APHG Unit 7 CED Vocabulary - Industrial + Economic Development
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Industrial Revolution
the term used for the transformation from an agricultural society to an industrial society as a result of new technologies and facilitated by the availability of natural resources (resulting in factories, mass-produced goods, and assembly lines that replaced handmade goods)
industrialization
process that occurs when countries evolve from primarily agricultural producing basic, primary goods to one based on mechanized mass manufacturing of goods (craftsmen are replaced by assembly lines)
primary sector
economic activity that involves extracting (raw materials) or harvesting (food) products, e.g. gathering industries (renewable resources): agriculture, forestry, hunting and gathering, fishing, grazing, e.g. extractive industries (nonrenewable resources): mining, quarrying
secondary sector
economic activity that processes raw materials and transforms them into finished goods, e.g. manufacturing industries
tertiary sector
economic activity that provides services, e.g. health, legal, restaurants, stores
quaternary sector
economic activity that involves collecting, processing & manipulation of information & capital, e.g. finance, insurance, computer services
quinary sector
economic activity consisting of high-level decision making and advancement of human capacities, e.g. scientific research, higher education, government
core
countries where economic power (wealth, innovation, technology) is concentrated that control and benefit from the global market on which periphery and semi-periphery countries depend, e.g. U.S., Western European countries, Canada, Australia, Japan
semi-periphery
countries that are industrializing that exert more power in the world economy than the periphery, but are dominated to some degree by the core, e.g. newly industrialized countries such as Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa, Turkey
periphery
countries with low levels of economic productivity and a disproportionately small share of the world's wealth with weaker state institutions, lower standards of living and are often dependent on the core, e.g. Sub-Saharan African countries (except South Africa), parts of South America and Asia
break of bulk point
the transfer of transported cargo from one kind of carrier to another, e.g. port- from ship to truck
Least Cost Theory
Alfred Weber, theory that describes the optimal location of an industry in relation to costs of transport, labor, and relative advantages of agglomeration, an industry is located where it can minimize its costs, and therefore maximize its profits
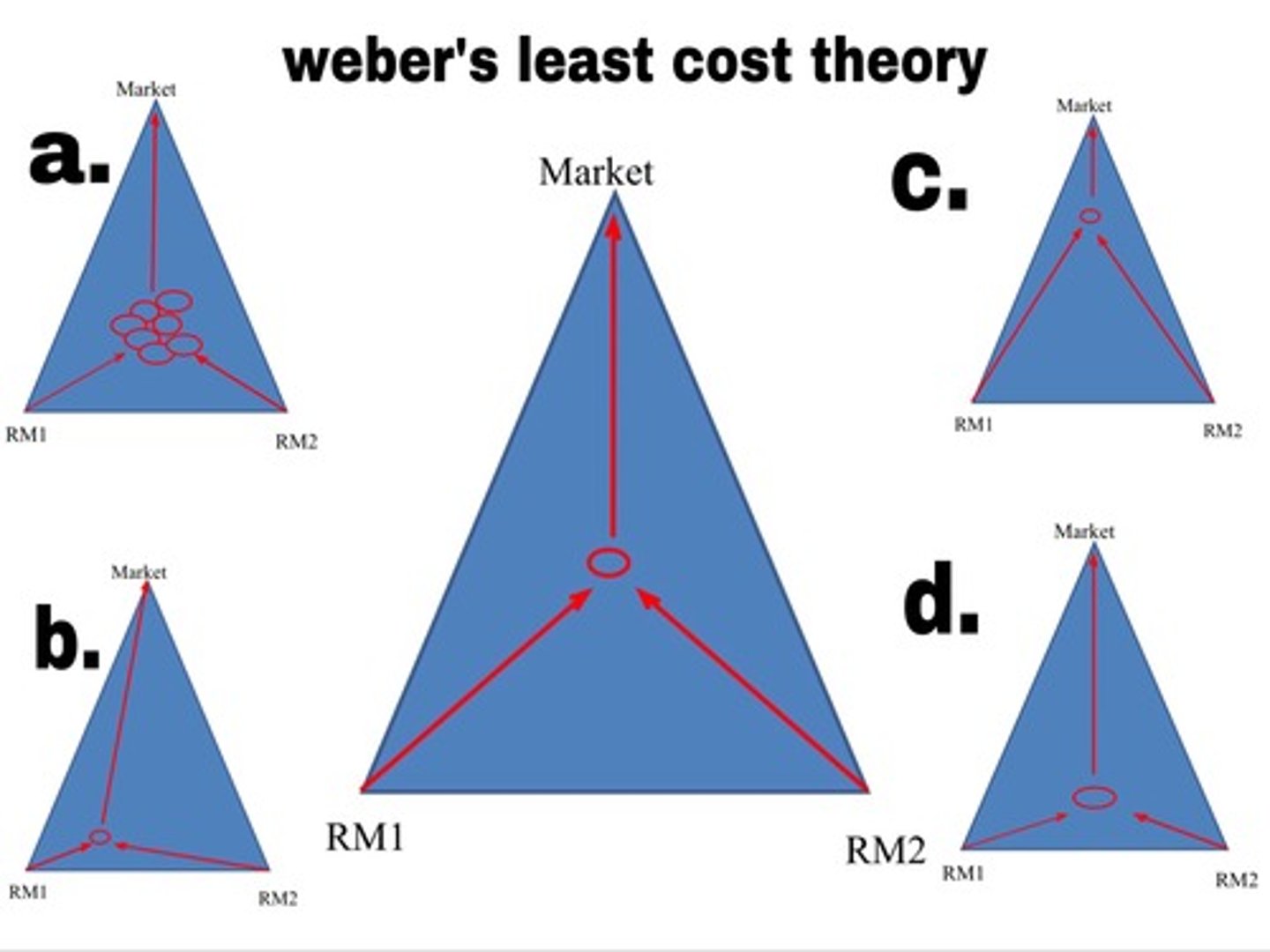
agglomeration
the clustering of businesses that can benefit from close proximity because they share skilled-labor and customer base
footloose industries
industry in which the location is not impacted by the cost of transporting either raw materials or finished products
LDC (less developed country)
countries with low levels of industrialization, urbanization and low standards of living that are mainly focused on primary activities, predominantly agriculture
NIC (newly industrialized country)
less developed countries with growing industrial economies and a developing trade status in the global marketplace (BRICs: Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa)
MDC (more developed country)
countries with highly developed economies, high levels of industrialization, urbanization, advanced technological infrastructure and high standards of living
post-industrial society
a society in which the economy has transitioned from a manufacturing-based economy to a service-based economy
GDP (gross domestic product)
measurement of the total value of goods and services produced within the borders of a country during a specific time period, usually one year
GNP (gross national product)
measurement of the total value of goods and services produced within the borders of a country plus the net income from companies that are located outside the country and foreign investments during a specific time period, usually one year
GNI per capita (gross national income per capita)
measurement of the total value of goods and services produced within the borders of a country plus the net income from companies that are located outside the country and foreign investments, but minus dividend payments and indirect business taxes during a specific time period, usually one year, divided by the population
Gini coefficient
measurement of income distribution within a population
fertility rate
the average number of children a woman will have during her childbearing years (15-49)
infant mortality rate
number of deaths under one year of age per 1,000 live births during a given year
access to health care
refers to the ease with which an individual can obtain needed medical services
literacy rate
percent of population who can read and write
gender inequality
acknowledges that gender affects an individual's lived experiences; gender inequality is experienced across different cultures; tradition and culture pose obstacles to women's economic development, especially in less developed countries
GII (gender inequality index)
measurement that evaluates women's status in a country based on participation in economic, political, and labor-market participation, as well as reproductive health issues, indices of empowerment, and labor-market participation
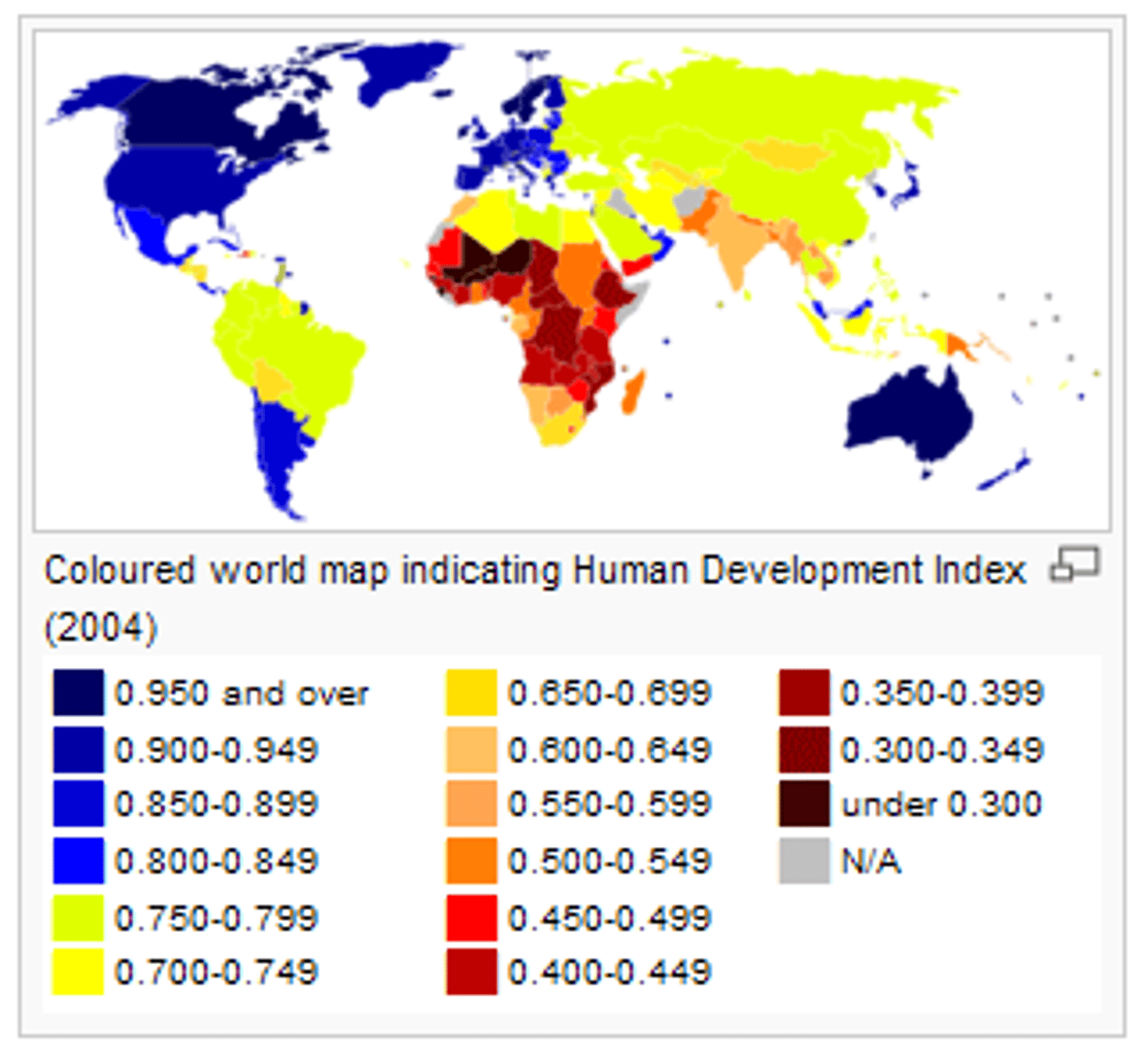
HDI (human development index)
measurement used by the United Nations to calculate development in terms of human welfare (using both economic and social indicators)
gender parity
measurement of the relative access to education of males and females, e.g. ratio of females to males enrolled in a given stage of education (primary, secondary)
objective of gender equality
a society in which women and men enjoy the same opportunities, rights, and obligations in all spheres of life and is linked to sustainable development
microloan
low interest loans usually for smaller sums of money to provide extremely poor people the opportunity to open a small local business and is often targeted to women in less developed countries to lift them out of poverty and is helping to improve standards of living
Rostow's Stages of Economic Growth
theory that assumes all countries are capable of development along the same trajectory which encompasses five stages of linear development towards self-sustained economic growth and high levels of mass consumption
Wallerstein's World Systems Theory (Core-Periphery Model)
model that describes how economic power is distributed between dominant regions and less powerful regions and proposes that less developed countries are defined by their dependence on a developed core
Dependency Theory
theory that maintains that less developed countries are kept in a position of dependency due to the existing economic and political power structures sustained by more developed countries; the concentration of wealth in more developed countries makes it difficult for less developed countries to compete and improve their situation
commodity dependence
the extent to which a country is dependent on primary commodities for export; dependency on primary commodities can leave a country vulnerable to unpredictable price fluctuations and can significantly reduce national revenue
neo-colonialism
theory that proposes that countries which may be free from political colonial control, continue to remain economically dependent on rich, industrialized countries
comparative advantage
advantages to locations that combine lower operating costs (labor, taxes, relaxation of environmental regulations) resulting in trade/sale opportunities that produce goods/services for a lower price, e.g. oil producing nations have a comparative advantage when making products that require oil such as chemicals
complementary advantage
advantages created when producing goods that are consumed together, e.g. cars and gas, e.g. printer and ink cartridges
neoliberal policies
characterized by free market trade agreements, deregulation of financial markets, individualism, and the shift away from state welfare provision have created new organizations, spatial connections, and trade relationships that foster greater globalization
free trade agreements
treaty between two or more countries to establish a free trade zone where goods and services can be conducted across common borders, without tariffs but labor or capital may not move freely
European Union (EU)
originally began as an economic union and has evolved into a political organization encompassing security, human rights, climate, environment, health and political issues; the EU is based on the rule of law; founded on treaties, voluntarily and democratically agreed upon

WTO (World Trade Organization)
global international organization dealing with the rules of trade between nations; negotiates the bulk of the world's trade agreements that are signed and ratified by their legislatures

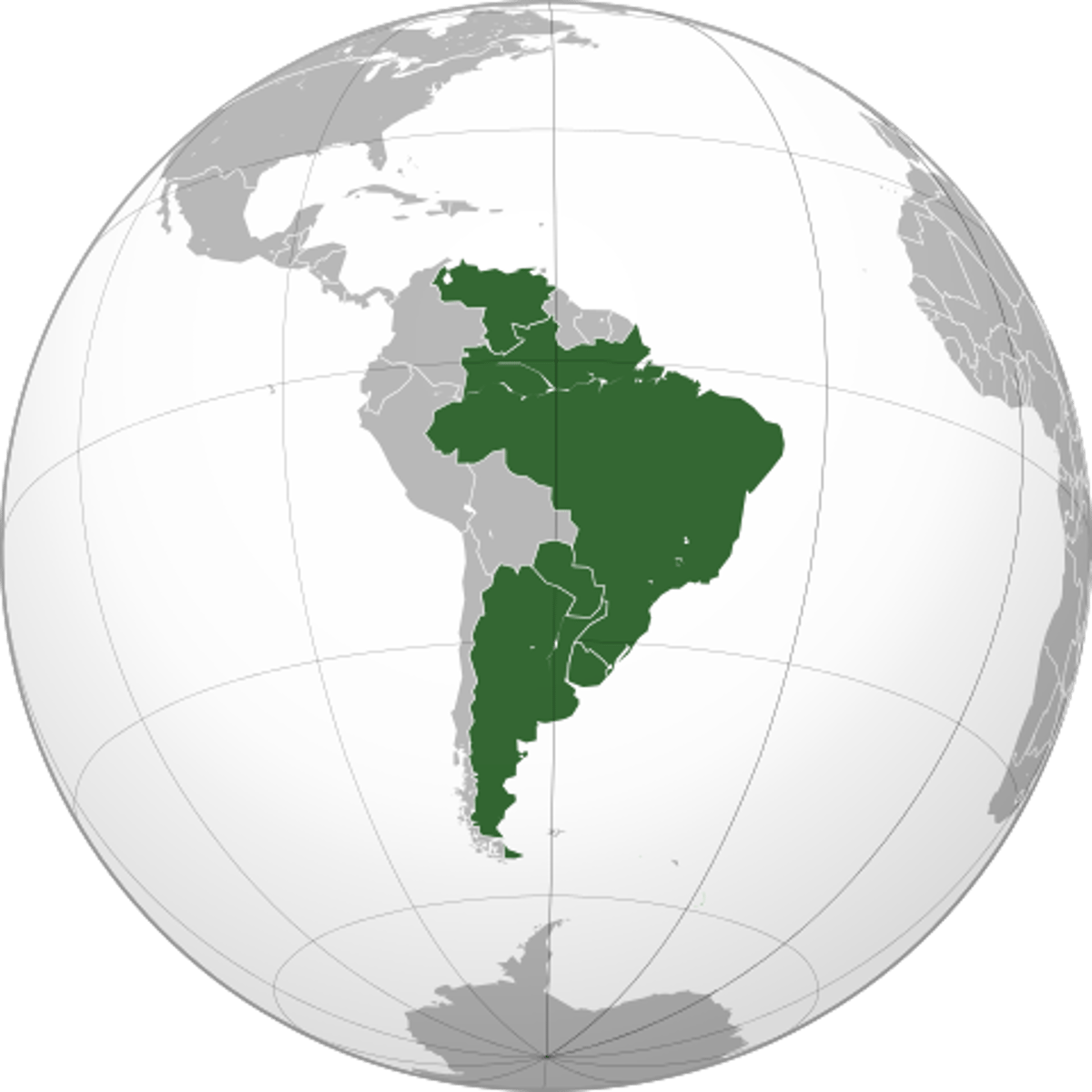
Mercosur
an economic union creating a common market for the free movement of goods, services, and factors of production between countries in South America compromising Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, Uruguay and Venezuela, with associate countries of Chile, Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Guyana, and Suriname
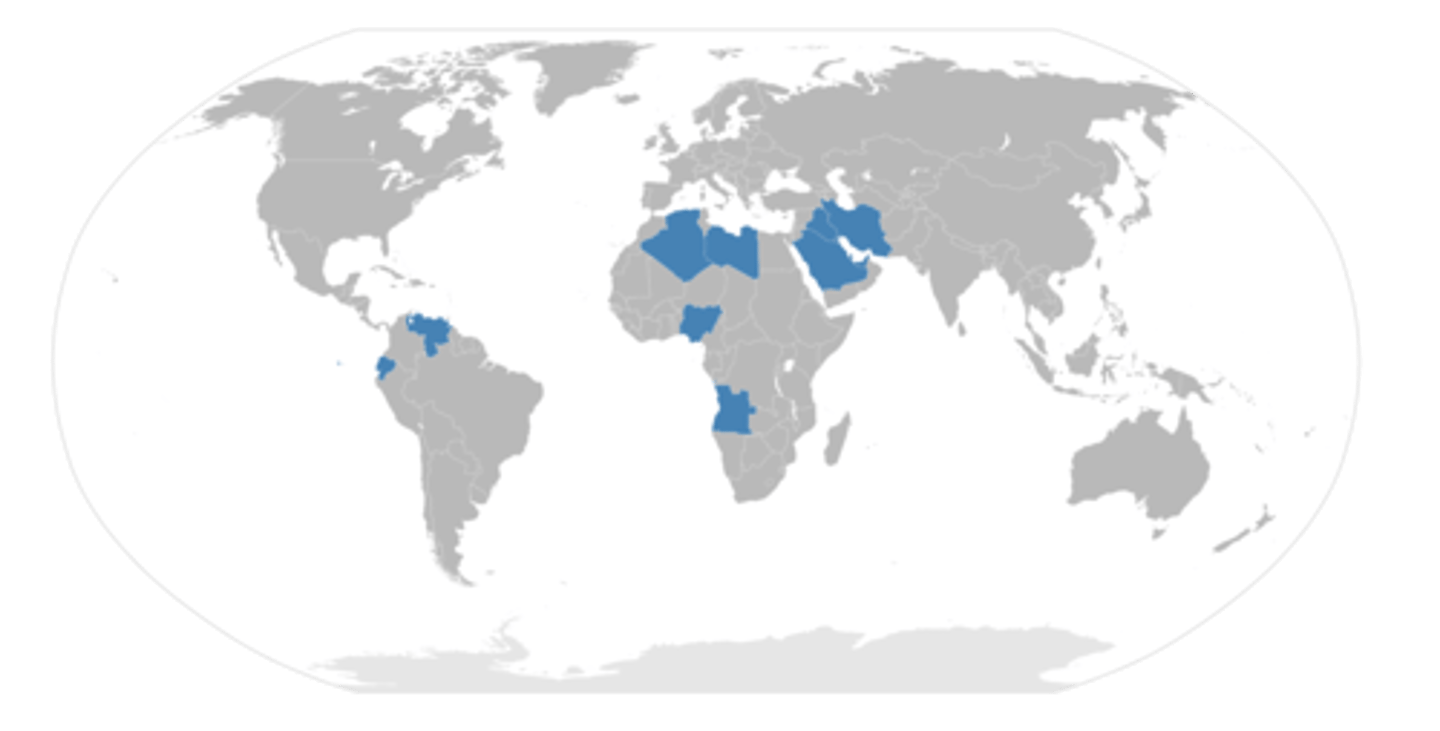
OPEC
an economic union of oil producing countries that coordinates and unifies the policies of member countries to ensure the stabilization of oil markets in order to secure an efficient supply of oil (Saudi Arabia, U.A.E., Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Libya, Nigeria, Venezuela, Gabon, Ecuador, Angola, Algeria, Congo, Equatorial Guinea)
tariffs
a tax imposed by a government on goods imported from other countries that serves to increase the price and make imports less desirable/less competitive compared to domestic goods
global financial crisis
period of extreme stress in global financial markets and banking systems (2007-2009) caused by deregulation in the financial industry that led to the Great Recession
debt crises
situation in which a country is unable to pay back its government debt caused when spending exceeds revenues for a prolonged period of time
international lending agencies
institutions that specialize in providing loans, grants, and financial expertise to less developed countries that focuses on poverty reduction, stimulating growth, building infrastructure, encouraging foreign investment, and fighting corruption
International Monetary Fund
an organization of 189 countries working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world

microlending
the lending of small amounts of money at low interest to the poor, particularly women, in less developed countries to encourage development of small businesses with the goal of improved standards of living
NGOs (nongovernmental organizations)
international organizations that are not run by state or local governments and are influential in international initiatives on economic, social, and environmental issues and usually try to improve conditions in the most impoverished regions of LDCs (periphery OF the periphery)
outsourcing
when a company sends goods/services out for external production, typically where labor is cheaper to achieve comparative advantages have led to a decline in jobs in core regions and an increase in jobs in newly industrialized countries
economic restructuring
the process in which economies in the core move from manufacturing to the service sector and as a result of the loss of manufacturing jobs and growth of the service sector, a widening occurs in the social hierarchy where high income salaried professional jobs expand alongside an increase of low wage/low skill service jobs and a "missing middle" develops in the wage structure
manufacturing zones
created by the growth of industry in countries outside of the core where governments create favorable investment and trading conditions to attract export-oriented industries
Special Economic Zones
designated area that has economic laws that are more free-market-oriented than a country's typical national laws, e.g. Shenzhen, China
free trade zone
designated area where goods may be landed, stored, handled, manufactured, reconfigured, and re-exported under specific customs regulations and generally not subject to customs duty
export processing zone
designated area generally in developing countries by their governments that offer exemptions from certain taxes and business regulations to promote industrial and commercial exports
international division of labor
refers to the shift in the core to service industries and an associated shift to manufacturing in the semi-periphery and periphery as companies search for the cheapest locations to take advantage of low-cost labor to manufacture and assemble components which has been facilitated by improvements in transportation/communication technology
post-Fordist methods of production
flexible production that is no longer centralized in one manufacturing facility and takes advantage of outsourcing or just-in-time delivery and is reliant on advanced technology
multiplier effect
happens when an increase in spending produces and increase in national income and consumption is greater than the initial amount spent, e.g. a new factory will increase employment, which will stimulate employment in other businesses
economies of scale
cost advantages gained by an increased level of production, e.g. a large-scale (Walmart, Costco) business can afford to invest in technology that improves stock control, which increases revenue, that can be used to make further improvements
just-in-time delivery
system of production that is centered around using modern transportation to only order parts as needed and not by keeping large stockpiles in warehouses as in traditional mass production, the goal is to reduce costs by saving money on overhead inventory
high technology industries
an industry (chemicals, aircraft) that uses advanced methods and modern equipment or is devoted to research, development, and sale of high-technology products (e.g. computers, semiconductors)
high technology corridor
area that is devoted to research, development, and sale of high-technology products, e.g. Silicon Valley in California
growth poles
concentration of highly innovative and technically advanced industries that stimulate economic development in linked businesses and industries
sustainable development
development that addresses issues of natural resource depletion, mass consumption, costs and effects of pollution, the impact of climate change, as well as issues of human health, well-being, and social and economic equity
ecotourism
tourism based in natural environments that are often threatened by looming development and helps to protect the environment in questions while also providing jobs for the local population
Sustainable Development Goals (Global Goals)
a universal call to action by the U.N. to end poverty, protect the planet, and ensure that all people enjoy peace and prosperity; progress in development is measured through activities such as microloans (lending to small scale borrowers) and public transportation projects (infrastructure)
