Developmental Psychology
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Nature
genetics influence the person you become
nurture
life experiences influence the type of person you become
behavioral genetics
the study of how genetic factors influence behaviors, traits, and psychological characteristics
50%
genetic factors account for approximately what percentage of the risk of alcohol dependence
40%
genetic heritability accounts for approximately what percentage of the risk of antisocial and criminal behavior
60%
genetic factors account for approximately what percentage of the variance in IQ
40%
genetic factors account for approximately what percentage of the variance in income
60%
genetic factors account for approximately what percentage of the variance in gpa and college plans
40%
genetic factors account for approximately what percentage of the variance in risk of infidelity and in lifetime number of sexual partners
30%
genetic factors account for approximately what percentage of political attitudes
40%
genetic factors account for approximately what percentage of the variance in how much tv you watch
determinism
philosophical view that all events in the universe, including human decisions and actions, are causally inevitable.
deterministic thinking.
the downside of the behavioral genetics findings
when people are primed to disbelieve in free will they behave dishonestly, support harsher punishment from crimes, engage in less prosocial behavior, exhibit lower empathy toward others, and more racial prejudice toward marginalized groups
why is deterministic thinking a problem?
Even when group averages show a statistically significant difference for a trait, it provides very little ability to predict differences between two individuals.
what is the purpose and logic of this figure?
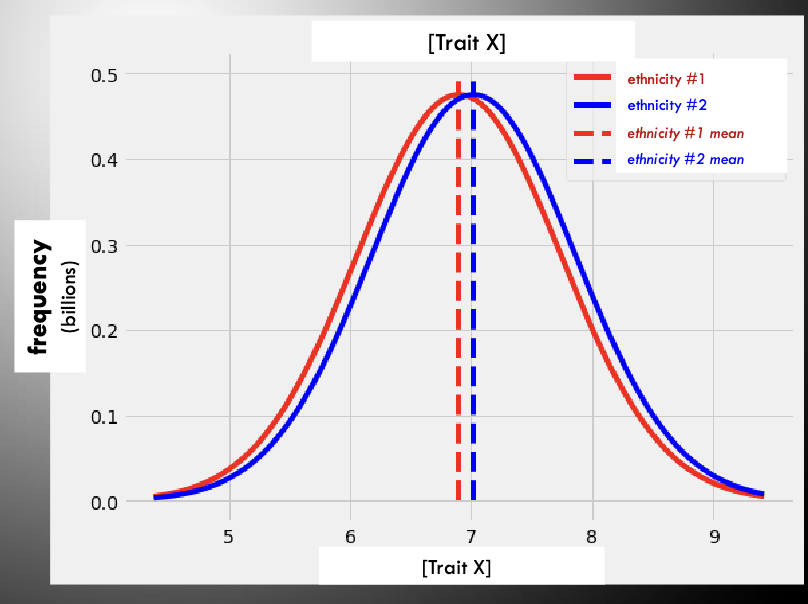
between groups variability is always miniscule in comparison to within-groups variability.
why is there virtually zero value in prejudiced thinking
Piaget’s stages of cognitive development
jean piaget proposed that cognition develops through distinct stages, each characterized by new ways of interacting with the world
sensorimotor stage
birth → around 2 years
infants primarily learn through sensory-motor experiences and develop object permanence (objects continue to exist when out of sight)
preoperational stage
2-7 years
development of symbolic thought. learn to use language and images to represent objects and animism (attributing life to inanimate objects). experience egocentrism followed by the development of theory of mind. also experience difficulty understanding the brules of conservation which is often due to centration (overly focusing on one dimension).
theory of mind
the ability to have a theory about what’s going on in the mind of others
concrete operational stage
7-11 years
emergence of logical thinking about concrete objects and events and mastery of conservation tasks.
formal operational stage
11 + years
ability to think abstractly and reason hypothetically, development of deductive reasoning and systematic problem solving, and capacity fro cognitively grappling with abstract concepts such as justice, love, or hypothetical scenarios.
major criticisms of piaget’s stages of cognitive development
development is messy and different for every kid. deliberate guidance can speed up development of targeted abilities.
erikson’s psychological stages of development
erik erikson proposed that personality develops through eight sequential stages, in each stage, a central conflict or crisis must be resolved, and
the outcome influences future development.futment
trust vs mistrust
infancy, 0-1 year
Core Conflict: The infant develops trust when caregivers provide consistent care and affection. If caregivers are unreliable or neglectful, the child may develop mistrust.
autonomy vs shame and doubt
1-3 years
Core Conflict: As toddlers begin to explore, they strive for independence. Successful experiences foster autonomy, while excessive criticism or control may lead to feelings of shame and doubt about their abilities.
initiative vs guilt
3-6 years
Core Conflict: During this stage, children assert themselves through initiating activities and interacting with others. When their initiatives are met with encouragement, they develop a sense of purpose; if not, they may experience guilt over their needs and desires.
industry vs inferiority
6-12 years
Core Conflict: Children develop skills and competencies through school and social interactions. Success leads to a sense of industry, while repeated failures or a lack of recognition can result in feelings of inferiority.
identity vs role confusion
12-18 years
Core Conflict: Adolescents explore different roles and ideas to develop a clear sense of self. Success results in a strong identity; failure or confusion can lead to uncertainty about one’s place in society
intimacy and isolation
18-40 years
Core conflict: Young adults seek to form deep, committed relationships. A successful resolution leads to strong bonds with others, while failure may
result in isolation and loneliness.
generativity vs stagnation
40-60 years
Core Conflict: During middle adulthood, individuals focus on contributing to society—through parenting, mentoring, or work—thereby achieving a sense of generativity. A lack of such contributions may lead to stagnation and self-
absorption
ego integrity vs despair
65+ years
Core Conflict: In later years, individuals reflect on their life. A sense of fulfillment and integrity comes from viewing one’s life as well-lived, whereas
regret and bitterness may lead to despair.
narrative fallacy
the tendency to explain complex outcomes with simple causes
parental mental health
high conflict homes
neighborhood safety
words spoken per day from parent to child
corporal punishment
sleep quality/ noise and chaos
food insecurity
over consumption of refined sugars
air pollution/toxins
parental praise (process vs traits)
preschool attendance
family dinners
disorganization
authoritarian parenting
screen time
What are the most impactful environmental
influences on psychological and life outcomes?