Ch 12.1 warehouse management
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
warehouse
essential component of any supply chain
increasingly outsourced to logistic service providers
SKU (stock keeping unit) = a specific item at a particular geographical location
SKU
stock keeping unit
= a specific item at a particular geographical location
roles of a warehouse
storing/ buffering products between points of origin and points of consumption
consolidation and product mixing
crossdocking
value added services, including reverse logistics
meaning crossdocking
a logistics strategy where goods from suppliers are directly transferred to outbound trucks for delivery to customers, bypassing traditional warehouse storage to speed up delivery and cut costs
warehouse function : storing/ buffering
allows different parts of the supplu chain to operate independently
increase operational flexibility (eg impact of seasonal demand, batch production, uncertainties)
reduce customer lead times
warehouse function : consolidation
allows product mixing and reduces transport costs
combines shipments from a number of sources in the same geographic area into larger, more economical shipping loads,
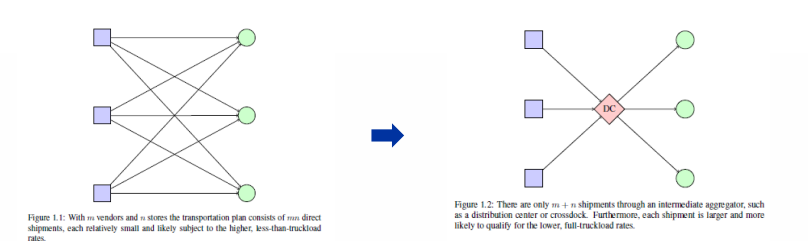
distribution center (warehouse function)
received large incoming shipments and splits them up into smaller outgoing shipments to demand points in a geographical area
warehouse function : crossdocking
allows to consolidate and transfer products directly without storage/ picking, customer is known
warehouse function : value added logistics
allow to meet specific customer demands, especially when a postponement strategy is adopted
warehouse benefits
achieving transportation economies (eg combined shipments)
achieving production economies (eg make-to stock polocy)
taking advantage of quantity discounts and forwards buys
meeting changing market conditions and uncertaunties (eg seasonality, demand fluctuations
overcoming time and space differences between producers and customers
providing temporary storage of material to be disposed or recycled (reverse logistics)
forward buys
you buy something now but only receive it later on
reverse logistics
the process of moving goods backward through the supply chain, from the customer back to the retailer, distributor, manufacturer, to recapture value through returns, repairs, recycling, refurbishment or disposal, effectively manageing the ‘after-sale’ life of a product
challenges related to warehouses
smaller orders, shorter response time, larger product variety
main warehousing activities
receiving
storage (transfer and put away)
order picking
accumulation/ sortation
crossdocking
shipping
warehouse management ≠ inventory management
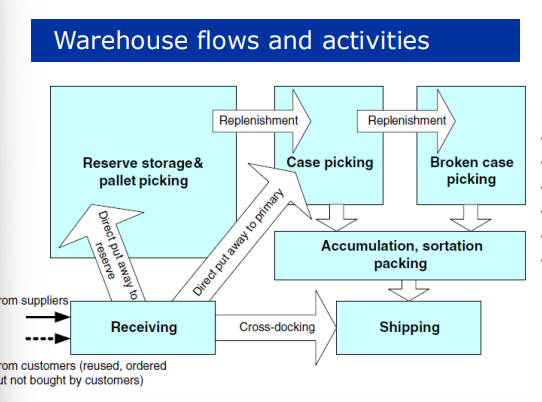
warehouse activities : receiving
unloading products from transport carrier (typically truck)
updating inventory records
inspecting quantity / quality inconsistencies
warehouse activities : storage (transfer and put away)
transfer incoming products to storage
possibly repackaging (eg full pallets to cases or standardized bins)
warehouse activities : order picking
most labor-intensive activity in many warehouses
obtaining the right amount of the right products for a set of customer orders → many different strategies
customer orders consist of one or more order lines (= SKU in specific quantity)
warehouse activities : shipping
accumulating picked orders into individual customer orders
performing value-added services (pricing, labelling, kitting)
packing and stacking customer orders on the right unit load
operations strategy
decisions related to operations, but not likely to be changed frequently
two aspects of operations strategy
storage strategy ; where to store each SKU (stock keeping unit)
order picking strategy : how to retrieve an SKU when ordered
obective : maximize service level subject to available resources (labor, machines, capital)
what are typical measures of service level
order delivery time
order integrity
order accuracy
storage assignment : forward-reserve allocation
large reserve area (bulk stock) and small forward area (pick stock)
advantage : picking efficiency through reduced distances
disadvantage : frequent replenishment from reserve area
all SKU’s in forward area ?
how many units per SKU in forward area
storage assignment : storage location assignment policies
a set of rules which can be used to assign SKUs to storage locations
random : assign SKUs randomly to eligible empty locations
dedicated : assign SKUs to a fixed location
full-turnover storage : assign SKUs generating the highest sales closest to the depot
class-based storage : combination of turnover and random strategy
family grouping : related SKUs should be stored closed to each other
class-based storage assignment :
apply pareto’s law to devide SKU s in three classes (ABC)
dedicated storage areas for each class, but random assignment within classes
order picking systems : picker to parts :zoning
picking area divided into zones → each order picker assigned to a single zone
order picker travel smaller distances and become familiar with locations
but : different SKUs of the same order may be in different zones → split orders shoudl be consolidated before shipping
order picking systems : picker to parts zoning: consolidation strategies
progressive zoning (pick and pass) → order is picked zone by zone : it goes to the next zone when completed in previous zone
synchronized zoning → order is picked in parallel : it is merged after picking has been done in all zones
order picking systems : picker to parts : batching
in the case of small orders (few order linesà, single-order picking is ineffcient
→ order batching reduces travel distances by picking a set of orders in a single picking tour
sorting needs to be done either during or after picking tour
criteria to decide which orders are batched
proximity of pick location (eg identical pick locations, distance between pick locations)
time windows : order due time must be respected
order picking systems : picker to parts : routing
pick list : list of SKUs (and their quantities) to be picked in a single order picking tour
assigned to a specific order picker
results of zoning and batching decisions
routing decisions
sequencing the items on the pick list to ensure a short route through the warehouse for the order picker
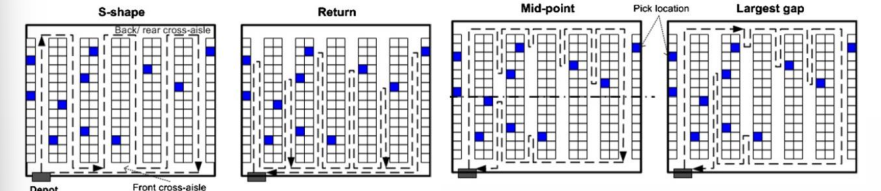
order picking systems : picker to parts : routing (different types)
s-shaped routing : works well in combination with within aisle storage
return routing works well in combination with across aisle storage or diagonal storage
mid-point routing and largest gap routing work well in combination with perimeter storage
picker-to-parts : technology
technology to support manual order picking
capital investment vs accuracy and or productivity improvements
eg scanning, voice picking, pick to light ext