Meiosis
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Meiosis
Type of cell division that results in four daughter cells each with 1/2 the # of chromosomes (n) of a diploid cell.
Haploid
Single set of unpaired chromosomes (n)
n
Abbreviation for haploid
2n
Abbreviation for diploid
Diploid
2 complete sets of chromosomes (2n)
Somatic cells
Regular body cells (2n)
Gamete cells
Sex cells (n)
Homologous chromosomes
Pair of chromosomes (one from each parent) with genes for the same characteristic; same size, centromere position.
3 ways homologous chromosomes are similar
Same type of genes
Same size & length
Same centromere position
Tetrad
Homologous chromosomes paired up with one another
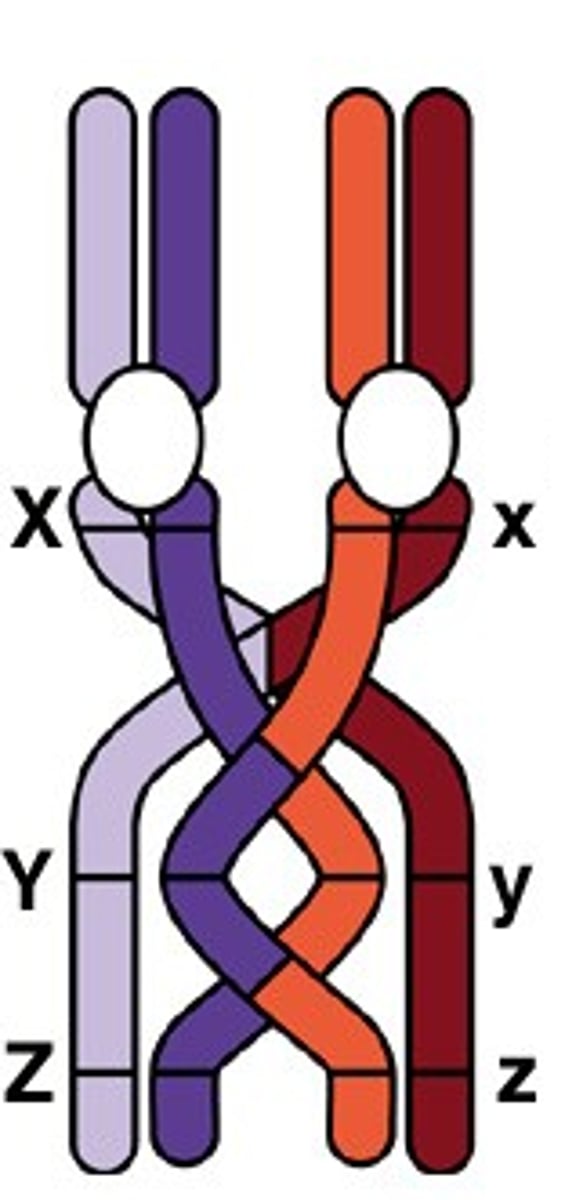
Crossing over
Exchange of DNA between homologous chromosomes. Creates genetic variability in gamete cells.
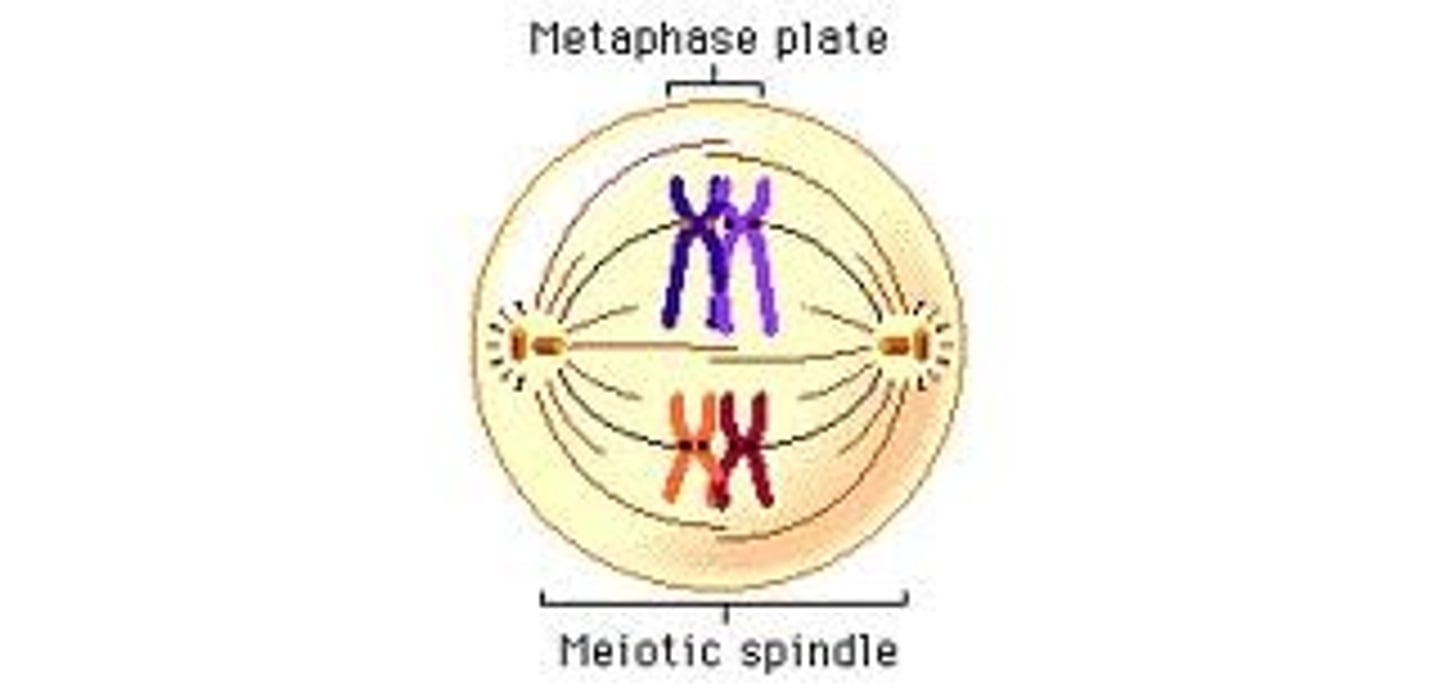
Metaphase 1
Tetrads line up at the center of the cell.
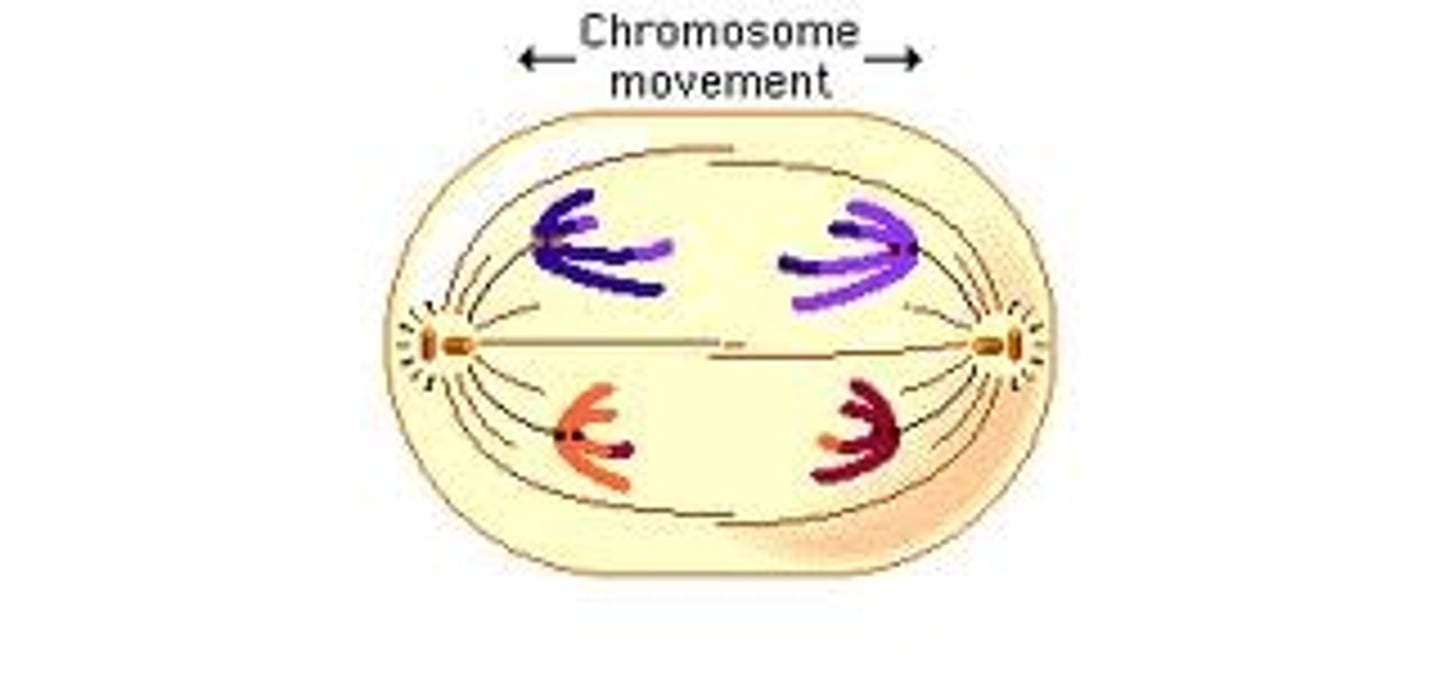
Anaphase 1
Tetrads are pulled apart. Chromatids remain attached.
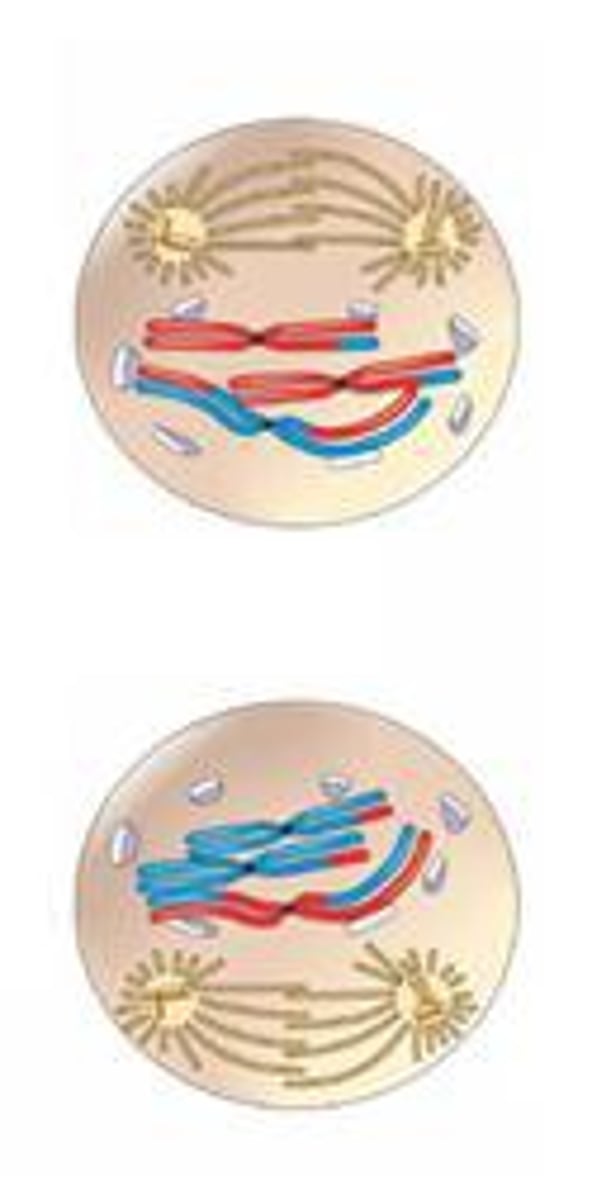
Prophase 1
Spindles form, centrioles move to poles, and nuclear envelope breaks down. Homologous chromosomes pair up with one another to form a tetrad and crossing over occurs.
Purpose of crossing over
To create genetic variability between gamete cells
Karyotype
Image of homologous chromosomes lined up in order; used to diagnose disorders, determine sex of baby, and determine # of chromosomes
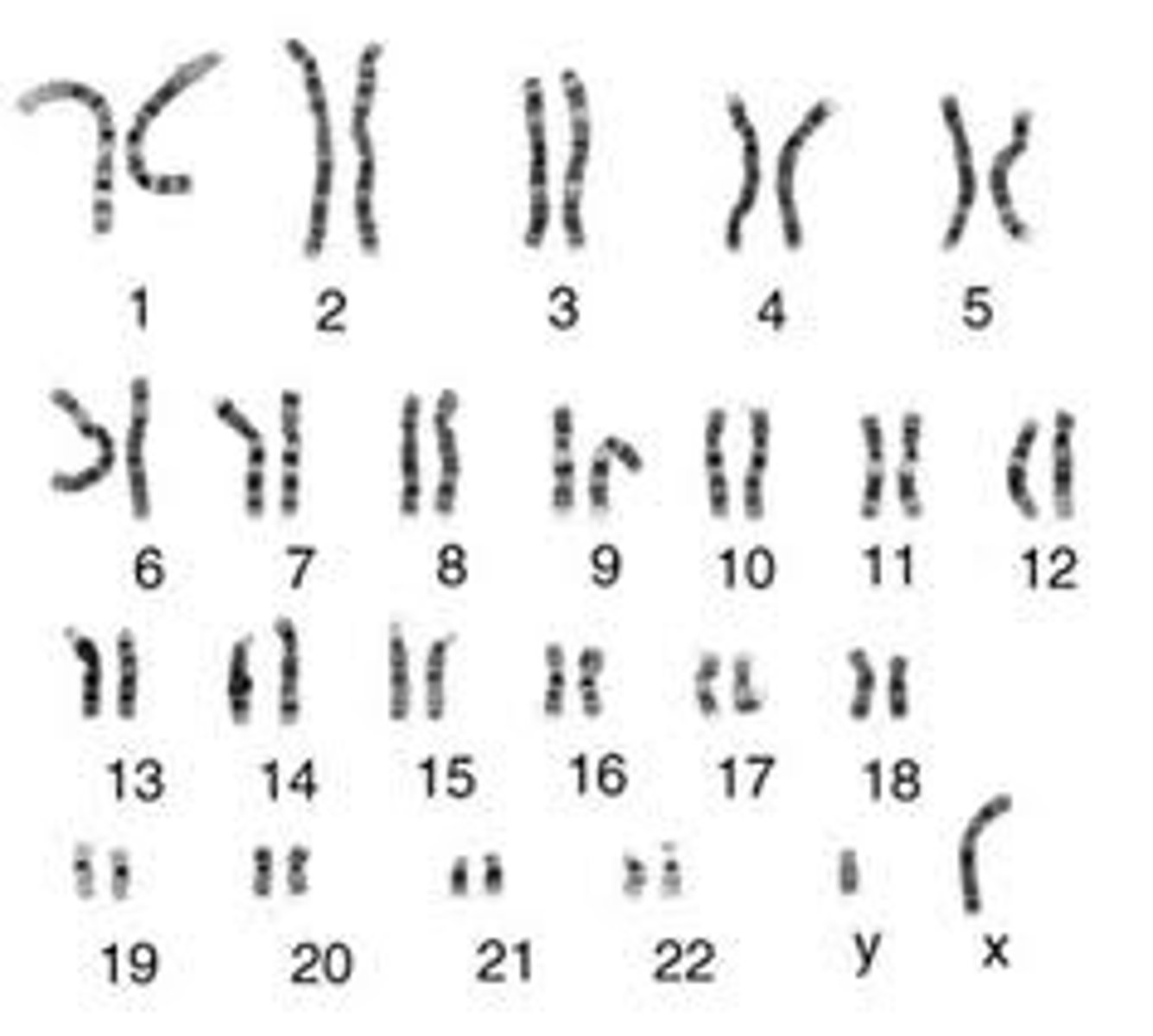
46
Number of chromosomes in somatic cells (2n) of humans
23
Number of chromosomes in gamete cells (n) of humans
XX
Female sex chromosomes
XY
Male sex chromosomes
Prophase 2
Nuclear envelope breaks down and spindles begin to form. Centrioles move to the poles.

Metaphase 2
Chromosomes line up at the center of the cell. Spindles attached to the centromeres.
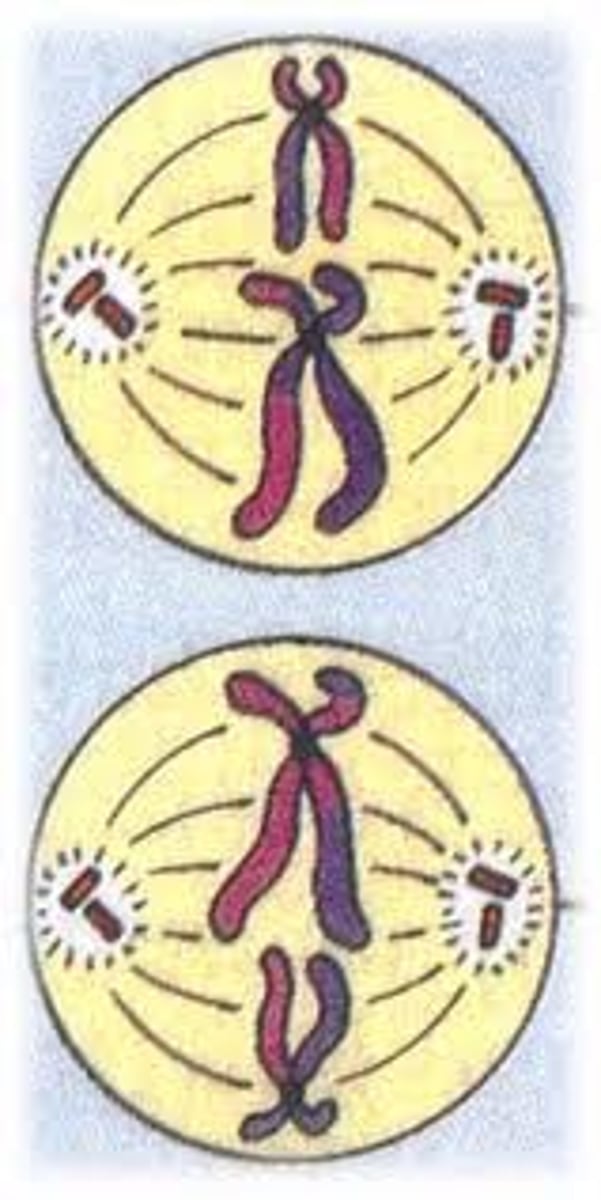
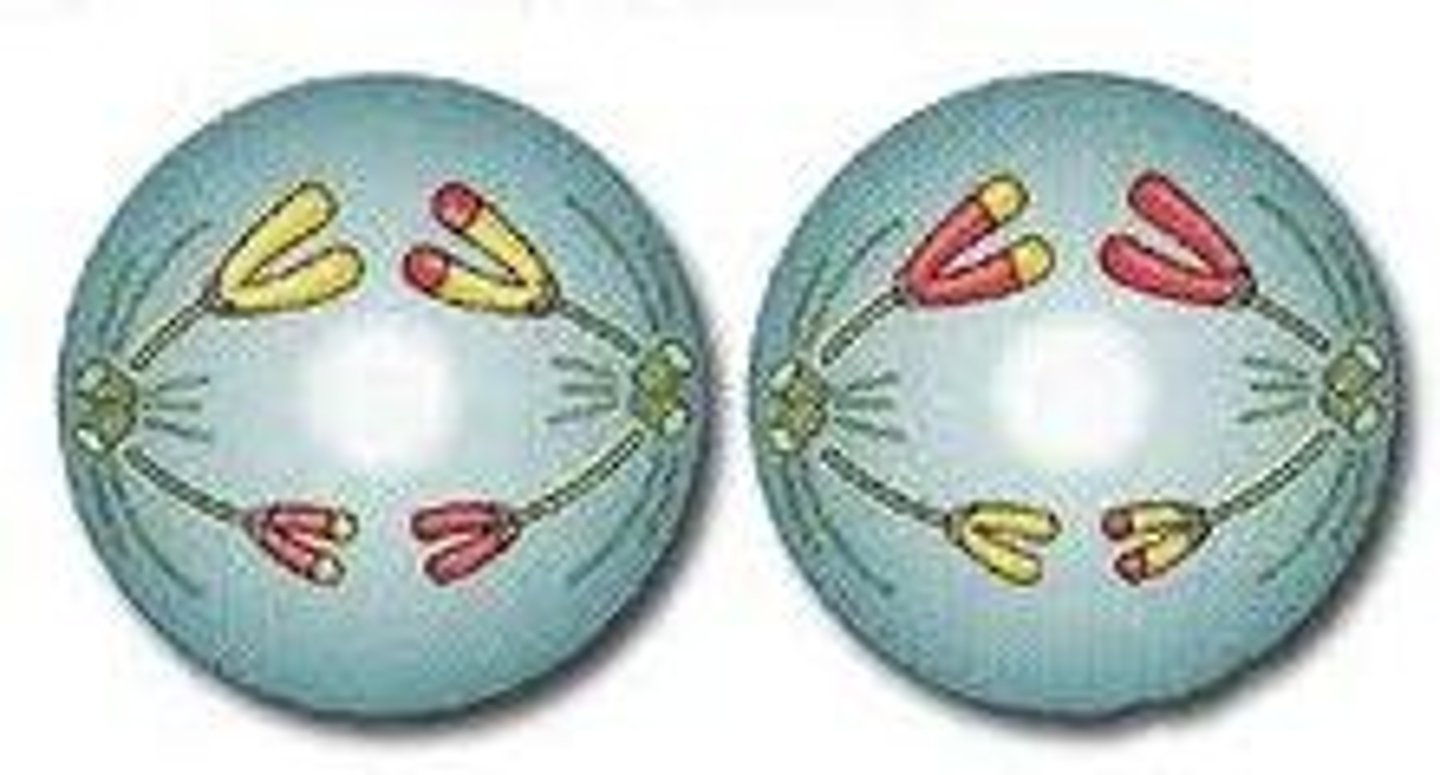
Anaphase 2
Chromatids are pulled apart.

Telophase 2
Nuclear envelope reforms, spindles begin to disappear and chromosomes start to uncoil
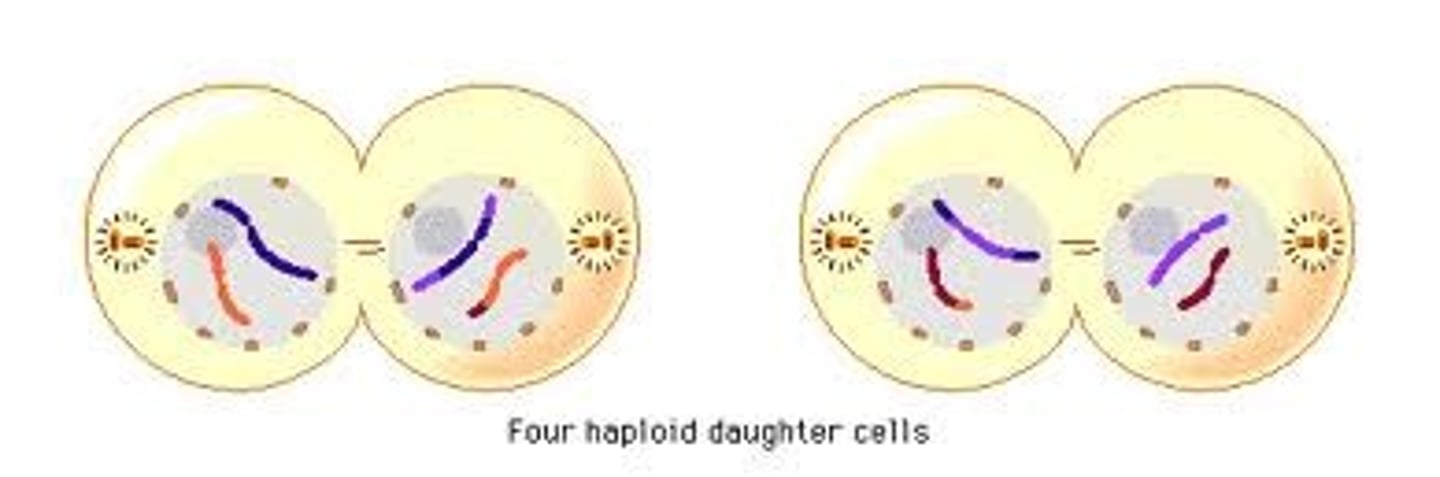
Cytokinesis 2
Division of cytoplasm and splitting of cells. 4 haploid daughter cells are produced.
Two
Number of divisions in meiosis
One
Number of divisions in mitosis
Similarities between mitosis and meiosis
Types of cell division
Create daughter cells
Go through interphase (G1, S, G2)
Go through PMAT (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase)
Go through cytokinesis
Start as diploid (2n)
Differences between mitosis and meiosis
Meiosis has 2 divisions; Mitosis has 1 division
Meiosis makes haploids; Mitosis makes diploids
Meiosis makes 4 cells; Mitosis makes 2
Meiosis makes gametes; Mitosis makes somatic
Meiosis pair during metaphase; Mitosis do not pair during metaphase
Meiosis makes genetically different daughter cells; Mitosis makes identical daughter cells
Purpose of Meiosis
To make gamete cells (haploid) for sexual reproduction
Purpose of Mitosis
To make somatic cells to repair or replace cells or form growth