Neuroscience: Module 3 - Anatomy & Physiology of Sleep + Disorders
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What is Sleep?
a state of reduced mental and physical activity in which consciousness is altered and certain sensory activity is inhibited
What is the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) ?
clusters of thousands of cells that receive information about light exposure directly from the eyes and control the behavioral rhythm
What is the Hypothalamus’ role in sleep?
contains groups of nerve cells that act as control centers affecting sleep and arousal
What does the SCN do?
send signals to the pineal gland increasing the production of the hormone melatonin, once the lights go down
What are the 2 basic types of sleep?
rapid eye movement (REM) sleep
non-REM sleep
Memory consolidation most likely requires both non-REM and REM sleep
What is Stage 1 of non-REM sleep?
Stage 1 sleep (change over from wakefulness to sleep)
short period (5% of total sleep)
light sleep
slow eye movements
muscles relax with occasional twitches
What is Stage 2 of non-REM sleep?
Stage 2 sleep
Longer stage (45%)
Deeper sleep
The heartbeat and breathing slow, and muscles relax even further
Body temperature drops
What is Stage 3 of non-REM sleep?
Stage 3
It takes about 25% of total sleep.
Deepest sleep people need to feel refreshed in the morning.
It may be difficult to be awakened
What is REM Sleep?
It occurs every 90 minutes
The eyes move rapidly from side to side behind closed eyelids.
Breathing becomes faster and irregular, and your heart rate and blood pressure increase to near waking levels
Most of dreaming occurs during REM sleep
arm/leg muscles become temporarily paralyzed, prevents you from acting out dreams
decreases in elderly
What is Parasomnia?
sleep disorder that involves unusual and undesirable physical events or experiences that disrupt your sleep
can occur before or during sleep or during arousal from sleep.
What are characteristics of parasomnias?
Abnormal movements
Talking and express emotions or do unusual things
What are non-REM parasomnias?
physical/verbal activity
not completely awake or aware
usually don’t remember or only partially remember the event the next day
occur between 5 and 25 years of age
often in people who have a family history
What are sleep terrors? (non-REM)
Usually brief
younger children
screaming, crying
What is somnambulism (non-REM)?
Sleepwalkers get out of bed, move about with the eyes wide open, but they are asleep.
Mumbling or sleep talking.
Performing complex activities (driving, playing a musical instrument, or move furniture)
It can lead to injuries
What are the other 2 types of non-REM sleep parasomnias?
sleep eating disorders
confusing arousals
What is Nocturnal lagophthalmos (non-REM)?
sleeping with eyes open
causes —>
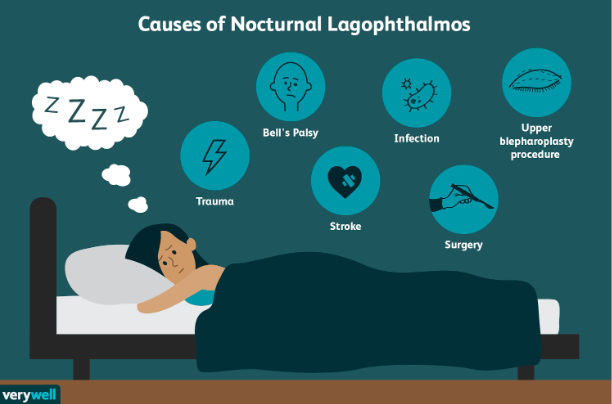
What is Nightmare Disorder (REM Sleep)?
Vivid dreams that cause feelings of fear, terror and/or anxiety.
People may feel a threat to their survival or security.
People are able to describe their dream in detail.
Trouble falling back to sleep.
More likely to occur if the person is under stress or experience a traumatic event, illness/fever, extreme tiredness or after alcohol consumption
What are Lucid Dreams (REM Sleep)?
A lucid dream occurs when a person is asleep but aware that they are dreaming.
A person can take control of their dream’s narrative to some degree, essentially guiding and directing the course of their dream.
There is a recognition that what is happening is not real and that it is taking place within a dream
What is Recurrent isolated sleep paralysis (REM Sleep)?
Inability to move the body or limbs during sleep
Scientists think the paralysis might be caused by an extension of REM sleep – a stage in which muscles are already in a relaxed state
It happens before falling asleep or while waking up
Episodes last seconds to a few minutes and are distressing, usually causing anxiety or fear
Sleep paralysis can be stopped if a person’s bed partner speaks or touches them
What is REM sleep behavior disorder (RSBD)?
People act out, vocalize (e.g., talk, swear, laugh, shout), or make aggressive movements (e.g., punching, kicking, grabbing) as a reaction to a violent dream
This sleep disorder is more common among older adults
Many people with this disorder have neurodegenerative disease, such as Parkinson’s disease, Lewy body dementia, or stroke
Why do we sometimes dream we’re falling?
A theory is that since your sleep is so light, your brain misinterprets it as being awake, but knows that your muscles aren’t moving. This makes your brain send a message to your muscles to make sure you’re okay, waking them up to protect you
Then, neurotransmitters are released and carry messages to your nerve cells which attach to your muscle protein cells
Then, a signal is sent to the receiving cells to get your muscles to move. This is why you feel movement such as falling or muscle stimulation during sleep