Economics IB HL - Unit 1 - Market failure
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
what is an externality
positive or negative effect for third parties. It is where the market fails to achieve allocative efficiency because MSMB is not equal to SMC
Definition of PMB
additional benefits for consumers from consumption of an additional unit of a good
Definition of SMB
additional benefits for society from the consumption of one more unit of a good
Definition of PMC
additional costs to producers from producing one more unit of a good
SMC
additional costs to society from the production of one more unit of a good
When is there no externality
There is no externality when D = S when SMB = SMC
What are the socially optimum price and quantity
the best quantity and best price from the point of view of what is most desirable from society’s point of view
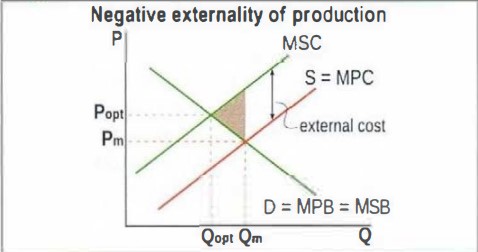
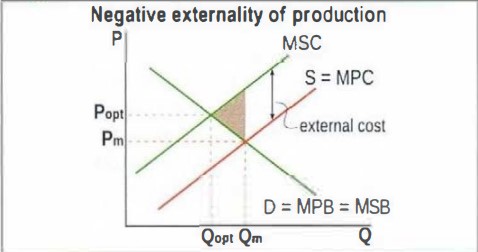
In this diagram what does PM and Qm represents
pm and qm shows the market outcome
What happens in the allocation of resources when there is negative externalities
the market overallocates resources - too much is produced
draw and labell a negative externality of production
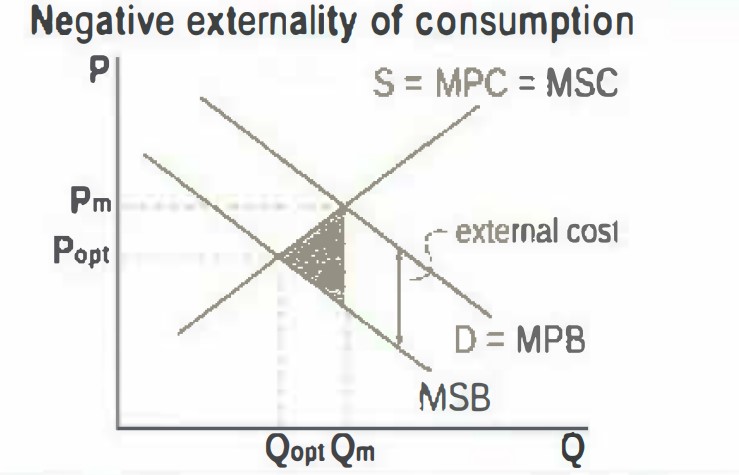
draw and label a negative externality of consumption
What is an example of a negative externality of production
production of goods using fossil fuels leading to carbon emissions, hence there are external costs including pollution of celean air etc
example of neagtive externality of consumption
smoking, where there are negative health effects on non-smokers and increased health care costs.
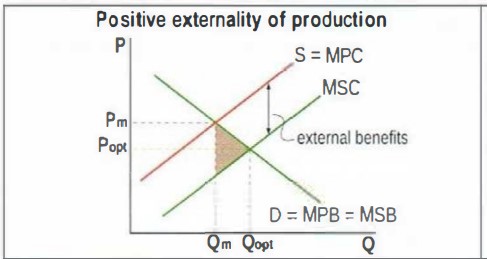
draw a positive externality of production
positive externality of consumption
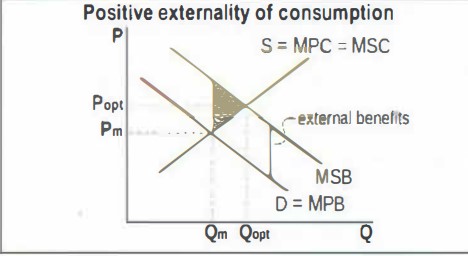
example of positive externality of production
research by firms leaeds to develeopment in new technologies that benefit the whole society
example of positive externality of consumption
education leads to benefits for society including lower unemployment, increased productivity
merit goods
goods when consumed creates positive consumption externalities; are socially desirable but underprovided and consumed in the market.
example of merit goods
education, health care, infrastructure.
demerit goods
goods whose consumption creates negative externalities of consumption. are socially undesirable but are over provided and over consumed by the market
example of demerit goods
cigarettes, fuel for cars
how can the government respond to externalities
using
regulations
legislation
advertising
education
direct government provision
using market based policies how can externalities be addressed.
using
indirect taxes
subsidies
examples of government command approaches - legislation, regulations, and advertising for negative production externalities
impose restrictions on emissions
limit the amount of output produced
Force firms to install non-polluting technologies
Create protected area
restrictions on logging, fishing and hunting
negative advertising to influence consumers to avoid buying products off highly polluting firms
What are three positives of government command responses
Simpler to implement compared to market based policies
effective in partial achievement
in some cases are more appropiate than market solutions
What are 3 negatives of government command responses
involve costs of monitoring and enforcement
do not provide incentives in the market to switch to cleaner technologies
there is incomplete knowledge on extent of damage done by pollutants so hard to tell how much to restrict activities
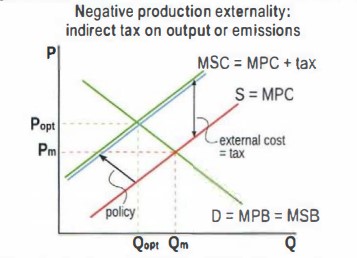
how does an indirect tax help with negative externalities of production
An indirect tax on output causes the supply curve to shift from PMC towards SMC, leading to the socially optimum P aND Q. This means the externality is eliminated so welfare loss is eliminated.
explain how an indirect tax on emissions also addresses the negative externality of production
this also cause the uspply to shift from PMC TO SMC leading to socially optimum Q and P. This works by creating incentives for firms to reduce emissions and shift to clean technologies to avoid paying tax.
What is a tradable permit and what is an example of one
a max permissible amount of a particular pollutant is determined, and permits to emit this pollutant are distributed to firms by the government. these can then be sold and bought in a market which creates incentives to switch to clean energy to lower production costs. An example is when the european union emissions trading system covering power and heat generation etc
What are 5 positives of using market based policies to address a negative externality of production
Can internalize the externality by making the producers pay for the external cost
greater efficiency (lower cost) in reducing pollution than gov regs
the most efficient policies are (a) taxes on emissions and (b) tradable permits. firms that face low costs of reducing emissions face the incentive to lower emissions and pay lower tax and perhaps sell the permits for profit. SIMILARLY firms with higher costs of reducing their emissions can pay the tax or buy permits
Taxes and tradable permits on emissions can provide incentive to switch to clean technologies
cleaner technologies shifts the SMC to the right so reduces the overall size of the externality
negatives of using market based policies to address a negative externality of production
There are difficulties in identifying the most harmful pollutants and the value of external costs
in case of taxes, hard to find the value of tax that will equal the value of harm
for both indirect taxes and tradable permits there are difficulties in ensuring compliance and enforcement
Draw a graph showing a Negative production externality and the effect of an indirect tax on output or emissions
How can command approaches help negative consumption externalities ?
These can influence the behaviour of consumers and reduce demand so that the PMB curve shifts closer to SMB leading to the socially optimum Q and P
GIVE ME 3 examples of command approaches to address a negative consumption externalities
legislation, no smoking in public places, no drinking and driving
negative advertising to change consumers’ preferences like informing them of the dangers of smoking
educate consumers
What are the positives of government command policies to tackle a negative consumption externality
Simple to implement
effective in at least partially reducing demand for the good
some cases more appropriate like banning smoking in public places
What are the negatives of government command policies to tackle a negative consumption externality
very unlikely to reduce demand to the required level. so only partially eliminates the externality
advertising and education have opportunity costs as funds are diverted from other objectives
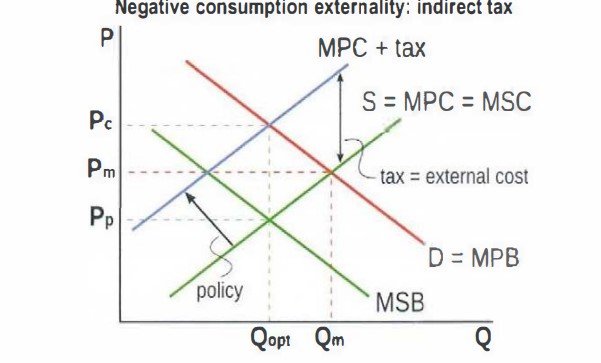
How can market-based policies be used to address a negative externality of consumption
An indirect tax on a good causing the negative externality causes supply curve to shift upwards. this causes P to increase and Q to fall. If the tax is exaclty equal to the value of the external cost, ‘PMC+tax’ will intersect PMB at the level of socially optimum quantity.
draw a graph to shows the effect of an indirect tax on a negative consumption externality
what are the positives of using market based policies when correcting a negative externality of consumption
can internalize the externality - make the consumers pay for the external cost
can be more efficient because they are based on price mechanism so uses price incentives for consumers to respond to
if the good being taxed has inelastic demand the tax will result in a higher revenue that can be used to finance government advertising and education programs because as price increases the quantity demanded stays the same
what are the negatives of using market based policies when correcting a negative externality of consumption
difficult to measure the exact value of external costs
therefore difficult to determine the size of the tax that will be equal to the external costs
If the good taxed has inelastic demand the tax is unlikely to result in a significant fall in Q produced and consumed so will not be very effective in eliminating the externality
Indirect taxes are regressive affecting poor people more strongly which could lead to them switching to lower quality substitutes which are cheaper but may be more harmful
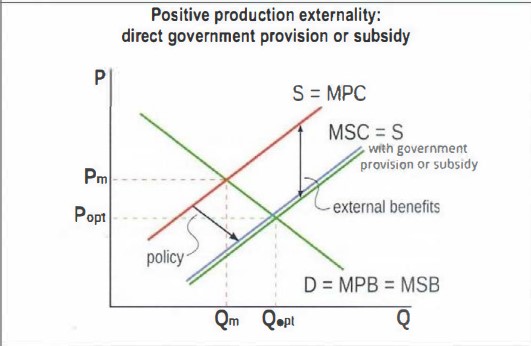
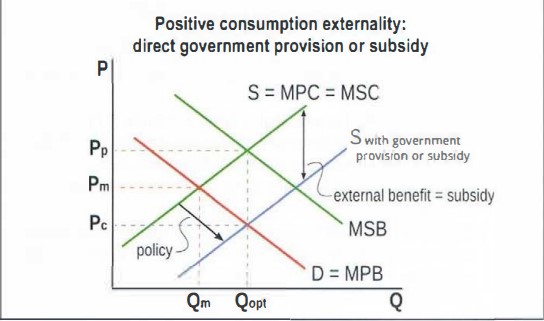
How can direct government provision help with positive production externalities?
This has the effect of shifting PMC curve closer to the SMC curve so therefore help reaches the socially optimum quantity and P.
What is an example of when the government would chose direct provision to correct a positive production externality.
In the case of research and development. For the development of new scientific knowledge, new technologies, new products.
What market side policy could be used to correct a positive production externality?
Provision of subsidies to private firms from the gov involved in reasearch and development shift the PMC closer to SMC
What is a positive of using direct government provision and subsidies
are highly effective in increasing the amount of research and development carried out
What are the negatives of using direct government provision and subsidies
Negatives of using direct gov provision and subsidies
difficulties in estimating the value of the external benefits
Difficult to determine the size of the subsidy or the funds that should be allocated toward direct provision in order to match the value of the external benefits
Government funding involves opportunity costs
The government selection process on what activities to support is often subject to political pressures with choices made on political grounds instead of economics
Draw a graph showing a positive production externality corrected by direct government provision or subsidy
How can command approaches be used to correct positive consumption externalities
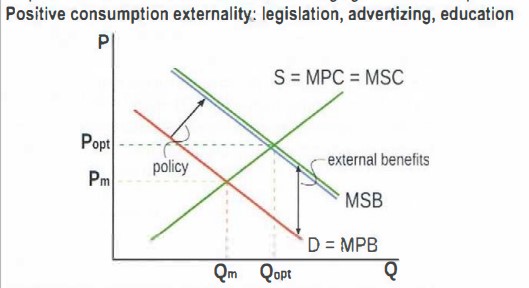
command approaches include legislation, advertising and education that aim to influence the behaviour of consumers to INCREASE demand so that the PMB curve shifts closer to the SMB
What are the positives of legislation, advertising and education when tackling positive externality of consumption
Positives of command approaches when tackling a positive consumption externality
simple to implement
effective in partially increasing demand for the good
What are the negatives of legislation, advertising and education when tackling positive externality of consumption
Positives of command approaches when tackling a positive consumption externality
advertizing and education alone are unlikely to increase demand to the required level.
- adverts and education both have opportunity costs as funds are diverted from other objectives
Difficulties of compliance and enforcement of legislation
Increase in demand leads to higher P which makes goods unaffordable for lower income groups. therefore should be used besides direct provision and subsidies
draw a graph showing a positive consumption externality corrected by command approaches
draw a graph showing a positive consumption externality corrected by government direct provision
What are common access resources
natural resources without ownership, so have no price so can be used by anyone. they are non-excludable but are rivalrous because when one person uses them it makes them less available for another
What are some examples of common access resources
forests, rivers, lakes, oceans, soil quality,
What is the definition of sustainability
the use of natural resources at a rate that allows them to reproduce themselves. this results in future generations being able to use the resources to satisfy their wants and needs.
what is the concept of sustainable development
Development which meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
give one example common access resources pose a threat to sustainability because they are often overused, depleted and degraded
Example 1 - Forests. Anyone can chop down trees which poses a threat to sustainability if trees are chopped down more quickly than new trees can grow. Forests become depleted while the environment is reduced in quality due to a loss of natural habitat for animals, a loss of biodiversity and global warming.
Explain how the use of fossil fuels is a threat to sustainability
The use of fossil fuels in production and consumption creates negative externalities resulting from overuse, depletion and degradation of common access resources which then causes external costs of climate change, depletion of the ozone layer, acid rain, and lots of health care issues that cause a surge in healthcare costs.
how is poverty a threat to sustainability
In economically LDE’s poverty can lead to people uses open access resources unsustainably in order to survive on super low incomes. Also high population growth exerts additional pressures on unsustainable resource use.
What are six ways in which the government can respond to threats to sustainability
ways gov can respond to threats on sustainability
legislation and regulations
funding for clean technologies
carbon taxes
cap and trade schemes - tradable permits
elimination of environmentally harmful subsidies
government subsidies for the development of clean technologies
Why is there a need for international collaboration
Negative environmental externalities extend far beyond national boundaries, and therefore require international collaboration for a solution.
what is a private good
a good that is rivalrous and excludable so people can be prevented from using it by charging a price.
What are some examples of private goods
cars, computers, houses, education, NHS etc
What is a public good?
a good that is both non-rivalrous and non-excludable.
what are some examples of public goods
police force, light house, knowledge, streetlights
What is the free ride problem?
this happens when people use a good without paying for it. This causes a market failure because even though the good may be socially desirable private firms will not produce it because without the ability to charge a price it would be impossible for them to cover the costs.
What are quasi-public goods?
good that are not rivalrous but are excludable.
what is an an example of quasi public goods?
toll roads, museums, public swimming pools.
What is
Asymmetric Information
a type of market failure occurring when one party in a transaction has more information than the other party, leading to allocative efficiency.
give and explain an instance when sellers have more information than the buyers
for example a seller of used cars knows more about the car’s condition than the buyer. Because of this it often leads to an under allocation of resources t