2.1.1 - 2.1.5 PLTW
5.0(4)Studied by 39 people
Card Sorting
1/148
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:21 AM on 2/15/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
149 Terms
1
New cards
primary care physician
provide care for any health problems that a patient might have; usually the first contact for a person with a basic health concern; provides routine checkups and physicals, and care to those with chronic, or persistent and long-lasting, illnesses.
2
New cards
chronic illness
A disease or condition that usually lasts for 3 months or longer and may get worse over time.
3
New cards
medical student
a person enrolled in medical school who is training to become a physician
4
New cards
medical assistant
Unlicensed caregiver who works primarily in doctors' offices and clinics. They assist their medical director through a wide variety of duties.
5
New cards
nurse
licensed healthcare professional who is skilled in promoting and maintaining health
6
New cards
medical technician
Uses sophisticated equipment and has different responsibilities. Some work directly with patients while others work in a lab.
7
New cards
patient liasion
Works with patients and their families to address needs and concerns. Acts as an intermediary between patients, their families and the hospital administration.
8
New cards
non-physician practicioner
health care provider who practices either in collaboration with or under the supervision of a physician
9
New cards
pediatrician
A specialist physician who provides medical care to infants, children, and adolescents.
10
New cards
medical history
A record of information about a patient’s past and current health. Includes information about the patient’s habits, lifestyle, and even the health of their family.
11
New cards
chief complaint
The patient’s description of what they feel is their main health problem.
12
New cards
physical signs
Pieces of evidence that indicate an illness that can be observed externally, such as a rash, coughing, or elevated temperature.
13
New cards
symptoms
Any subjective evidence of disease a patient perceives, such as aches, nausea, or fatigue. Allow the health care provider to narrow down the possible conditions that may be affecting the patient and then run tests to make a diagnosis.
14
New cards
diagnosis
The process of determining which disease or condition explains a person’s symptoms and signs.
15
New cards
current history
Patient’s chief complaint and any other current health issues, symptoms, and any treatments or tests the patient has recently had or is scheduled to have related to these conditions. Nutrition, allergies, medication, and health habits, such as exercise are also part of the patient’s current history.
16
New cards
previous history
Includes information about any past health issues, procedures, medications, vaccinations, and previous hospital stays.
17
New cards
social history
Addresses aspects of the patient’s life, such as living situation, occupation, school, travel, and other activities that could have a direct or indirect impact on health.
18
New cards
family history
Includes medical information about the patient’s close relatives.
19
New cards
demeanor
Outward behavior or bearing. A doctor might have a cheerful, peaceful, or friendly demeanor and put the patient at ease. (CHEERFUL)
20
New cards
Tact
Discretion and sensitivity in dealing with others. When doctors choose their words carefully so as to not upset a patient when they must deliver bad news. (SENSITIVE)
21
New cards
empathy
The ability to understand and share the feelings of another person. (UNDERSTANDING)
22
New cards
vital signs
Measurements—specifically pulse rate, temperature, respiration rate, oxygen saturation, and blood pressure—that indicate the state of a patient’s essential body functions.
23
New cards
homeostasis
The maintenance of stable internal physiological conditions (like body temperature or the pH of blood), which enables the optimal functioning of an organism.
24
New cards
triage
The sorting and prioritization of patients based on the urgency of their need for care.
25
New cards
pulse
number of heart beats in one minute
26
New cards
how is pulse measured
with a in BPM (beats per minute)
27
New cards
respiratory rate
number of breaths taken per minute
28
New cards
how is respiratory rate measured
in BPM (breaths per minute)
29
New cards
blood pressure
the force of blood moving through blood vessels
30
New cards
how is blood pressure measured
with a sphygmomanometer in mm Hg (millimeters of mercury)
31
New cards
Body mass index (BMI)
a measure of body fat that is the ratio of the weight of the body to its height
32
New cards
how is BMI calculated
(weight (lbs) / \[height (in)\]² x 703
33
New cards
oxygen saturation (SpO2)
the amount of oxygen in the blood
34
New cards
how is oxygen saturation measured
as a percentage % using a pulse oximiter
35
New cards
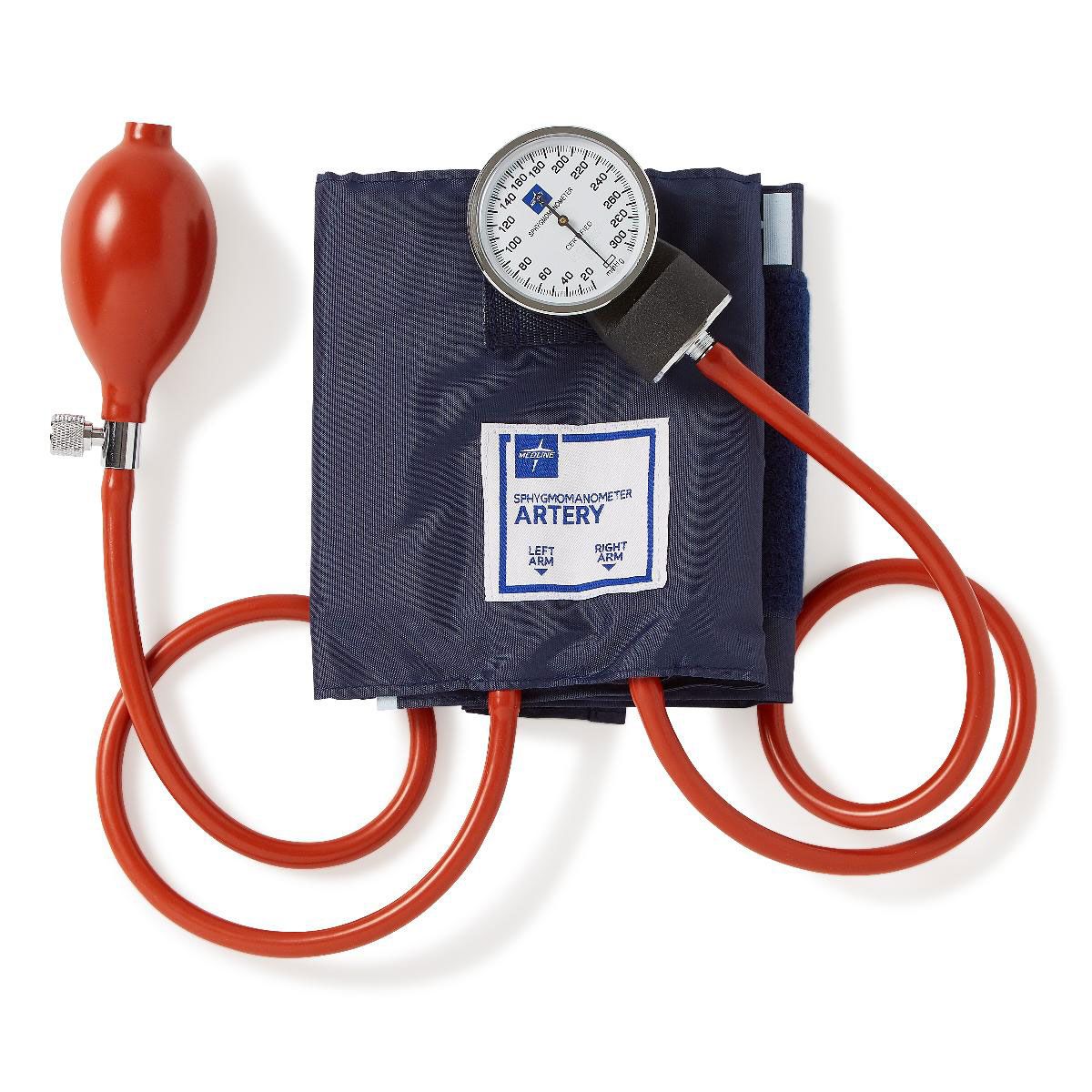
what is this and what does it measure
Its a sphygmomanometer and it measures blood pressure
36
New cards
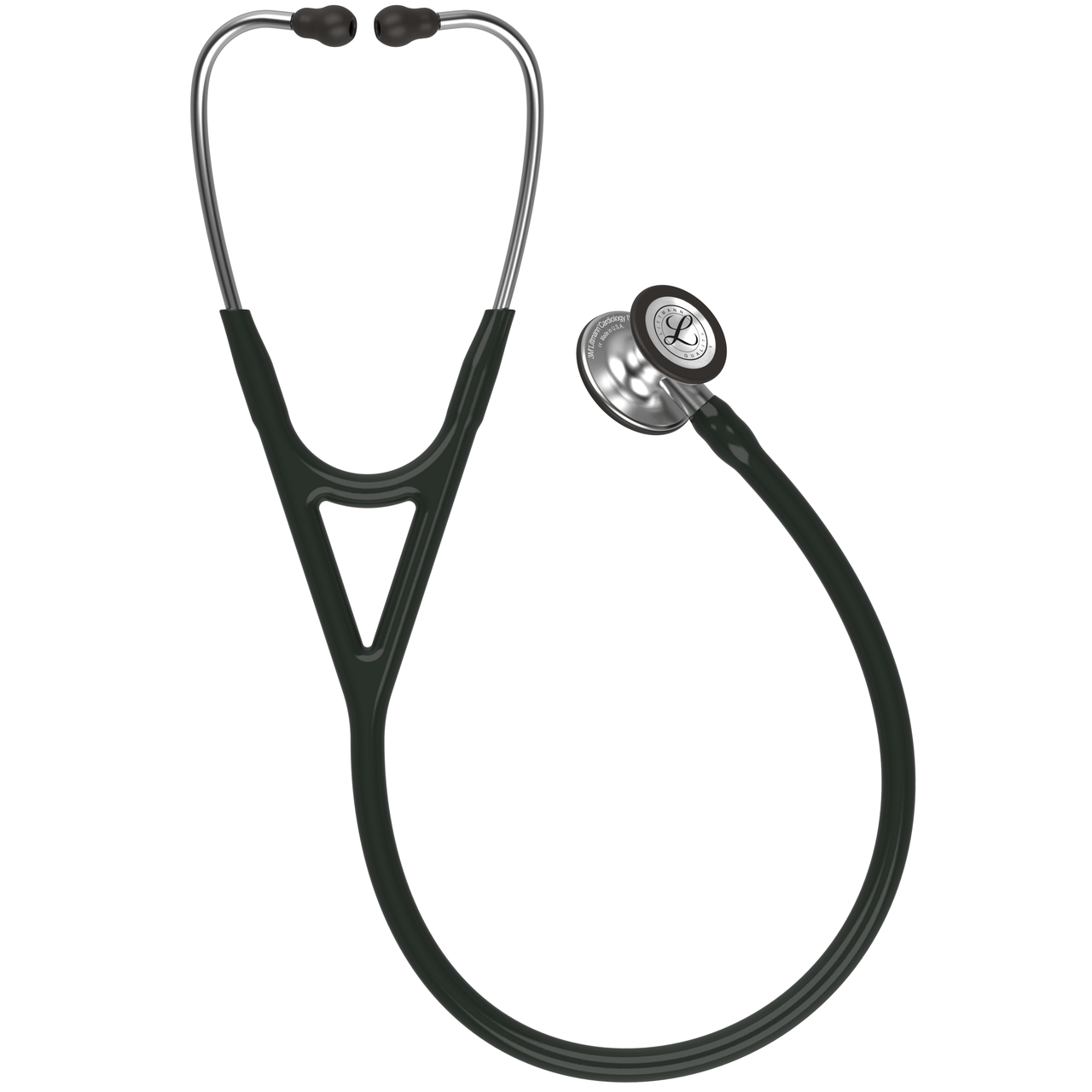
what is this and what does it measure
its a stethoscope and it measures lungs/breathing sounds
37
New cards

what is this and what does it measure
its a calculator and it measures body mass index (BMI)
38
New cards
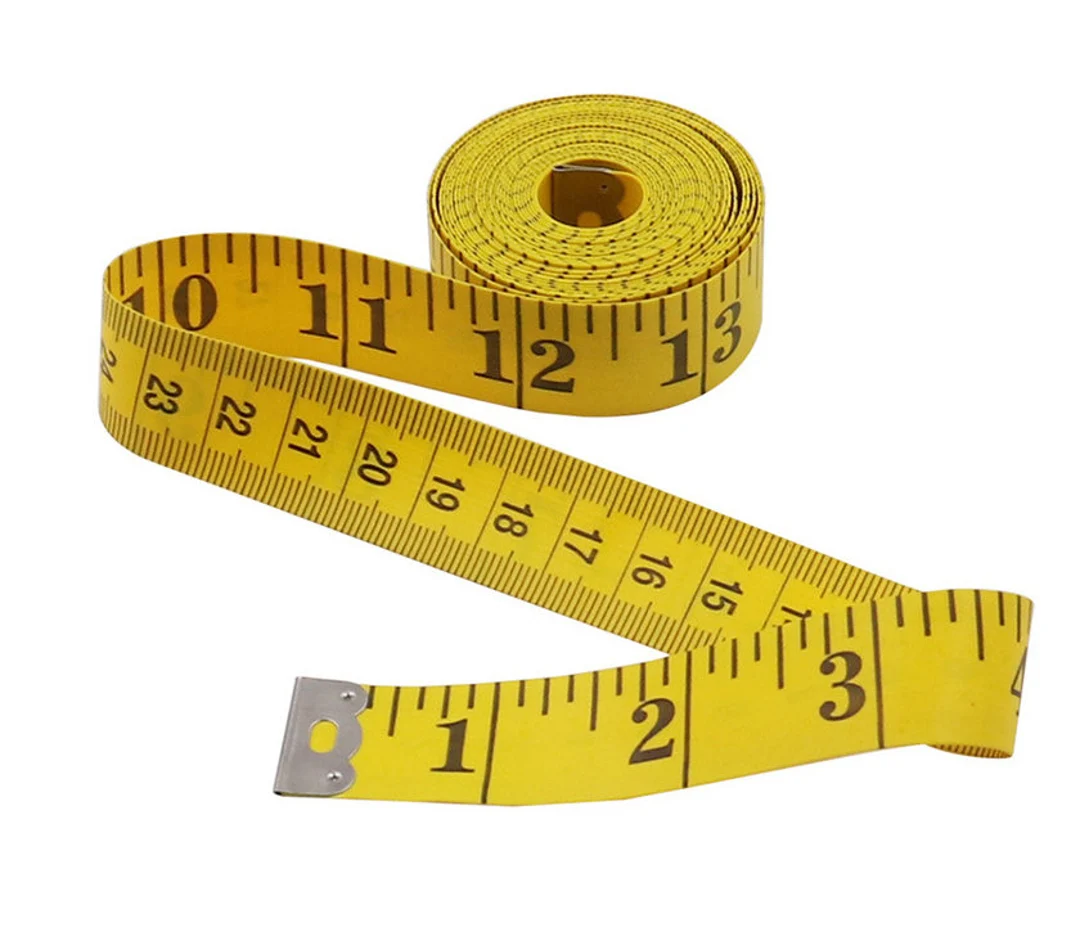

what is this and what does it measure
its a measuring tape and it measures height
39
New cards
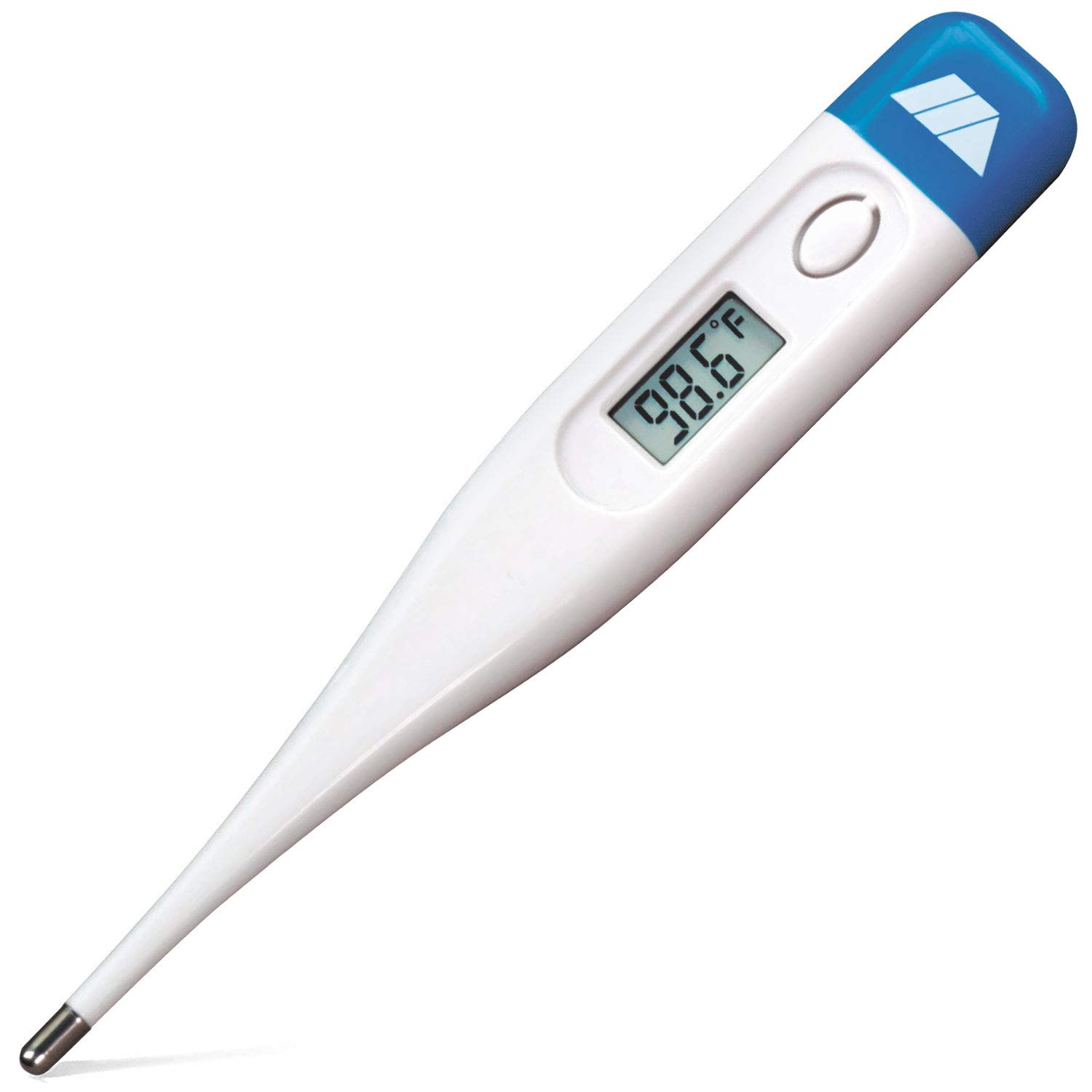
what is this and what does it measure
its a thermometer and it measures body temperature
40
New cards
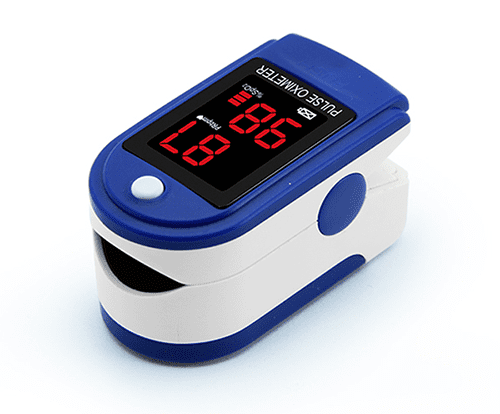

what is this and what does it measure
its a pulse oximeter and it measures oxygen saturation (SpO2)
41
New cards
licensed practical nurse (LPN)
provides patient care under the supervision of an RN, nurse practitioner, clinical nurse specialist, physician, dentist, or podiatrist. They provide bedside nursing care and emotional support to patients.
42
New cards
registered nurse (RN)
provide and coordinate patient care, educate patients and the public about various health conditions, and provide advice and emotional support to patients and their families.
43
New cards
nurse practitioner (NP)
registered nurses who work to diagnose and treat patients who are ill. Their extensive qualifications enable them to examine patients, diagnose illnesses, prescribe medication and treatment and ensure quick recoveries. They either work alone or with a variety of other medical professionals.
44
New cards
what is the normal range for body temperature in an adult
97\.8 to 99 °F
45
New cards
what is the normal range for an adults heart rate
60-100 beats per minute (BPM)
46
New cards
what is the normal range for an adults respiratory rate
12-20 breaths per minute (BPM)
47
New cards
what is the normal range for an adults oxygen saturation
95-99%
48
New cards
what is the normal blood pressure range for an adult
__less than 120__ mm Hg
less than 80
less than 80
49
New cards
where can the pulse be measured
in the carotid or radial arteries
50
New cards
where is the carotid artery
either side of the neck
51
New cards
where is the radial artery
wrists
52
New cards
systolic pressure
The pressure in the arteries when the heart is pushing blood throughout the body.
53
New cards
diastolic pressure
The pressure in the arteries when the heart is at rest and not pumping blood
54
New cards
where is the blood pressure measured
the brachial artery
55
New cards
where is the brachial artery
bicep
56
New cards
hypertension
An abnormally high blood pressure.
57
New cards
prehypertension
__120-129__
less than 80
less than 80
58
New cards
hypertension stage 1
__130-139__
80-89
80-89
59
New cards
hypertension stage 2
__140 or higher__
90 or higher
90 or higher
60
New cards
hypertensive crisis
__higher than 180__
higher than 120
higher than 120
61
New cards

what is this and what does it test
this is a snellen eye chart that tests visual acuity
62
New cards
first number (visual acuity)
Distance (in feet) that you stand from the chart
63
New cards
second number (visual acuity)
Distance (in feet) at which a person with normal eyesight could read the same line you read correctly.
64
New cards
how do medical professionals examine the external anatomy of an eye
with an ophthalmoscope
65
New cards
cornea
the outermost layer of your eye. It is clear and shaped like a dome. helps to shield the rest of the eye from germs, dust, and other harmful matter. It also helps your eye to focus.
66
New cards
pupil
helps control the amount of light entering the eye
67
New cards
retina
light sensitive tissue at the back of the eye that processes images and converts them into nerva signals
68
New cards
how do doctors examine the ear
with an otoscope
69
New cards
Erythrocytes
red blood cells
70
New cards
Leukocytes
white blood cells
71
New cards
Thrombocytes
platelets
72
New cards
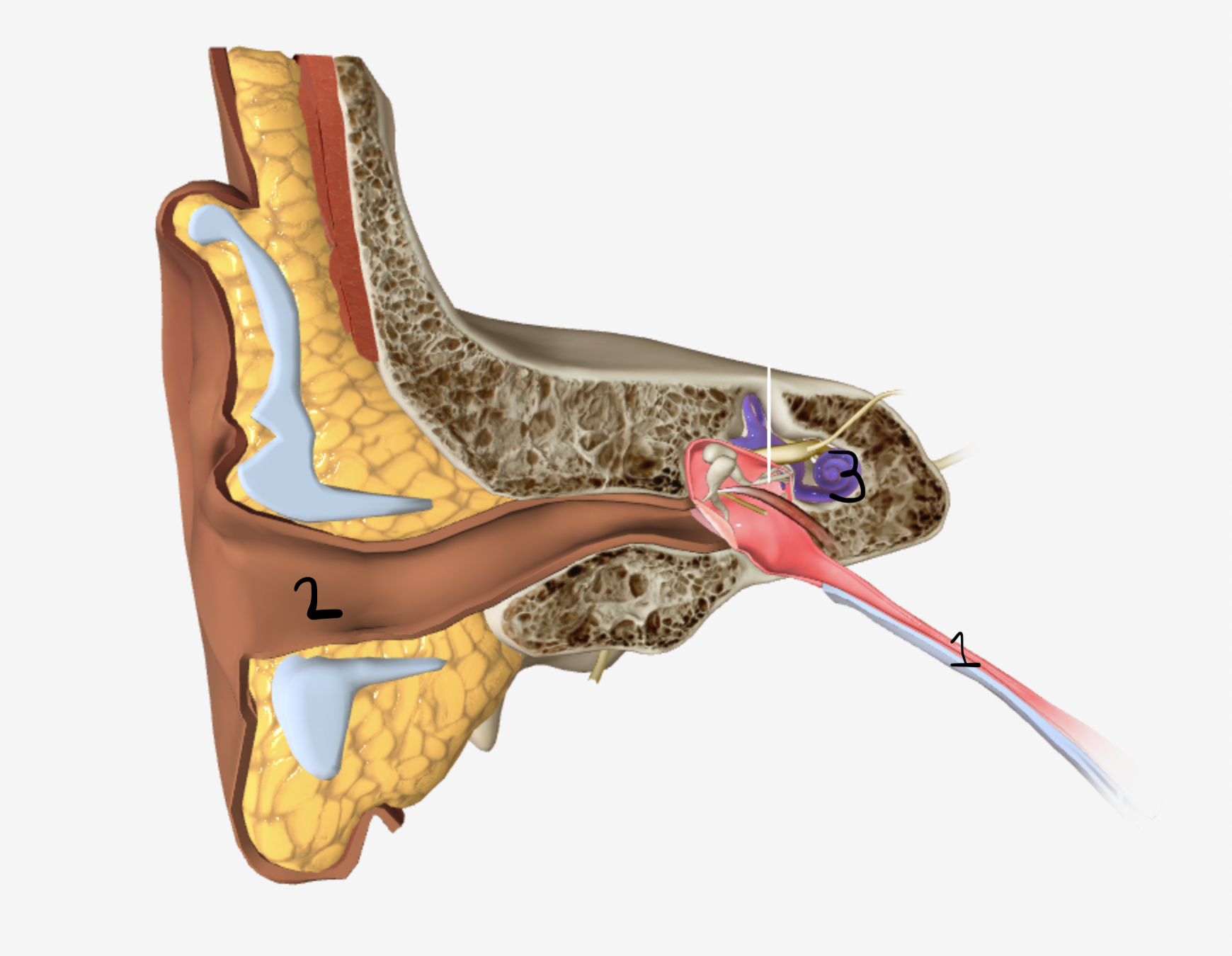
Which part of the ear is shown by #1
eustachian tube
73
New cards
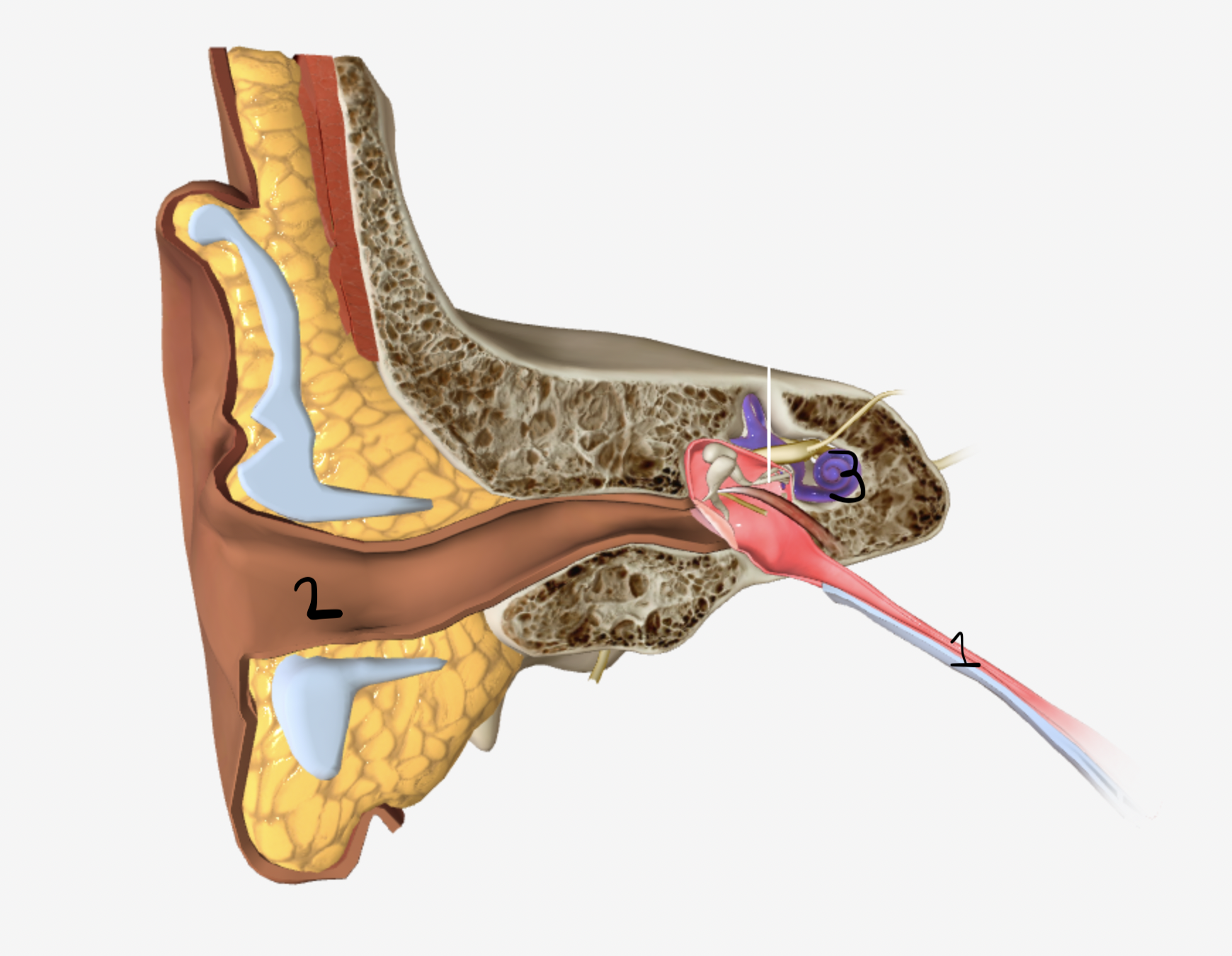
which part of the ear is shown by #2
ear canal
74
New cards
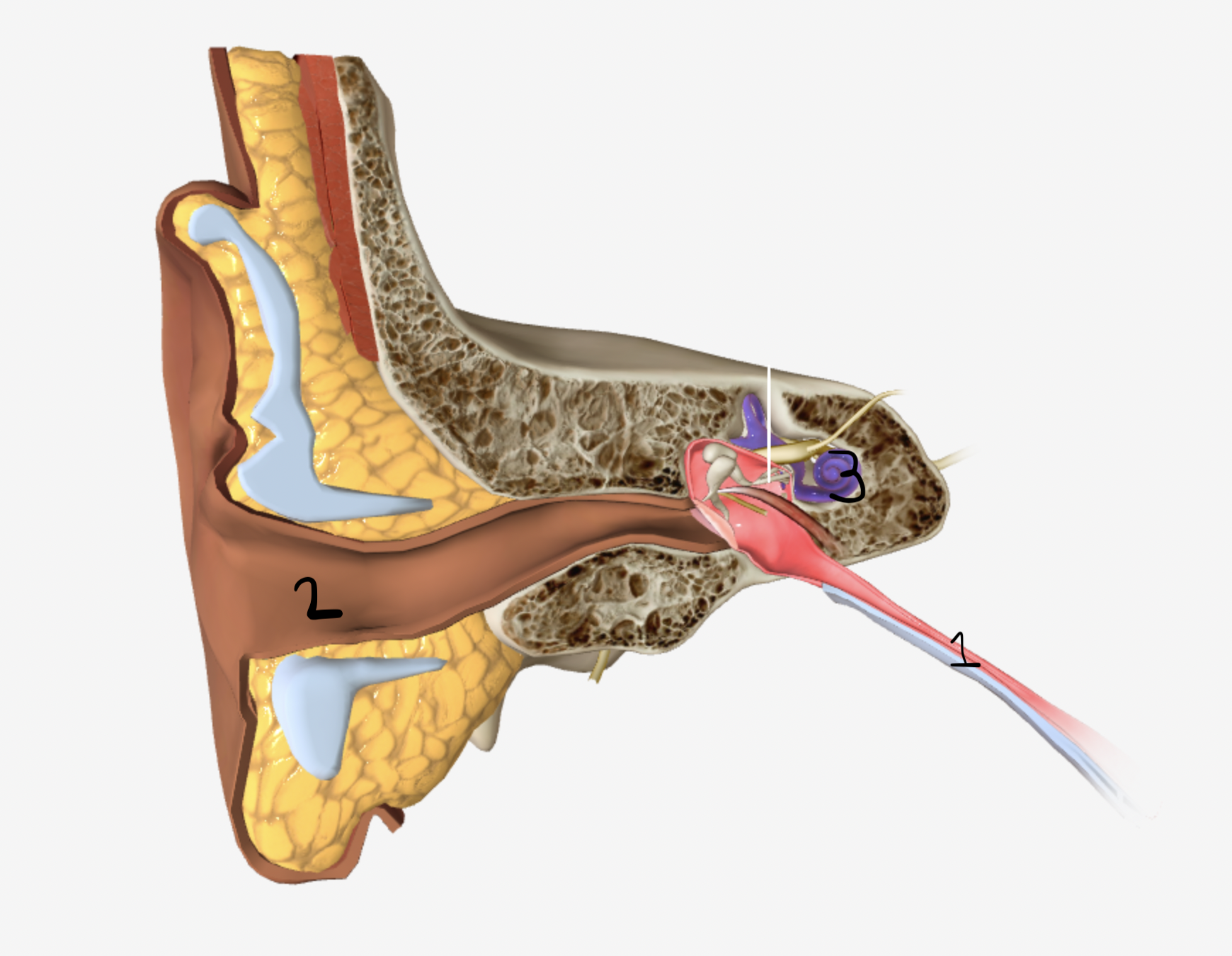
which part of the ear is shown by #3
cochlea
75
New cards
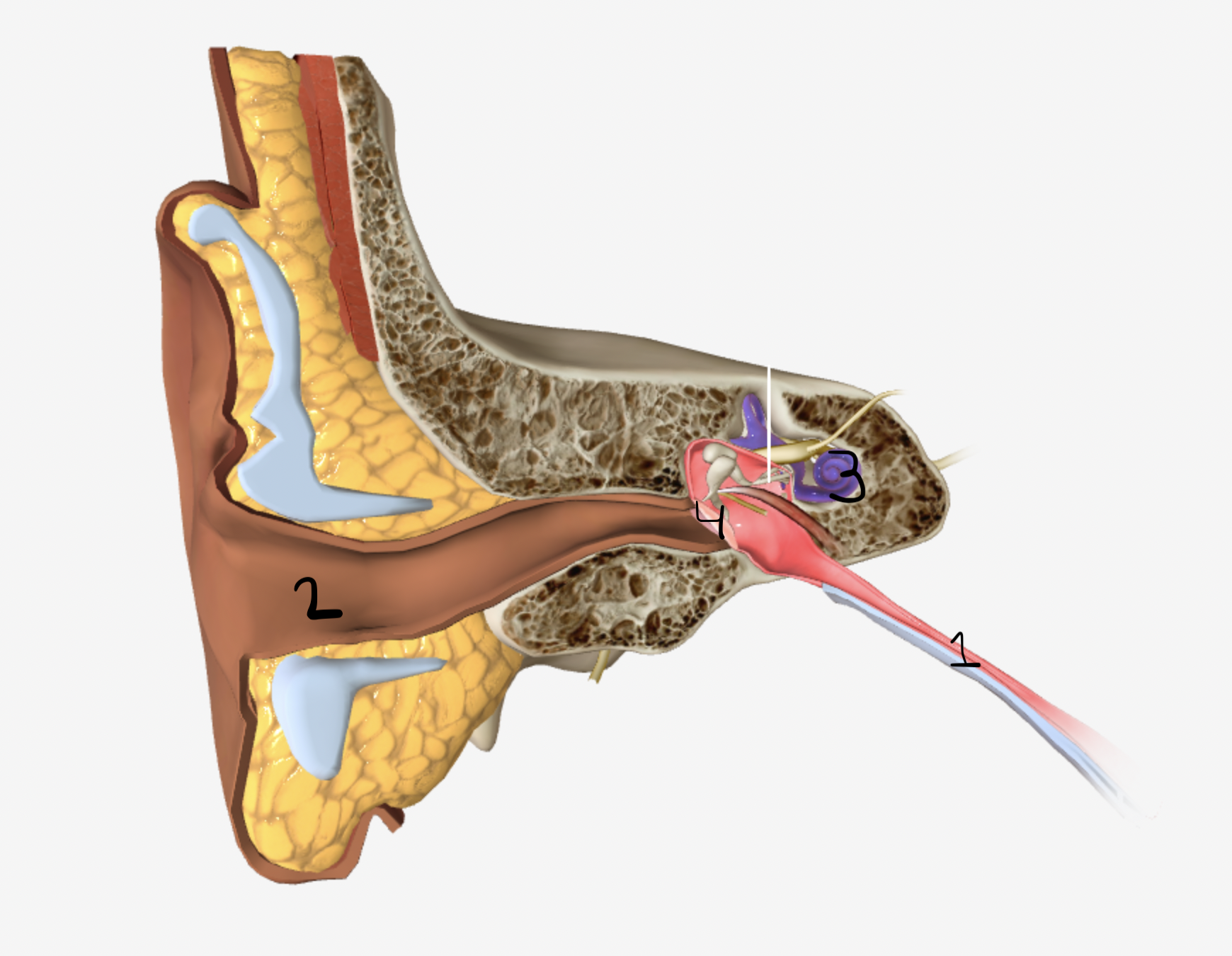
which part of the ear is shown by #4
tympanic membrane
76
New cards
what tool do doctors use to examine nasal passages
an otoscope
77
New cards
what do tonsils do
work in the lymphatic system and help to fight infections
78
New cards
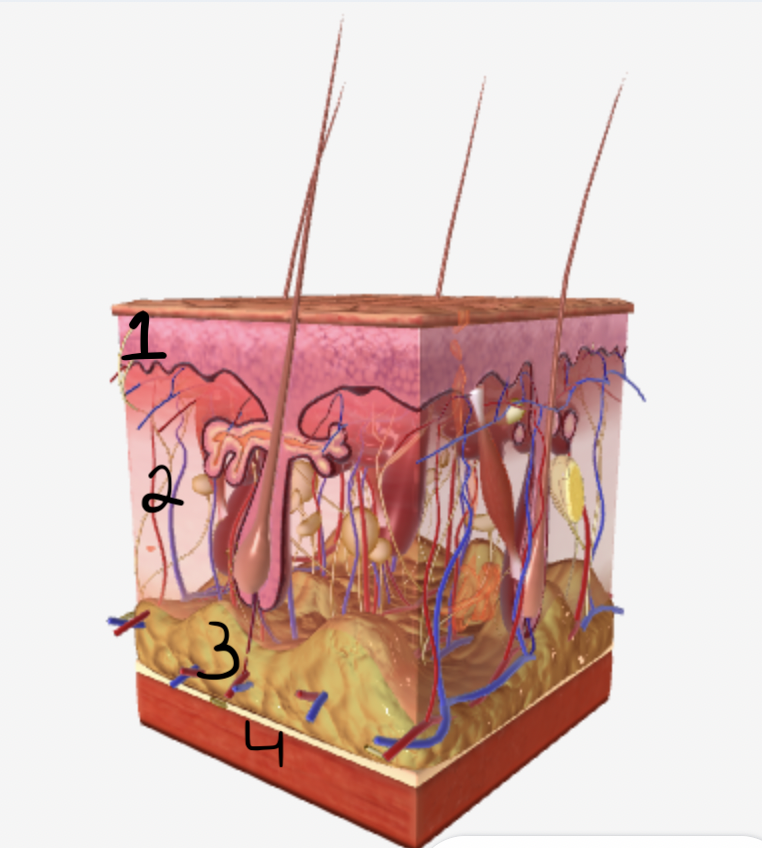
which part of the skin does #1 show
epidermis
79
New cards
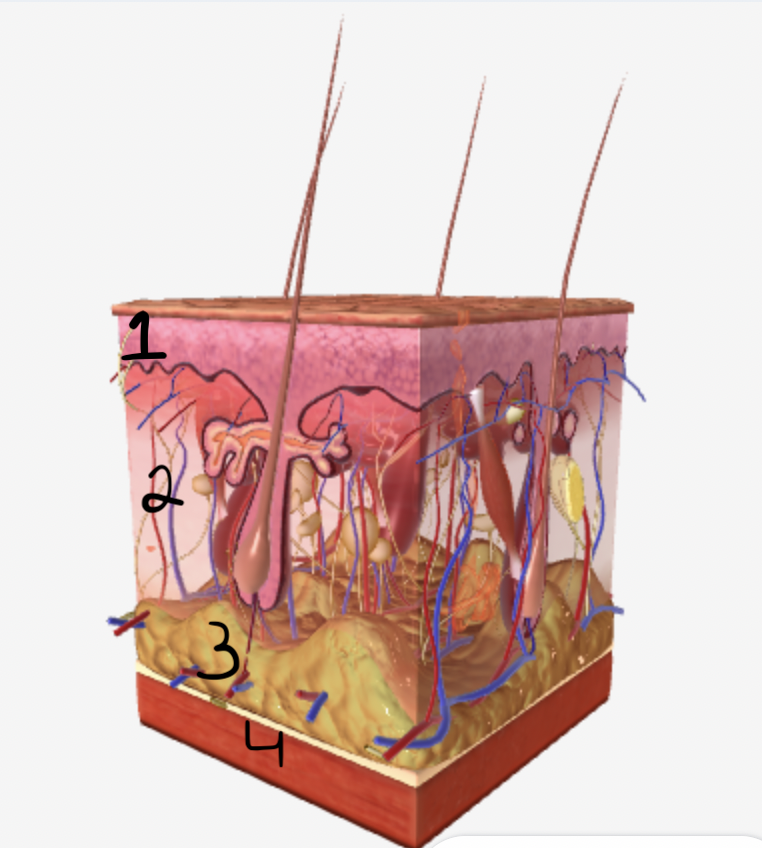
which part of the skin does #2 show
dermis
80
New cards
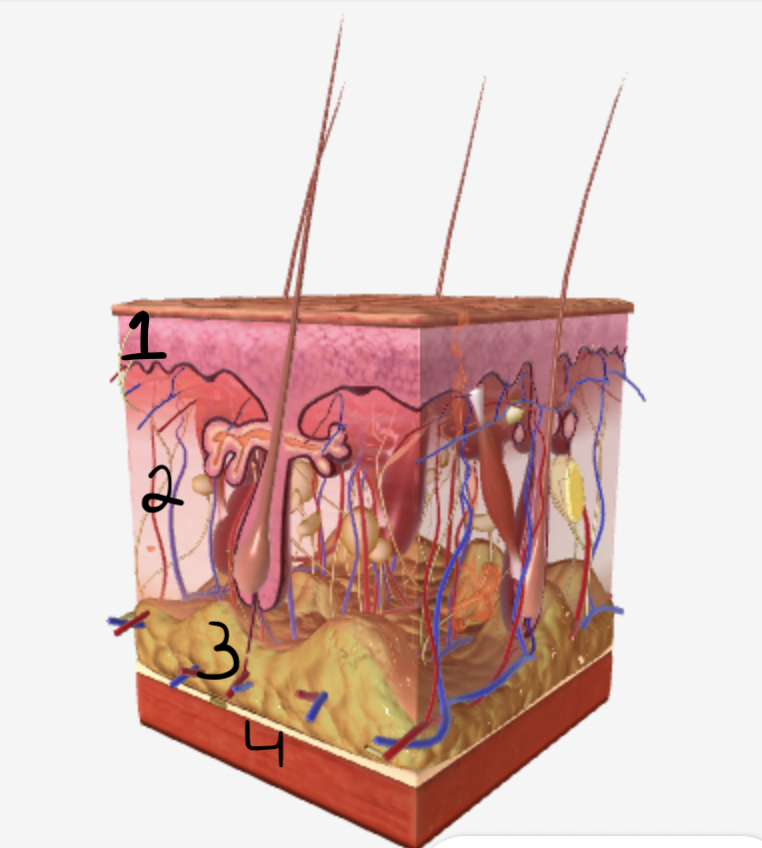
which part of the skin does #3 show
subcutaneous fatty tissue
81
New cards
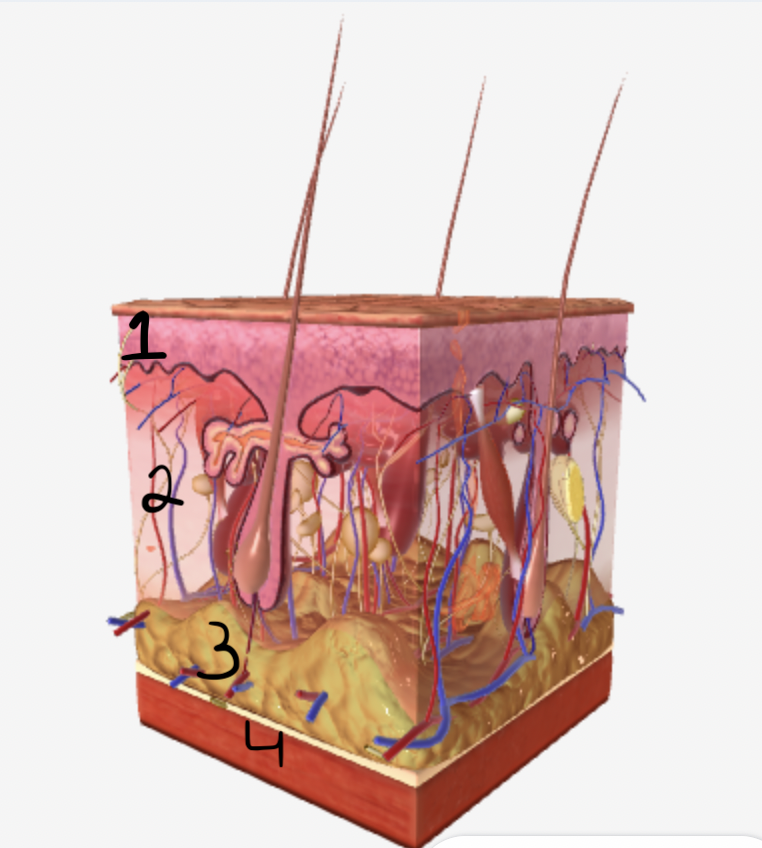
which part of the skin does #4 show
muscle fibers
82
New cards
what system do dermatologists refer to when examining moles/growths on skin
ABCDE method
83
New cards
what does ABCDE stand for
asymmetry, borders, color, diameter, evolving
84
New cards
what does MVR stand for and what is it
it stands for mitral valve regurgitation and occurs when there is backflow from the left ventricle to left atria (mitral valve does not close properly)
85
New cards
clear breathing sounds
A clear woosh of air with each inhalation and exhalation.
86
New cards
wheezing sounds
A high-pitched whistling sound due to narrowed air ways
87
New cards
crackles (rales)
Short and intermittent clicking, rattling, or popping sounds heard during inhalation when air is forced through an airway narrowed by fluid.
88
New cards
stridor
Harsh, shrill sound, similar to wheezing, usually heard closest to the back of the neck, as it is caused by a partially obstructed windpipe.
89
New cards
rhonchi
A snore-like sound heard when airways are partially obstructed.
90
New cards
what does AOM stand for and what is it
it stands for acute otitis media and is an infection of the middle ear
91
New cards
Where do doctors typically draw blood from
the median cubital vein
92
New cards
93
New cards
what is a phlebotomist
a technician trained to draw blood from patients
94
New cards
too much cholesterol can be
a risk factor for heart disease
95
New cards
what are ways cholesterol can be produced
by being naturally produced by the liver, and being absorbed by food as it passes through the intestines.
96
New cards
what are examples of things cholesterol is needed to make
vitamins, hormones, cell membranes
97
New cards
what does CBC stand for and what does it measure
complete blood count and measures the amount of blood cells in our system
98
New cards
White blood cells (WBC)
The five types of cells that the body uses to fight infection and injury and maintain our health.
99
New cards
Red blood cells (RBC)
The cells that transport oxygen around the body.
100
New cards
Hemoglobin (HB/Hgb)
The oxygen-carrying protein in red blood cells.