Psych Profiling and Fingerprints
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
Where are fingerprints useful for identification?
On a stolen vehicle, left at a crime, sometimes computers, phones etc…
William Herschel:
Required indians to put their fingerprint on contracts, and used fingerprints as a mean of identifying prisoners.
Henry Faulds:
Scotsman he worked in Tokyo, used fingerprints to exonerate innocent burglary suspects.
Alphonse Bertillon:
Propsied body measurements as a means of identification; termed anthropometry.
Francis Galton:
1st to dtufy fingerprints and classify them from filing
Edward Richard, Henry:
develops the prototype Fingerprints classifications system now used Europe and the U.S
Jaun Vucentich:
Developed a fingerprint classification system based on Galton that is used in spanish-speaking countries.
What kind of pattern is this:

Loop Fingerprint
What kind of pattern is this:
Whorl Fingerprint
What kind of pattern is this:

Arch Fingerprint
How common are Loops?
65%
What are the two types of Loop:
Radial which is when it opens towards the thumb
Ulnar which is when it opens towards the pinky
How common are Whorl?
30% common in Asian ancestry
Variations of Whorl:
Plain, central pocket, double loop, and accidental
How common are Arch?
5% found in African ancestry
What kind of arch is the 1st fingerprint (left):

Plain
What kind of arch is the 2nd fingerprint (right):

Tented
What are the most common and least common types of print?
loops and arch
What is the study of the uniqueness of friction ridge structures and their use for personal identification?
Ridgeology
Dactyloscopy is the study of ____.
and comparison of fingerprints for the purpose of identifying individuals.
What are minutiae?
Characteristics of ridge patterns
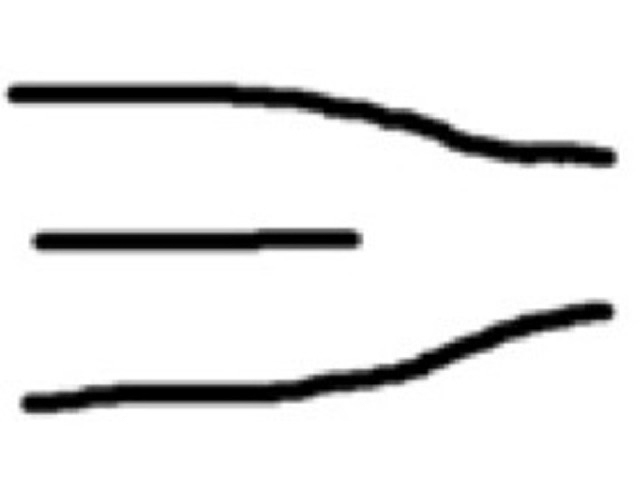

Ridge Ending
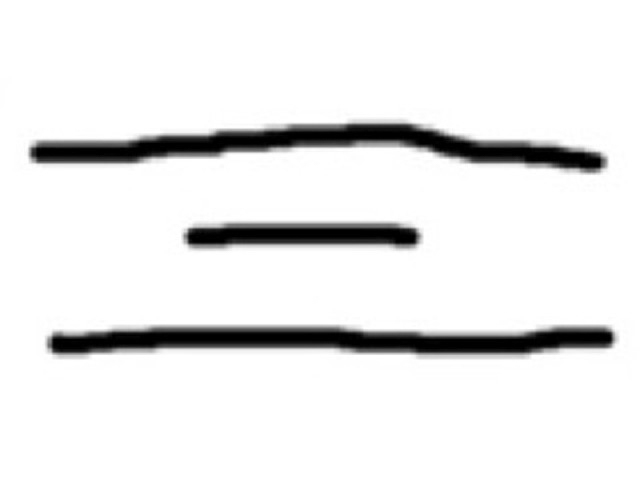

Island
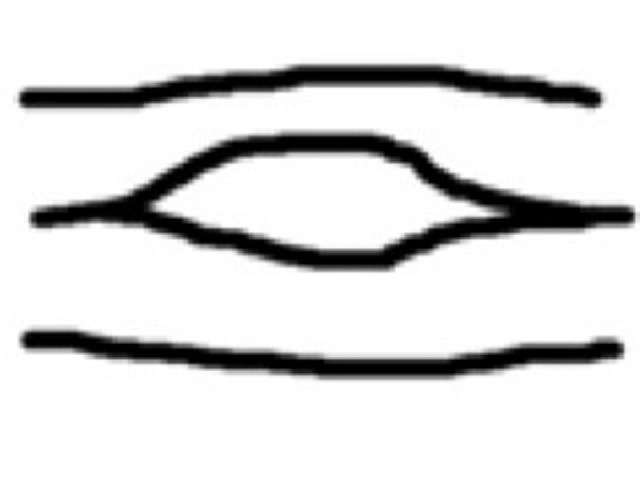
Eye
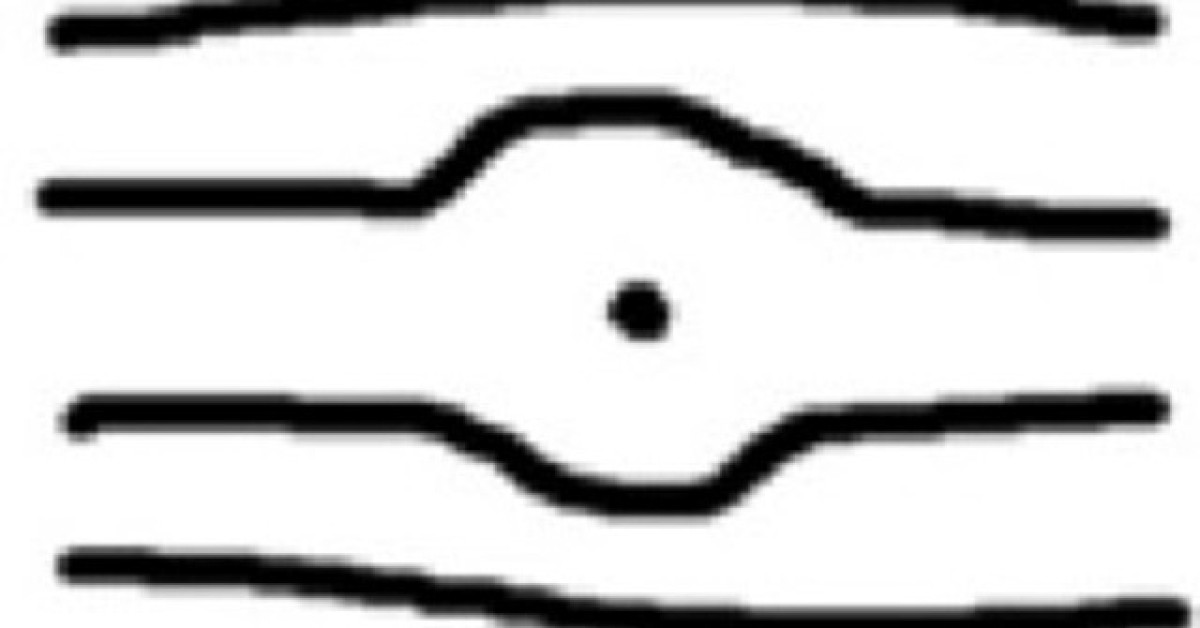
Dot
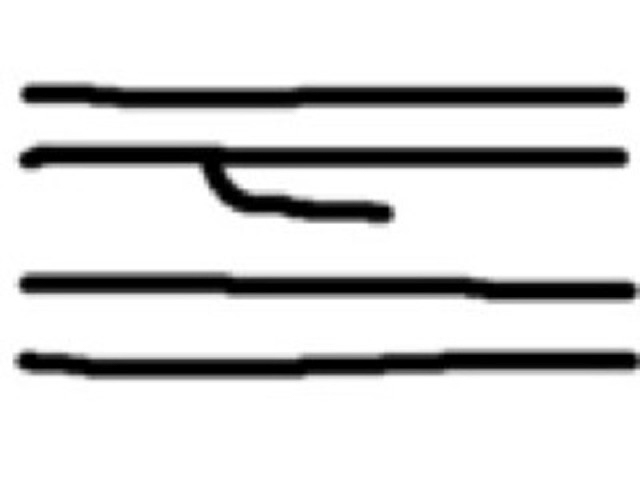
Spur

Delta
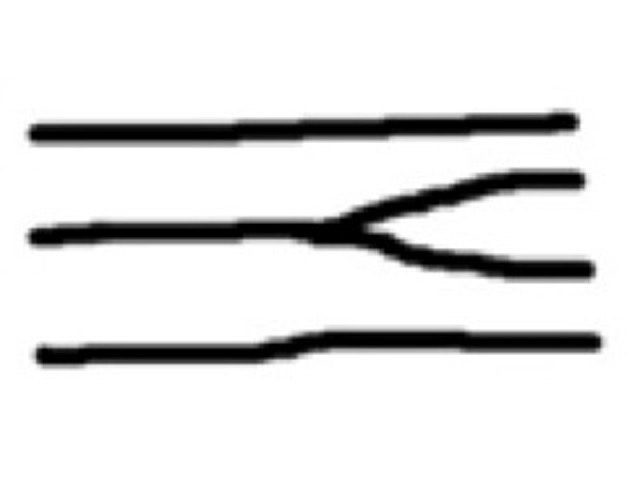
Bifurcation
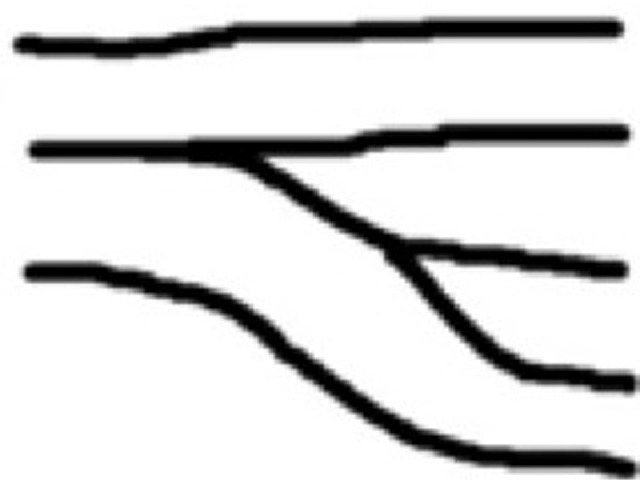

Double Bifurcation
What are Patent prints?
Visible prints left on smooth surfaces when blood, link, or some other liquid comes in contact with the hands and is then transferred to the surface
What are Plastic prints?
Actual indentations left on some sort of material such as clay, putty, or wax
What are Latent prints?
Hidden prints caused by the transfer of oil and other body secretions onto a surface
What chemicals and powders are used to lift prints?
Non-porous surfaces require aluminum, graphite, or magnetic are used with blushes, then lifted with tape, while porous surfaces require ninhydrin and cyanoacrylate.
How are latent fingerprints collected?
by first making the invisible print visible, often by dusting non-porous surfaces with powder or using specialized chemicals and light sources on porous surfaces
What is used to lift prints?
Black, white, and fluorescent power. Ninhydrin, iodine,silver nitrate, cyanoacrylate.
What’s the most common technique, or standard identification method used for latent prints?
Powder
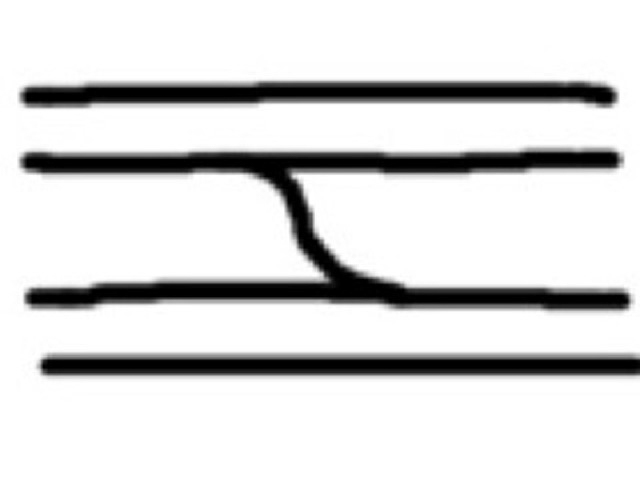
Bridge
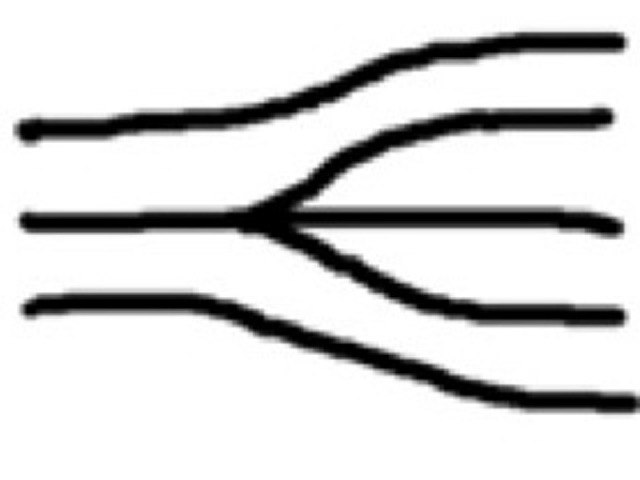
Trifurcation
What is conformity?
When a person adjust thoughts, feelings and behaviors to match that of a group.
What is flashbulb memory?
A vivid recollections of framatic or emotionally charged life events.
What are false memories?
Recollections that your brain makes up without realizing.
A serial killer is someone who....
Commits 3 or more murders over an extended period of time and return to ‘normal’, “Mask of Sanity”
A spree murderer is someone who…..
Commits multiple murders in different locations over a period of time that may vary from a few hours to a couple of days
What type of serial killer is more likely to be, IQ below average, 80-95 range, socially inadequate, live alone, usually does not date.
Disorganized type
What type of serial killer is more likely to be be, IQ above average, 105-120+ range, usually contracts police to play games, a police groupie or a wannabe.
Organized type
What did Stanley Milgram's obedience experiment prove?
Most people would stop before administering an electric shock for 450 volts to other people.
Examples that can affect your memory:
Poor lighting, distance in viewing, short exposure, smith covering perpetrator face, high stress/anxiety, presence of weapon
What are some inconsistencies with relying on witnesses:
race-bias, distance in viewing, poor lighting
What makes memories inaccurate?
Time and imagination
How can false memories be created?
By implanting an idea using pictures, word, suggestions, connections.
What is the Hofling experiment?
95% of nurses were easily influenced into carrying out orders. They couldn't take instructions over phone or exceed dose amount, when nurse were asked to discuss what they would do in similar situations they said they wouldn't comply with order.He found that ppl are unwilling to question supposed authority even when they might have good reason to.
What is the Zimbardo experiment?
The stanford prison; stimulated prison life college kids became prisons and guards. Had to end 5 days early because of abuse.
Will people be obedient?
Yes
Common actions of mass killers?
They commit suicide, meaning the knowledge of their state of mind and what triggers their actions is often left to more speculation than fact, mass murders when caught say they can’t remember clearly.
What differentiates mass killers from serial killers?
serial killers have cooling periods in between killings and seem normal they have a “mask of Sanity”
Who are common victims of organized killers?
Prostitutes people that will voluntarily go with them.
How do Organized type killers react to their killing?
Returns to crime scene to see what police have done, usually contacts police to play games, a police groupie/wannabe, doesn't seem self help.
What are the Mixed types of serial killers-characteristics?
Disorganized or organized trait will be stronger some descend from being organized into being disorganized. At first they are carful and methodical but as time goes on they get more careless
What is a common attack for disorganized killer?
“Blitz” pattern depersonalizes victim to a thing or it
Do disorganized killers put much thought into their kills?
no they perform impulse killings
Why are Serial killers hard to catch?
Once they stare they can’t stop, only commit to few and spaced out murders, police don’t like admitting they’re serial killers.
What are the Common motives for serial killers?:
Money or to fulfill some sort of desire or fantasy: lust or trill
What is offender profiling?
Is used to help find suspects. It involves forensic physical and behavioral evidence to help police narrow the field of investigation.
What is Corpus delicti?
The “body of crime” evidence that proves a crime took place (ex: missing items, fingerprints, etc)
What is Modus Operandi?
The method of operation used by the criminal, all the actions and behaviors that were needed to commit the crime.
what is the American Top-down approach to profiling:
Builds classification system using info that’s alr known (interviews with known criminals) together with behavioral analysis I of crimes scenes and info from victims and witnesses.
What is the British Bottom-up approach to profiling?
Used data processing the aim being to identify associations between offense and offend characteristics
What are the differences between the “top-down” approach and the “Bottoms up” approach?
British starts with evidence we do interviews and subjective conclusions
Inductive criminal profiling:
uses stats and correlations in order to see whether the shared characteristics between the crimes
Deductive Criminal profiling:
If the 1st statement is true, so is the conclusion
Correctional Psychologist:
A forensic psychologist who works in a correctional setting with inmates and offenders to prepare individuals for societal integration