Biology: 3A - Sexual and Asexual reproduction (PLANT)
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
What happens during Asexual reproduction?
Usually cells in one part of the body divide by mitosis and then break off from the parent to form a new organism.
All the offspring are genetically identical
What happens during sexual reproduction?
sex cells called gametes are produced.
There are two types: a male gamete and a female.
The male gamete must move to the female gamete and fuse with it.
This is called fertilisation.
The new cell formed is called a zygote
Can you give examples of organisms that perform asexual reproduction?
Fungi - Yeast
Bacteria - E-coli
Animal- Hydra
Plant - Strawberry
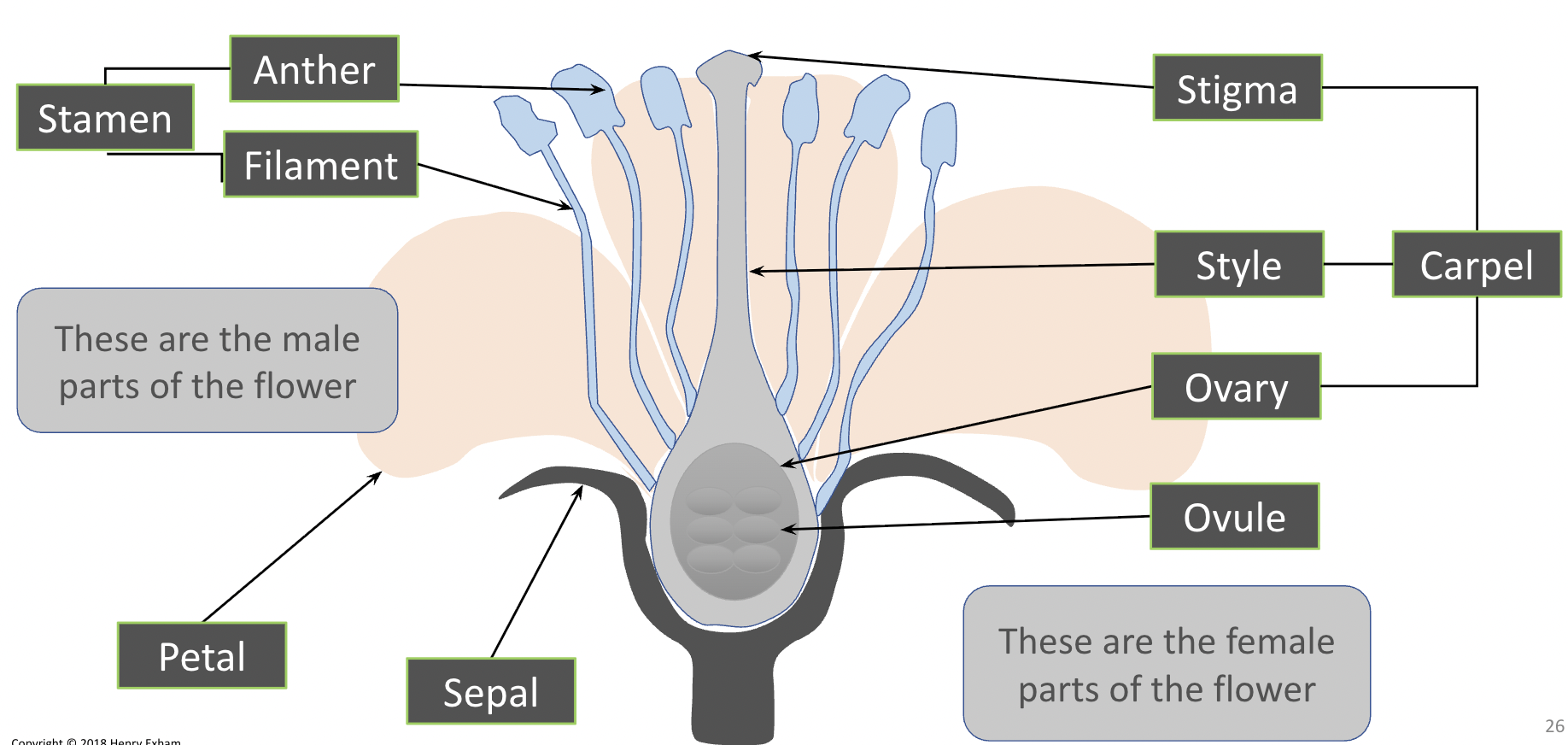
Name all the parts of a plant.
Female:
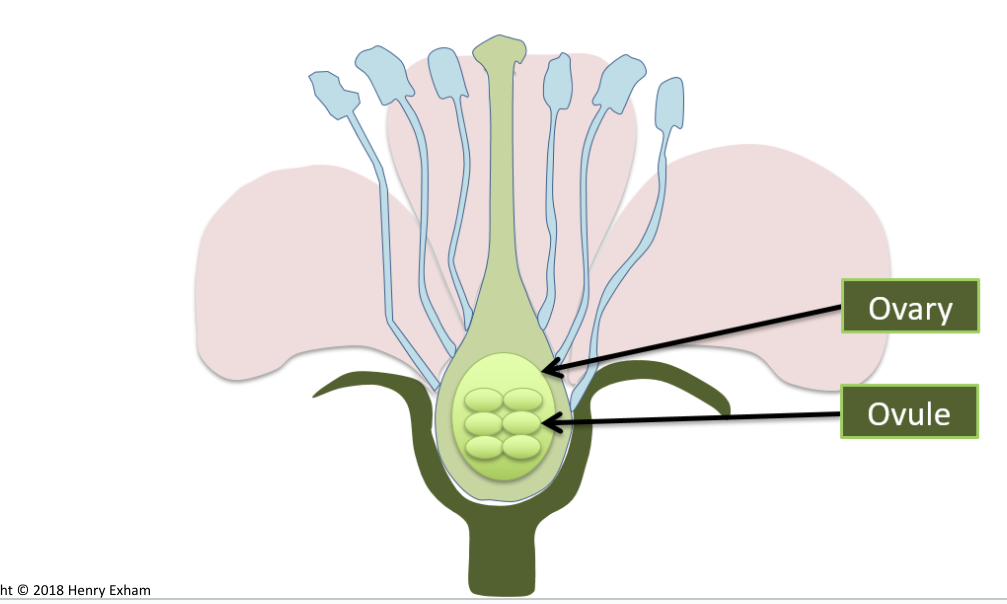
Carpel: stigma style and ovary
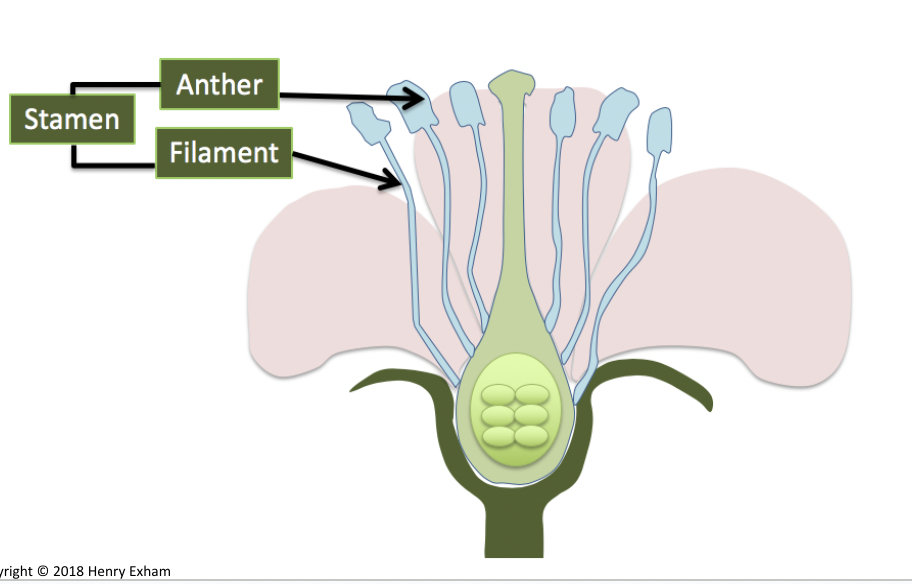
Male
Stamen: Anther and filament.
- Petal
- Sepal
- Stem
- Receptacle
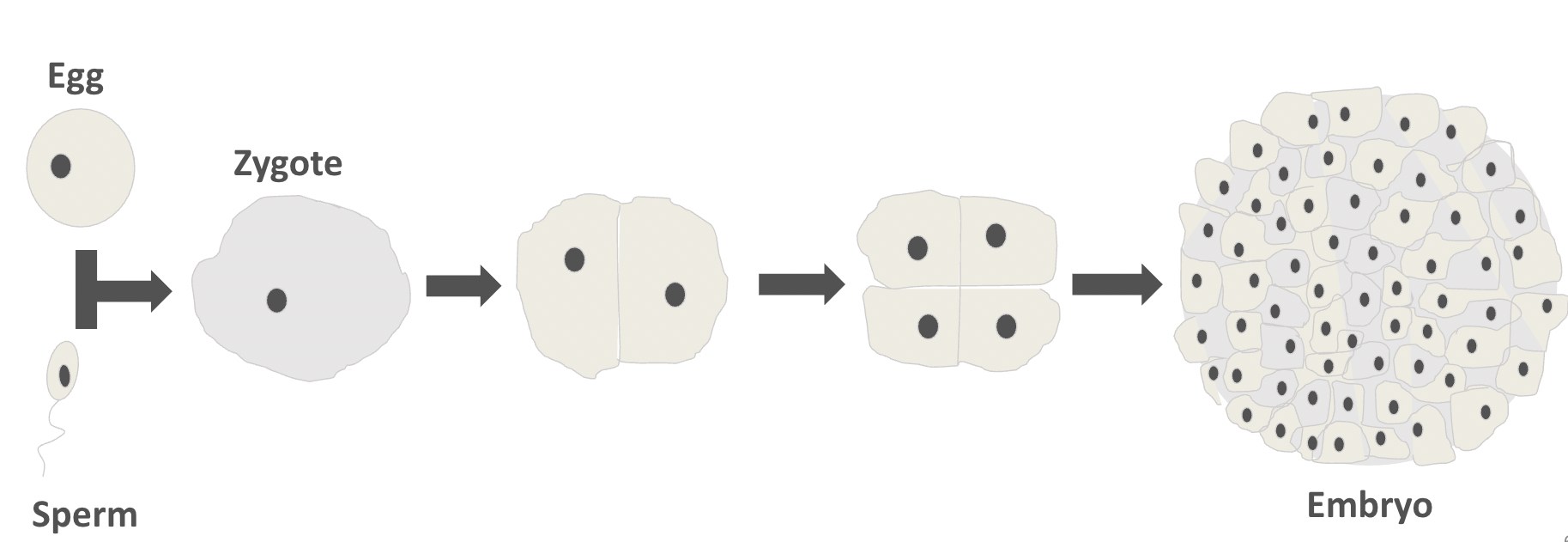
What process is carried out on zygote cell?
this new zygote cell it divides many times by mitosis to form the new organism.
Where are gamete produced for humans and the process carried out to the cells in the organs?
In humans the male gametes, sperm, are produced in the testes.
In the female the ova are produced in the ovaries.
The cells inside these organs divide by meiosis.
Meiosis produces cells that are not genetically identical.
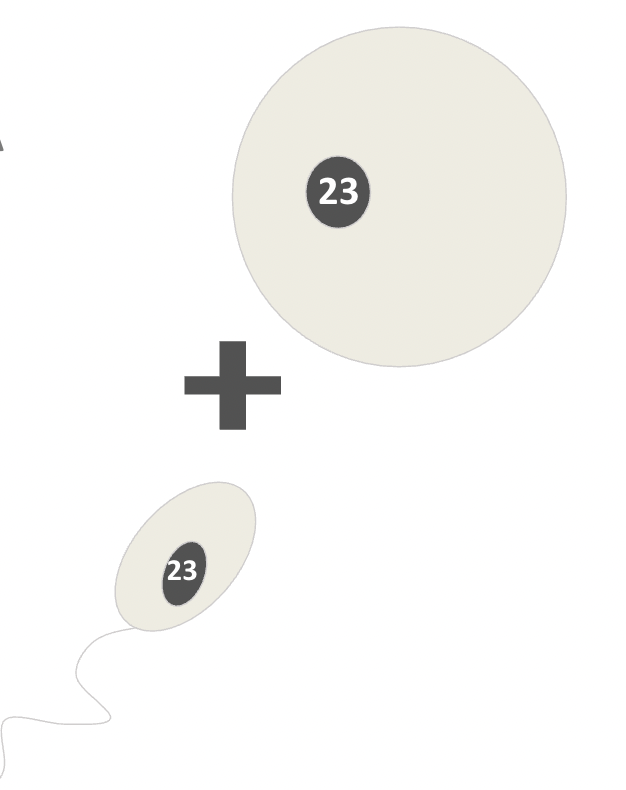
What are gametes?
Gametes are what we call haploid cells.
This means they have half the amount of DNA (23 chromosomes) of a normal cell.
This is because they are going to fuse with another gamete to form the zygote which needs the full amount of DNA (46 chromosomes).
What is a natural method that plants reproduce asexual by?
Some plants produce runners, which come off from the main plant, grow roots and become their own plant.
What is an artificial method that plants reproduce asexual by?
By taking cuttings.
What is the order that plants follow during sexual reproduction
Gamete formation → Pollination → Fertilisation → Seed and fruit formation → Seed dispersal → Germination
During gamete formation, which male and female sex cells are produced in plants?
Male sex cells are pollen grains.
Female sex cells are ova/ovule.
How is pollination carried out?
Through wind or insects.
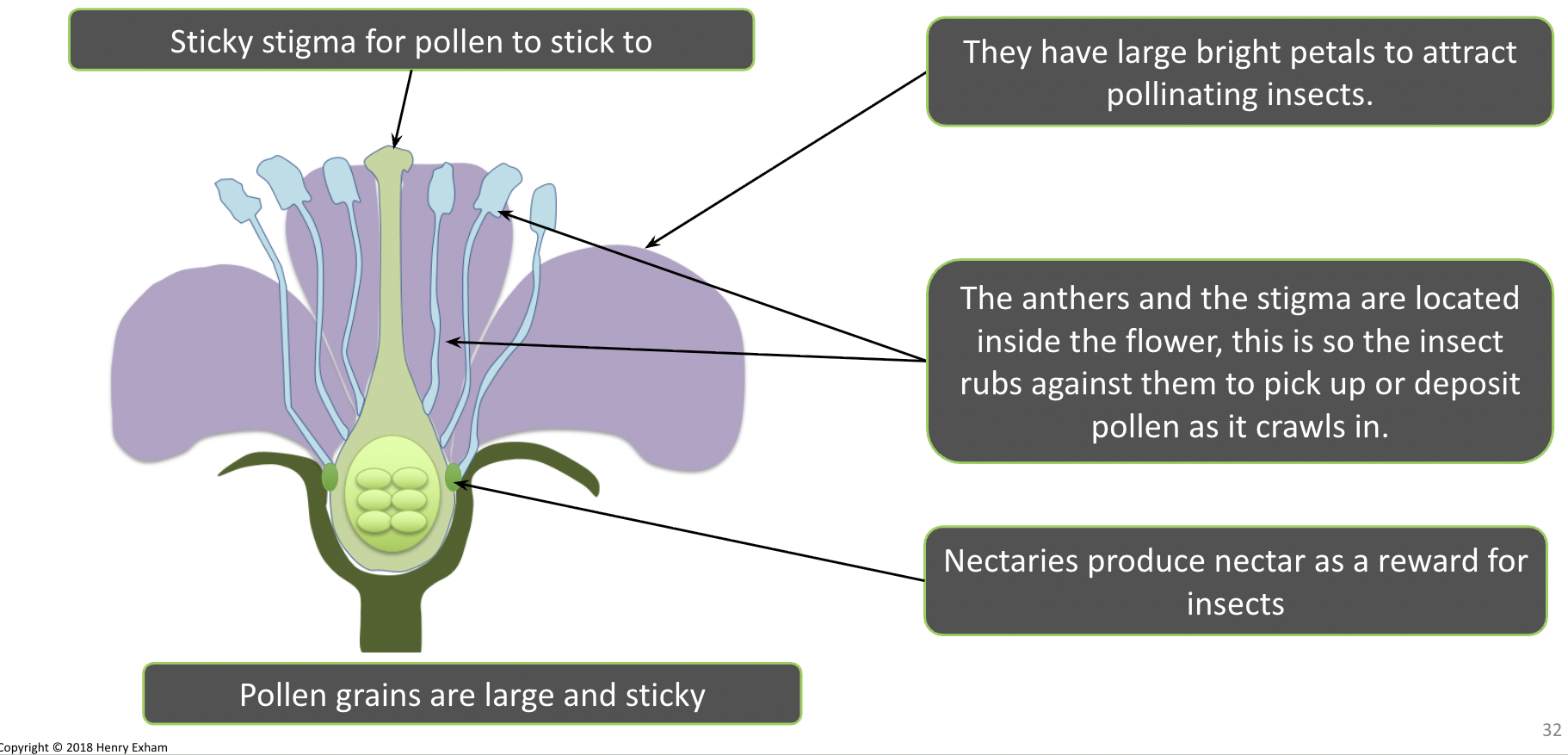
How have insect pollinated plants adapted based on the method of pollination?
They have large, bright petals to attract pollinating insects.
Sticky stigma for pollen to stick to
he anthers and the stigma are located inside the flower; this is so the insect rubs against them to pick up or deposit pollen as it crawls in.
Nectaries produce nectar as a reward for insects
Pollen grains are large and sticky
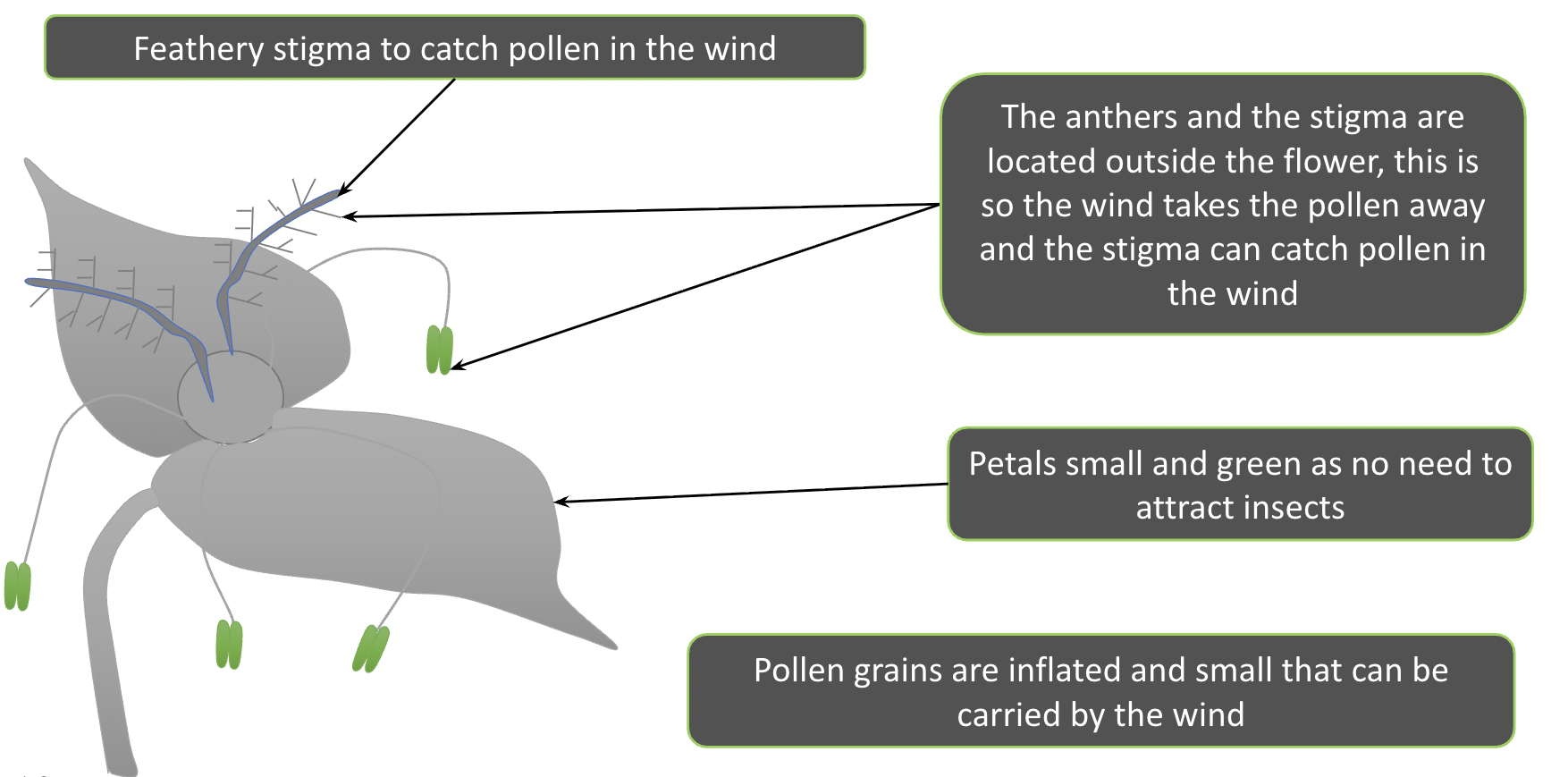
How have wind pollinated plants adapted based on the method of pollination?
Feathery stigma to catch pollen in the wind
The anthers and the stigma are located outside the flower, this is so the wind takes the pollen away and the stigma can catch pollen in the wind
Petals small and green as no need to attract insects
Pollen grains are inflated and small that can be carried by the wind
Where is pollen produced?
in the anthers of the stamens.
Where is ova produces?
In the ovules inside the ovaries
What is self pollination?
When pollen grains are transferred into the same flower.
Where are pollen grains transferred to?
from the anthers to the stigma.
What is cross pollination?
if the pollen grains are transferred to a different flower
What is fertilisation for plants?
The fusion of the nucleus of the pollen grain with the nucleus of the ovum
What does the pollen grain have to do to transfer the nucleus and what does it do?
grow a pollen growth tube, which digests it’s way through the tissue of the style and into the ovary.
What happens in seed and fruit formation?
fertilised ovule becomes a seed and the ovary in which it is found becomes a fruit
What happens to the ovule wall in seed and fruit formation and its function?
It becomes the seed coat (Testa), which is a hard protective outer layer composed of tough, waterproof material. Function is to safeguard the contents.
What is the cotyledon inside the seed and its function?
nutrient-rich storage tissue that contains essential starch reserves for development of the plant. Supplies initial nutrition for embryo and energy during early stages of germination before the plant can photosynthesise.
What is the plumule inside the seed and its function?
The embryonic shoot that contains future leaves and stem tissues. This structure deploys into the plant’s first shoot system.
What is the radical inside the seed and its function?
Located at the bottom of the seed embryo is the root, and it is the first part of the plant to emerge during germination. Establishes the initial root system and begins the process of absorbing water and initial nutrients.
What is the micropyle inside the seed and its function?
A small pore located near seed’s hilum (attachment point), allows the pollen tube to enter the ovule, facilitating fertilization. During germination, serves as important entry point for water absorption → triggers germination.
How can seeds be dispersed?
Animals: The seed has hooks that catch onto animals’ fur and are transported by the animal until they fall off.
Eaten by animals: The seeds pass through the animal and are deposited in the droppings elsewhere.
Pods: explosive to fire the seeds away from the parent.
How can seeds be dispersed (Wind related)?
“parachute” method.
Some seeds have wings to help them fly in the wind.
The poppy uses the “pepper pot” method to shake the seeds out when the wind blows.
When are seeds dispersed?
In its dormant state.
What are the 3 essential factors required for germination?
Water, Oxygen and warmth.
What does water do in germination?
When water is absorbed, it causes seed to swell, breaking the seed coat. Activates essential enzymes that start metabolic process.
What does oxygen do in germination?
vital for cellular respiration. Provides energy required for metabolic activities, supporting cell division and growth processes. Oxygen enables the mitochondria to produce energy for the embryo to develop.
Why is warmth important in germination?
Influences enzyme activity and metabolic rates and also boosts the chemical reactions necessary for germination.
What is tube A being tested for when it is filled with a dry cotton wool and cress seeds?
Water is not available, meaning it is being tested.
What is tube B being tested for when it is filled with a moist cotton wool and cress seeds?
Warm/suitable temperature is being tested.
What is tube C being tested for when it has its seeds covered in water with a layer of oil on top?
No access to oxygen, which is what is being tested.
What is tube D being tested for when it is filled with a moist cotton wool and cress seeds, but placed in a fridge?
It is being tested on temperature as it is too cold.