joints
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
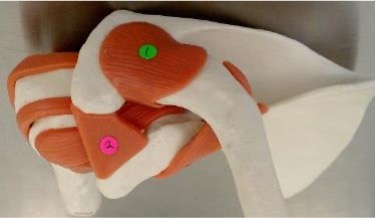
1
acromioclavicular ligament: acromion + clavicle
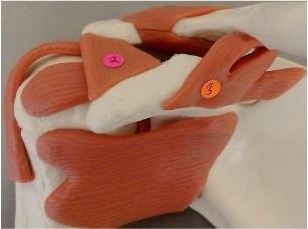
2
coracoacromial ligament: coracoid process + acromion
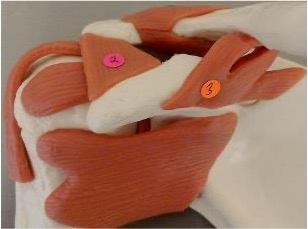
3
coracoclavicular ligament: coracoid process + clavicle
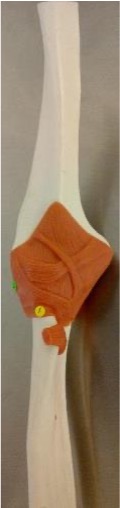
1
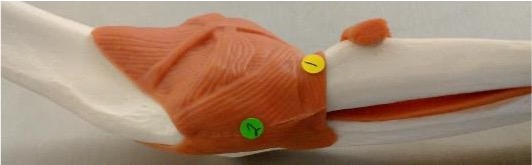
annular ligament: binds head of radius to ulna, can tear known nursemaids elbow where head of radius pops out of the ligament
2
radial collateral ligament: lateral surface of elbow is stabilized by this ligament

3
ulnar collateral ligament: medial surface of elbow is stabilized by this ligament
1
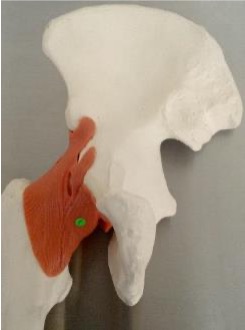
pubofemoral ligament: pubis + femoral head
2
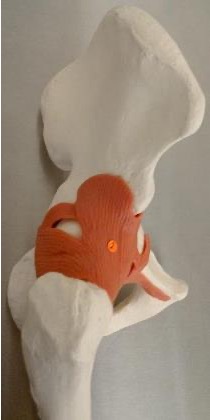
iliofemoral ligament: ilium + femoral head
3
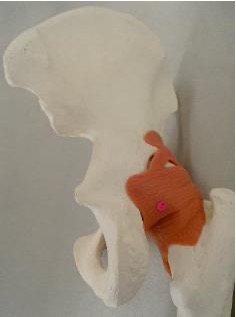
ischiofemoral ligament: ischium + femoral head
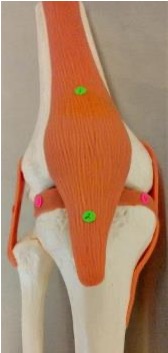
1
quadriceps tendon
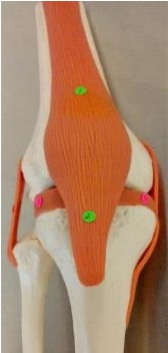
2
patellar ligament
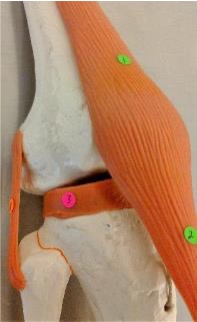
3
lateral meniscus: found under lateral condyle of femur
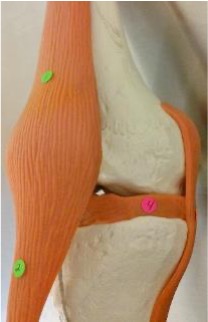
4
medial meniscus: found under medial condyle of femur
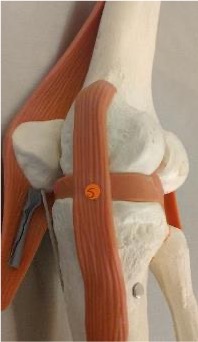
5
tibial collateral ligament
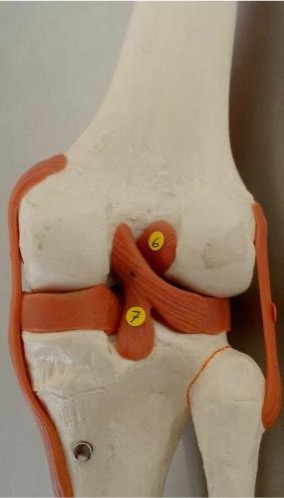
6
anterior cruciate ligament: found in between the femoral condyles on the anterior side
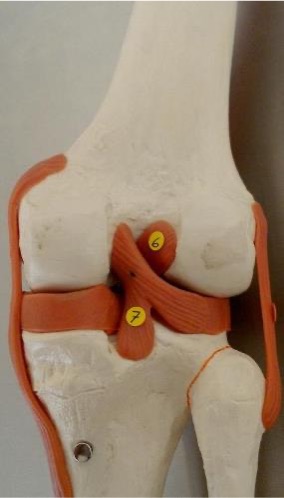
7
posterior cruciate ligament: found in between the femoral condyles on the posterior side

8
fibular collateral ligament
what is an articulation
a joint, where bones meet
synarthrosis joint
no movement, very strong
amphiarthrosis joint
slightly moveable joint, articulations through collagen fibers or cartilage
diarthrosis joint
freely movable joint, has many planes of movement
suture
synarthrosis joint, located only between the bones of the skull
gomphosis
synarthrosis, binds the teeth to bony sockets in the maxillae and mandible
peridontal ligament
fibrous connection between tooth and its socket
synchondrosis
synarthrosis, cartilaginous bridge between two articulating bones. vertebrosternal ribs and manubrium
synostosis
synarthrosis, when two bones fuse and the boundary between them disappears. epiphyseal lines of mature long bone, fusion of an infant’s left and right mandibular bone
syndesmosis
amphiarthrosis, bones are connected by a ligament
symphysis
amphiarthrosis, articulating bones are connected by a wedge or pad of fibrocartilage
synovial joint
diarthrosis, permits a wider range of motion than do other types of joints. typically ends of long bones
monoaxial
movement in one plane
biaxial
movement in two planes
triaxial
movement in three planes
pathologic synostosis
synostoses can occur outside of their desired locations. often functionally impairing, but not always
joint capsule
surrounds the joint
articular cartilage
covers the articulating surfaces of the bone, helps reduce friction
synovial membrane
the tissue lining the cavity that secretes synovial fluid
synovial fluid
the fluid inside a joint, lubrication, distribution of nutrients, shock absorption
meniscus
fibrocartilage between 2 bones
fat pads
adipose tissue usually superficial to the joint capsule
bursae
small fluid filled pouches by joints-helps to reduce friction and act as a shock absorber
ligaments
accessory ligaments help support the joint capsule
the structure of the bones making up the joint determine…
its motion
gliding joint
have flattened or slightly curved surfaces that slide across one another but the amount of movement is very slight. acromioclavicular and claviculosternal joints. slight nonaxial or multiaxial
hinge joint
permit angular motion in a single plane, like the opening and closing of a door. monoaxial. elbow, knee, ankle joint.
condylar joint
have an oval articular face nestled within a depression on an opposing surface. biaxial. radiocarpal joint.
saddle joint
complex articular faces and fit together like a rider on a saddle. each face is concave along one axis and convex along the other. biaxial. first carpometacarpal joint.
pivot joint
only permit rotation. monoaxial. proximal radioulnar joint, atlantoaxial joint.
ball and socket joint
the round head of one bone rests within a cup shaped depression in another. triaxial. shoulder joint and hip joint.
facet joints
articulation of superior and inferior articular processes and facets. allows for slight flexion, extension, lateral side bending and rotation. majority at cervical and lumbar spine.
symphyseal joints
between the bodies of the vertebrae and the intervertebral discs
annulus fibrosis
tough outer layer of fibrocartilage. surrounds the nucleus pulpous.
nucleus pulposus
gelatinous core, helps with shock absorption and reduces compressive loads.
herniated disc
nucleus pulposus “herniates” or breaks through the annulus fibers
what kind of joint is the shoulder
ball and socket, diarthrosis
glenoid labrum
fibrocartilage that fills the glenoid cavity- increases surface area and creates a larger socket.
which ligaments stabilize the shoulder joint to prevent the humeral head from moving superiorly
coracoacromial, acromioclavicular, coracoclavicular
what kind of joint is the elbow
hinge joint
annular ligament
binds the radius to the ulna, this allows radius to rotate
radial collateral ligament
stabilizes the lateral side of the elbow
ulnar collateral ligament
stabilizes the medial side of the elbow
what kind of joint is a hip joint
ball and socket, diarthrodial- femoral head articulates with the acetabulum
does a hip joint have a labrum
yes which is a piece of cartilage found in joints, or “lip”
ligamentum teres
deep in joint, attaches to fovea capitis on femoral head
what are the ligaments that reinforce the joint capsule of the hip joint
pubofemoral, ischiofemoral, and iliofemoral ligament
what kind of joint is the knee joint
modified hinge joint
what are the three articulations of the knee joint
medial condyle to medial condyle, lateral condyle to lateral condyle, and patella and femur
what are some special features in the knee joint
menisci and fat pads
does the knee have a sesamoid bone
yes, the patella
lateral collateral ligament/ fibular collateral ligament
stabilizes the lateral side of the knee joint
medial collateral ligament/ tibial collateral ligament
stabilizes the medial side of the knee joint
anterior cruciate ligament
originates on the anterior surface of the tibia, resists anterior tibial translation and knee hyperextension, most commonly injured ligament, taut with the knee extended
posterior cruciate ligament
originates on the posterior surface of the tibia, resists posterior translation of the tibia on the femur, strongest ligament in the knee, taut with the knee flexed
patellar ligament
extends from the patella to the anterior tibia
quadriceps tendon
tendon from the quadriceps muscle, attaches to the patella and continues to the tibial tuberosity/ tibial tubercle
medial meniscus
on the medial side of the tibiofemoral joint
lateral meniscus
on the lateral side of the tibiofemoral joint
what are the functions of menisci
increase knee stability, act as shock absorbers, spread load over cartilage
six functions of skeletal muscle
produce skeletal movement, maintain posture and body position, support soft tissues, guard body entrances and exits, maintain body temp, and store nutrients
skeletal muscle
striated, multinucleated, three types: fast, slow, intermediate
cardiac muscle
striated, one nucleus, intercalated discs, only located in the heart
intercalated discs
connects cardiac muscle cells to assist with contraction as a single organ
smooth muscle
nonstriated, one nucleus, involuntary muscle tissue
what do the cells look like in skeletal muscle
long, cylindrical, striated, and multinucleate
locations of skeletal muscle
combined with connective tissues and neural tissue in skeletal muscles
functions of skeletal muscle
moves or stabilizes the position of the skeleton. guards entrances and exits to the digestive respiratory and urinary tracts, generates heat, protects internal organs
what do the cells of cardiac muscle look like
short, branches, and striated, usually with a single nucleus. cells are interconnected by intercalated discs
location of cardiac muscle
heart
functions of cardiac muscle
circulates blood, maintains blood pressure
what do smooth muscle cells look like
short, spindle shaped, and nonstriated with a single central nucleus
locations of smooth muscle
found in the walls of blood vessels and in digestive, respiratory, urinary, and reproductive organs
functions of smooth muscle
moves food, urine, and reproductive secretions. controls diameter of respiratory passageways. regulates diameter of blood vessels.
what does cardiac muscle have that smooth muscle doesn’t
A bands and I bands
intercalated discs have a lot of…
gap junctions and desmosomes