TV4101 - Haemostasis 3
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
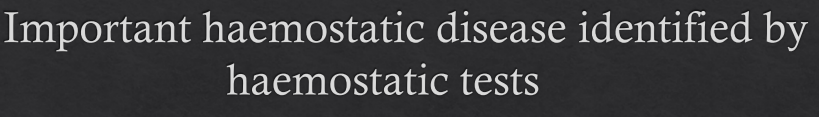

Primary Haemostasis - Broad issues
PLT #?
PLT #

Primary Haemostasis
Cause affecting PLT # i.e. Thrombocytopaenia
Causes? In what way?

Primary Haemostasis
Cause affecting PLT # i.e. Thrombocytopaenia
Immune version aka?
Prevalence in who?
Severity?
#PLT?
Immune mediated thrombocytopenia (IMT)
Platelet destruction
Common in dogs, but also documented in cats & horses
Severe thrombocytopenia
< 3 platelets /hpf (100x)
Primary Haemostasis
Cause affecting PLT # i.e. Thrombocytopaenia
Bracken Fern (Ruminants)
What do we see physically in calves?
Primary Haemostasis
Cause affecting PLT # i.e. Thrombocytopaenia
Diseases in ruminants?
What are their respective blood profiles?


Primary Haemostasis
This cow had vulvar haemorrage
What do we suspect?
Bracken poisoning
Primary Haemostasis
Cause affecting PLT # i.e. Thrombocytopaenia
Ruminants
How does this relate to food?
Poorly stored grain can lead to contamination with
trichothecene mycotoxins
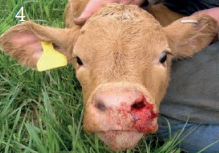
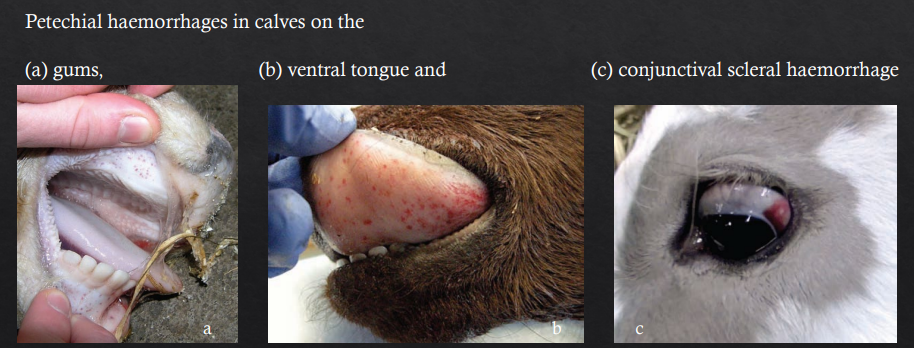
Primary Haemostasis
Cause affecting PLT # i.e. Thrombocytopaenia
Ruminants
What can we see?
Suspected dz?
Epistaxis from thrombocytopaenia
Bleeding calf syndrome/Bovine neonatal pnacytopaenia
Primary Haemostasis
Cause affecting PLT # i.e. Thrombocytopaenia
Bracken Fern
What does it cause?
Acute haemorrhagic syndrome ass. with leukopaenia, thrombocytopaenia and anaemia
Bovine enzootic haematuria with severeal urinary bladder tumours
Primary Haemostasis
VWD
Function of vWB factor?
1. Platelet adhesion
- damaged blood vessels
- Platelets to each other
2. Stabilising & protective carrier molecule
Primary Haemostasis
VWD
What does it causein terms of blood cells? What way?
Thrombocytopaenia - abnormal PLT function from vWF deficiency
Primary Haemostasis
VWD
Prevalence?
Most common hereditary bleeding disorder in dogs
Rare in cats, horses & cattle
Primary Haemostasis - Which breeds are most commonly affected by VWD? List a few
Poodle
GSD
Corgi
Doberman
Golden Retriever
Rough collie
Primary Haemostasis - VWD
Diff types, severity and breeds?

Primary Haemostasis - VWD
CX?
Prolonged haemorrhage from nonsurgical or surgical trauma
Dogs: usually present at young age with excessive bleeding with teething or spaying/neutering
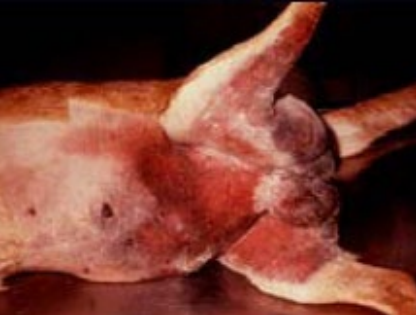
Primary Haemostasis - VWD
Pattern of haemorrhage?

Primary Haemostasis - VWD
Lab signs?

2ndary Haemostasis
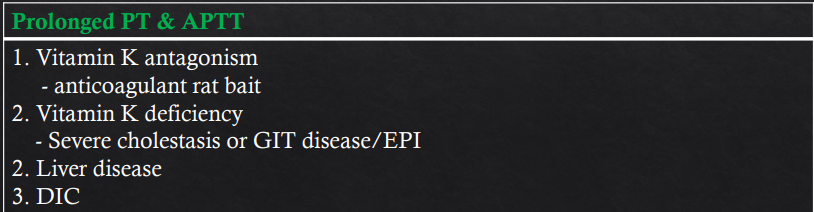
Acquired defects?
PT and APTT features?
2ndary Haemostasis
Inherited Aspects and their respective PT or APTT changes
Factor VII def - Prolonged PT
Factor XII, XI, IX, VIII deficiency - Prolonged APTT
Factor X, Factor V, prothrombin, fibrinogen or combined factor deficiency - Prolonged PT & APTT
2ndary Haemostasis - Inherited Haemophilia
Types?
Signalment?
What happens?
DX tests?
Haemophilia A (factor VIII def)
Haemophilia B (factor IX def
Male (female carriers)
Spontaneous bleeds
- bleeding into body cavities
- haematomas
- haemarthroses
- epistaxis
Diagnostic tests
- Prolonged ACT & APTT

2ndary haemostasis - Acquired coag factor deficiencies (usually multiple factors)
Includes?

2ndary haemostasis - Acquired coag factor deficiencies (usually multiple factors)
DX tests? In which order?
Increased PT (first) & then APTT
2ndary haemostasis - Acquired coag factor deficiencies (usually multiple factors)
Anticoagulant Rodenticides
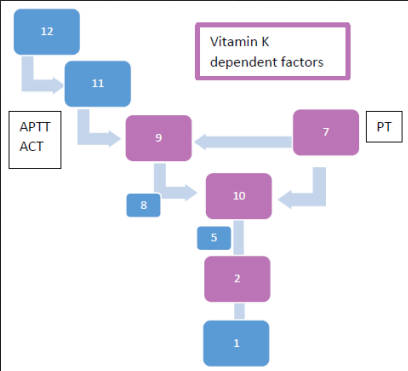
How does it work?
Vit K absent/antagonised by poison → Vit K needed to carboxylate/activate factors II, VII, IX, X → Can’t be activated → Relative factor def due to inactivity
Carboxylation of these clotting factors is necessary to bind phospholipid membrane
surfaces in a Ca2+-dependent manner
2ndary haemostasis - Acquired coag factor deficiencies (usually multiple factors)
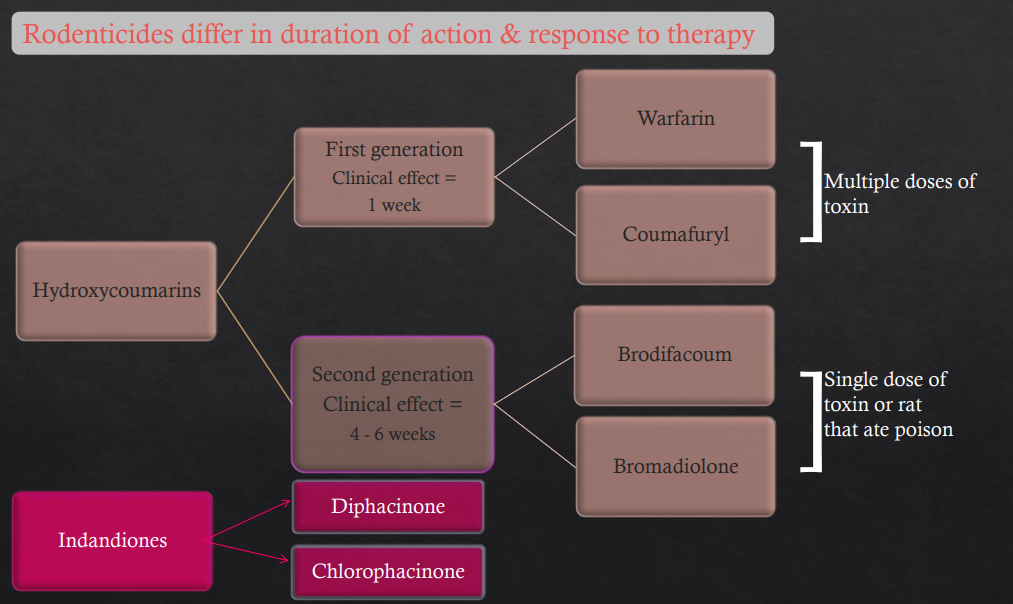
Anticoagulant Rodenticides (Vit K antagonism)
The different types, time to take effect and examples
Hydroxycoumarins
First gen - 1 wk to take effect (Multiple doses needed)
Warfarin
Coumafuryl
2nd gen - 4-6wks to take effect (Single dose or eat rat that ate poison)
Brodifacoum
Bromadiolone
Indandiones
Similar to 2nd gen
Diphacinone and Chlorophacinone
2ndary haemostasis - Acquired coag factor deficiencies (usually multiple factors)
Anticoagulant Rodenticides
Basic Overview

2ndary haemostasis - Vitamin K deficiciency
Significance?
Describe Vit K behaviour?
Deficiency with?
(usually multiple factors def, rarely deficient enough to cause haemorrhage)
Vitamin K is fat soluble - need bile (liver), functioning GIT and Pancreas
• Cholestatic hepatopathy
• GIT pathology (fat malabsoption/maldigestion)
2ndary haemostasis - Vitamin K deficiciency
What tests are done?

2ndary haemostasis - Acquired coag factor deficiencies (usually multiple factors)
Liver Dz
Liver disease can result in haemostatic disease due to?
1. Cholestatic hepatopathy (Vit K def)
2. Acute or fulminant liver disease ending in DIC
3. Coagulation Factor Deficiencies
2ndary haemostasis - Acquired coag factor deficiencies (usually multiple factors)
Liver Dz
Bleeding aspect?
Cat bleeding aspects?
Tests for dog?
Bleeding uncommon but can occur with severe liver disease
Cats with major complications – association with APTT > 1.5 x mean of reference interval
Predicative value of haemostatic tests for bleeding during biopsy in dogs not good
2ndary haemostasis - Acquired coag factor deficiencies (usually multiple factors)
Liver Dz
Even though bleeding is uncommon for liver dz, Bleeding complications in dogs & cats – more strongly associated with ?
What else can be abnormal in liver dz?
Thrombocytopenia than prolonged PT & APTT
Platelet number or function can also be abnormal
2ndary haemostasis - Acquired coag factor deficiencies (usually multiple factors)
Liver Dz
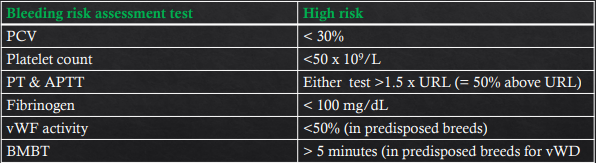
Tests to determine risk of blleding complications in dogs with chronic hepatitis? What are the high risk values?
2ndary haemostasis - Acquired coag factor deficiencies (usually multiple factors)
Liver Dz
Lab tests
Coagulation panel shows? What does this mimic?
Thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopathy
Prolonged BMBT
Prolonged PT, APTT, ACT,
TT prolonged [fibrinogen - decreased]
Increased FDP &/or D-dimer
Can mimic consumptive coagulopathy/DIC
2ndary haemostasis - Acquired coag factor deficiencies (usually multiple factors)
DIC
aka?
How does it occur?
Disseminated intravascular coagulation
Always secondary to another disease process - trigger
2ndary haemostasis - Acquired coag factor deficiencies (usually multiple factors)
DIC
How does it work?
2ndary haemostasis - Acquired coag factor deficiencies (usually multiple factors)
DIC
What tests are done?