Chapter 9 - Higher Invertebrates
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
Feeding and Digestion in molluscs
Radula for grinding food; Digestive gland connected to the stomach
Feeding and digestion in arthropods
Maxilipeds to sort food; food passes to a 2 chambered stomach (cardiac for storage and pyloric for digestion)
feeding and digestion in echinoderms
Starfish locate prey and evert their cardiac stomach into a bivalve to digest them.
Echinoids are grazers and scrape algae or are deposit feeders
Crinoidea are suspension feeders
How does the nervous system (ganglia) function work in molluscs
They have a set of ganglia or "local brains"
How does the nervous system work for arthropods
They have a highly developed nervous system (compound eye, small/simple brain, keen sense of "smell", detect chemicals in water, capacity for learning) they have a pair of statocysts for balance and use body movements for communication
How does the nervous system work for echinoderms
a nerve ring that surrounds the mouth. A radial nerve branches off of the nerve ring and extends to each arm.
How does the reproduction (sexual or asexual) function work for molluscs
They are gonochoric and hermaphroditic. The male has a slipper shell but it can turn into female along with a penis amputation, then it can be a female. They have internal fertilization along with some that don't have a planktonic larval stage and a veliger.
How does the reproduction (sexual or asexual) function work for arthropods
They have external fertilization and a nauplius
How does the reproduction (sexual or asexual) function work for echinoderms
Reproduce asexually by regeneration or fragmentation.
Echinoderms may also have the ability to reproduce sexually as eggs and sperm are released into the water to be fertilized.
How does the circulation (open vs. closed circulatory, heart) function work for molluscs
They have a dorsal, muscular heart that pumps blood and they have an open circulatory system
How does the circulation (open vs. closed circulatory, heart) function work for arthropods
They have an open circulatory system and their gas exchange is carried out by gills attached to appendages
How does the circulation (open vs. closed circulatory, heart) function work for echinoderms
Echinoderms possess an open circulatory system, which carries fluid that does become exposed to the external environment
What is the ecological role of mulluscs
Food for humans and other animals
What is the ecological role of arthropods
zooplankton
huge role as food
competition and community structure
symbosis
nutrient cycle
fouling
What is the ecological role of echinoderms
Spiny skin deters most predators. Predators of mollusks, other echinoderms, cnidarians, and crustaceans. Black sea urchins control algae growth on coral reefs. Sea cucumber poison has potential as medicine.
CaCO3
calcium carbonate shell
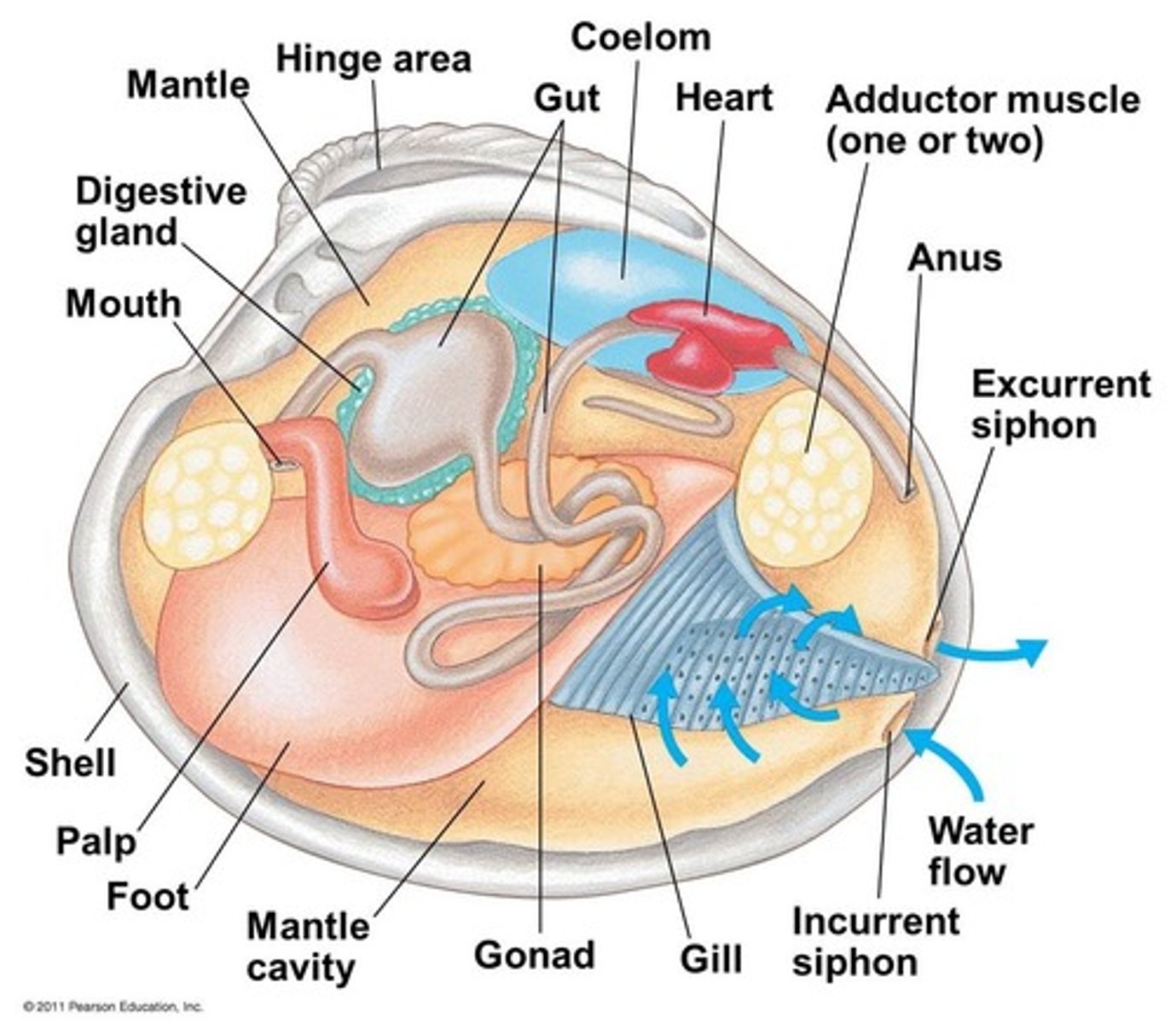
What is the mantle?
The dorsal body wall which covers the visceral mass
What are the layers of a shell?
periostracum layer, prismatic layer, nacreous layer
What animals are apart of the class Cephalopoda?
cuttlefish, squid, nautilus, octopus
What animals are apart of the class Bivalvia?
scallops, cockle, ship worm
What animals are apart of the class Gastropoda?
sea slug, nudibranch, cerata, portugese man-o-war, conch, abalone
What is in the class Polyplacophoran?
chiton
What is in the class Scaphopoda?
tusk shells
What is in the class Monoplacophorans?
limpet
Parts of a clam
What is the difference between an arm and a tentacle
Tentacles --> elongated structures and are generally longer than the length of the arms. Animals use their tentacles to catch prey from farther away
Arms --> have suction cups the entire length of the limb and can perform finer, more complex actions than tentacles
What are chromatophores?
color change
What is the internal shell
It is located inside the body and provides additional support and protection. The internal shell is made of protein and is attached to the body by a series of muscles
What is sepia
A dark fluid containing melanin
What is a natural pearl
came directly from an oyster
What is a cultured pearl
made of plastic
What is the umbo
oldest part of shell, around hinge
What is a siphon
Fused sections of the mantle that allow clams to feed and obtain oxygen while buried in sediment
What are abyssal threads
attach oysters to rocks
What is crystalline style
Enzyme secreting rod in stomach, rotates and helps digest food
What is the head and foot in a mullusc
Head --> mouth and sensory organs
Foot --> animal's organ of locomotion
What is visceral mass
Dorsal body region containing the other organ systems
What is operculum
Covering over the shell's aperture which allows it to be closed
What is a radula
a ribbon of tissues containing teeth used for scraping, piercing, tearing, or cutting pieces of food
What is a veliger
free-swimming planktonic larva
What is proboscis
a tube-like mouth that is often longer and larger than their body, to suck bodily fluids out of their prey
What is uniform growth
what is punctuated growth
Chelicerate (non crustacean)
Have a pair of chelicerae (oral appendages) and lacks moth parts for chewing food
Mandibulata (crustacean)
Have appendages called mandibles that can be used to chew
What is an exoskeleton
body armor, stuctural support
What is molting
shedding of the exoskeleton
cardiac stomach
stomach used for storage
pyloric stomach
stomach used for digestion
Label parts of a crayfish
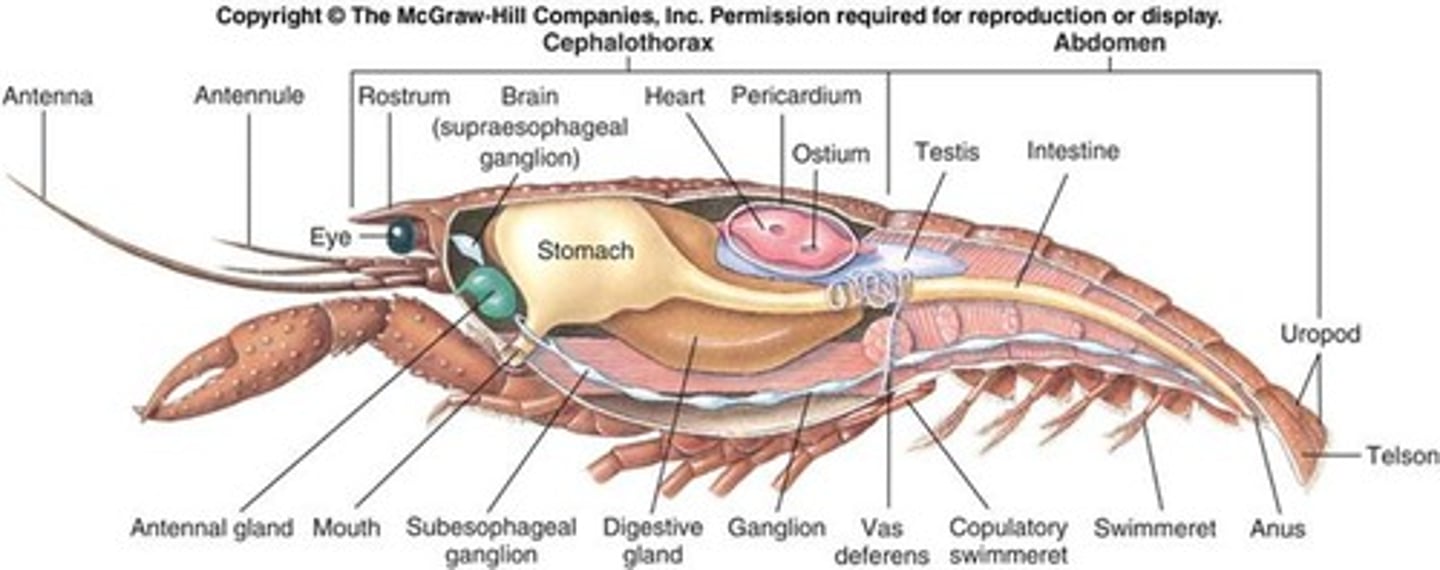
What is the difference between a male and female crayfish
male --> Swimmerets are larger and stiff
female --> Swimmerets are smaller and feathery
What are copepods
plankton, use first pair of antennae to swim, parasitic
What are barnacles
Filter feeds, fouling organism, highly successful parasite, cirri
Fouling organisms
Organisms that live attached to surfaces that are underwater, causing negative effects to ships and pilings
cirri
in barnacles, pairs of feathery appendages that catch food particles
What are amphipods
body compressed from side to side, under 2cm long, crawl in sea weed, burrow into skin of whales
What are isopods?
Flat from top to bottom, pill bugs, fish lice (parasites on fish and crustaceans), tongue louse
krill
small, shrimplike creatures, food for whales and fish. Found in antarctic
shrimp
Decapod (5 pairs of walking legs), usually have claws for feeding, scavengers, remove parasites from skin of fish
mantis shrimp
Relative of the true shrimp that has modified appendages used to strike and kill their prey with amazing force
lobster
Nocturnal, filter feeders but also catch prey, bully netting
How can you tell the difference between and male and female crab
male --> V shape plate
female --> U shape plate
horseshoe crabs
Class Merostomata, horse shoe shaped carapace, 5 pairs of legs, unchanged throughout history
Blue blood in horseshoe crabs
Limulus Amoebocyte Lysate (LAL). Chemical in blood forms jello like substance in presence of bacteria. Used to make vaccines and medication that is safe for humans.
What are insecta
arthropods with a wide variety of adaptations for feeding, ability to fly, and metamorphosis
sea spiders
Class Pycnogonida, 4 pairs of legs, male carries eggs, cold water
What does echinodermata mean
spiny skinned
Pentamorous
5 way symmetry
oral vs aboral
oral side with mouth
aboral without mouth
Ossicles
Plates of calcium carbonate on endoskeleton
pedicellariae
tiny pincers that are used for keeping algae off skin by sea stars and some sea urchins
ambulacral groove
contains the tube feet on the oral side and used to pry open the shells of bivalves
madreporite
opening used to filter water into the stone canal of echinoderms
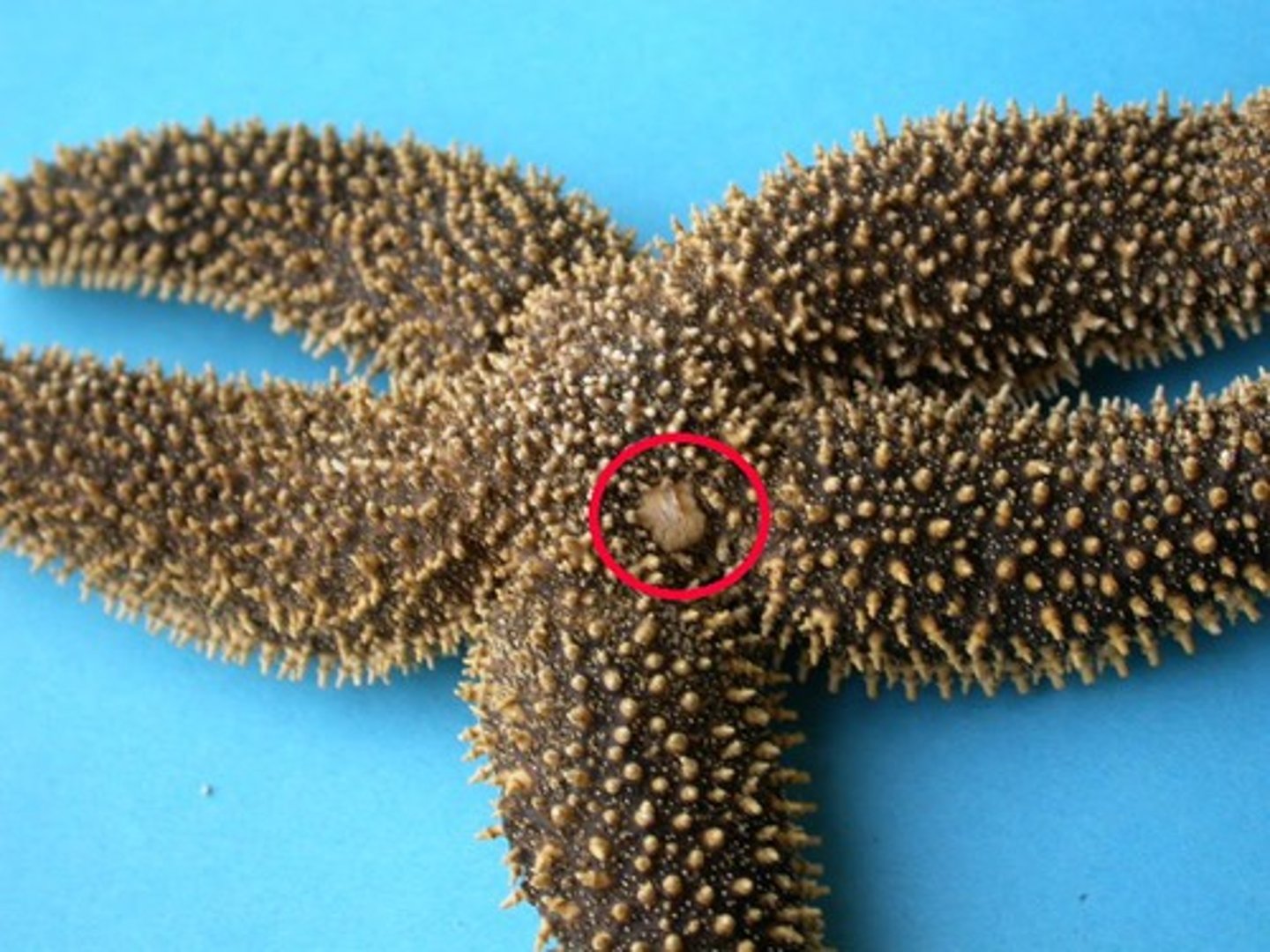

stone canal
tube that connects the madreporite to the ring canal
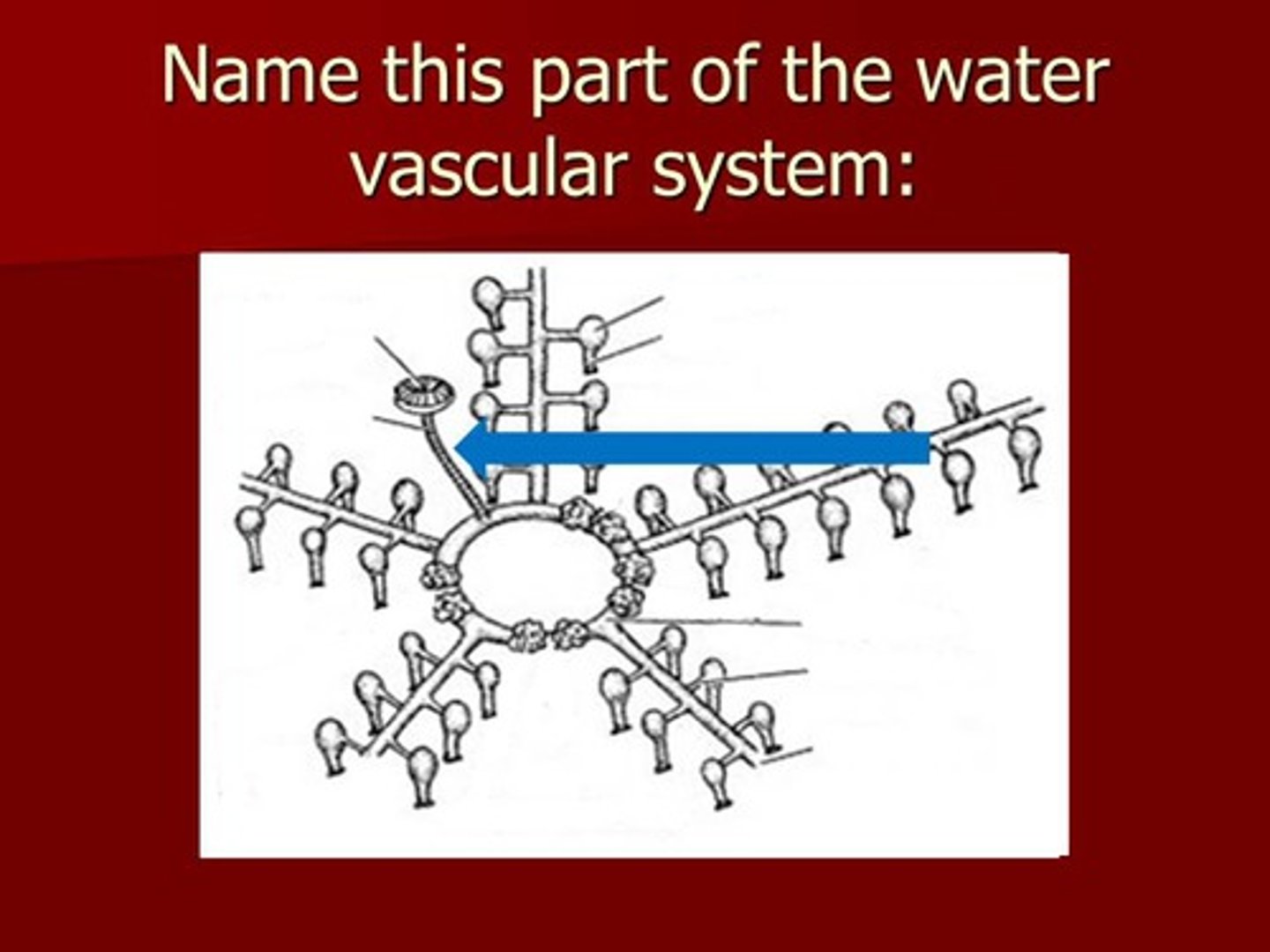
ring canal
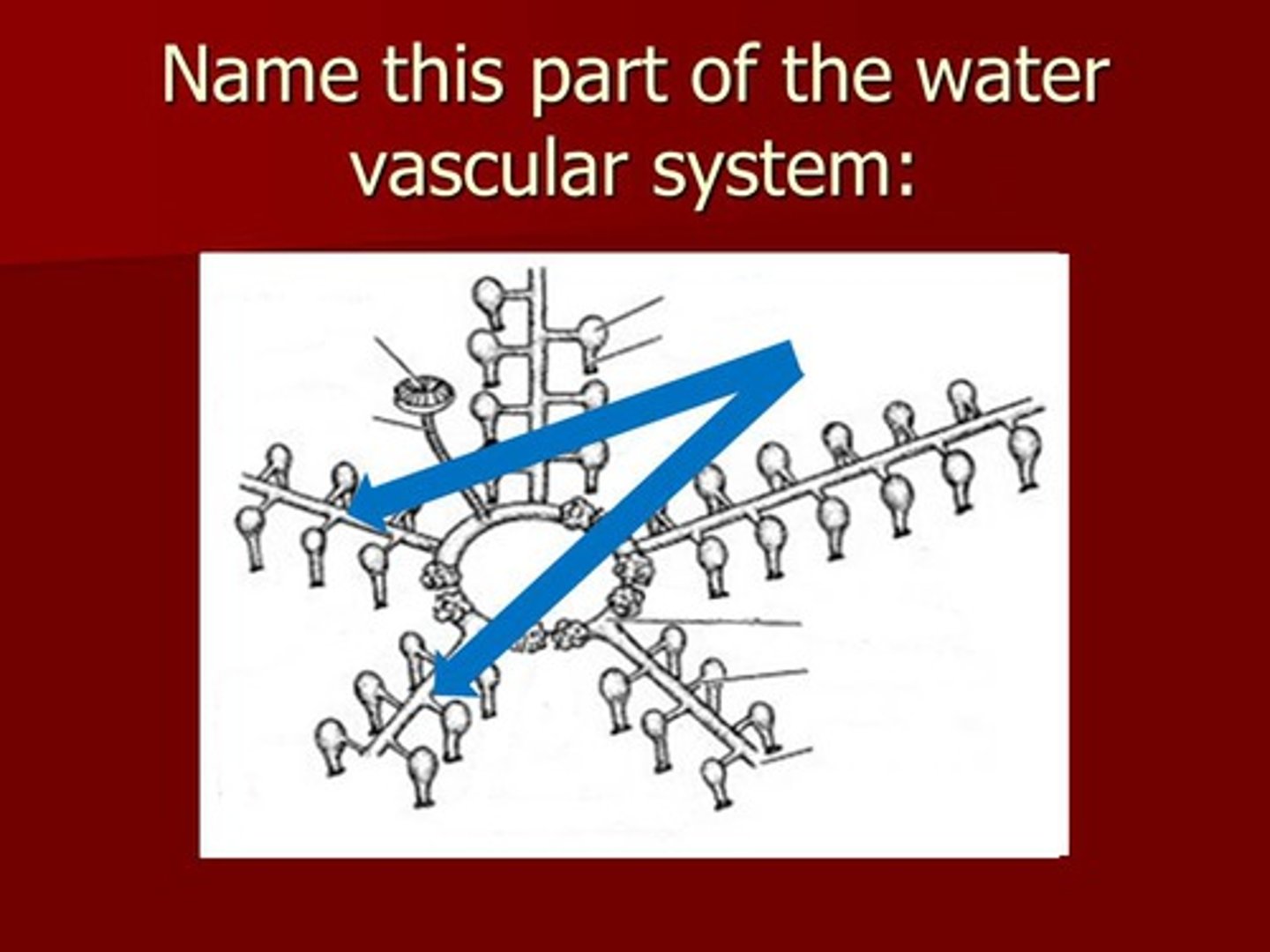
connects the stone canal to the radial canals for water movement in a starfish
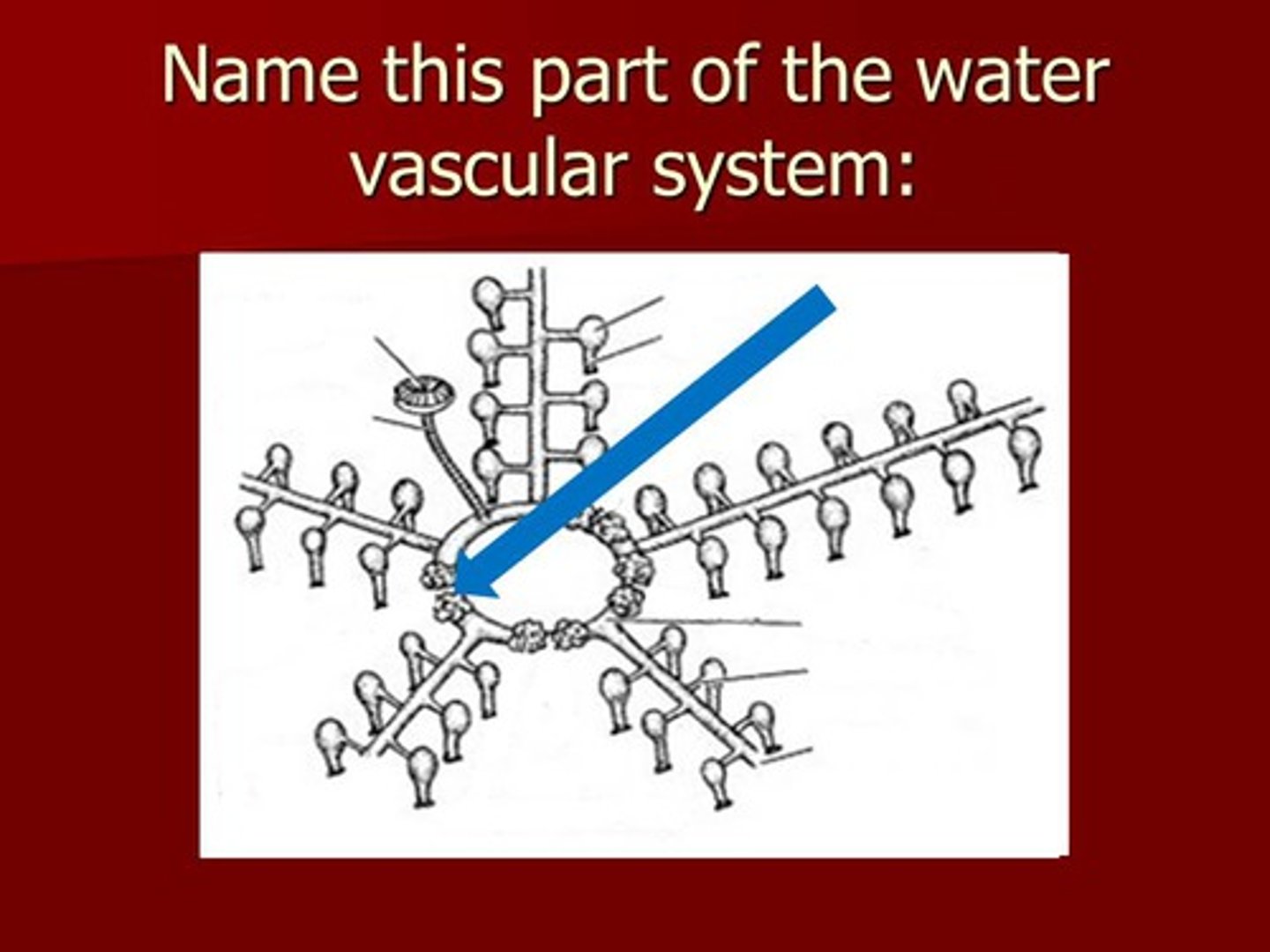
radial canal
water vascular canal that travels down each arm and provides water for the tube feet to contract
Class Holothuroidea
sea cucumbers
Cuvierian tubules
sticky tubules ejected from the anus of some sea cucumbers that function in defense
Holothurin
a toxic substance produced by sea cucumbers
Class Asteroidea
sea stars, starfish
tube feet
branches of water vascular system that function in locomotion, feeding and respiration
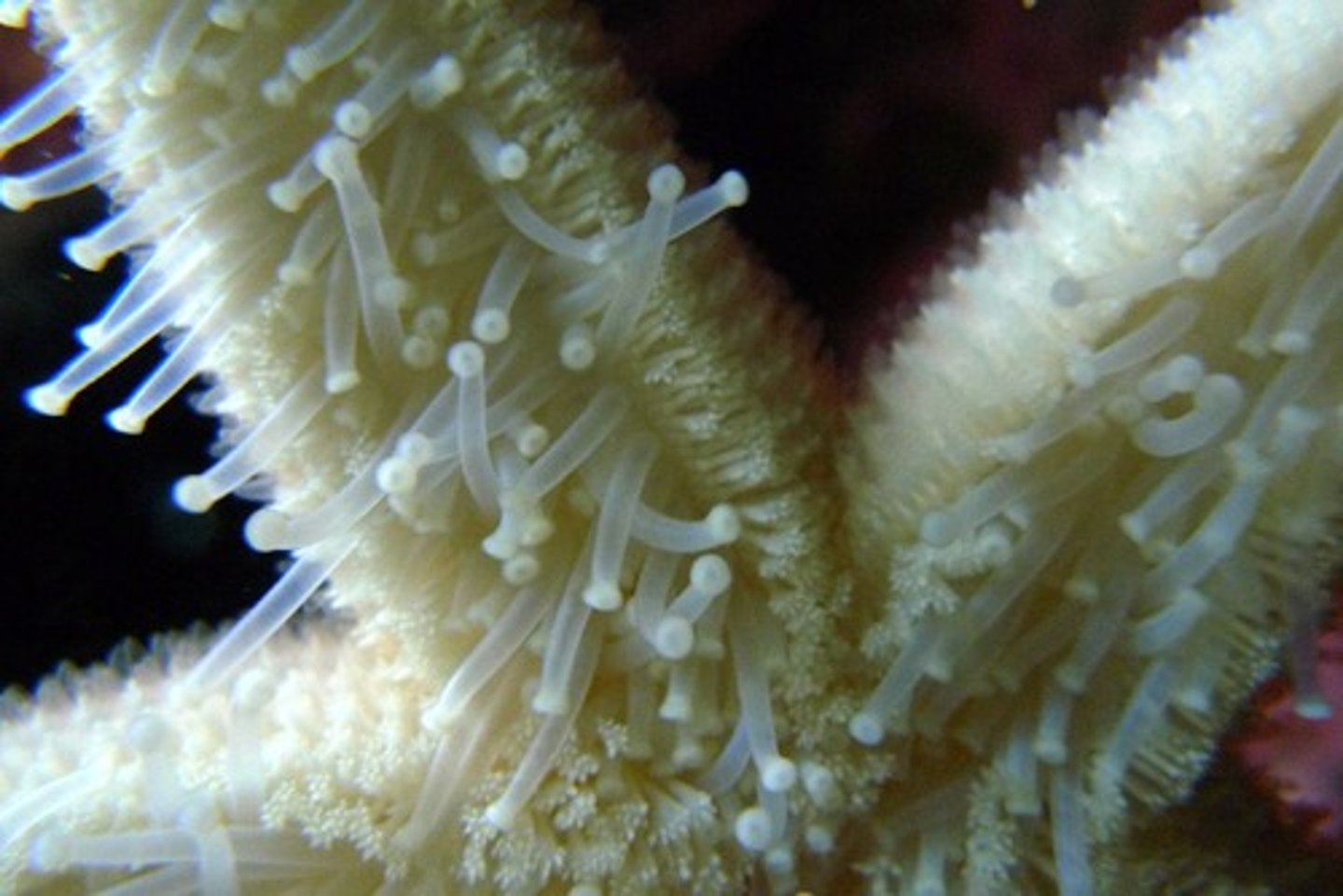

Evisceration
evert their stomachs through their mouths to eat their prey. The starfish then retracts its stomach back inside of its body.
Class Echinoidea
sea urchins, sand dollars, sea biscuits
Aristotle's lantern
a chewing structure composed of five teeth found in the mouths of sea urchins.
Class Ophiuroidea
brittle stars, basket stars, serpent stars
Automize
voluntarily drop their arms if attacked by a predator.
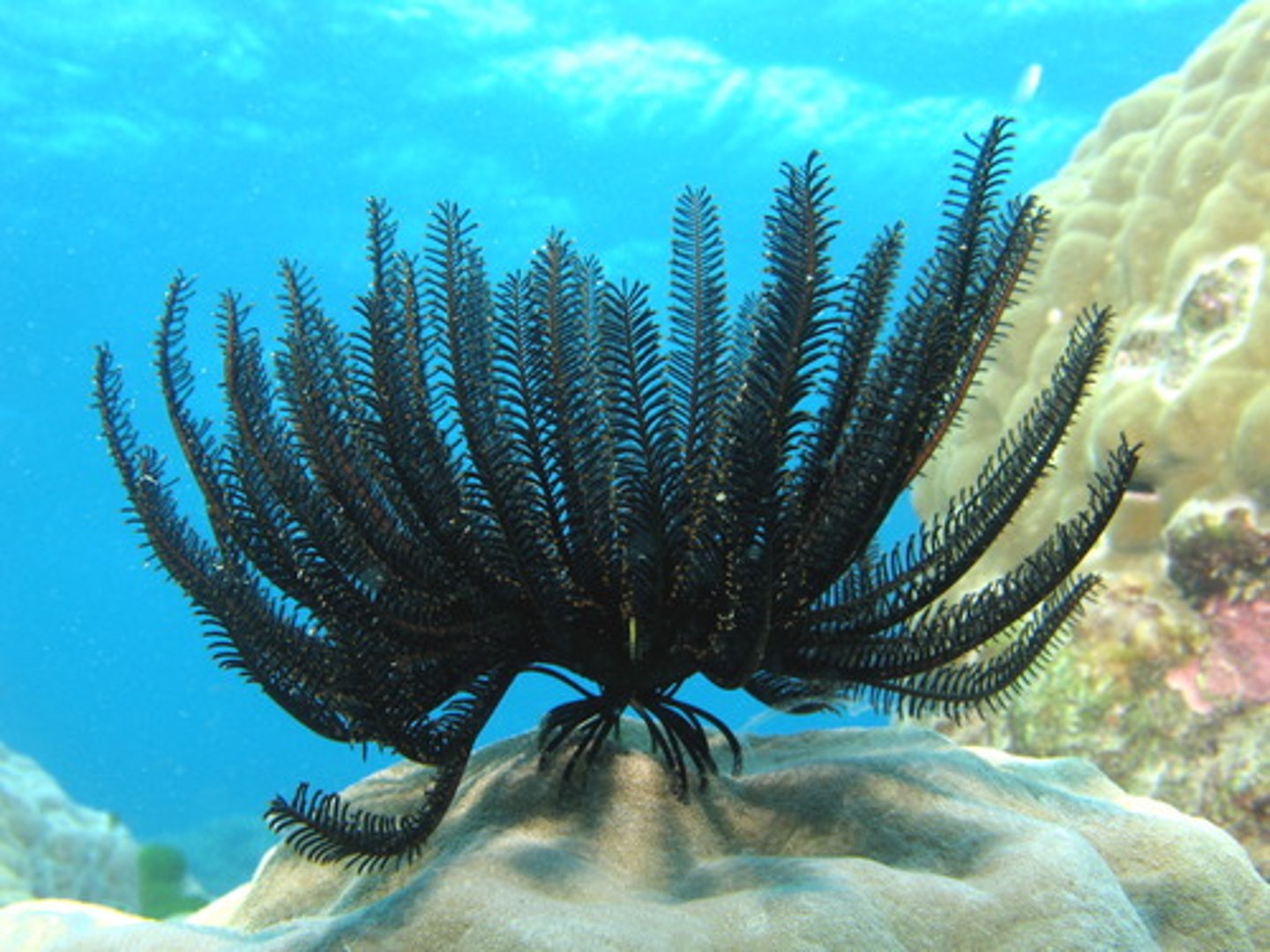
Class Crinoidea/Crinoids
sea lilies and feather stars
Feather Star
Crinoids that move by means of flapping their feathery arms
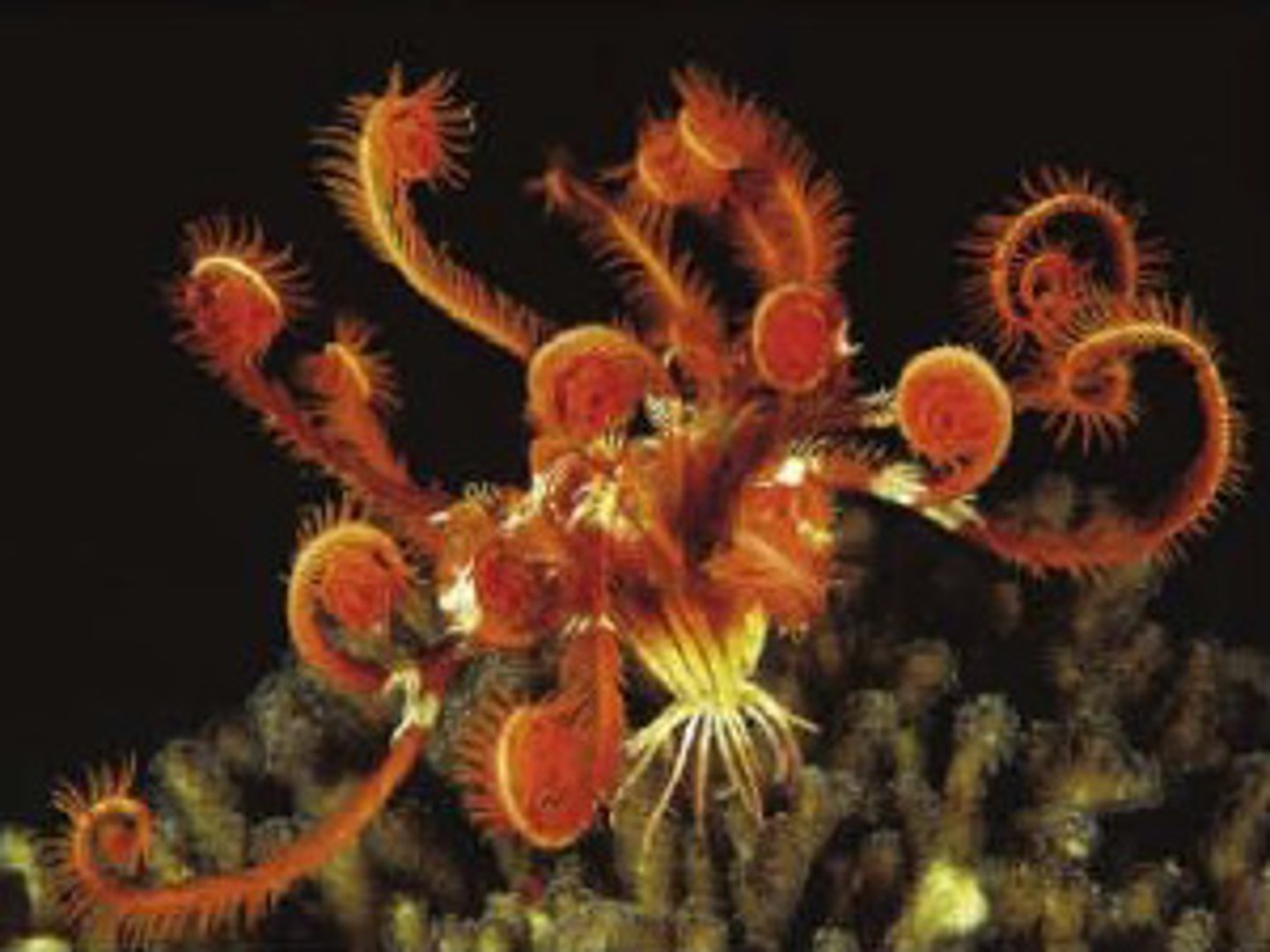

Sea lily
Sessile crinoids with feathery arms; live attached by a stalk to the seafloor
