Case 10: Sade A.
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
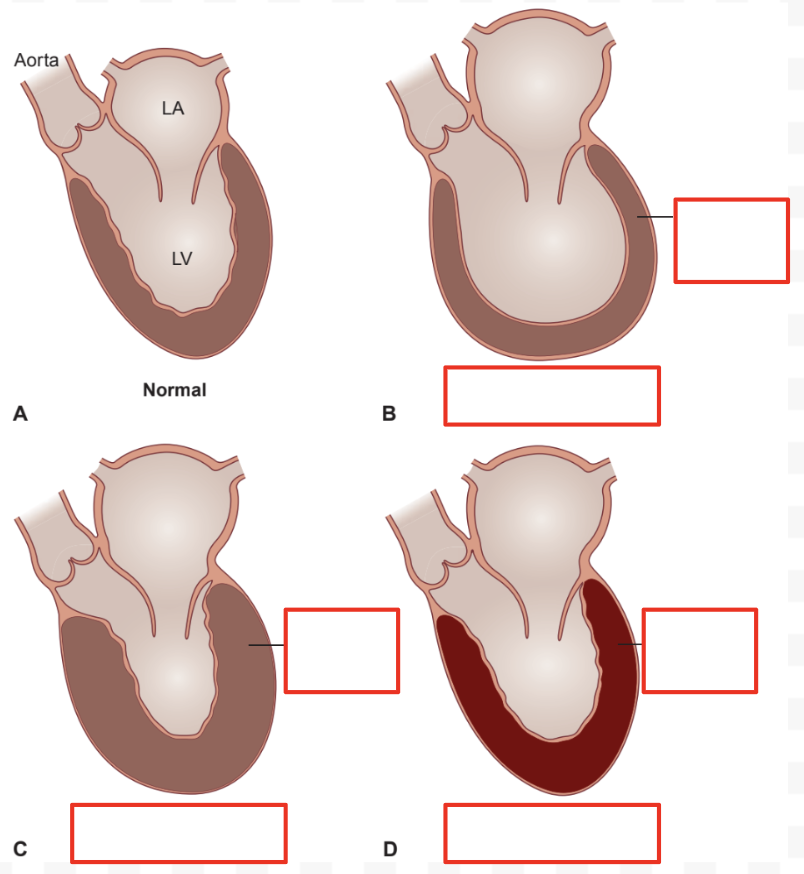
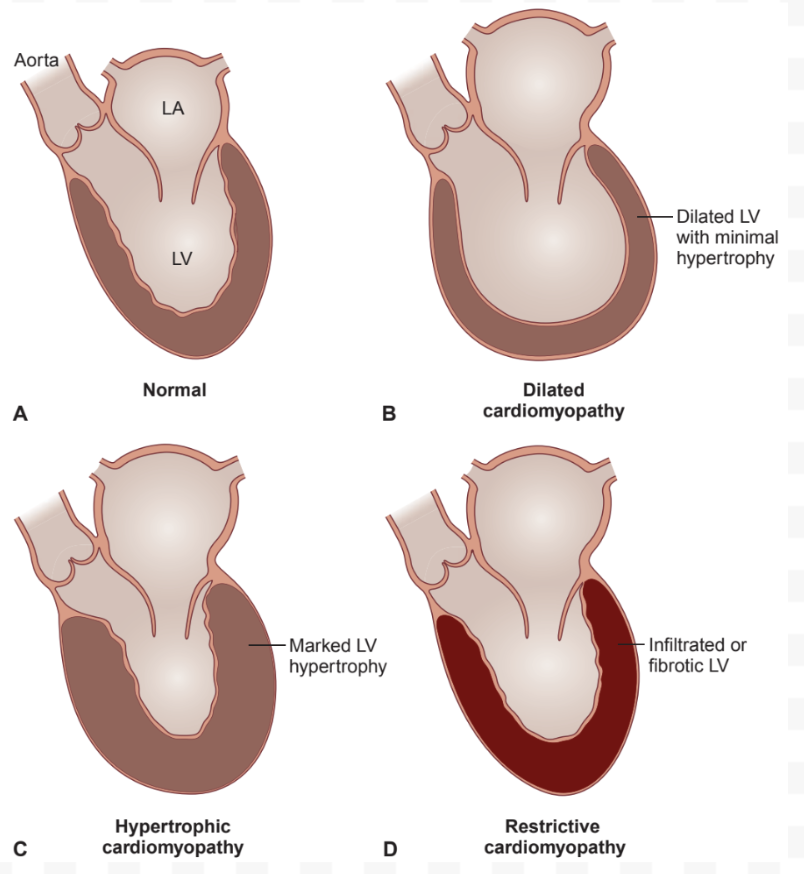
Cardiomyopathy (CM): Description
Heart muscle disorders
CM: Types
Dilated (DCM)
Hypertrophic (HCM)
Restrictive (RCM)
DCM: Description
Enlarged LV
Diastolic Function: Normal
Systolic Function: Decreased
HCM: Description
Thick ventricular wall
Concentric hypertrophy not from pressure overload
Diastolic Function: Decreased
Increased LV filling pressure
Systolic Function: Normal
RCM: Description
Stiff myocardium from fibrosis and infiltrative processes
Diastolic Function: Decreased
Systolic Function: Normal
DCM: Etiology
Primary: Idiopathic
Genetic abnormalities
Inflammatory myocarditis
Cocaine
DCM: Pathogenesis
Genetic:
Gene mutations cause abnormal proteins = Insufficient function
Compensatory myocardial stretch to increase CO = LV dilation + Decreased contractility = Alter force generation and transmission = Decrease SV and CO
Cell death
Start in LV, progress to RV
Acquired: Drugs suppress cardiac contractility and activate neurohormonal systems
DCM: Treatment
Treat underlying cause
HF:
Diuretics
Beta-blockers
Ca2+ channel blockers (CCBs)
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors (ACEIs)
Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs)
Limit Na+ intake
Reduce alcohol
Manage complications
HF
Thromboembolic events: Anticoagulants
Severe:
AICD
Heart transplant
HCM: Etiology
Dominant autosomal mutations change myofilament protein production
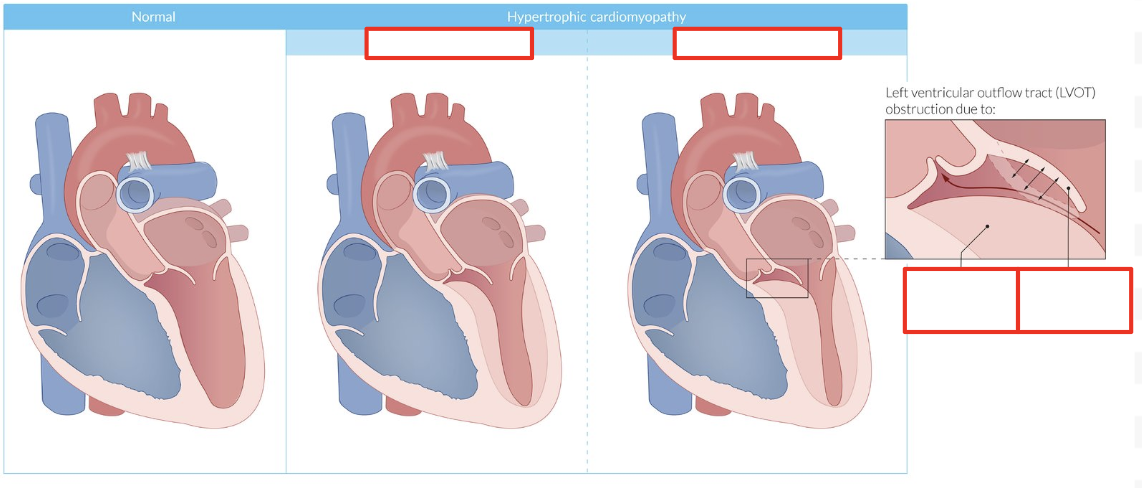
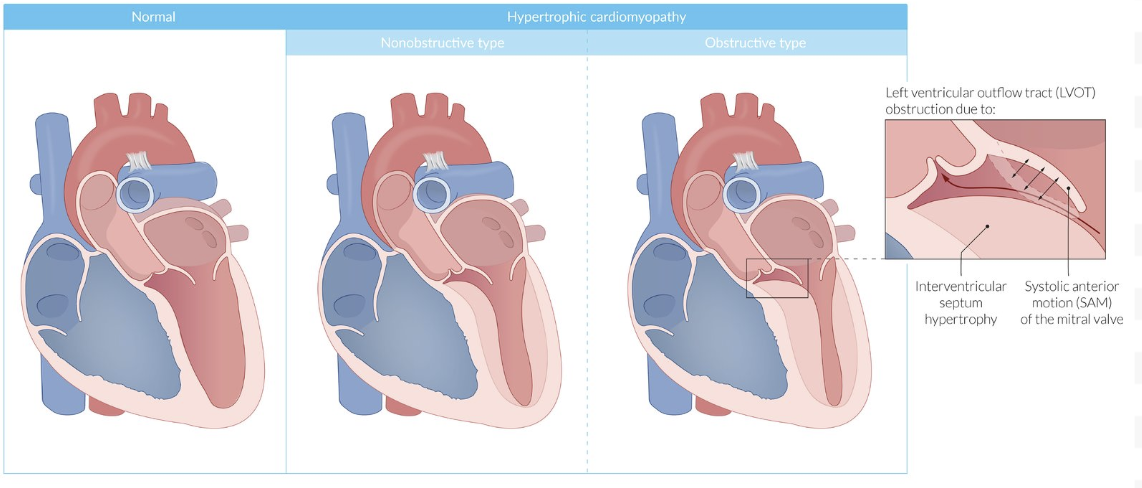
HCM: Pathogenesis
Ischemia = Scarring = Asymmetric interventricular septum hypertrophy
Hypertrophy = Decrease compliance + diastolic relaxation
No Obstruction: Increase outflow pressure (no block)
Obstruction: Systolic anterior motion (SAM) or mitral valve leaflets (dynamic)
From high flow producing Venturi forces (low pressure) = Pull in leaflets
Block outflow tract
HCM: Treatment
Lifestyle changes: Avoid activities causing vasodilation (high temp, exercise)
AICD: Prevent sudden cardiac death
Pharmacological: Reduce heart contraction and HR
Beta-blockers (first-line)
Nondihydropyridine CCBs (second-line)
AVOID DIURETICS
Septal reduction:
Surgery
Ablation
RCM: Etiology
Myocyte infiltration (amyloidosis depositing amyloid fibrils)
Abnormal storage in myocytes
Fibrosis
Idiopathic
RCM: Pathogenesis
Infiltration/fibrosis = Decrease LV compliance (elasticity) = Increase diastolic pressure + Decrease diastolic filling
Cause:
Increased systemic and pulmonary venous pressure (venous congestion)
Decreased SV and CO
RCM: Treatment
Difficult to treat (limited options, high mortality)
Treat underlying cause (HF)
Severe: Heart transplant
Cannot undergo = Palliative care
Compare and Contrast CM: Ventricular Chamber Size
DCM: Increased
HCM: Normal/decreased
RCM: Normal/decreased
Compare and Contrast CM: Ventricular Wall Changes
DCM: No hypertrophy
HCM: Hypertrophic (asymmetric)
RCM: Fibrotic and infiltrated myocardium
Compare and Contrast CM: Etiology
DCM: Genetic, inflammation (myocarditis)
HCM: Genetic
RCM: Genetic (amyloidosis)
Compare and Contrast CM: Symptoms
DCM:
Dyspnea
Fatigue
Weakness
Orthopnea
PND
HCM:
Dyspnea
Angina
Syncope
RCM:
Dyspnea
Fatigue
Compare and Contrast CM: Physical Exam
DCM:
S3
Pulmonary crackles
RV failure: Peripheral edema, hepatomegaly, high JVP
Systolic murmur (AV valve regurg)
HCM:
S4
Obstruction: Systolic murmur (mitral regurg)
RCM:
RV failure
Compare and Contrast CM: Systolic Contraction
DCM: Decreased
HCM: Normal/increased
RCM: Normal
Compare and Contrast CM: Diastolic Relaxation
DCM: Normal
HCM: Decreased (assess with Doppler)
RCM: Decreased (assess with Doppler)
Compare and Contrast CM: Atrial Size
DCM: Increased (decompensated)
HCM: Increased
RCM: Increased
Compare and Contrast CM: Cardiac Size on CXR
DCM: Enlarged
HCM: Normal/enlarged
RCM: Normal
Compare and Contrast CM: Echo
DCM:
Dilated
Poor LV contraction
HCM:
LV hypertrophy (septal)
Systolic anterior mitral valve movement + regurg
RCM:
Normal systolic contraction
Increased echogenicity (infiltration)
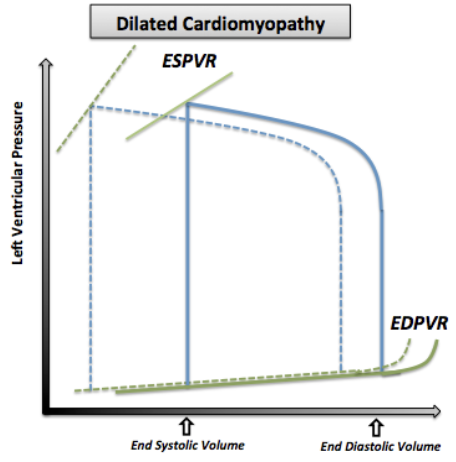
DCM: PV Loop Changes
Increased ESV: Enlarged LV = Increased LV volume
Increased EDV (Preload): Decreased contractility = Decreased SV and CO
Increased Afterload: RAS activation = Increase pressure against LV
Less Steep ESPVR: Decreased contractilty
High volume changes = Low pressure changes
Increased Ventricular Filling Pressure: Decreased compliance + Increased LV size
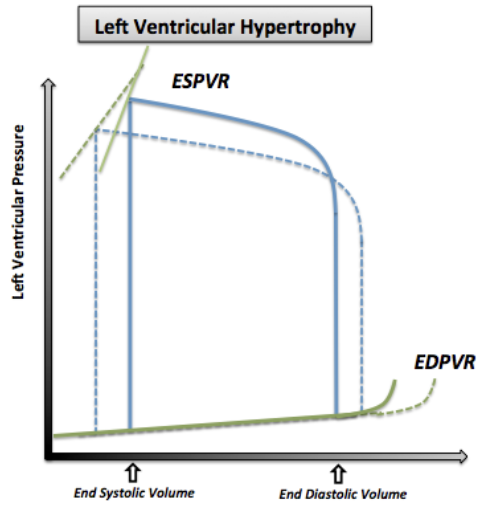
HCM: PV Loop Changes
Normal/Decreased ESV: No systolic dysfunction
Decreased EDV (Preload): LV hypertrophy = Decreased compliance + volume = Decreased SV and CO
Increased Afterload: In LV outflow obstruction
Steep EDPVR: Increased LV stiffness from hypertrophy = Decreased compliance + Diastolic function
Low volume changes = High pressure changes
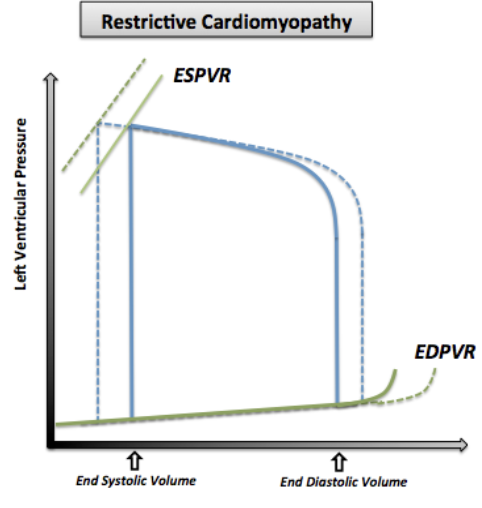
RCM: PV Loop Changes
Normal/Increased ESV: No systolic function changes
Normal/Decreased EDV (Preload): Decreased LV compliance (no dilation) = Decreased filling
Steep EDPVR: Increased LV stiffness = Decreased compliance
Low volume changes = High pressure changes
Diastolic HF: Description
In Alessandra W.
HF from low ventricular compliance (HFpEF)
Increased filling pressure
Abnormal relaxation
Increased ventricle stiffness
Diastolic HF: Epidemiology/Etiology
Hypertension (most common)
CAD
HCM
Diastolic HF: Pathogenesis
Decreased LV compliance
LV hypertrophy + stiffening = Poor LV relaxation
LV diastolic dysfunction = Low CO + Normal EF (no increase with stress)
Increased diastolic pressure = Decreased LV filling
Diastolic HF: Investigations
Echo (TTE) + doppler
ECG
Blood test
Natriuretic peptide biomarkers
Diastolic HF: Echo + Doppler
Diastolic dysfunction
LV hypertrophy
Diastolic HF: ECG
LV hypertrophy
Wide QRS
High R peak
Deep S peak
ST elevation
Diastolic HF: Blood Test
CBC
Electrolytes
TSH
Diastolic HF: Natriuretic Peptide Biomarkers
Increased
B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP)
N-terminal prohormone of B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP)
Diastolic HF: Clinical Presentation
Pulmonary edema
Dyspnea on exertion
Tachypnea
Hypertension
Irregular pulse (atrial fib)
S3 and S4
Diastolic HF: Treatment/Management
Prevent volume overload and maintain filling pressures
Healthy diet
Increased exercise
RAS inhibitors (ARBS, angiotensin receptor-reprilysin inhibitors (ARNIs))
Diuretics (lower dose)
SGLT2 inhibitors
Atrial Fib leading to HF
Loss of coordinated atrial contraction
Structural remodelling
Increased LA pressure and volume
Loss of Coordinated Atrial Contraction
Decrease ventricular filling = Decrease CO = HF
Chronic: LV systolic dysfunction + Dilation = Worsen HF
Structural Remodelling
Atrial and ventricular fibrosis = Decreased ventricular compliance + Contractility = HF
Increased LA Pressure and Volume
Increased pressure + volume = Increased atrium size + Pulmonary venous pressure = Worsen HF
Troponin (Tn)
Regulatory protein in muscle cells controlling interaction between myosin and actin
Released from normal cell turnover
Serum Tn Elevation
Indicate cardiomyocyte injury
Serum Tn Elevation Mechanism
Cardiomyocyte injury = Disrupt sarcoplasma membrane = Tn leak from intracellular compartment into circulation
Prolonged myofibril degradation = Prolonged Tn release
B-Type/Brain Natriuretic Peptide (BNP)
Biomarker produced by ventricular myocardium under hemodynamic stress
Cause vasodilation (decrease BP) and Na+/water excretion (decrease volume)
Serum BNP Elevation
Indicate volume/pressure overload (HF)
ProBNP (prohormone) → BNP + N-terminal proBNP (NT-proBNP)
Normal BNP: < 100 pg/mL
Normal NT-proBNP: < 300 pg/mL
Correlated with severity
Serum BNP Elevation Mechanism
Myocardial wall tension/stretch = Activate mechano-ion channels = Increase Ca2+ influx
Activate BNP gene transcription + translation = Secrete proBNP
ProBNP cleave into BNP and NT-proBNP → Circulation
Hypertrophy Types
Concentric
Eccentric
Concentric Hypertrophy
Thickening myocytes in parallel = Increased wall thickness without proportional chamber dilation (decrease wall stress)
From chronic pressure overload
Ex: Hypertension, valve stenosis
Eccentric Hypertrophy
Elongating myocytes in series = Increased wall thickness with proportional chamber dilation
From chronic volume overload
Ex: Regurg