Management of Common Infections & Current Antimicrobial Prescribing & Resistance Patterns
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
examples of URTIs
pharyngitis, tonsillitis, laryngitis
examples of LRTIs
bronchitis, pneumonia
examples of lowers UTIs

what are the main causative organisms of URTIs?
Viruses (≈40%) & streptococci (≈25%) – mostly S. pyogenes
symptoms of Streptococcal infection
fever, sore throat, enlarged lymph glands and
bright red pharynx & uvula - may be pus
symptoms of viral pharyngitis
Usually mild with variable associated symptoms e.g. glandular fever
investigations for URTIs?
Rapid latex agglutination tests for streptococci & immunofluorescence for
viruses
What is pneumonia?

diagnostic tools of pneumonia?
based on signs and symptoms (cough, fever, sputum, SOB, chest pain/discomfort)
- confirmed by chest X-ray
what are the 3 classifications of pneumonia?
anatomical, bacteriological and clinical

what is the severity assessment for pneumonia in primary care?
CRB-65

what is the severity assessment for pneumonia in hospital care?
CURB-65 score

what are the investigations for moderate-high severity CAP?
• Take blood & sputum cultures
• Consider pneumococcal & legionella urinary antigen tests
• Chest X-ray (within 4hrs)
causative organisms of CAP- typical/classical?
usually caused by S. pneumoniae but can be due to
Haemophilus influenzae
what organisms causes atypical pneumonia?
Mycoplasma pneumoniae,
Chlamydia pneumoniae or, more rarely, Legionella pneumophila
describe classical lobar pneumonia

describe atypical pneumonia

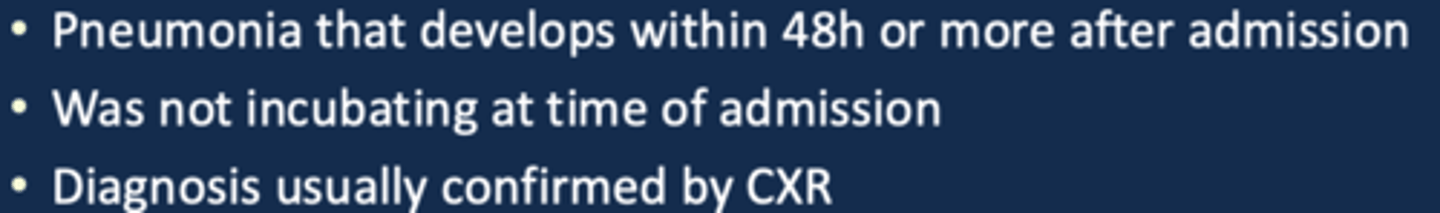
what is HAP (criteria)?
what are the causative organisms of HAP?
E. coli, Klebsiella, Pseudomonas, also MRSA
what are the investigations for HAP?

examples of uncomplicated UTIs?
cystitis in an adult, non-pregnant woman
example of a complicated UTIs?
infections in pregnancy, children, men, sites
other than the bladder, or with structural or functional defects
causative organisms of lower UTIs?
e.coli

clinical syndromes of lower UTIs?

Cellulitis / erysipelas are ...
Skin & soft tissue infections
what is the difference between cellulitis and erysipelas?
• Erysipelas affects the superficial dermis
• Cellulitis reflects deeper dermal involvement
what are the common causes of Cellulitis / erysipelas?
Streptococcus pyogenes and Staphylococcus aureus

1st line treatment of HAP?
Co-amoxiclav 500/125mg TDS 5/7
clinical presentation of Cellulitis / erysipelas?
Redness, pain, swelling & heat [rubor, dolor, tumour, calor]
![<p>Redness, pain, swelling & heat [rubor, dolor, tumour, calor]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/5cae4bdc-eb73-4fe3-89e5-5a7bb5bb4654.png)
What can you expect from patient examination with suspected Cellulitis / erysipelas?
