Congenital and Misc Defects of the Neurological System
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
What is hydrocephalus?
Accumulation of CSF within the ventricular system
How many ventricles do we have?
4
What divides the 3rd and 4th ventricles?
Mesencephalic aqueduct
What does the foramina of Luschka do?
Allows CSF to flow from the subarachnoid space of the 4th ventricle into the central canal
What produces CSF?
80% from the choroid plexus
Rest by ependymal cellsand interstitial fluid.
What does hydrocephalus cause?
Distention of the ventricular system and thus atrophy and necrosis of adjacent structures
What are the most common site for congenital obstruction causing hydrocephalus?
Mesencephalic aqueductand foramina of Monroe
What are the causes of hydrocephaly?
Congenital
Acquired
Compensatory
What can cause an acquired hydrocephaly?
CSF obstruction from tumors or masses
What breeds are more susceptible to congenital hydrocephaly?
Chihuahua or other min dog breeds
Can also be from In utero viral infections
What causes compensatory hydrocephaly?
Secondary to loss of brain tissue due to senescence, intracranial hemorrhage, FIP in cats
What is senescence?
Age-related atrophy
What can quadrigeminal arachnoid cysts cause?
Depends on size and severity of compression of brain stem, cerebellum, and aqueduct
What causes cholesterol granumlomas?
Unknown
What do cholesterol granulomas do?
Obstruct the interventricular foramina causing hydrocephalus
Why does Chiari malformation cause an acquired hydrocephalus?
Chiari malformation is developmental, but the hydrocephalus is acquired
What does Chiari-like malformation do?
Acquired hydrocephalus secondary to obstruction
Crowding and coning of the cerebellum
Syringomyelia
Describe hydrocephalus due to FIP
Due to a combination of compensatory change and acquired change due to partial occlusion of the ventricular system
What is hydranencephaly?
In utero loss of brain tissue with cavitation and replacement by fluid
What is the spectrum of hydranencephaly?
Complete loss of cerebral hemispheres to large cystic cavities
What usually causes hydranencephaly?
In utero neuroteratogenic viral infections
What are some viruses that can cause hydranencephaly?
Bluetongue, Akabane, Schmallenberg, Cache Valley, felin panleukvirus, and Zika virus.
What can cause cerebellar hypoplasia?
FPV, BVDV
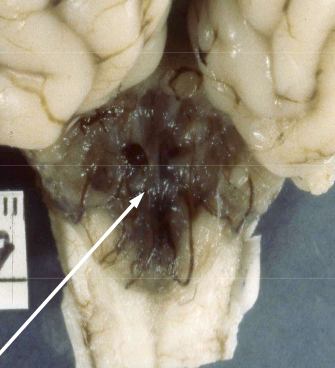
Cerebellar hypoplasia
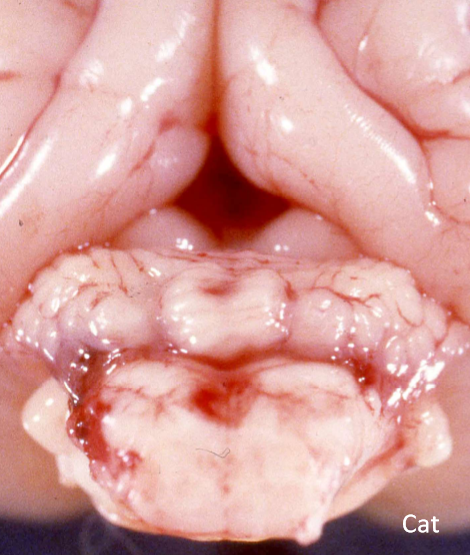
Cerebellar hypoplasia
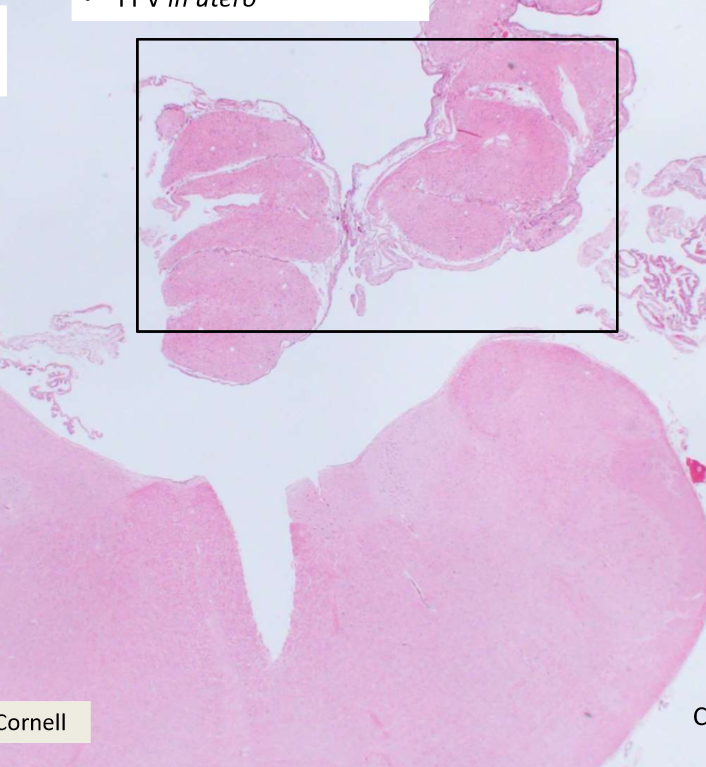
Cerebellar hypoplasia
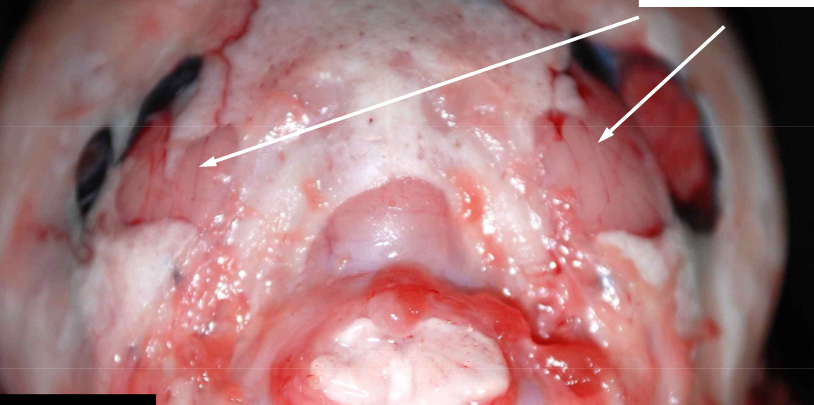
Occipital dysplasia
What is occipital dysplasia?
An abnormal finding where the occipital bone is thin, clinically inapparent
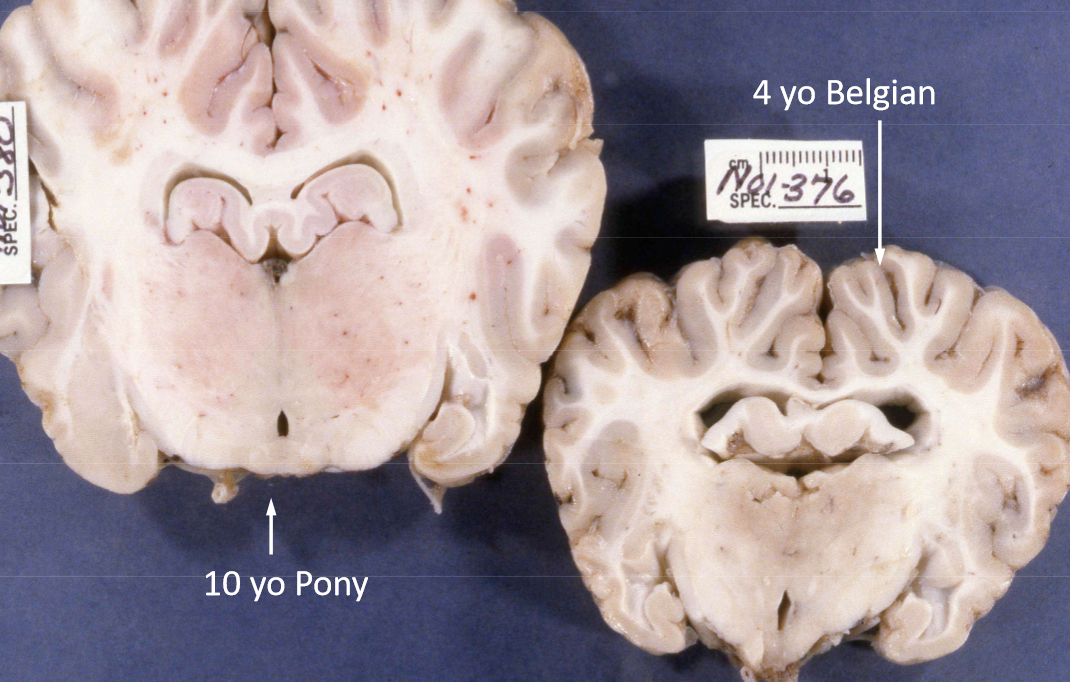
What is lissencephaly?
Smooth brain
What are the clinical signs of lissencephaly?
Typically young dogs that have seizures. Also, training difficulty, behavior problems, no menace response
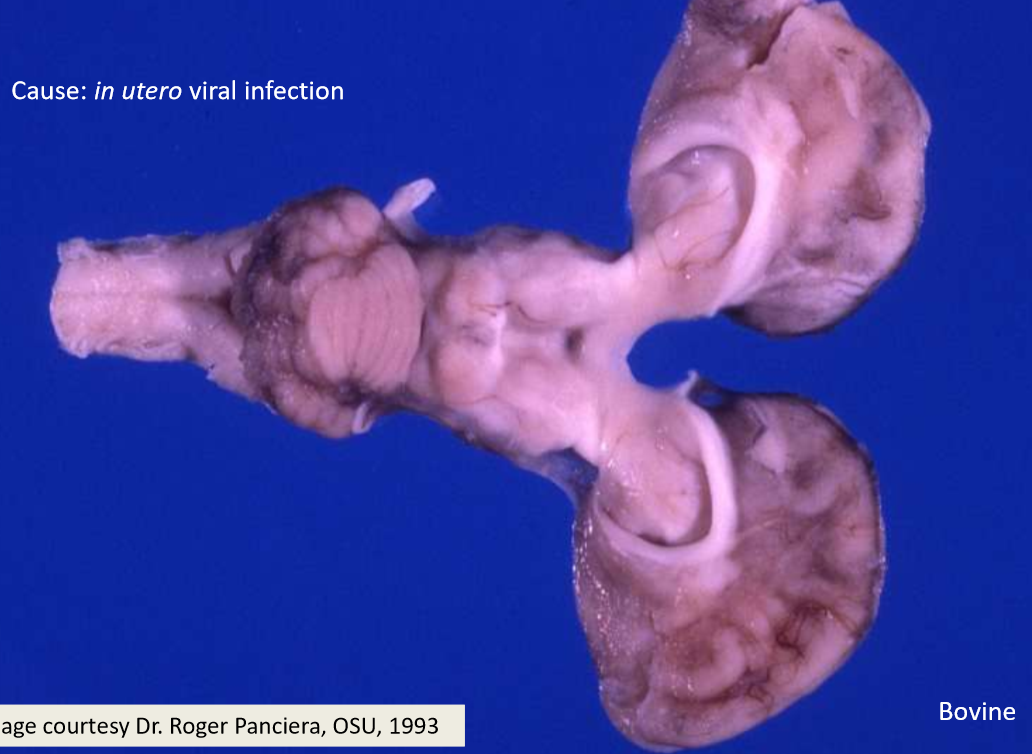
Microencephaly
Microencephaly
What is cranium bifida?
Defect in the boney encasement of the skull
What is spina bifida?
Defect in the bony encasement of the spinal cord
What are meningoencephaloceles?
Meningoceles plus gray/white matter remnants
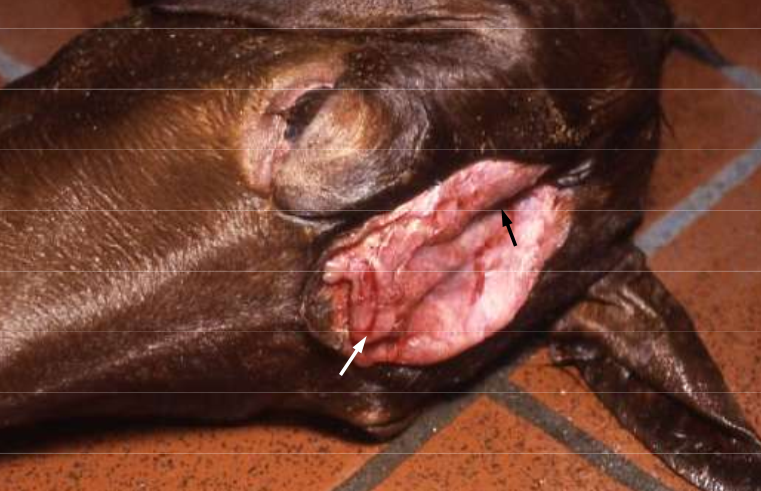
Black: Cranium bifidum
White: Meningocephalocele
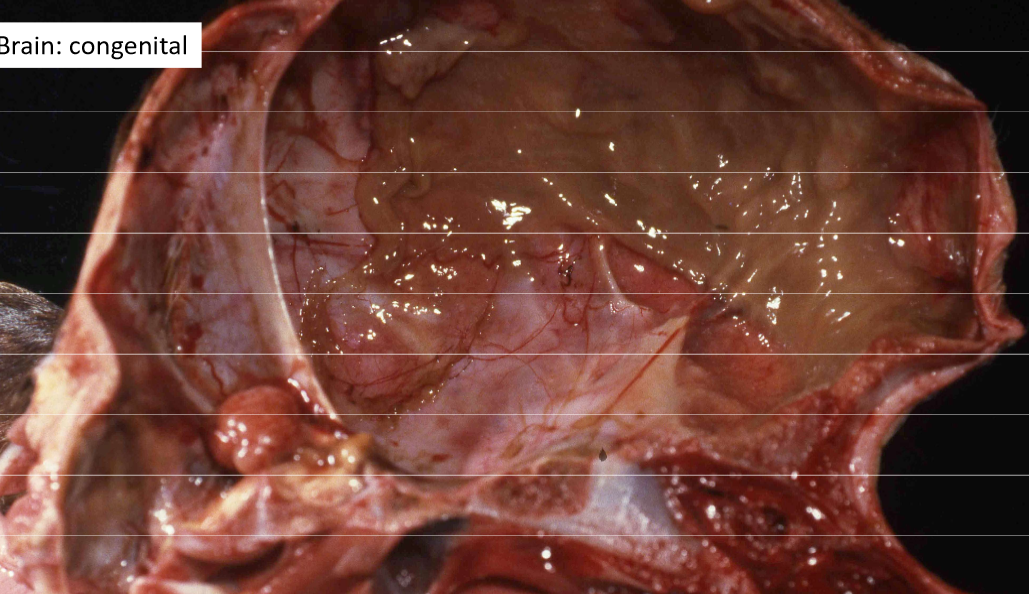
Cranium bifidum
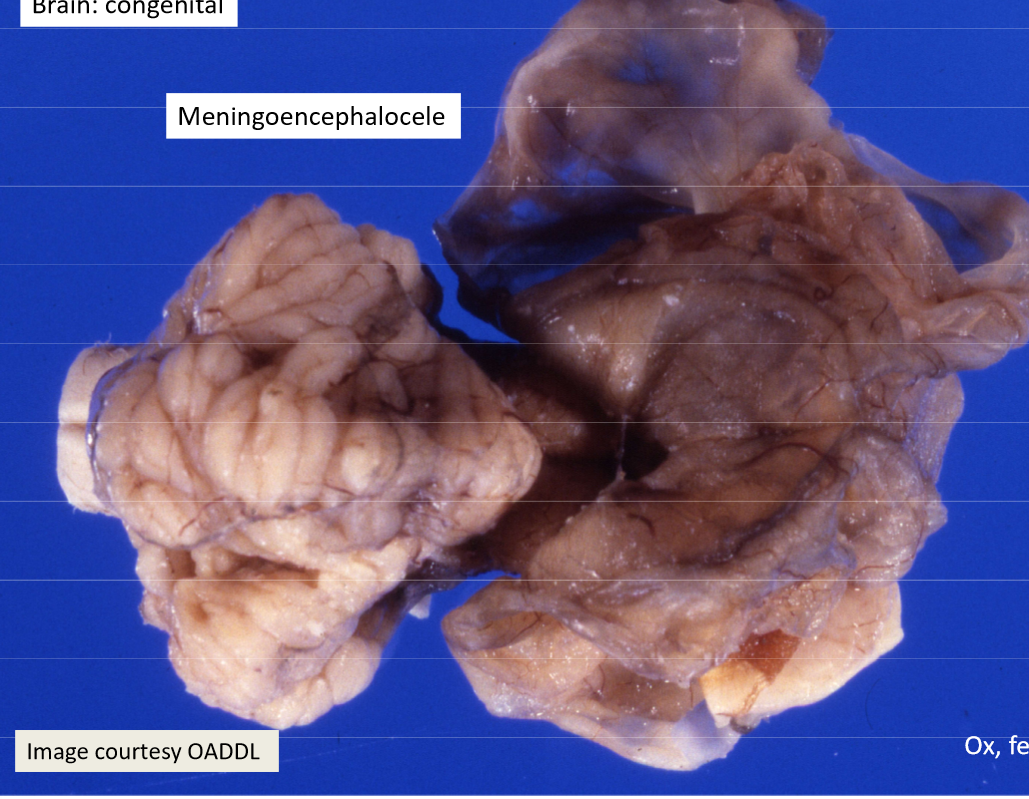
Meningoencephalocele
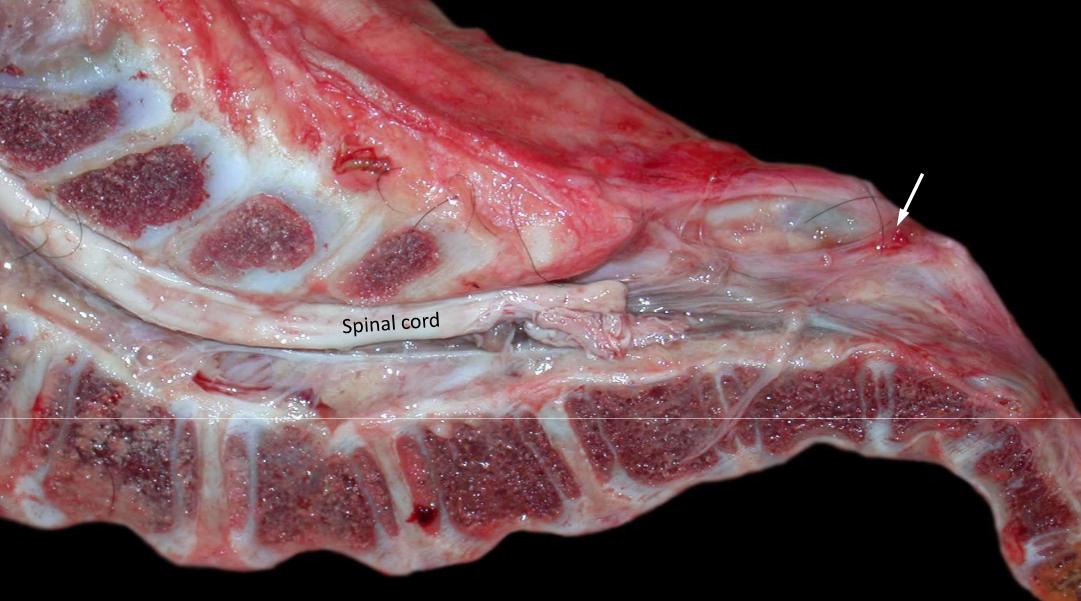
Spina bifida
What can cause congenital tremors in piglets?
Atypical porcine pestivirus caused by decreased absence of myelination of nerves. Shake constantly while awake and still while asleep
What can cause hairy shaker lamb?
In utero border disease virus infection that causes decreased or absence of myelination of nerves
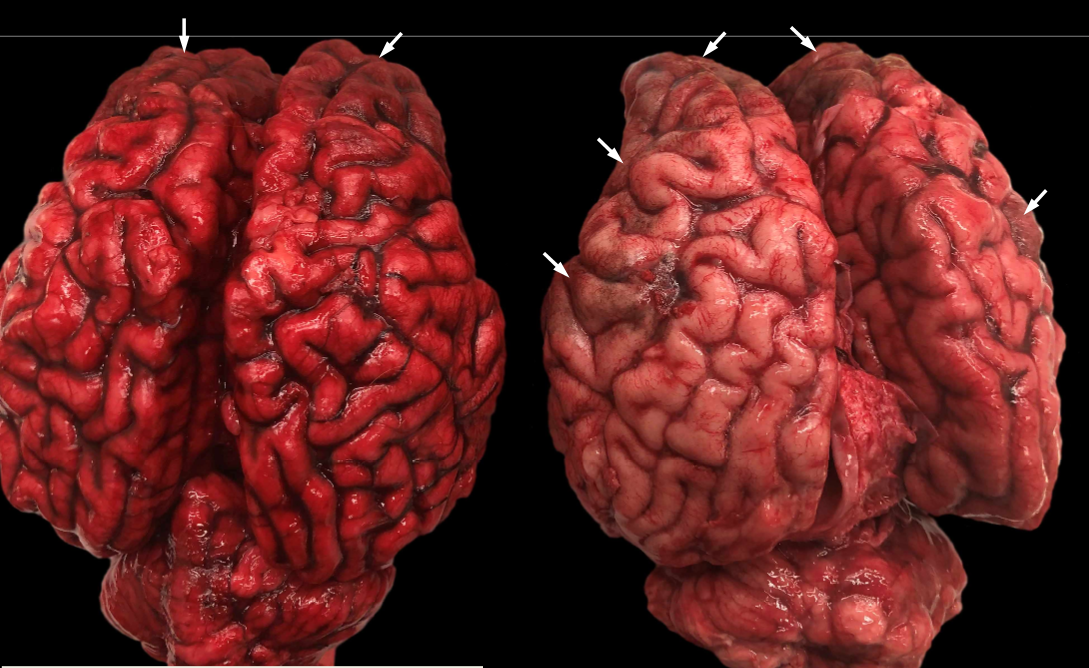
Meningeal melanosis
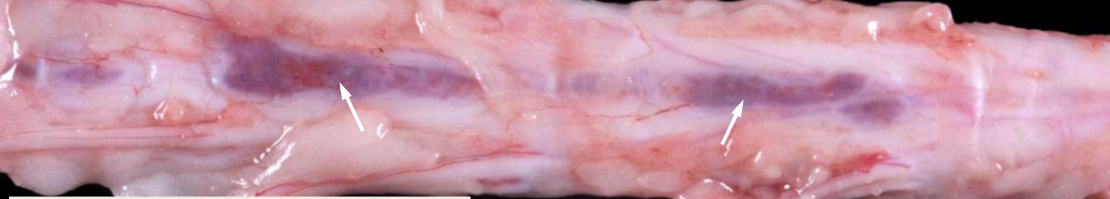
Spinal dura osseous metaplasia
What is spinal dura osseous metaplasia?
A senescent change of the meninges that is uncommon
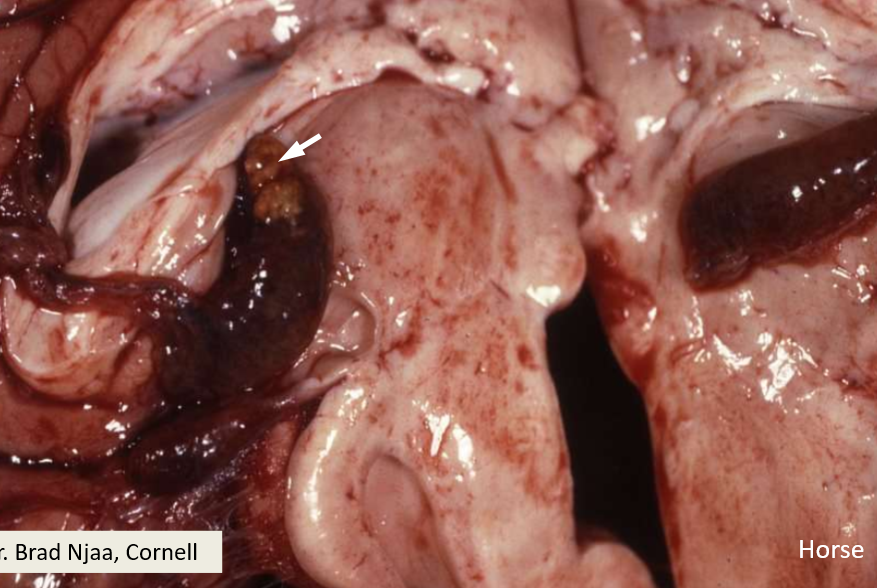
Cholesterol granuloma
T/F cholesterol granulomas are also called cholesteatomas?
False
What is a cholesterol granuloma?
A common finding in the choroid plexus of the lateral ventricle in horses. Incidental finding
What are cholesterol clefts?
Clear clefts of spaces seen on histology of cholesterol granulomas
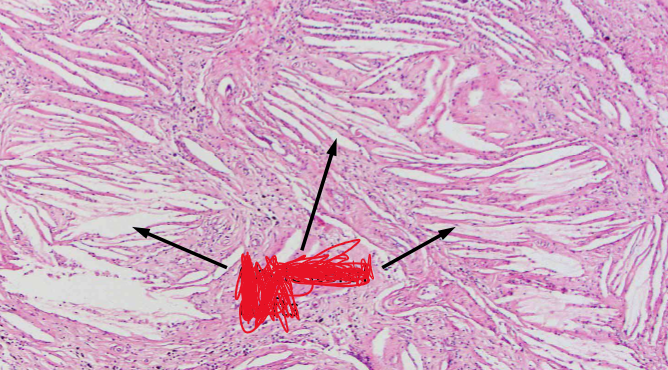
Cholesterol clefts in a cholesterol granuloma