Computation of Volume from Graphs, Arc Length, Average Value
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
volume of cylindrical shells formula
x = radius
f(x) = height
the above ONLY apply for functions revolving around the normal axes and not functions revolving around other vertical/horizontal lines
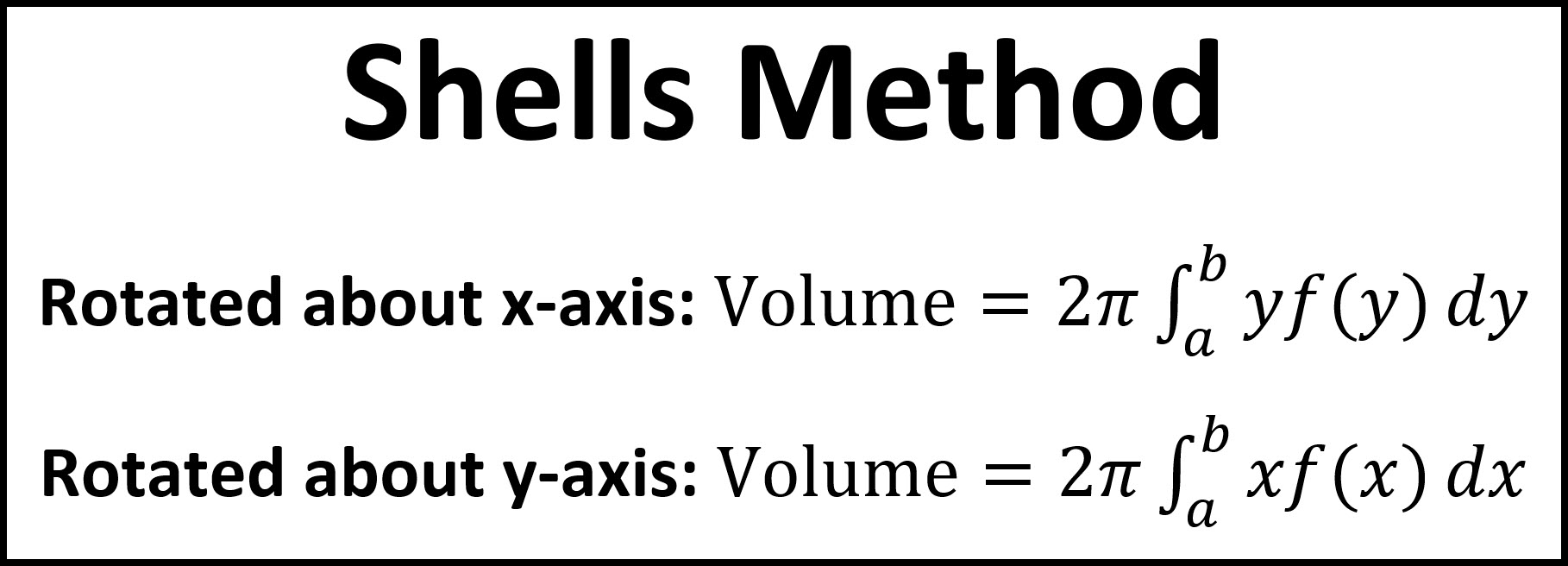
if the cross section of the volume is parallel to the y-axis, integrate with respect to ___
if the cross section of the V is || to the x-axis, integrate w.r.t ____
x; y
volume using disc method
method is for solids WITHOUT a hollow center
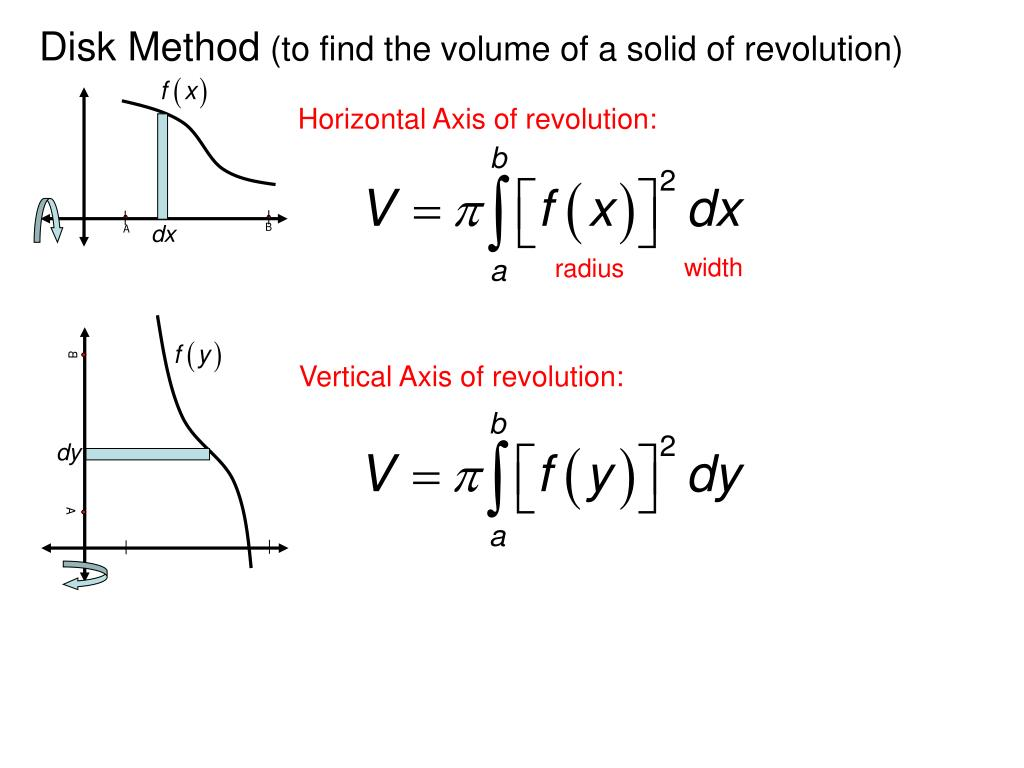
volume using washer method
method is for solids with a hollow center
washer method is for TWO functions that bound some area that rotates around some axis
“outer” circle function minus “inner” circle function

work =
force/”weight” x distance, aka the integral of the force function w.r.t distance
in terms of integration, work =
the definite integral of the force function moved from position a to position b [a,b] (meaning b is the upper bound, a is the lower bound)
force function for springs
F(x) = kx for some spring constant k
x denotes the DISPLACEMENT, the difference between initial position of the string and the final position)
the higher displacement = upper nound and the lower displacement = lower bound
take note of the NATURAL POSITION OF THE STRING
unit for work
Joule = kg * m²/s²
method of cylindrical shells w two functions
height (h) = f(x) - g(x)
where f(x) is the higher fn and g(x) is the lower function → FIND POINTS OF INTERSECTION
method of cylindrical shells: offset axis
if the axis is x = a where a is not 0:
if a is neg, then radius = a + x
if a is pos, then radius = a - x
average value
for interval [a,b]
![<p>for interval [a,b]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e873de52-35bd-48c7-a7d2-de8369c8096b.png)
mean value thm
if f(x) is continuous on [a,b], then there is a number c in that interval where:
f( c ) = average f num
arc length of f(x) on interval [a,b] formula
dy/dx = f’(x)
aim for a squared factor format
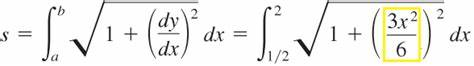
comparison Thm
a known convergent >= improper integral >= 0
if the above equality holds true, then the improper integral is also convergent
improper integral >= a known divergent >= 0
If the above equality is met, then the imp integral is also divergent
YOU MUST SHOW THAT ALL FNS CAN ONLY YIELD POS VALUES FOR THE GIVEN INTERVAL [a,b] (where one of the bounds is positive)
a known convergent 1/x^p
if p > 1, 1/x^p is convergent