International Human Resources Management Challenges
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What is PEST Analysis in the context of International Human Resources Management?
is an audit of a company's environmental influences, focusing on political, economic, socio-cultural, and technological factors to determine strategy and HR response.
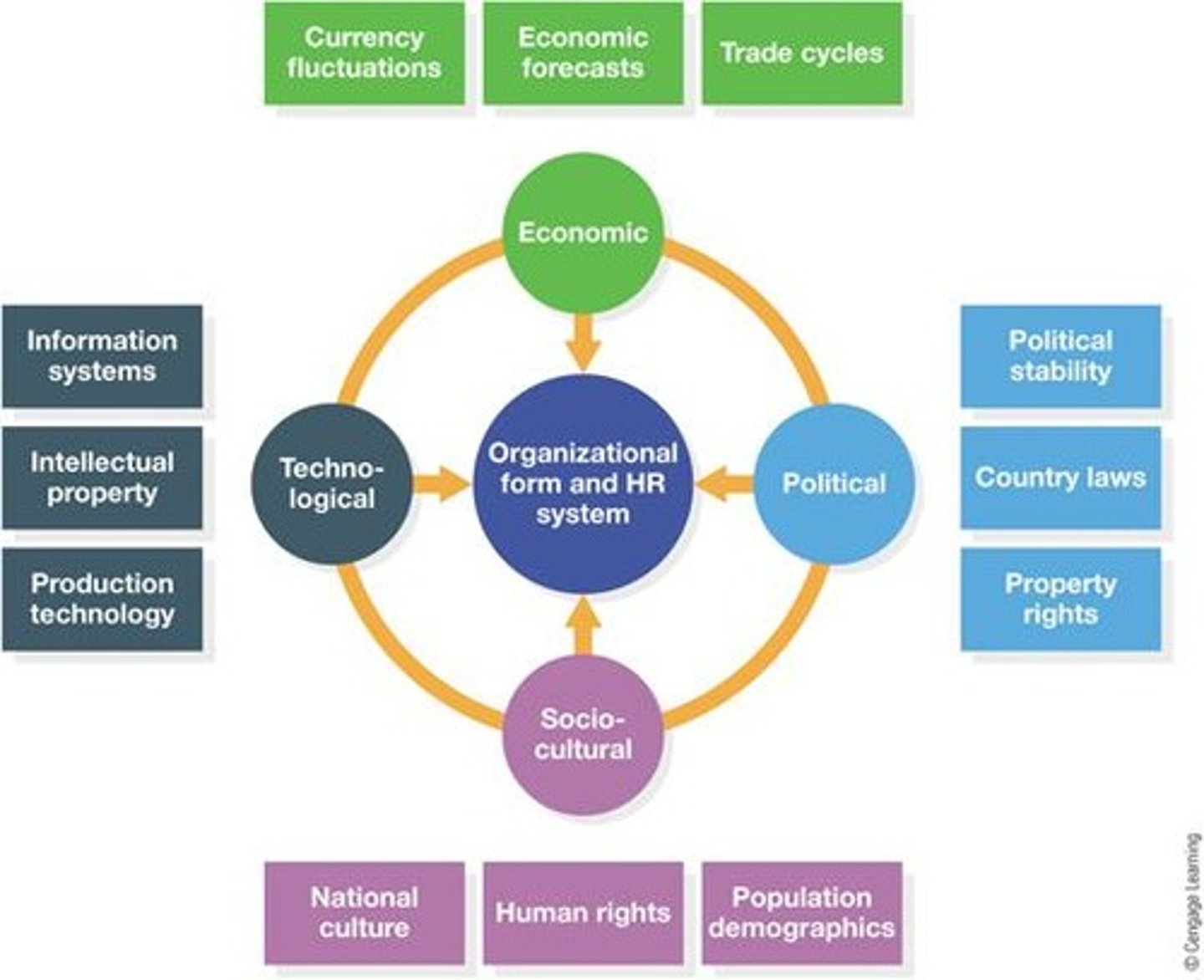
What are the advantages of conducting a PEST Analysis?
spotting business or personnel opportunities, identifying trends in the business environment, avoiding ineffective HR practices in certain countries, and fostering innovative management ideas.
Types of Organizations:
1) Global: views the world as a single market; operations are controlled centrally from corporate office
2) Transnational: Specialized facilities permit local responsiveness; complex coordination mechanisms provide global integration.
3) International: Uses existing capabilities to expand into foreign markets.
4) Multinational: Several subsidiaries operating as stand-alone business units in multiple countries.
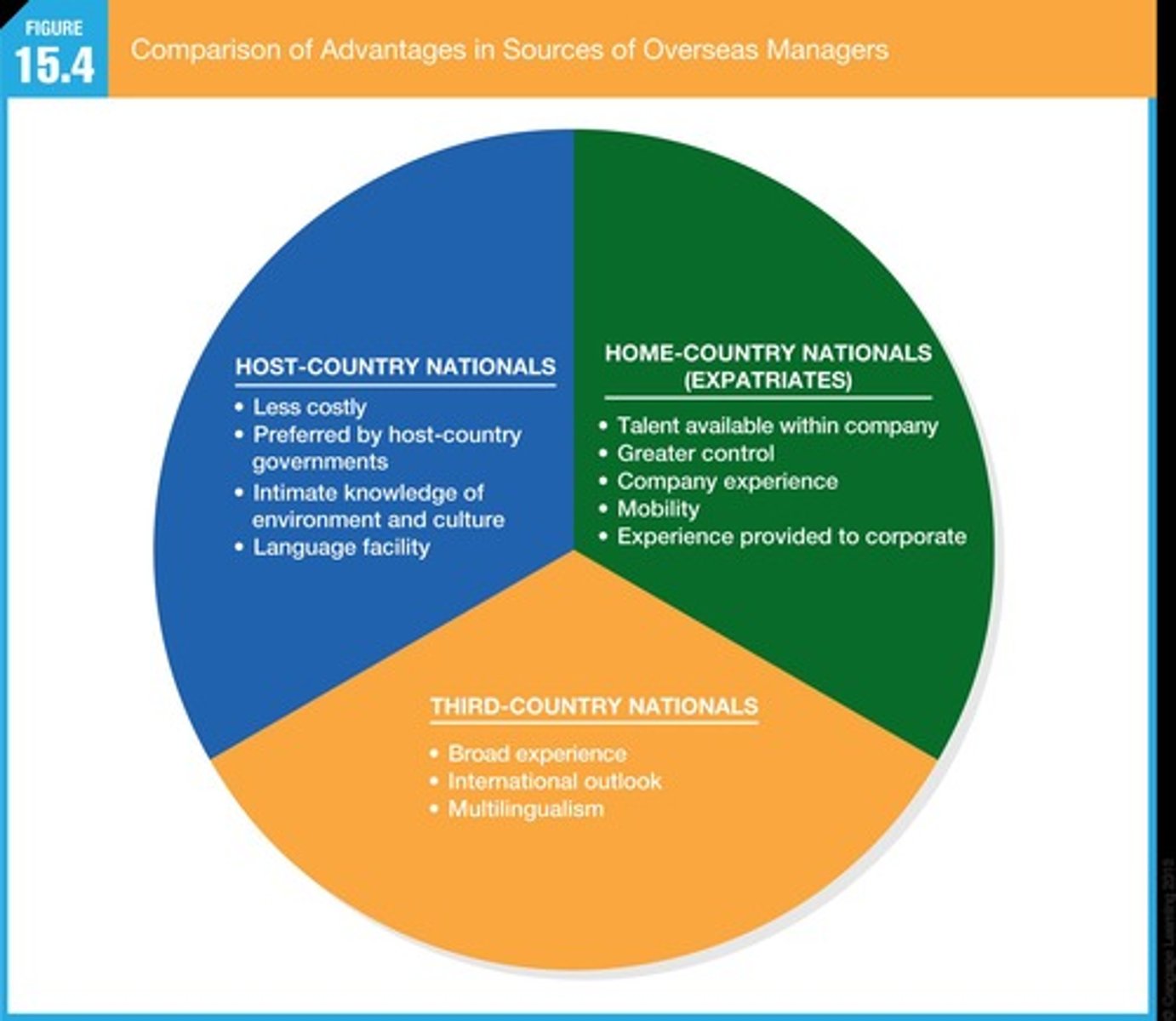
What are the three types of employees in international staffing?
1. Parent/Home-country Nationals: Employees from the home country on international assignment.
2. Host-country Nationals: Employees who are natives of the host country.
3. Third-country Nationals: Employees who are natives of a country other than the home or host country.
What is the Ethnocentric Staffing Model?
prioritizes home-based perspectives, primarily using parent-country nationals for higher-level foreign positions.
What are the HR focuses in the Ethnocentric Staffing Model?
selection, training for foreign assignments, compensation packages, and addressing adjustment issues on departure and return.
What characterizes the Polycentric Staffing Model?
emphasizes local responsiveness, predominantly employing host-country nationals throughout the organization.
What are the HR focuses in the Polycentric Staffing Model?
selection, training, coordination, and legal compliance.
What is the Geocentric Staffing Model?
treats parent-country nationals, host-country nationals, and third-country nationals equally, aiming to hire the best available person for each position.
What are the HR focuses in the Geocentric Staffing Model?
expansion, coordination, redevelopment of HR practices for each international location, and legal compliance.
What are some local recruiting and selection issues in international HRM?
assessing HR needs, understanding primary sources of labor, labor force skills, training requirements, and being aware of hiring regulations and norms in the host country.
Why is cultural awareness important for international business managers?
crucial for understanding cultural nuances and the impact of cultural differences and similarities among workers from diverse backgrounds.
What skills are critical for selecting home-country nationals for international assignments?
experience, decision-making, adaptability, team-building, resourcefulness, cultural sensitivity, and maturity.
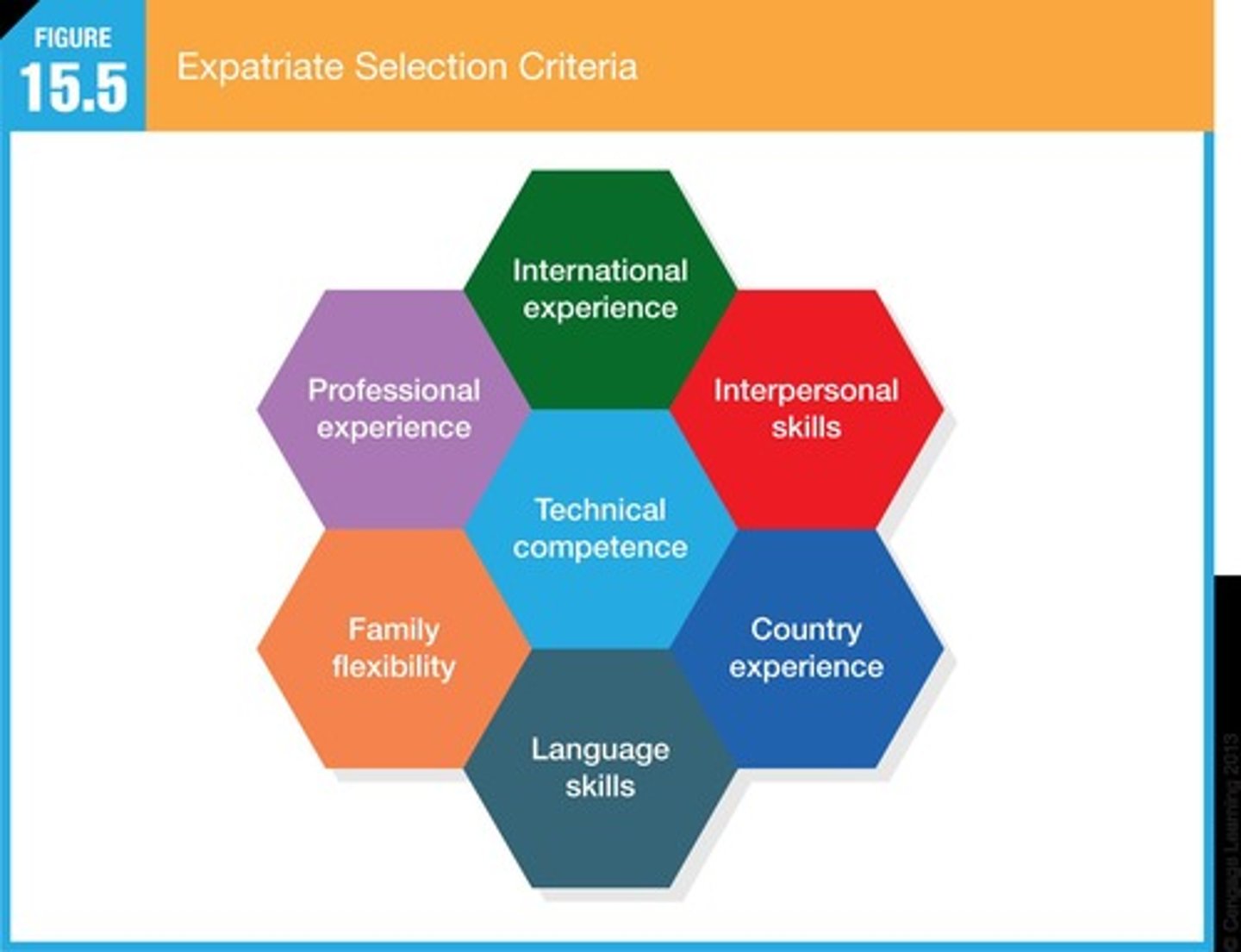
What factors should be considered when selecting expatriate managers?
job knowledge, relational skills, flexibility/adaptability, extra-cultural openness, motivation, and family situation.
What are essential training program contents for employees working internationally?
language training, cultural training, career development tracking, managing personal and family life, and addressing culture shock.
What are the developmental advantages of an international assignment?
increased responsibilities and influence, unique experiences beneficial to the individual and firm, enhanced understanding of the global marketplace, and opportunities to work on significant projects.
What are the general considerations for employee compensation in different countries?
financial versus non-financial incentives, individual rewards versus collectivist concerns, and the need for flexibility to customize policies for local needs.
What is the Balance-Sheet Approach to expatriate compensation?
matches an expatriate's purchasing power to their home country, calculating base pay, cost-of-living allowances, and additional incentives.
What are the challenges associated with expatriate repatriation?
high turnover rate (40% to 60% quitting within 3 years) and ensuring expatriates and their families feel supported upon return.

What solutions can be implemented to aid expatriate repatriation?
matching expatriates with trained psychologists, keeping them informed about home office developments, and providing formal repatriation services.
What are the performance appraisal considerations for expatriates?
who should appraise performance, differences between home and host-country evaluations, and the need for clear performance criteria.
What is the significance of communication in global HR practices?
essential for integrating global tools into local systems, creating a strong corporate culture, and ensuring local people are treated as equal partners.
What should global HR practices avoid?
trying to implement everything the same way everywhere, yielding to every claim of uniqueness without proof, and ignoring cultural differences.
What is the role of technology in designing HR systems?
should not drive system design; it's important to consider varying levels of technology investment and access across locations.
What is the importance of training local people in global HR practices?
crucial for making informed decisions about which tools to use and how to implement them effectively.
What is the purpose of the 360-degree evaluation in performance appraisal?
aims to gather comprehensive feedback from various sources to assess expatriate performance more holistically.
What are some common cultural training methods for expatriates?
reviewing information about the host country, conversations with natives, sensitivity training, and temporary assignments for shared learning.
What is the significance of flexibility in global HR practices?
allows for local adaptations beyond core elements, enabling organizations to respond to specific cultural and operational needs.