Price Elasticity of Demand
1/21
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Price Elasticity of Demand Definition
When price of a good inc. quantity demanded decr.
When price of a good decr. quantity demanded inc.
Units of price elasticity
No units as it’s a ratio, so use a percentage or proportionate changes
Price Elasticity Equation
% change in quantity demanded / % change in price
Why is price elasticity always -ve?
Price and quantity move in opposite directions
Arc Elasticity Equation
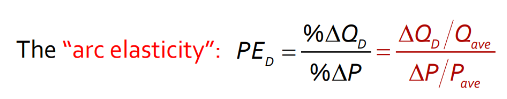
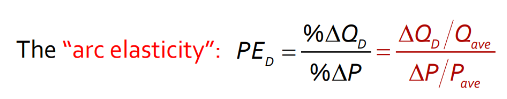
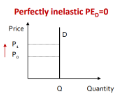
Perfectly Inelastic Demand
PED = 0
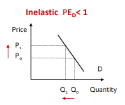
Inelastic Demand
PED < 1
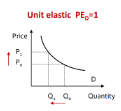
Unit Elastic Demand
PED = 1
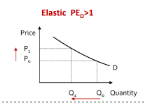
Elastic Demand
PED > 1
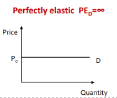
Perfectly Elastic Demand
PED = Infinity
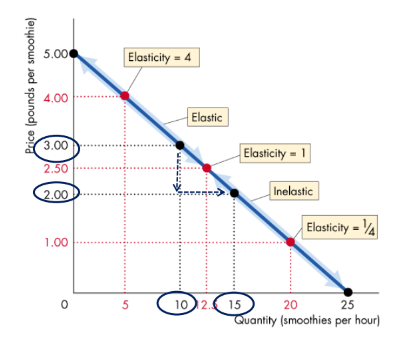
How does the Price Elasticity of Demand change along a linear demand curve?
Prices above average are greater than 1, prices below average are less than 1
Total Revenue Equation
Price of a good/service multiplied by the quantity sold (TR = P*Q)
Impact of Elasticity of demand on total revenue
When demand is elastic, a price cut increases revenue
When demand is inelastic, a price cut decreases total revenue
When demand is unit elastic, it equals the maximum total revenue
Factors that Influence the Elasticity of Demand
Closeness and availability of substitutes
Perfect substitutes e.g. printer paper, means when one place incr. price, overall demand falls as there’s a perfect alternative
Other things e.g. newspapers, not as easily substituted
Time elapsed since a price change
Proportion of income spent on a good
Price of a good in relation to a consumer’s budget
Cross elasticity of demand definition
It measures the responsiveness of demand for a good to a change in the price of a substitute or a complement, all other things remaining the same
For a substitute good, it’s +ve
For a complement good, it’s -ve
Cross elasticity of demand equation

Income elasticity of demand definition
Measures how the quantity demanded of a good changes in response to a change in income, all else being constant
Income elasticity of demand formula
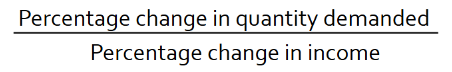
What happens as the value of income elasticity changes?
If income elasticity >1:
As income incr., income spent on goods incr.
In income elasticity is between 0-1:
As income incr., income spent on good decr.
If income elasticity <0:
Quantity demanded decr. and income incr.
Elasticity of supply definition
It’s a measure of the responsiveness of the quantity supplied to a change in the price of a good, when all other influences and selling plans remains the same.
Elasticity of supply equation
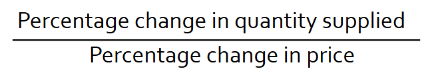
Determinants of elasticity of supply
Resource substitution possibilities
The easier it is to substitute among the resources used to produce a good or service, the greater the elasticity of supply
Time frame for supply decision
As more time passes after a price change, the greater the elasticity of supply
Momentary supply is perfectly inelastic, as the quantity supplied immediately following a price change is constant
Short-run supply is somewhat elastic
Long-run supply is mostly elastic