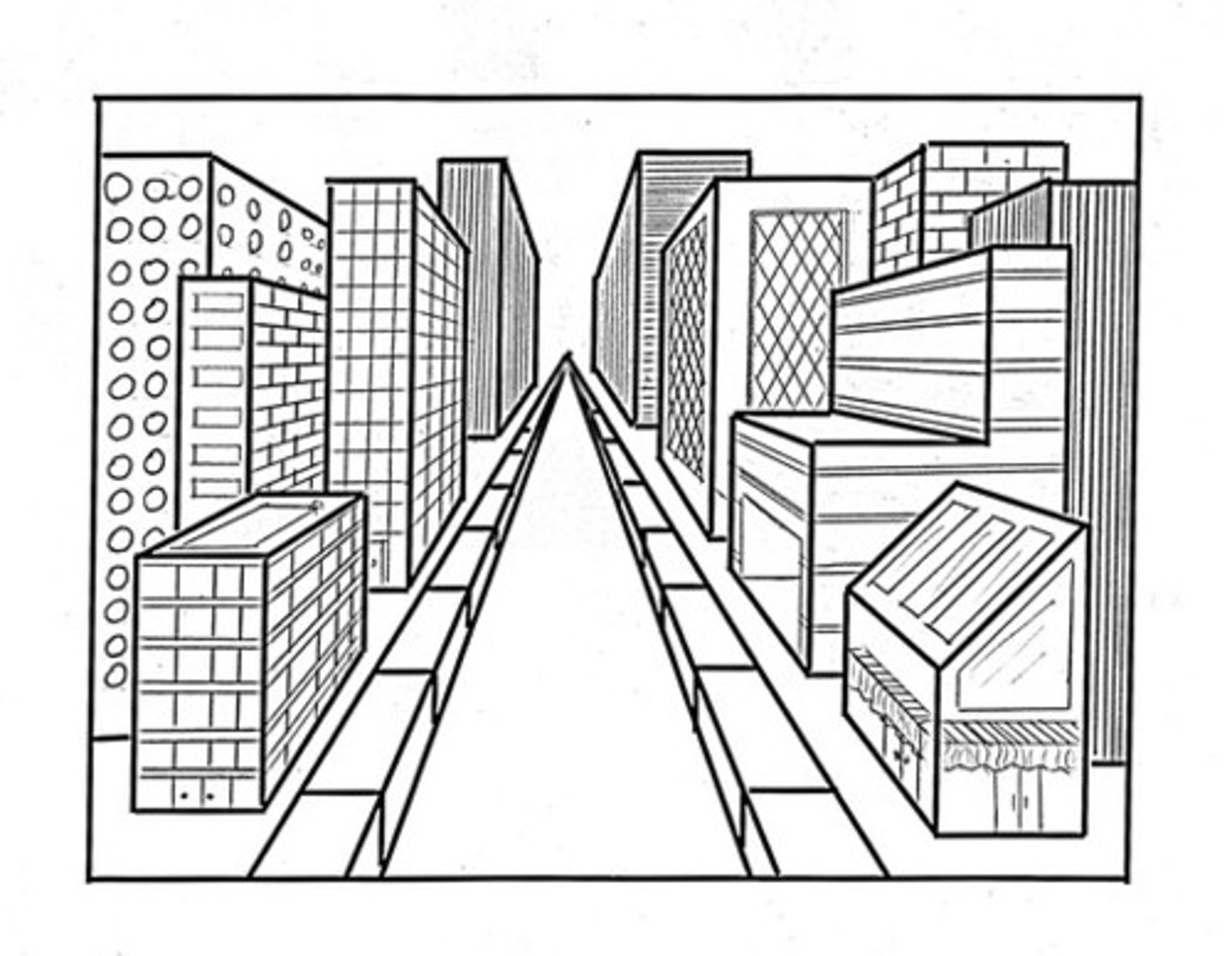
linear perspective
A monocular cue for perceiving depth; the more parallel lines converge, the greater their perceived distance.
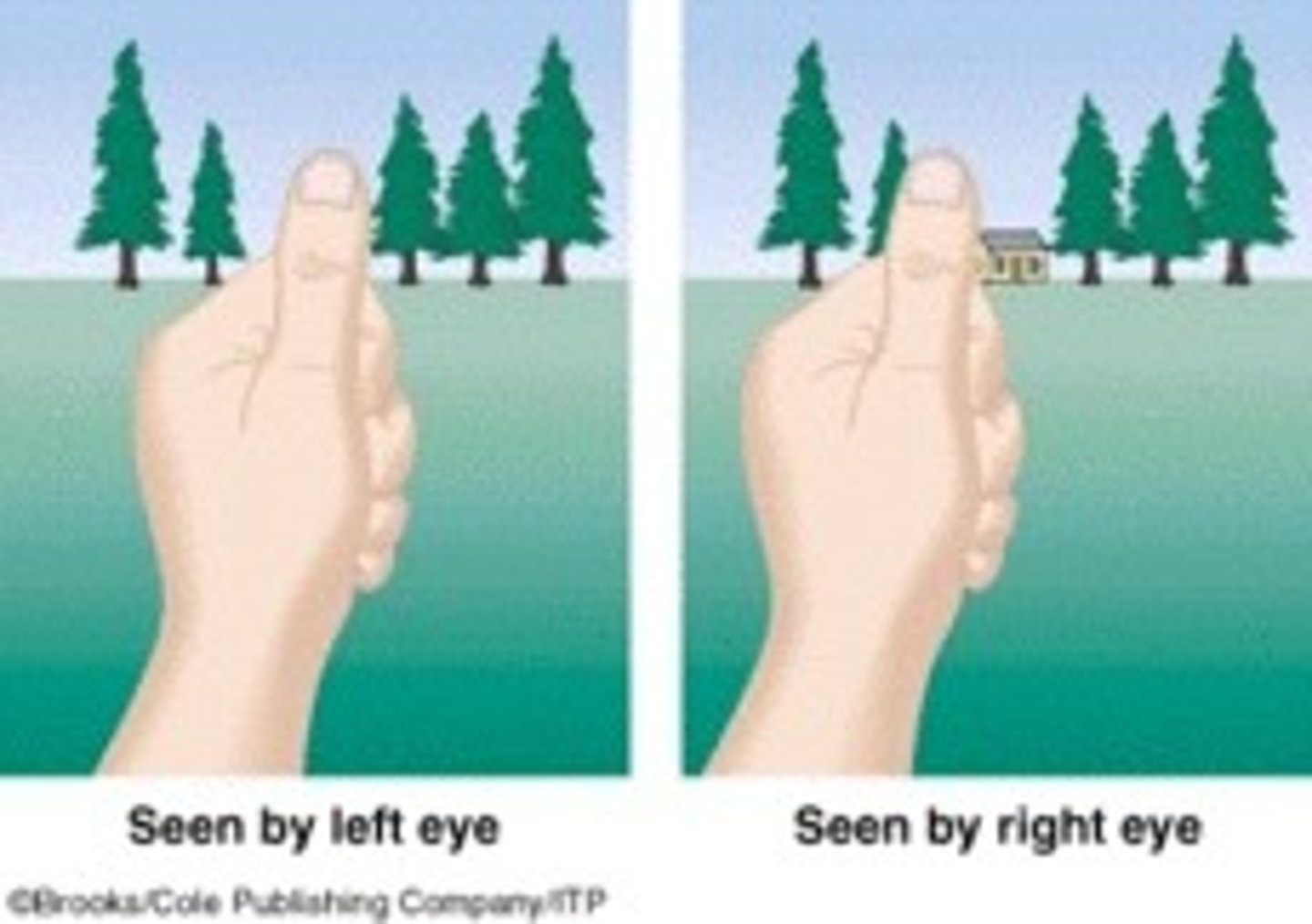
binocular disparity
the difference in the retinal images of the two eyes that provides information about depth
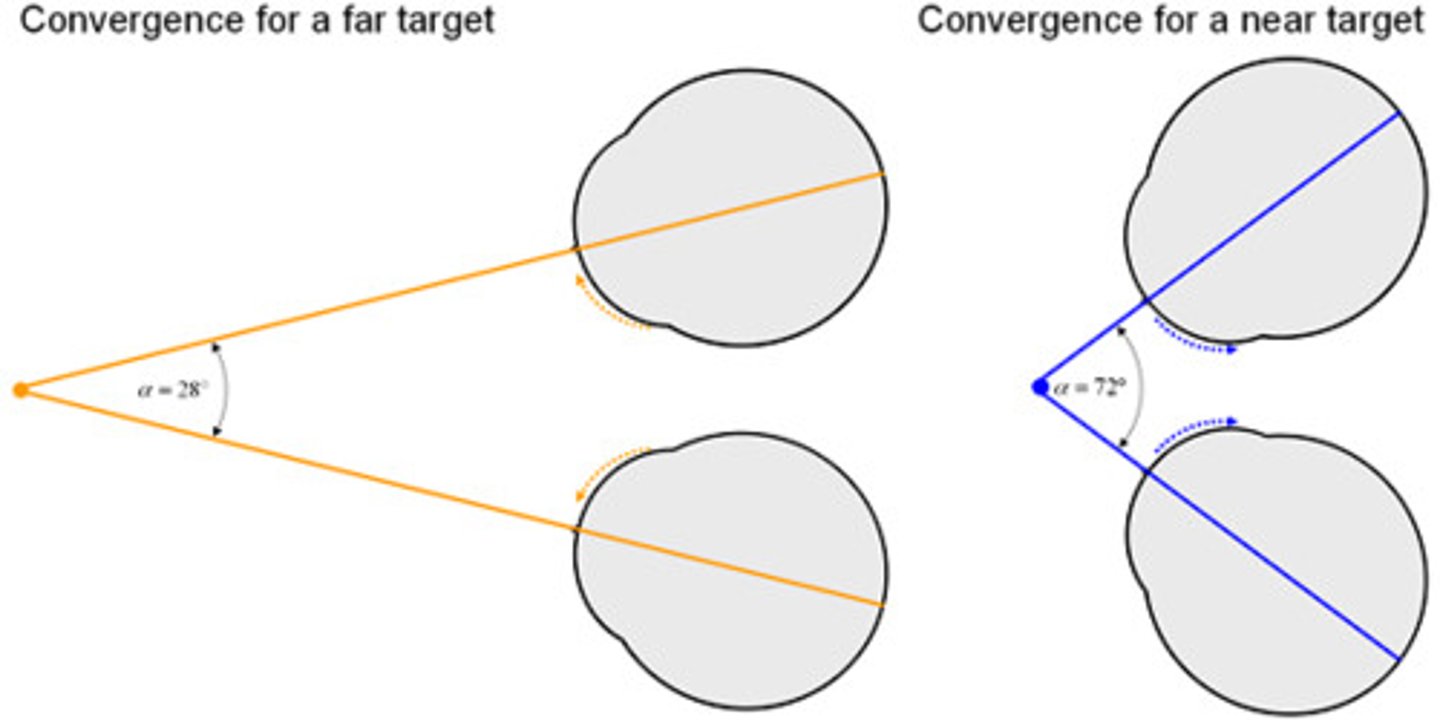
convergence
A binocular cue for perceiving depth; the extent to which the eyes converge inward when looking at an object
vestibular sense
the sense of body movement and position, including the sense of balance
Transduction
conversion of one form of energy into another. In sensation, the transforming of stimulus energies, such as sights, sounds, and smells, into neural impulses our brains can interpret.
change blindness
failing to notice changes in the environment

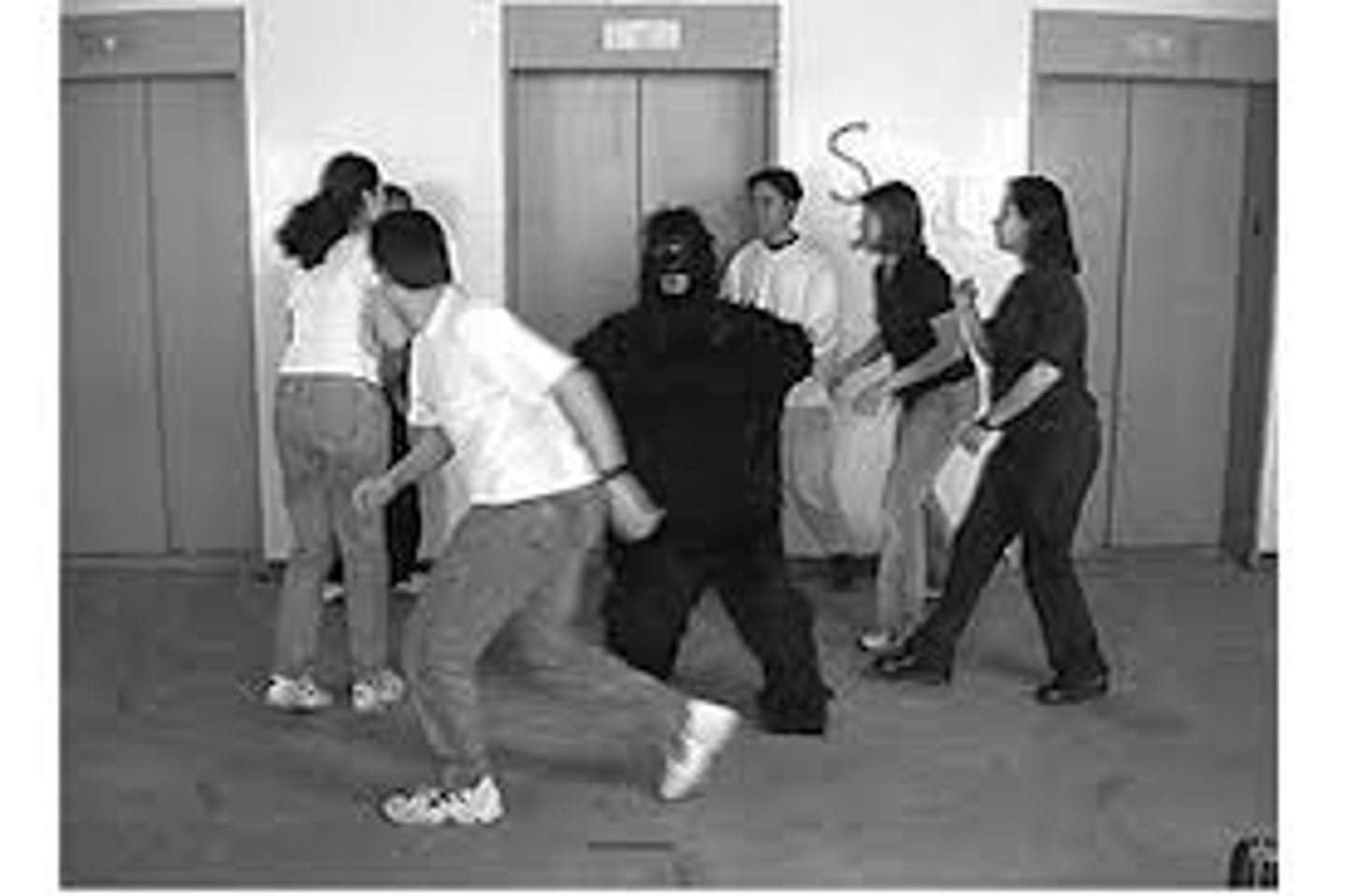
inattentional blindness
a failure to perceive objects that are not the focus of attention

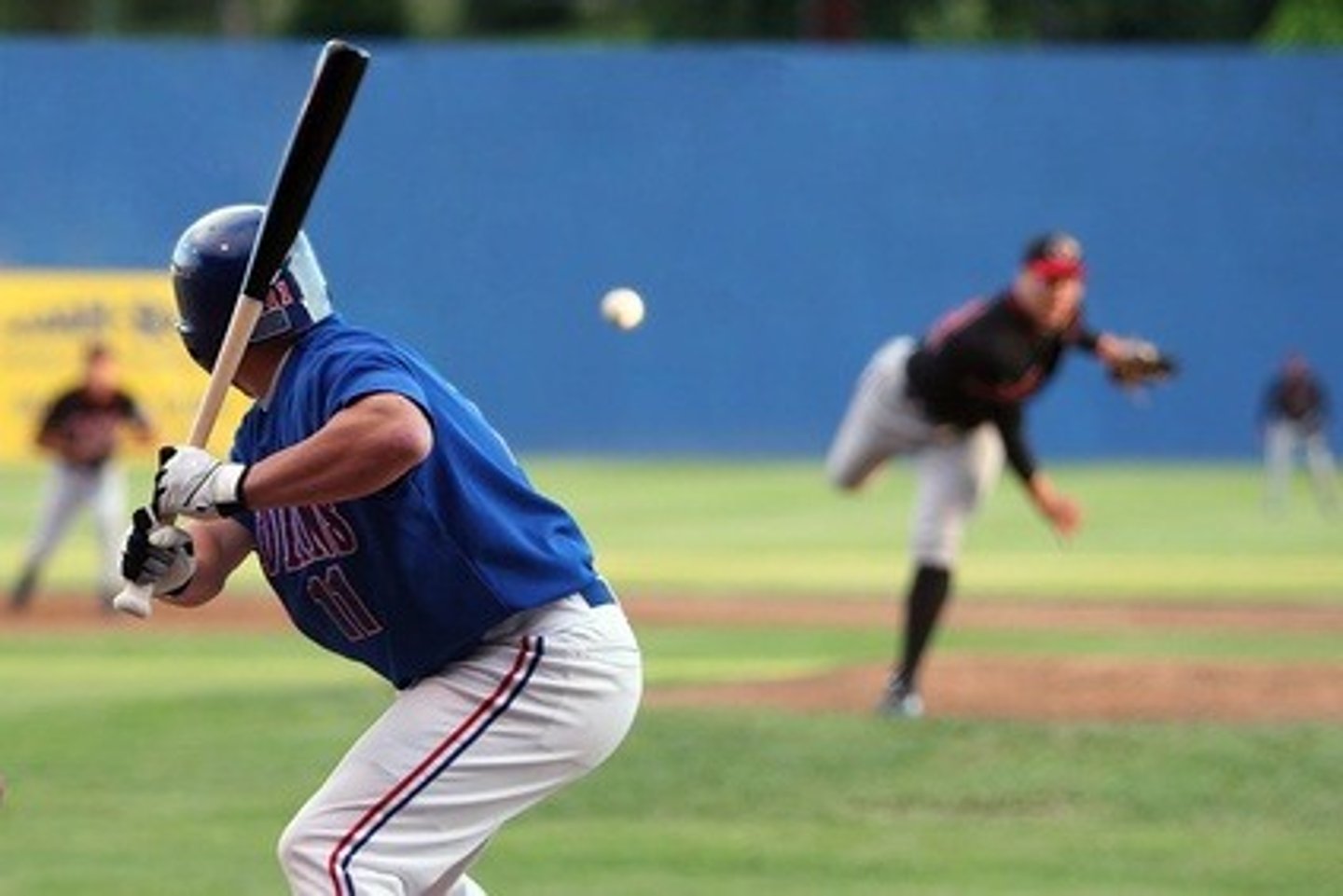
selective attention
the ability to focus on only one stimulus from among all sensory input

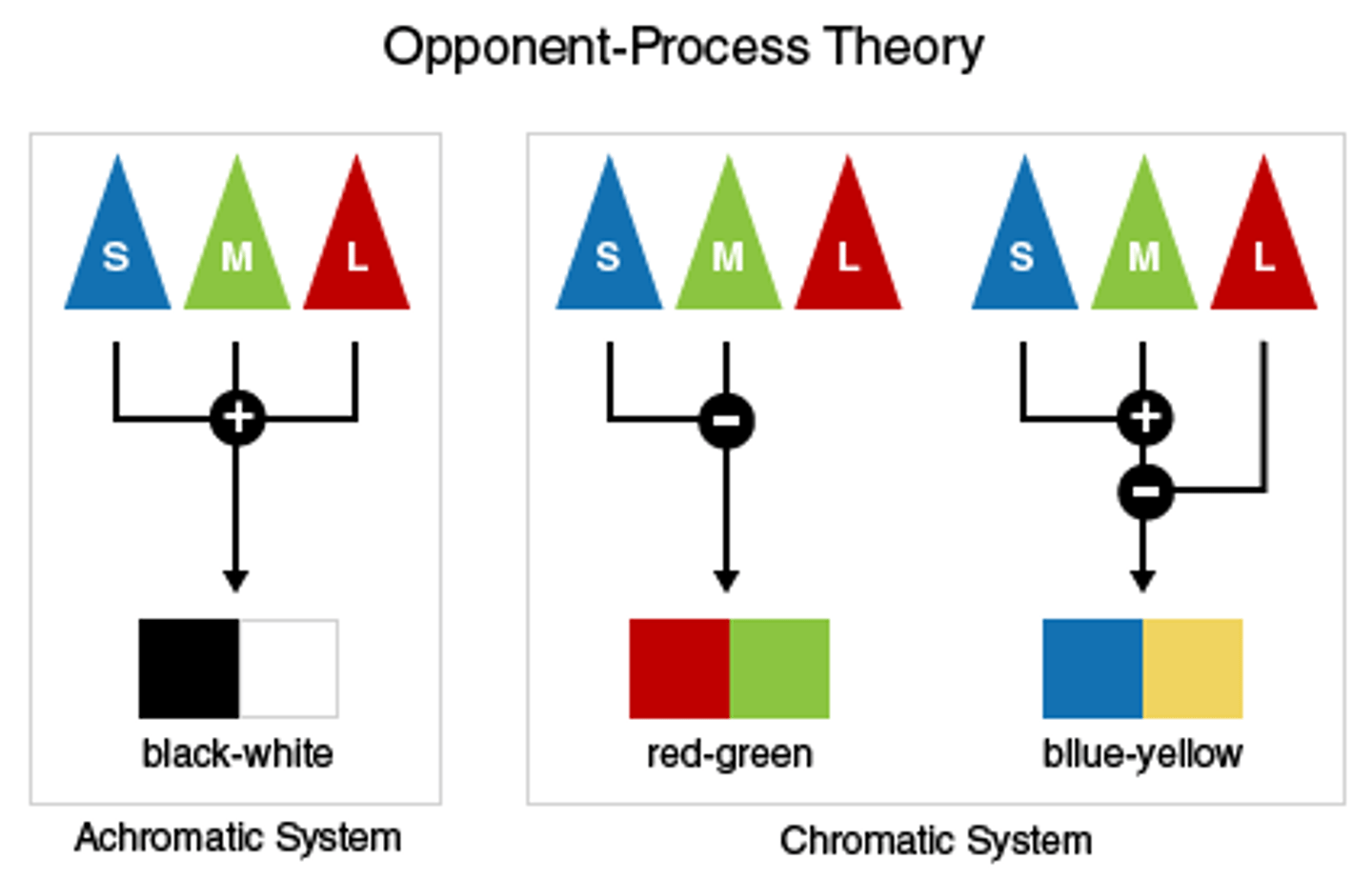
opponent-process theory
the theory that opposing retinal processes (red-green, yellow-blue, white-black) enable color vision. For example, some cells are stimulated by green and inhibited by red; others are stimulated by red and inhibited by green
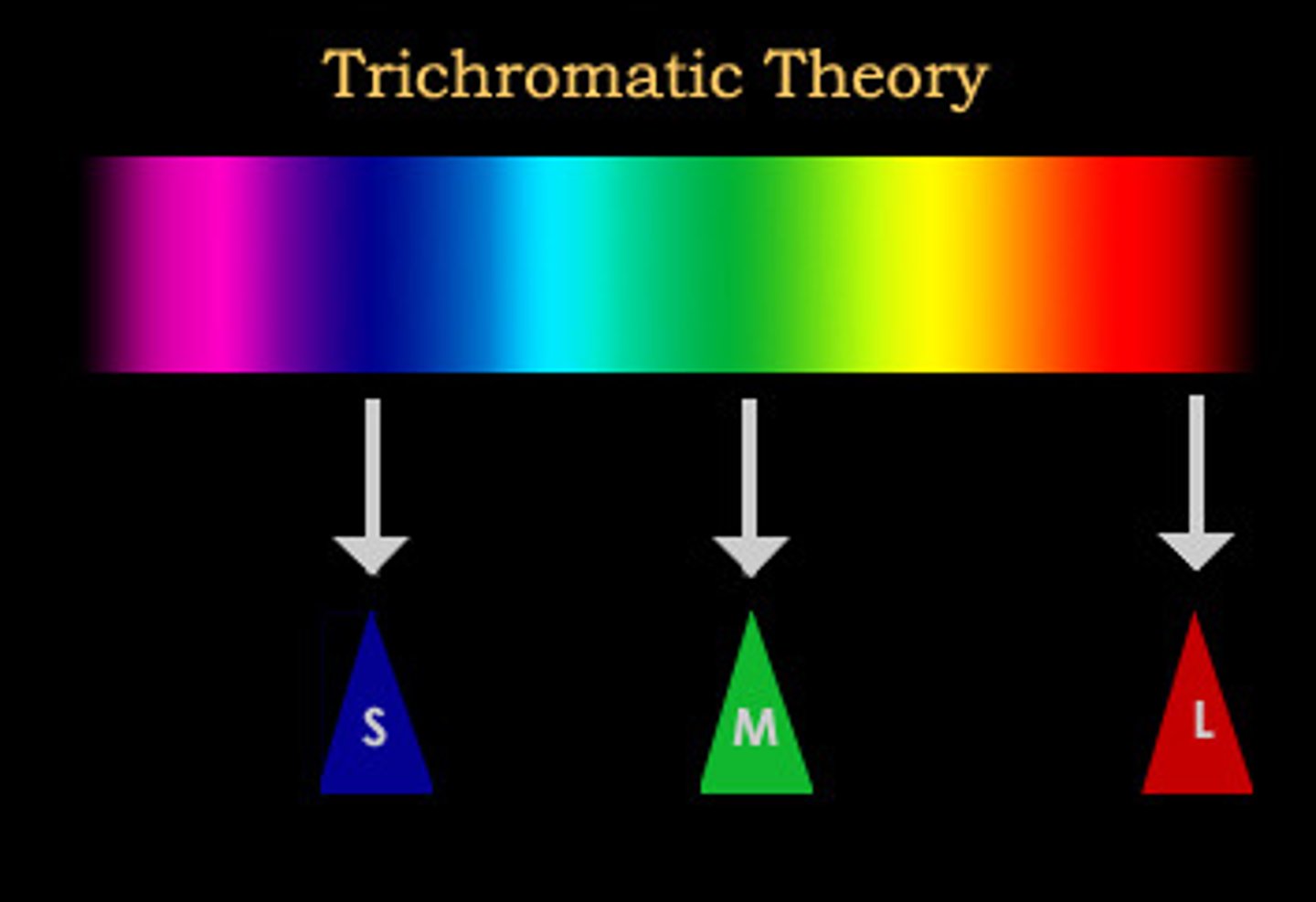
trichromatic theory of color vision
The theory that there are three kinds of cones in the retina, each of which responds primarily to a specific range of wavelengths
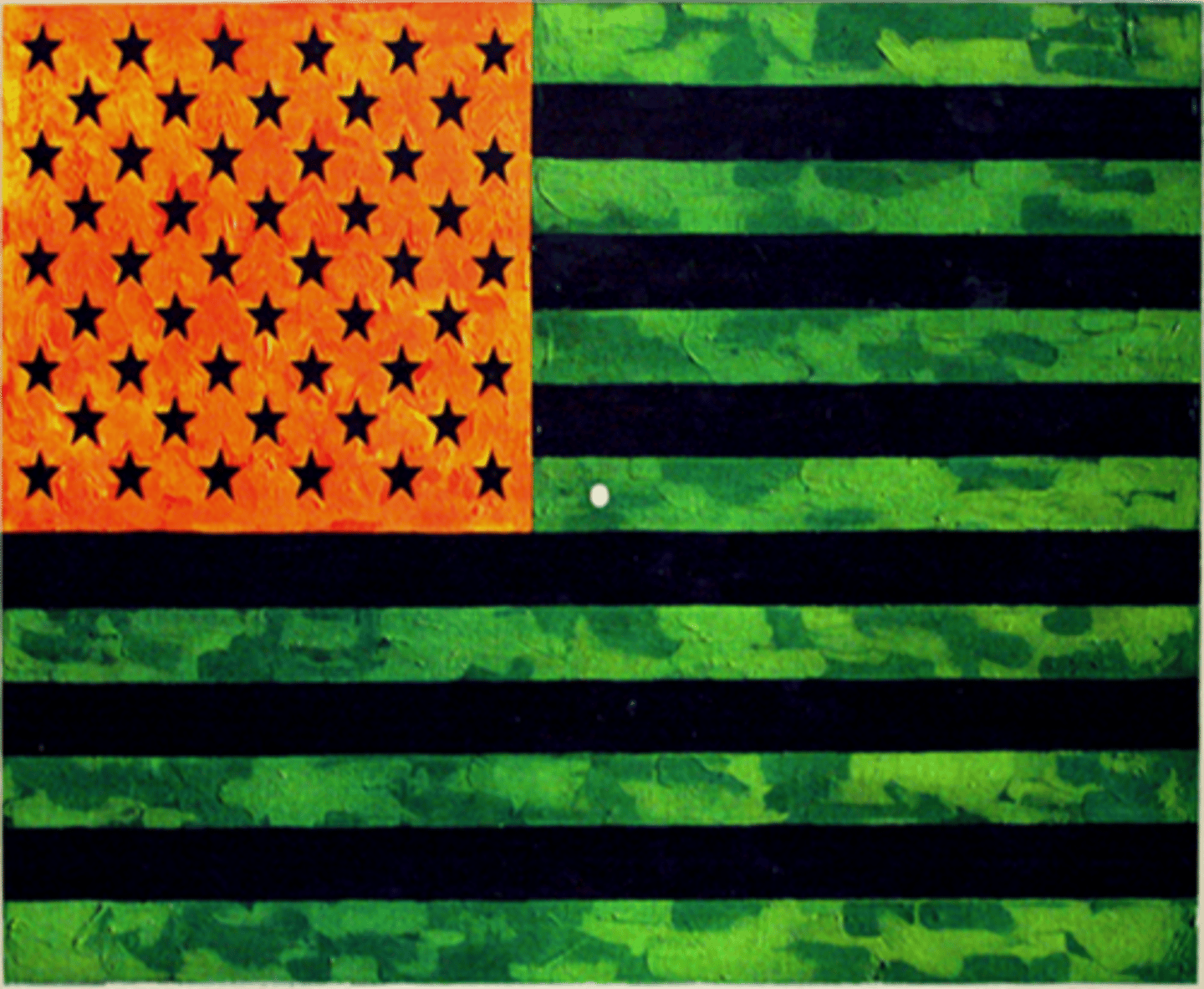
Afterimage
A visual image that persists after a stimulus is removed.

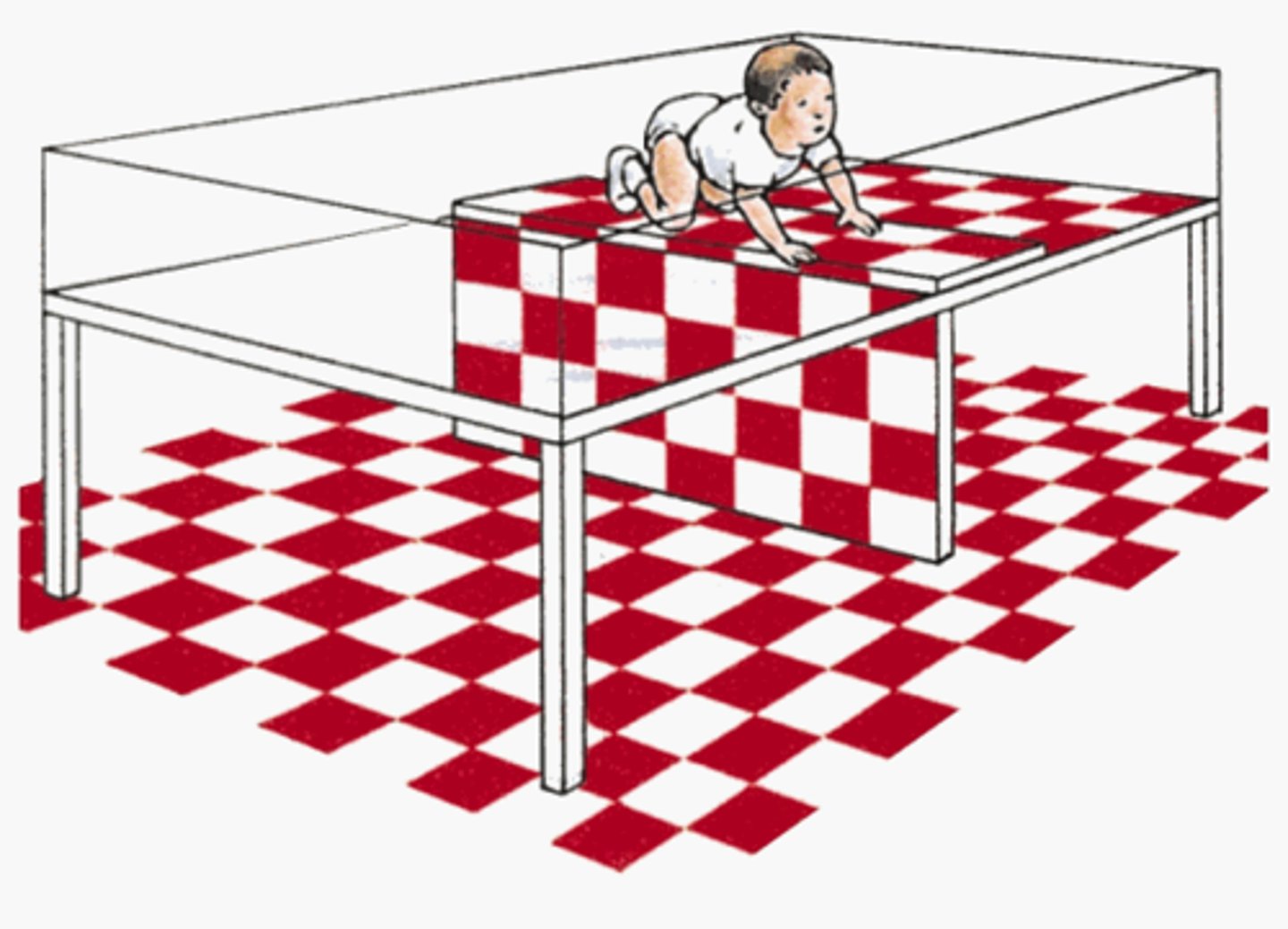
visual cliff experiment
created by E.J. Gibson, used to determine when infants can perceive depth
Habituation
decreasing responsiveness with repeated stimulation. As infants gain familiarity with repeated exposure to a visual stimulus, their interest wanes and they look away sooner.