Biology: Modules 1-6 (Paper 3)
1/1209
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
1210 Terms
Why are communication systems needed?
Respond to changes in internal and external environment
Coordinate activity of different organs
Give some examples of changes in environment to show the necessity of communication systems?
Buildup of carbon dioxide
Predator appearing
Seasons changing
What is cell signalling?
Chemical signal released by one cell is detected by another stimulating a change in activity
Describe how distant cells communicate in animals and their relative properties?
Neuronal system - travel large distance quickly and short acting
Endocrine hormones - slower but longer acting
How can adjacent cells communicate?
Gap junctions in animals (direct contact)
Paracrine signalling - diffusion of molecules short distances
Plasmodesmata in plants
What is the function of sensory receptors?
Monitor changes in internal or external environment
What is the function of effectors?
Bring about a response
Name some effectors in the body?
Muscle cells, glands, hepatocytes (liver cells)
Define negative feedback?
A stimulus brings the body’s environment away from normal and a response brings the body’s environment back to normal
Define positive feedback?
A stimulus brings the body’s environment away from normal and a response brings the body’s environment further away from normal
Describe the 3 key steps for feedback loops to occur?
Change is detected by receptors
Change is signalled to other cells
Effective response that reverses/increases change in conditions
Define homeostasis?
Maintaining a near constant internal environment despite changes in the external environment.
What is an example of positive feedback?
Release of oxytocin at the cervix
Depolarisation of a neurone
Define an endotherm?
Uses heat from metabolic activity to regulate core body temperature
Define an ecotherm?
Uses external sources of heat to regulate core body temperature
Describe some behavioural responses when too cold in ectotherms?
Bask in the sun - absorb warmth from sun
Face sideways on - increase SA exposed
Expand ribcage - increase surface area
Describe some behavioural responses when too hot in ectotherms?
Hide in burrows - move out of sun
Face head on to sun - decreases surface area
Climb up plants - avoid hot soil surface
What are advantages of ectotherms?
Less food used
More energy for growth/reproduction
Spend less time finding food
What are disadvantages of ecotherms?
Metabolism is lower in colder environments
Can be at risk of predators when body temperature is low
Unable to hunt for food when body temperature is low
How does thermoregulation occur?
Peripheral thermoreceptors in skin anticipate changes in temperature
Thermoreceptors in hypothalamus detect changes in blood temperature
Hypothalamus sends action potentials to skin and muscles to increase/decrease temperature
Describe some physiological responses in endotherms when too hot?
Vasodilation - more blood flow to skin so more heat lost via radiation
Hairs lay flat - more air flow over skin
Sweating - heat energy from blood used to evaporate water
Describe some physiological responses in endotherms when too cold?
Vasoconstriction - less blood flow to skin so less heat lost by radiation
Hairs stand erect - traps insulating layer of air above skin
Shivering - rapid contraction of muscles generates heat energy
Increased metabolic activity - more heat generated from respiration (exothermic reaction)
Describe some behavioural adaptations in endotherms when too hot?
Hide away from sun
Orientate body to decrease surface area facing sun
Remain inactive and spread out limbs
Wet skin to cool the body - e.g. elephants spraying water
Describe some behavioural adaptations in endotherms when too cold?
Lie in the sun
Orientate body to increase surface area facing sun
Move about to generate heat in muscles or roll into ball to reduce surface area exposed
Remain dry
What are the advantages of endotherms?
Maintain a fairly constant internal temperature
Remain active even in low temperatures to take advantage of prey
Inhabit colder habitats
What are disadvantages of endotherms?
Need more food
May overheat in hot weather
Use less energy from food for growth
Define excretion?
Removal of metabolic waste from the body
Why is excretion required?
Prevents buildup of metabolic waste
Buildup could inhibit enzyme activity or become toxic
Buildup of CO2 prevents effective transport of O2
Amino acids cannot be stored so are converted to keto acid but urea must be excreted
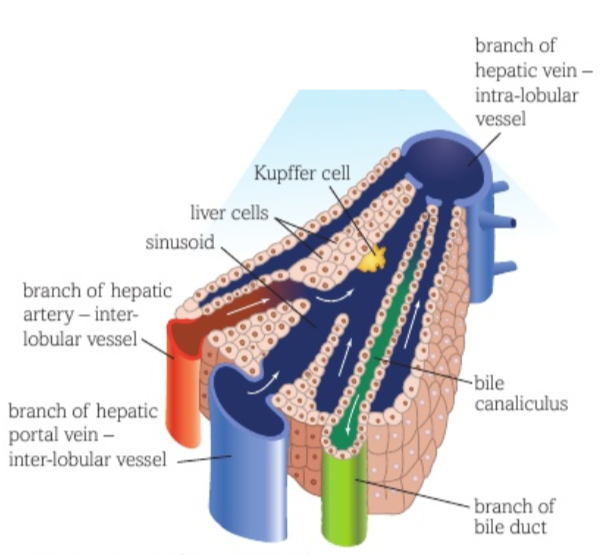
Describe the gross structure of the liver?
Hepatocytes grouped into lobules
Lobules have a central vein (branch of hepatic vein)
Interlobular vessels (portal vein and hepatic artery) run parallel to lobules
Blood from interlobular vessels travels down sinusoids
Kupffer and endothelial cells line the sinusoid
Sinusoids eventually drain into the central vein
Branches of the hepatic vein from lobules form the hepatic vein
Bile canulici run antiparallel to sinusoids and collect in a branch of the bile duct
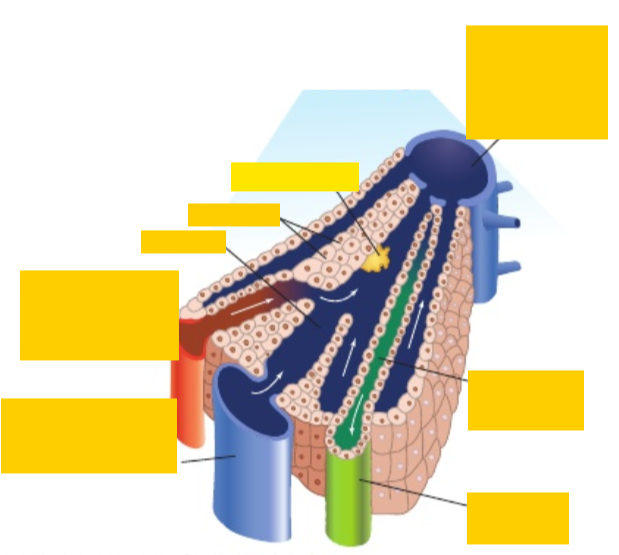
Fill in the labels clockwise from middle right?
Bile canuliculus, bile duct (branch), hepatic portal vein (branch), hepatic artery (branch), sinusoid, hepatocytes, kupffer cell, central vein
How are cells lining the sinusoid specialised?
Flattened to reduce diffusion distance
Fenestrations to allow molecules to enter
What are kupffer cells and what is their function?
Specialised macrophages
Breakdown worn out RBCs into bilirubin
How are hepatocytes specialised?
Dense cytoplasm
Many organelles for variety of functions
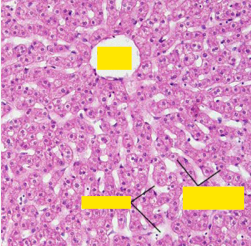
Label from top clockwise?
Central vein, hepatocytes, sinusoids
What are the roles of the liver?
Storing glycogen
Detoxification
Forming urea
Describe the role of enzymes for detoxification in the liver?
Cytochrome p450 - break down drugs
Catalase - break down hydrogen peroxide
Describe how ethanol (alcohol) is detoxified?
Oxidised to ethanal by ethanol dehydrogenase
2H removed which combine with NAD
Oxidised in the same way again to form ethanoic acid
Forms acetyl-coA to enter krebs cycle
Why does excess alcohol consumption cause fatty liver disease?
Too much NAD is used to accept hydrogen from detoxification of alcohol
Not enough NAD to respire fatty acids
Fatty acids stored as fats in hepatocytes
How are excess amino acids dealt with?
Deaminated forming a keto acid and ammonia
Keto acid can enter respiration
Ammonia reacts with CO2 in ornithine cycle to form urea
Why is ammonia converted to urea in the ornithine cycle?
Urea is less soluble and less toxic
Write an equation for the process of converting ammonia to urea?
2NH3 + CO2 → CO(NH2)2 + H2O
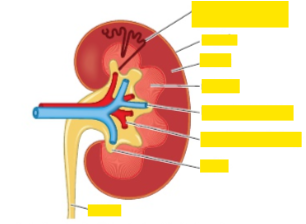
Fill in the labels top to bottom?
Nephron, capsule, cortex, medulla, renal vein (branch), renal artery (branch), renal pelvis, ureter
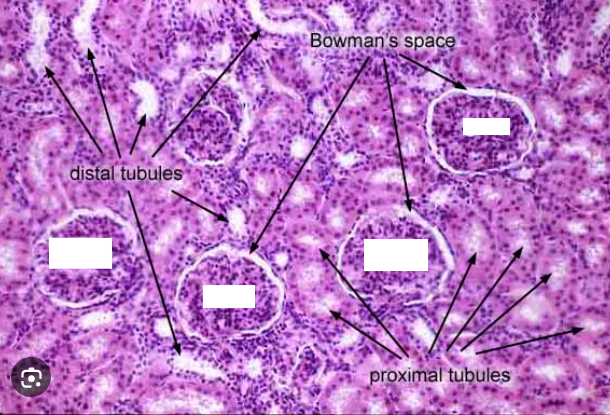
Describe the 3 main sections of the kidney?
Cortex - outer region
Medulla - inner region
Pelvis - leads to ureter
Describe the structure of a nephron?
Glomerulus, PCT, loop of henle, DCT, collecting duct
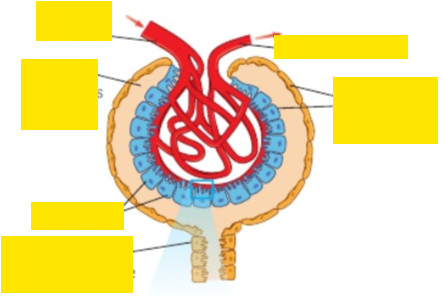
Fill in the labels clockwise from top right?
Efferent arteriole, epithelium of bowmans capsule, PCT (cells), podocytes, lumen of bowmans capsule, afferent arteriole
Explain how the structure of the bowman’s capsule is related to its function?
Efferent arteriole narrower than afferent to increase hydrostatic pressure forcing solutes out
Knot of capillaries increase surface and decrease blood flow to increase time for diffusion
Describe ultrafiltration in the bowman’s capsule?
Capillary endothelium - fenestrations allowing blood plasma and dissolved substances to leave
Basement membrane - fine mesh of collagen fibres and glycoproteins which stops anything with RFM > 69000
Podocytes - processes (projections) to hold cells away from capillary allowing fluid to pass between cells into lumen
What sections of the nephron are in the medulla?
Collecting duct and loop of henle
What is present in the glomerular filtrate (besides water)?
Glucose
Amino acids
Urea
Mineral ions
Very little protein
What is reabsorbed in the nephron?
Amino acids
Glucose
Some water
Some mineral ions
Explain the water potential of the blood after ultrafiltaration and its use?
Very low water potential
Large proteins remain in blood but lots of water has left
Useful for reabsorption of water in the PCT/collecting duct
Where does selective reabsorption take place?
PCT / proximal convoluted tubule
Describe the process of selective reabsorption?
Sodium ions actively pumped out of the cell into the blood
Sodium ions move down their concentration gradient from tubular fluid into PCT cell
They enter via facilitated diffusion - carrying either 1 glucose or amino acid with them
Known as secondary active transport
Water moves in the PCT cell via osmosis
Glucose and amino acids diffuse into blood
Water moves into blood via osmosis
How are PCT cells adapted?
Microvilli increase surface area
Cotransporter proteins in plasma membrane
Many mitochondria for active transport
Sodium/potassium pumps
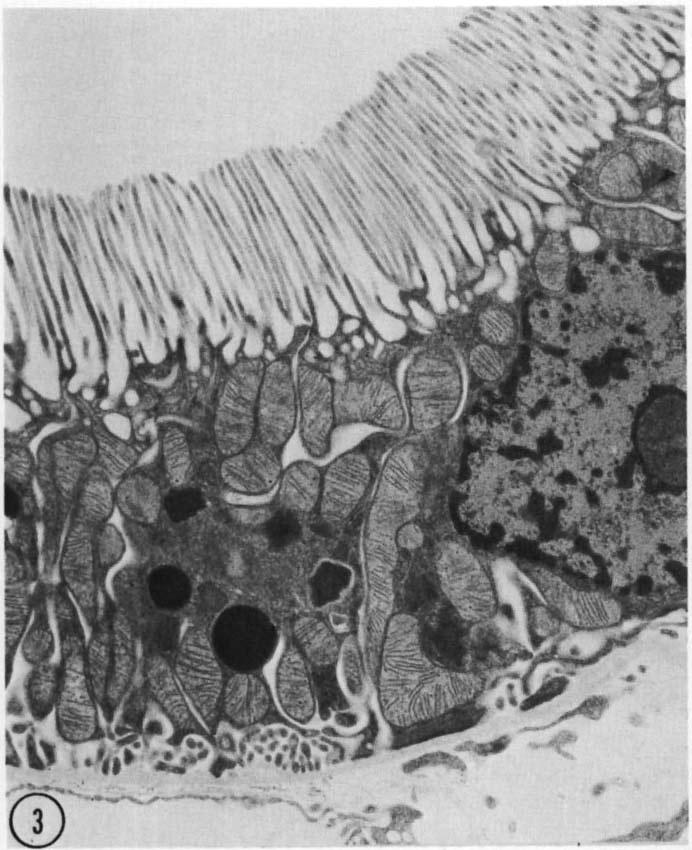
State and explain what part of the kidney this micrograph shows?
PCT wall cells
Microvilli shown
Fill in the labels from left to right. Give reasons for your choice?
DCT, PCT
PCT generally larger, have brush border and stain lighter
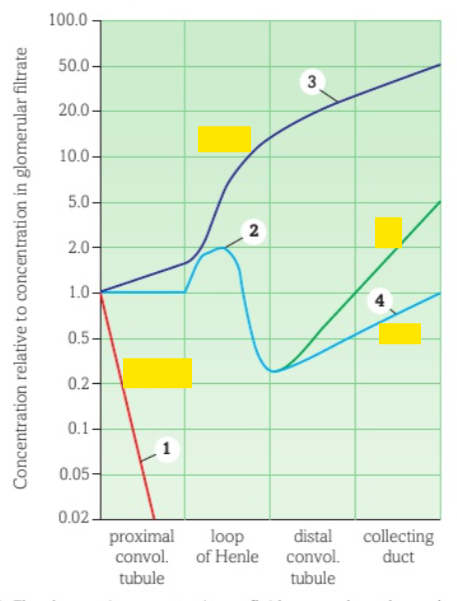
Describe how loop of henle causes increase of solute concentration?
Active transport of sodium/chloride out upper part of ascending limb
Ascending limb is impermeable to water
Diffusion of sodium/chloride into descending limb
Water leaves descending limb by osmosis
Sodium/chloride diffuse out lower part of ascending limb
Example of countercurrent multiplier
Describe the mechanism of action of ADH on the collecting duct?
ADH binds to complementary receptors on plasma membrane of cells in wall of collecting duct
Release of second messenger cAMP
Vesicles containing aquaporins fuse with plasma membrane
Increase permeability of collecting duct wall to water
More water moves down water potential gradient into cells
What effect does more ADH have?
More water reabsorption in the collecting duct
More concentrated urine produced with less volume
How is water reabsorbed in the collecting duct?
Medulla has a low water potential and tubule fluid has a high water potential
Water moves by osmosis into cells of collecting duct wall through aquaporins
Water moves by osmosis into surrounding tissue
Fill in the labels in number order?
Glucose, Na+, K+, urea
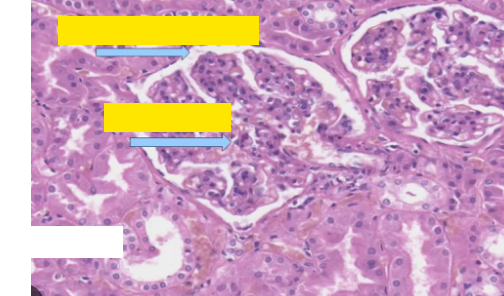
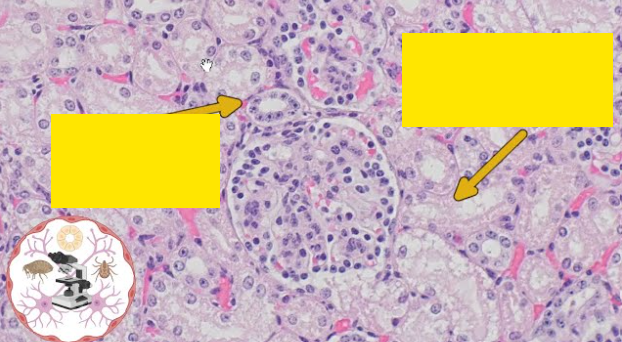
Fill in the labels from top to bottom?
Bowman’s capsule, glomerulus
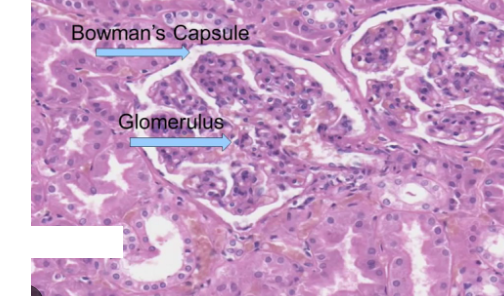
Explain where specifically is this micrograph of?
Cortex of kidney
Bowman’s capsule present
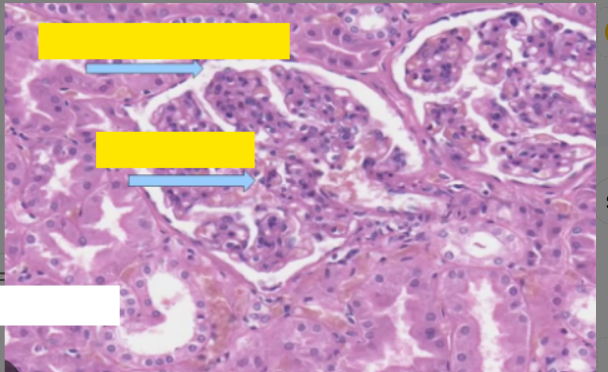
Fill in the labels from the top clockwise?
Bowmen’s capsule lumen, PCT, glomerulus, DCT
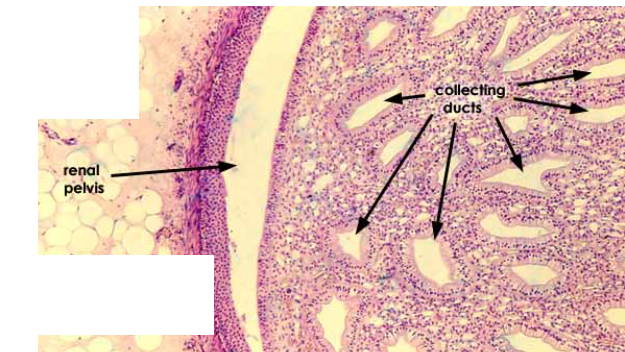
Fill in the labels from left to right?
Renal pelvis, collecting duct
Describe osmoregulation when water potential of blood is too high?
No details of mechanism of ADH is required
Osmoreceptors in hypothalamus detect increase in water potential of blood
Stimulate less release of ADH from posterior pituitary
Less water reabsorbed in the collecting duct
More dilute urine is produced and blood water potential decreases
Describe osmoregulation when water potential of blood is too low?
No details of mechanism of ADH is required
Osmoreceptors in hypothalamus detect decrease in water potential of blood
Stimulate more release of ADH from posterior pituitary
More water reabsorbed in the collecting duct
More concentrated urine is produced and blood water potential increases
Describe the relative location of adrenal glands?
Just above the kidneys
After tubular fluid has travelled through the collecting duct, where does it go?
Renal pelvis, ureter, bladder
How does kidney failure affect glomerular filtration rate (GMR)?
Reduces
Give approximate values for GMR of healthy kidney, chronic kidney failure and acute kidney failure?
Healthy: 90-120cm3min-1
Chronic: <60cm3min-1
Acute: <15cm3min-1
How does kidney failure affect electrolyte balance?
Too much or too little sodium in blood - too much is most common
Too much potassium in blood
What problems can occur from kidney failure?
Buildup of waste products in blood
Electrolyte imbalance
Dehydration or swelling of cells (particularly brain)
What are potential treatment for kidney failure?
Hemodialysis
Kidney transplant
Describe the process of haemodialysis?
Heparin is added to blood to prevent clotting
Blood from vein passes through many artificial capillaries with partially permeable membranes
Dialysis fluid flows on the opposite side
Countercurrent system of blood and fluid
Bubbles are removed before blood re enters body
Heparin removed just before dialysis is finished so blood clots when machine removed
Describe the advantages of haemodialysis as treatment for kidney failure?
No surgery required
No waiting list
No immunosuppressants
Buys time for a transplant
Describe the disadvantages of haemodialysis as treatment for kidney failure?
Performed 2-3x a week at hospital
Time consuming (several hours each session)
Diet must be carefully monitored
Short term solution
What are the advantages of kidney transplant as treatment for kidney failure?
Freedom from time consuming dialysis
Feel physically fitter
Improved quality of life
Improved self image
What are the disadvantages of kidney transplant as treatment for kidney failure?
Requires immunosupressant drugs
Side effect of immunosupressants - fluid retention, high BP, risk of infection
Major surgery - risk of infection
Regular checkups to check for rejection
How can urine by analysed to give information?
Presence of glucose - diabetes
Alcohol - blood alcohol in drivers
Recreational drugs - work
Anabolic steroids/PEDs - sport competitions
hCG - pregnancy testing
How do pregnancy tests work?
Tests for hCG
Mobile monoclonal antibodies bind to hCG in urine
Antibodies have visible blue pigment attached
Antibodies with hCG bind to test line forming blue line
Antibodies without hCG bind to control line forming blue line
How is anabolic steroid tested for in urine?
Gas chromatography (in labratory)
What is a transducer?
Convert one energy type to another
Describe a sensory receptor?
Transducer which detects changes in surroundings
What does the Pacinian corpuscle detect?
Pressure changes on skin
How does a pacinian corpuscle stimulate an AP?
Lamallae deform transmitting the pressure to the membrane
Membrane deforms causing mechanically gated Na+ channels to open
Influx of Na+ depolarises membrane to threshold
Known as generator potential
Voltage gated Na+ channels open further depolarising membrane creating an AP
What receptor detects chemical in air?
Olfactory cells in epithelium of nose
What receptor detects chemicals in food?
Chemical receptors on tongue
Where do sensory neurones carry AP?
CNS
Where do relay neurones carry AP?
Sensory to motor neurone
Where do motor neurones carry AP?
CNS to effector
Describe and explain the general structure of neurones?
Long to transmit information long distances
Many gated ion channels in plasma membrane for polarisation/depolarisation
Sodium/potassium pumps to reestablish concentration gradients
Cell body with nucleus, many mitochondria and ribosomes
Many dendrites to connect to other neurones
An axon which carries AP away from cell body
Some have Schwann cells to myelinate neurone and increase speed of transmission
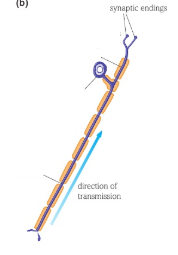
What type of neurone is this?
Sensory
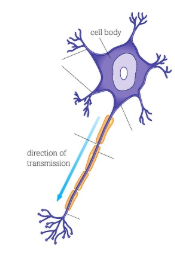
What type of neurone is this?
Motor
Summarise the features that make a motor neurone unique?
Cell body in CNS
Long axon that carries AP from CNS to effector
Summarise the features that make a sensory neurone unique?
Long dendron to carry AP from sensory receptor to cell body
Cell body positioned outside CNS
Short axon to carry AP to CNS
Summarise the features that make a relay neurone unique?
Short dendrites and short axon
Variable number of dendrites and divisions
Describe the differences in AP transmission of myelinated and non-myelinated neurones?
Conduction faster in myelinated neurone
Depolarisation can only occur where Na+ channels present
Myelinated neurones have longer section with no Na+
Depolarisation only takes place at nodes of ranvier
Longer local currents
Saltatory conduction - AP jumps from node to node
Describe the difference in structure of myelinated and non-myelinated neurones?
Myelinated have tightly wrapped schwann cells making up a myelin sheath
Nodes of ranvier occur every 1-3mm with no myelin sheath
Non-myelinated neurones often have one loosely wrapped schwann cell along its length
What is the advantage of myelination?
Transmit AP much faster to travel longer distances in less time