Biology Chapter 6 - DNA and Gene Expression
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
DNA
A nucleic acid that stores hereditary information and the instructions for the proper functions for a cell.
Make up of nucleotides
Deoxyribose (5 carbon sugar), a phosphate group attached to the sugar, Nitrogenous bases
Nitrogenous Bases in DNA
Adenine, Guanine, Thymine, Cytosine.
Nitrogenous Bases
The 4 bases that make up the genetic code for all living organisms.
Thymine
Adenine and ______ bind together.
Guanine
______ and Cytosine bind together.
Linear
The physical structure of eukaryotic DNA
Double Helix
The twisted, spiraled staircase or ladder form for DNA.
DNA Structure
Twisted ladder shape made up of two strands of DNA where the sugar and phosphate groups form the backbone, and the bases form the rungs of the ladder and the bases extend out from the backbone into the middle and pairs via hydrogen bonds.
Genome
The full set of DNA found in an organism.
Plasmids
Where all genetic information is contained prokaryotes.
Linear strands
In eukaryotic organisms, genetic information is laid out in _______ _______
Chromosomes
The divided genetic strands of DNA. Humans’ DNA is divided into 23 pairs (46 total) and get one set from our mom and one set from our dad.
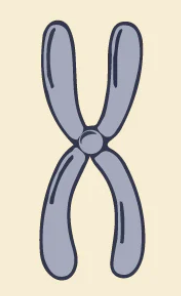
Genes
Specific sequences of DNA located at a specific locus on a chromosome and code for specific traits an organism has.
Locus
The position of a gene along a specific chromosome.
Traits
Hair color, height, eye color
Alleles
Alternative versions of genes that code for the same trait and is what codes for the trait that is seen on the surface.
Trait
Any single physical characteristic or feature of an organism.
Coding DNA
The DNA sequences that actually code for a protein product. It’s what codes for each individuals’ traits.
Junk DNA/Non-Coding DNA
DNA that doesn’t code for an actual trait and seems to serve no purpose and is found on the chromosome within the spaces between genes as well as within the genes themselves.
Prokaryotes
Don’t have a lot of non-coding DNA, 90% or more of their DNA codes for a product.
Eukaryotes
Have a lot of non-coding DNA interspersed with the coding DNA.
Exons
The coding regions of the gene.
Introns
The non-coding regions of the gene.
Non-coding regions
regions of DNA that consist of areas within the gene that repeat themselves thousands of times.
Components of non-coding DNA
Gene fragments, duplicate versions of genes, and pseudogenes.
Pseudogenes
Sequences that evolved from actual genes but accumulated mutations that made them lose their protein coding ability.
non-coding DNA
Some of the _________ DNA does encode extremely short RNA molecules (~20 nucleotides long) that function in gene regulation.
Genotype
The actual genes that an organism has that codes for a trait.
Phenotype
The physical manifestation of the genes an individual has.
Traits
The result of various proteins being produced in the cells.
Transcription and Translation
The two processes involved from going from the genes in your DNA to the proteins that are produced.
Transcription
Copying the gene information from the DNA into mRNA.
Translation
Translating the message in mRNA into an actual protein product.
Promoter Site
The area on the gene that tells the enzyme where to start the process of copying.
Step 1 of Transcription
The enzyme RNA polymerase recognizes the promoter site and binds to the DNA. This begins the process of unwinding the helix so it can be copied.
Step 2 of Transcription
The RNA polymerase moves down one side of the DNA strand copying the message. RNA polymerase builds an mRNA strand by binding RNA nucleotides together that match with the bases on DNA.
Nitrogenous Bases in RNA
Adenine, Uracil, Guanine, Cytosine
Step 3 of Transcription
Gene sequences are not infinite, when the end of the gene sequence is reached, the process terminates. The RNA polymerase stops copying and releases from the DNA strand.
Step 4 of Transcription
Editing the mRNA sequence by cutting out the introns and getting it ready for transport out of the nucleus.
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
The molecules that translate the mRNA code by linking specific bases on the mRNA with specific amino acids that will be used to build a protein.
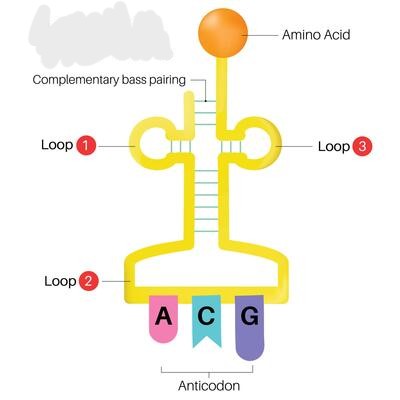
Codon
A 3 base sequence on mRNA that matches with tRNA that carriers one particular amino acid.
Attachment Site
A 3 base sequence that matches up with a 3 base sequence on the mRNA.
The Codon Table
Describes which tRNA and which amino acid is specified by each codon in the mRNA with 64 total codons possible where 61 specify amino acids and 3 are stop sequences.
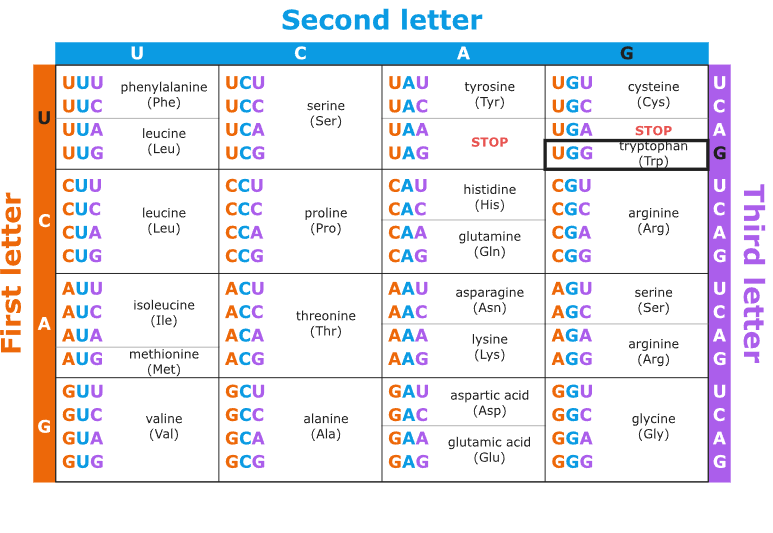
Stop Sequences
Codons that indicate the end of translation.
Step 1 of Translation
Recognize and initiate protein building by recognizing the start sequence AUG and then having ribosomal subunits attach to the mRNA which signals the tRNA to start bringing in the matching amino acids. This is where protein synthesis begins.
Step 2 of Translation
Elongation. The ribosome attached to mRNA moves down the strand reading it one codon at a time and at each codon, a tRNA brings in a new amino acid which are all linked together by peptide bonds, causing the protein to grow at one amino acid at a time.
Protein Synthesis
The production of a protein
Step 3 of Translation
Termination. The ribosome keeps moving down the mRNA sequence until it reaches one of the 3 stop codons and then detaches from the mRNA and releases the completed protein. Then the mRNA can be used repeatedly for several days until it’s broken by enzymes in the cytoplasm.
The 3 stop codons
UAA, UAG, and UGA