Tibia + Fibula
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
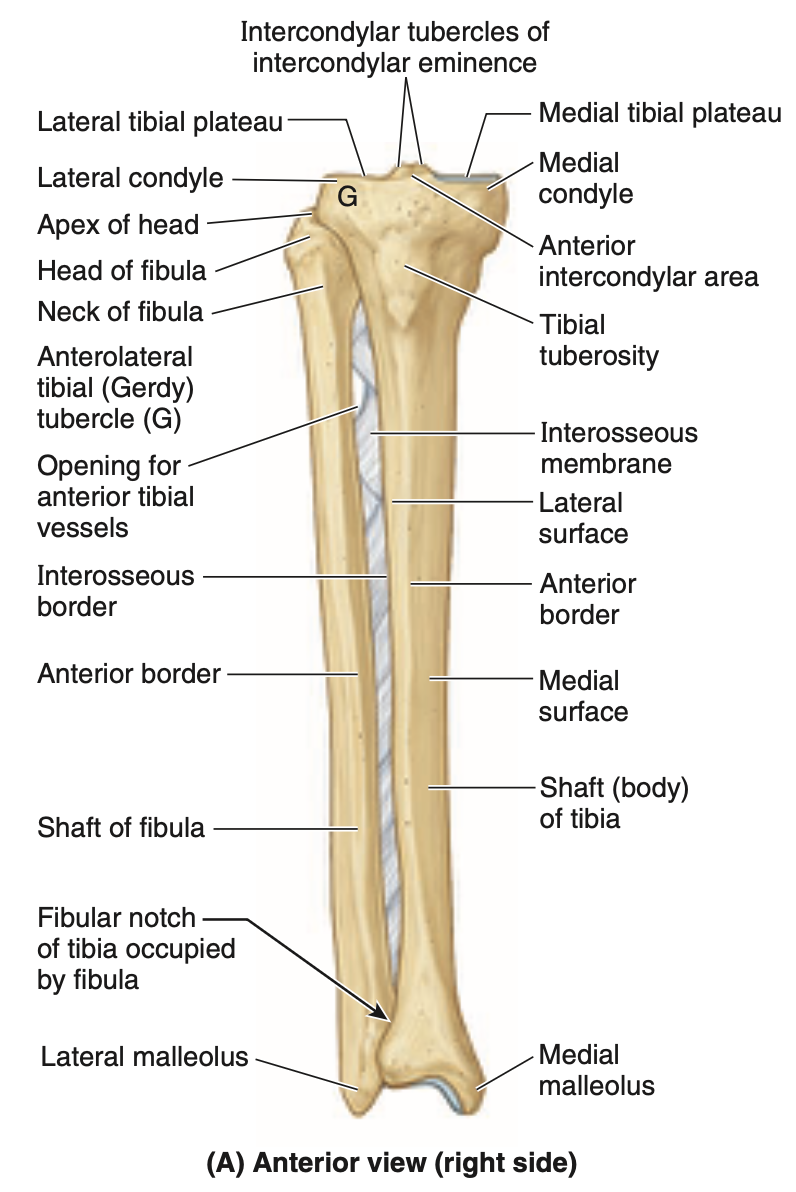
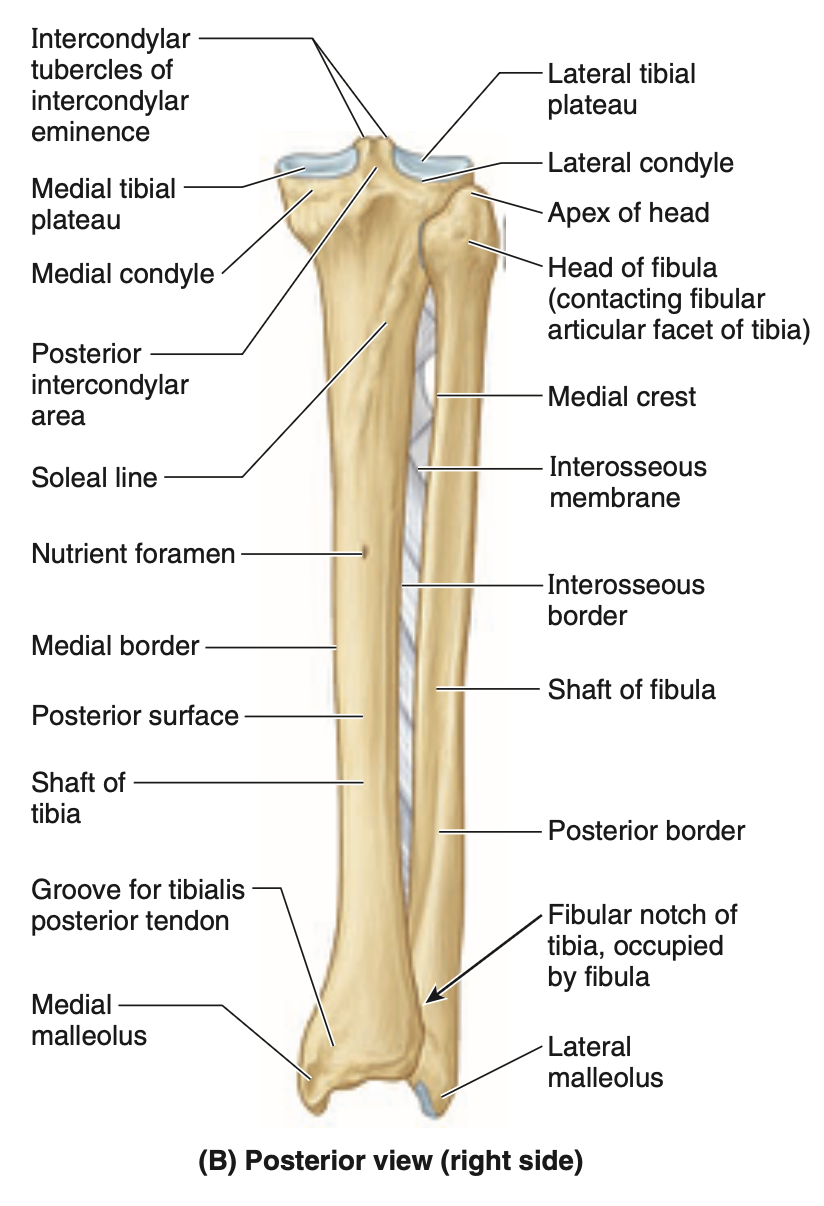
what are all the things the tibia articulates with + how (3)
Femoral condyles superiorly
Talus inferiorly
Fibula laterally at its proximal and distal ends
difference between distal and proximal ends of tibia
distal end smaller than proximal
has facets (sides) for articulation with fibula and talus
what is the medial maleollus of tibia + where
inferiorly directed projection from medial side of distal end of tibia
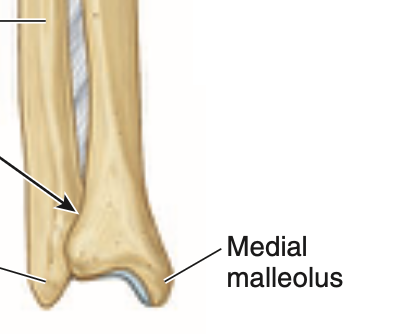
what is the nutrient foramen of tibia + where is it located
from it, the nutrient canal runs inferiorly in tibia before it opens into medullary cavity. it is located on posterior aspect of proximal third of the bone
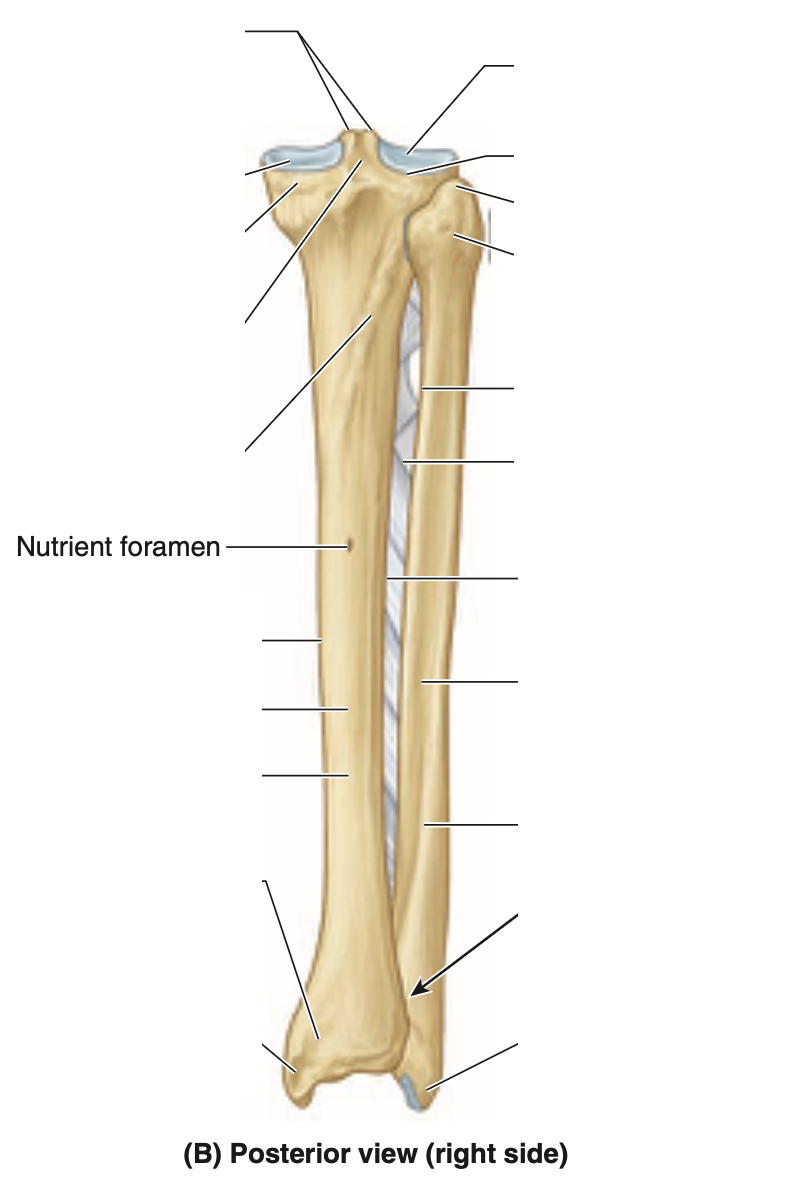
where is the fibula and what is its use
lies posterolateral to tibia, serves mainly for muscle attachment
what does the proximal end of fibula consist of
an enlarged head superior to a narrow neck
what is the distal end of fibula like + explain what it’s more than
fibula enlarges to form lateral malleolus, which is more prominent and more posterior than the medial malleolus and extends approximately 1cm farther distally
is the fibula directly involved in weight bearing?
no
what does the lateral malleolus of fibula form that connects to the foot
it forms the lateral part of the socket for the trochlea of the talus
what are the shafts of the tibia and fibula connected by throughout most of their lengths
interosseous membrane
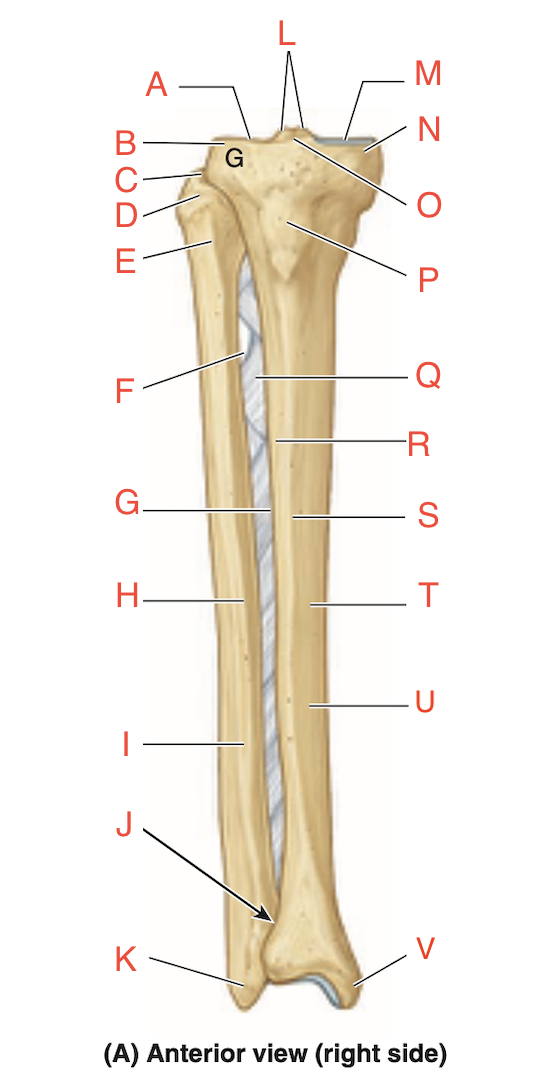
what is the most common site of fracture of tibia and why
the junction of its inferior and middle thirds due to the tibial shaft being narrowest here
why is the tibial shaft the most frequent site of open fractures (compound fractures) or a diagonal fracture
because its anterior surface is subcutaneous
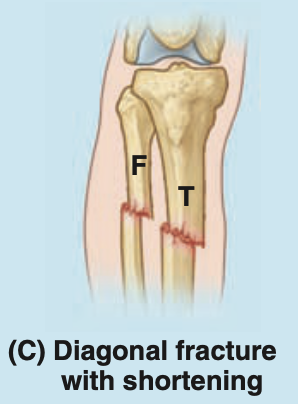
what is an open fracture
one in which the skin is perforated by the bone and blood vessels are torn
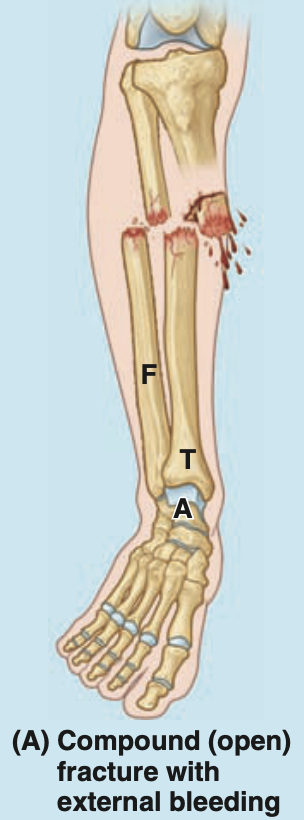
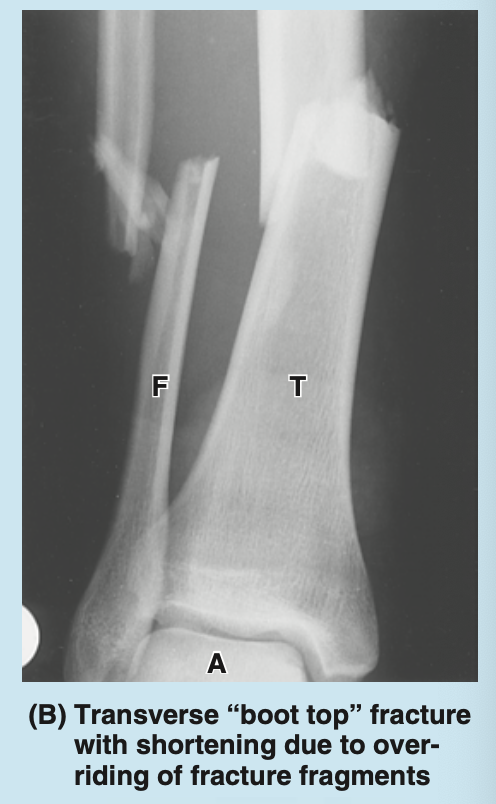
what is an injury commonly sustained by over-riding of fracture fragments (e.g. skiers)
boot top fracture - occurs above the ski boot, often closed but can be open fracture
what happens if the tibia fractures through the nutrient canal
predisposes to nonunion of the bone fragments resulting from damage to the nutrient artery
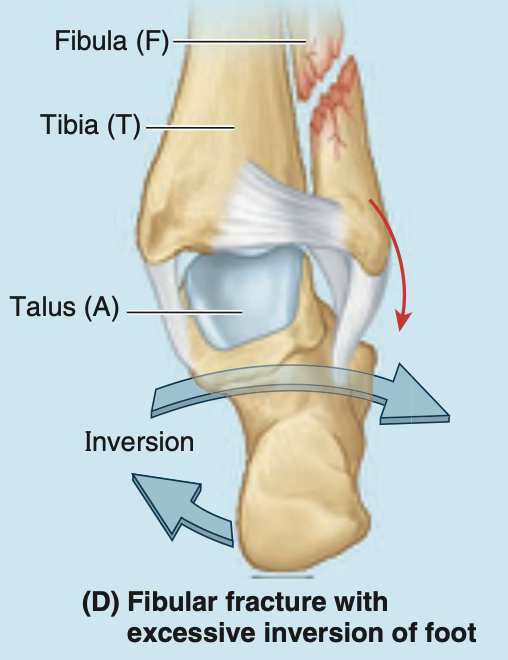
where do fibular fractures commonly occur
just proximal to the lateral malleolus
what are fibular fractures often associated with + how does this thing you mentioned happen
often are associated with fracture-dislocations of the ankle joint
when a person slips, forcing the foot into an excessively inverted position, the ankle ligaments tear, forcibly tilting the talus against the lateral malleolus and shearing it off
why is the fibula a common source of bone grafting
even after a segment of the fibular shaft has been removed, walking, running, and jumping can be normal
2 things free vascularised fibulas (bone grafts) been used for
to restore skeletal integrity to limbs in which congenital bone defects exist
to replace segments of bone after trauma of excision of a malignant tumour
what needs to be removed along with the piece of fibular bone + why
the periosteum and nutrient artery are also removed so that the graft will remain alive and grow when transplanted to another site
when does the primary ossification centre for the superior end of the tibia appear and what does it join
appears shortly after birth and joins the shaft of the tibia during adolescence (16-18y)
when are tibial fractures in children more serious and why
tibial fractures in children are more serious if they involve the epiphyseal plates because continued normal growth of the bone may be jeopardised

what characterises the fractures of the immature skeleton
the Salter-Harris classification that describes the pattern of involvement
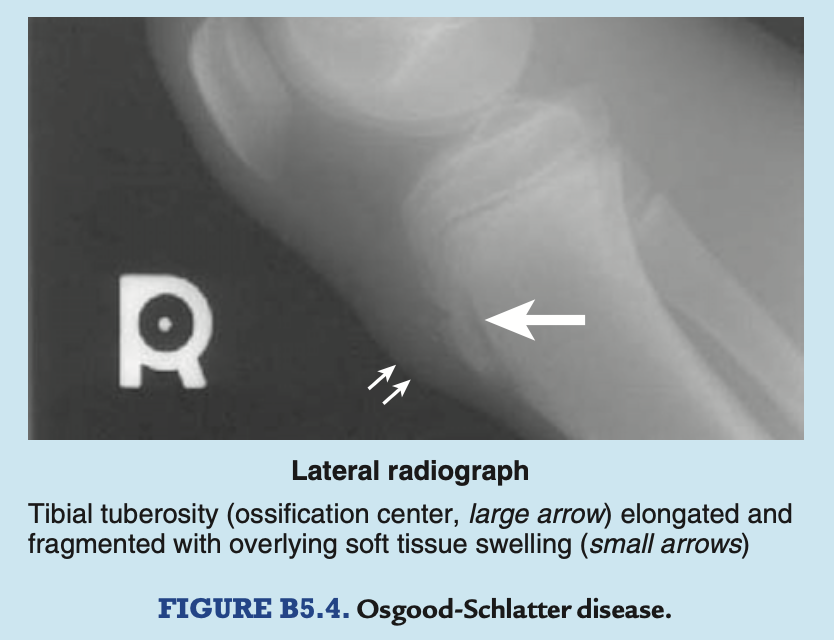
development of the tibial tuberosity (full details)
the tibial tuberosity usually forms by inferior bone growth from the superior epiphyseal centre at approximately 10y, but a separate centre for the tibial tuberosity may appear at ~12y
what can disruption of the epiphyseal plate at the tibial tuberosity cause
may cause inflammation of the tuberosity and chronic recurring pain during adolescence (Osgood-Schlatter disease), especially in young athletes