Ecology of Aquatic Systems: Abiotic and Biotic Factors
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Ecology
The study of interactions among organisms and their environment.
Abiotic factors
Non-living chemical and physical parts of the environment that affect living organisms.
Biotic factors
Living components of an ecosystem that affect the organisms within it.
Aquatic biomes
Biomes that are primarily water-based, characterized by specific abiotic factors.
Energy source in ecosystems
Solar energy for terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, with a food chain starting from plants to grazers to carnivores.
Dark environments energy source
Chemical energy from deep ocean vents supporting bacteria and grazers.
Temperature range for life
Narrow range of 0°C - 45°C due to physical constraints like ice crystal formation and protein denaturing.
Water balance in organisms
Aquatic organisms must balance solute concentration, with hypotonic (freshwater) and hypertonic (saltwater) osmosis.
Nutrients in aquatic systems
Availability of inorganic nutrients such as Nitrogen and Phosphorus.
Dissolved O2
Amount of dissolved oxygen in water, which is temperature dependent.
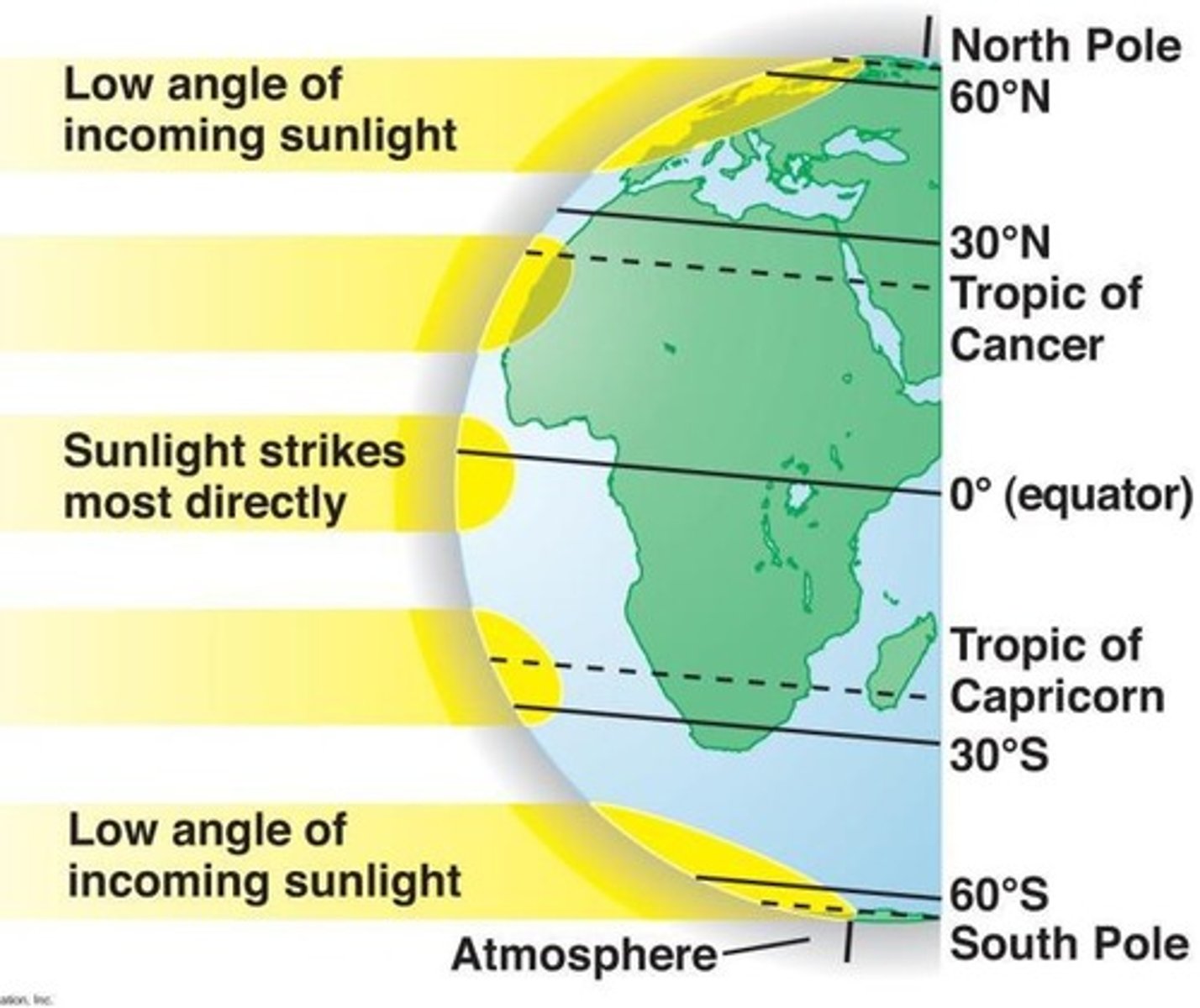
Solar radiation
Varies with latitude and seasons, affecting climate and ecosystems.
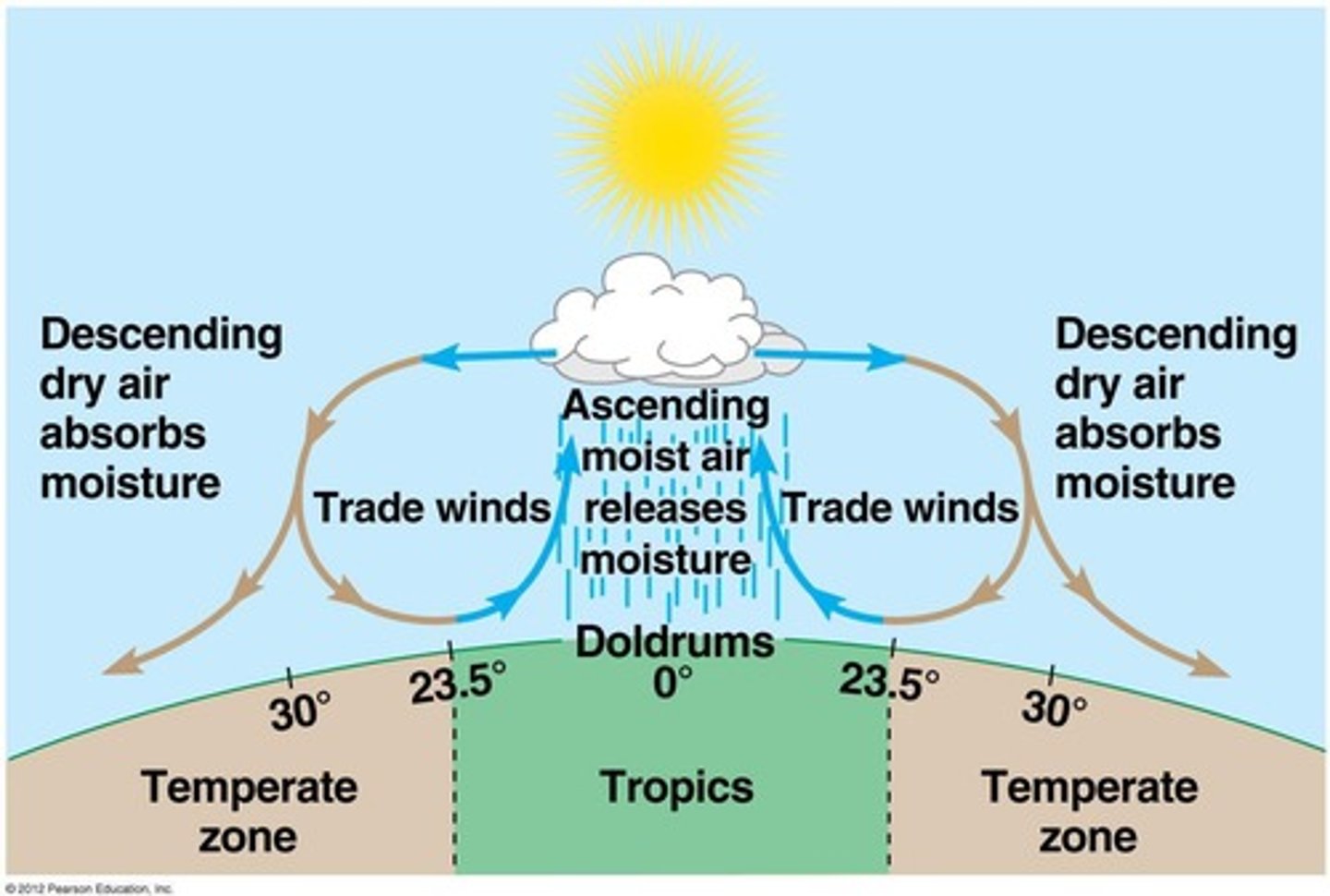
Global air circulation
Patterns that influence precipitation and climate across the globe.
Impact of oceans
Oceans affect local climate through their heat and moisture.
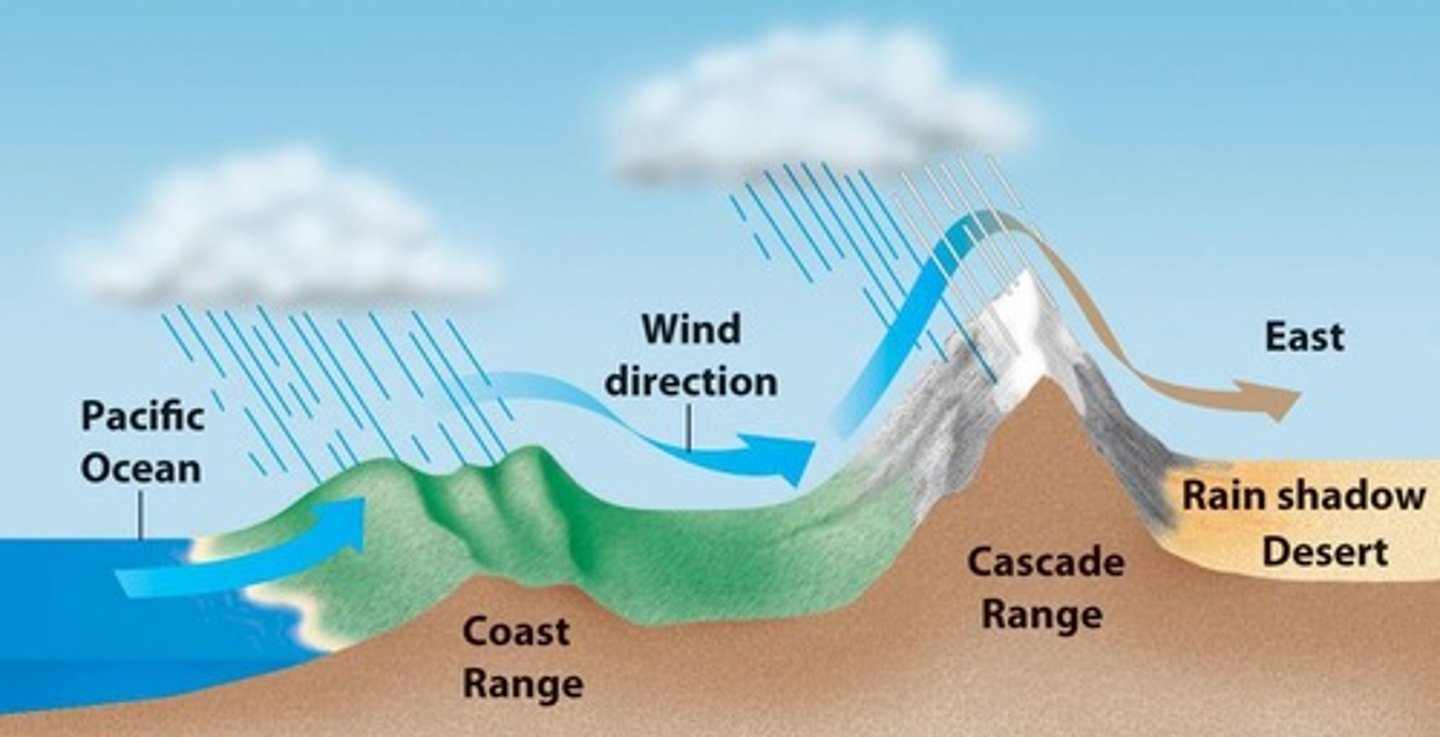
Impact of landforms
Mountains can affect precipitation patterns in regions like southern British Columbia.
Species evolution
Species evolved from ancestors in specific locations or dispersed and survived in new locations.
Natural selection
The process by which organisms adapt to abiotic and biotic factors to survive and reproduce.
Positive biotic factors
Factors that benefit organisms, such as plants needing pollinators.
Negative biotic factors
Factors that harm organisms, such as predation.
Field research
A method of studying ecology by observing organisms in their natural environment.
Laboratory experiments
Controlled experiments conducted to study ecological interactions in a regulated setting.
Sea urchin
A possible predator in studies analyzing the impact on seaweed cover.
Limpet
A grazer whose removal showed no significant impact on seaweed cover in studies.
Seaweed cover
Percentage of seaweed cover affected by the presence or absence of grazers.
Ecology
Interactions of natural organisms with their environments.
Organizational levels of ecology
Four primary levels: Organism/individual, populations, communities, ecosystems.
Abiotic factors
Non-living environmental factors such as temperature, rainfall, nutrients, CO2, and solar radiation.
Biotic factors
Living environmental factors such as predation, competition, and insect & fungal parasites.
Environmental science methods
Three kinds: field, experimental, and modelled.
Global change impact on ecology
Both abiotic and biotic vectors are changing.
Aquatic biomes
Include saltwater, freshwater, and transitional areas.
Freshwater aquatic environments
Often have a strong seasonal component.
Saltwater environments
Strongly structured by depth, with conditions and biodiversity highly variable by depth.
Transition environments
Highly productive areas between different ecosystems.
Light attenuation in water
Limits productivity in aquatic systems.
Salt exposure ability
Affects community ecology in aquatic environments.
Migration and dispersal in aquatic systems
Can be passive and over long distances.
Gigantism in aquatic systems
A niche adaptation observed in some aquatic organisms.
Oxygen concentrations in water
Inversely proportional to temperature.
Lakes & ponds
Seasonal mixing redistributes O2 and nutrients.
Rivers & streams near source
Colder, clear, and lower in nutrients.
Rivers & streams downstream
Warmer, slower, and more sediment.
Estuary
Transition between freshwater and ocean, with variable saltiness.
Wetlands
Transition between aquatic (usually freshwater) and terrestrial, typically rich in biodiversity.
Oak Hammock Marsh
A wetland in Manitoba that improves water quality by removing contaminants.