Skeletal System: Bone - Flashcards
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards for Skeletal System
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Skeletal System Function
Provides firm framework
attachment points for muscles
allows articulation.
Protects vital organs
What does the skeleton store?
mineral salts and fats (Ca, P, Na, K)
and red marrow for blood cell production.
Divisions of the skeleton
Axial and appendicular
Parts of the axial skeleton
skull
vertebral column
ribcage (there is a sternum the front)
Appendicular Skeleton
´Pectoral girdle (scapula, collerbone/clavicle, bones of the limbs)
´Upper limbs (the whole of the hand, the whole of the foot)
´Pelvic girdle (pelvis)
Lower limbs
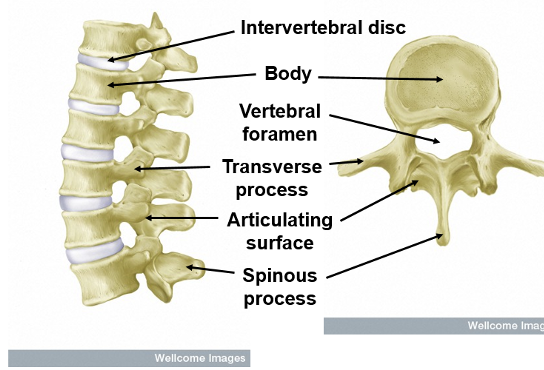
What is the structure of the spine?
is made up of 33 vertebrae divided into five regions.
the intervertebral disc provides cusioning and support for the body, protecting the spinal cord within it.
It also allows for flexibility and movement.
Structure of bone- what does a long bone typically consist of?
Diaphysis: the main portion (shaft)
Epiphysis: enlarged, rounded ends of bone (ends)
What are the epiphyses covered by?
covered by thin layer of cartilage, the articular cartilage)
Flat Bone Function
Protects internal organs
Sesamoid Bone Function
Protects tendons
Irregular Bone Function
Variable nature helps to protect different structures
Short Bone Function
Provide stability and some movement
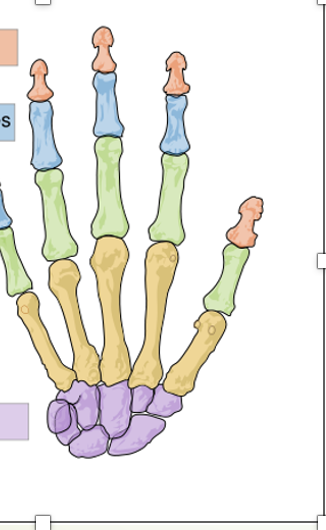
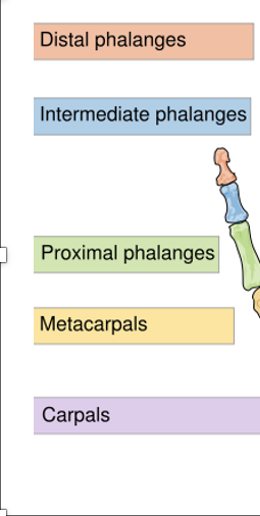
Upper Limb Bones
Humerus, radius, ulna, carpals, metacarpals, and phalanges.
Lower Limb Bones
Femur, patella, tibia, fibula, tarsals, metatarsals, and phalanges.
Long Bone Structure
Shaft (diaphysis) and ends (epiphyses) covered by articular cartilage.
Diaphysis
Hollow cylinder of compact bone surrounding a cavity with yellow bone marrow.
Epiphyses
Compact bone on the outside, spongy/cancellous bone on the inside containing red bone marrow.
Spongy bone
less dense, porous type of bone tissue found within the interior of bones.
Compact bone
the hard, dense outer layer of bones throughout the human bond, providing strength and protection
Periosteum
Dense, white, fibrous connective tissue covering the outer surface of bone.
Compact Bone microscopic structure
Consists of units called osteons or haversian systems.
What type of structure is bone?
it is a connective tissue
What is matrix?
the cells seperating from each other by large amounts of non-cellular material
What is the function of this matrix?
Inorganic salts (e.g. calcium) are deposited into matrix à increase rigidity and strength
What is an osteon and its structure? What is the other name with which they are referred to?
the units within compact bone
Haversian system
at the centre of each osteon, there is a central canal
Lamalle
the central canal within the osteon that is surrounded by concentric layers of bony matrix called lamellae.
Lacunae
Small spaces between lamellae that contain osteocytes (bone cells).
Canaliculi
Tiny canals running between lacunae, allowing bone cells to contact adjacent cells and pass materials.
- it always contains at least 1 blood capillary, and sometimes nerves and lymph capillaries.
Spongy (Cancellous) Bone
Irregular arrangement of thin, bony plates called trabeculae.
the osteocytes occupy spaces within the trabeculae
Not arranged in osteons
Matrix in spongy bone
not arranged in concentric layers
nerves, blood vessels pass through irregular spaces in matrix
Osteoblasts
bone cells that form new bones, grow and heal old ones
osteoclasts
bone cells that break down old bone tissue
calcification
refers to the buildup of calcium salts in tissues, which can harden them.
occurs withthe deposits of calcium phosphates in the matrix.
Ossification
Bones of embryos are largely made of cartilage and are soft.
these provide a template for ossification
cartilage undergoes calcification
chondrocytes die to lack of nutrients
osteoblasts lay down bone on the disintegrating calcified cartilage template.
label
Epiphyseal Line
The fusing of the diaphysis and epiphysis, indicating the bone can no longer increase in length.
Epiphyseal (Growth) Plate
Site of increase in bone length.
Bone Remodelling
Constant process of bone breakdown by osteoclasts and new bone creation by osteoblasts.