Chapter 2: Cells" The Living Units"
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
What is the organization of a living organism?
atom, molecule, macromolecule, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and organism
What are cells (five points)
Smallest living units in the body
Perform all functions necessary to sustain life
Obtain nutrients from the surrounding body fluids
Disposes of its wastes and maintains its shape and integrity
Produced by the division of preexisting cells, they can replicate themselves
Function of Cells due to
organelles, enzymes, and metabolism
Function of an organelle
“Little organs” carry on essential functions of cells”
Function of an Enzyme
direct chemical reactions in cells
What is metabolism?
the sum of all chemical reactions in the cell
What are the three main components of a cell
Plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus
What is a Plasma Membrane?
It is the wall of the cell
Determines which substances enter or leave the cell
What are the types of membrane proteins?
Integral proteins and Peripheral proteins
What is an integral protein
firmly imbedded in, or attached to lipid bilayer
what is a transmembrane protein?
it is a type of integral protein that span across the entire membrane
What is a peripheral protein?
attach to membrane surface
What is the function of the Plasma Membrane? (four points)
Physical isolation
Regulation of exchange with the environment
sensitivity
structural support
What is Osmosis
a diffusion of water across a membrane (movement of water)
Simple Diffusion
molecules move from a region where they are more concentrated to an area where they are less concentrated → uncharged and fat-soluble molecules (high to low)
Facilitated Diffusion
molecules move from a region where they are more concentrated to an area where they are less concentrated → charged and water-soluble molecules (high to low)
Active Diffusion
molecules move from a region where they are less concentrated to an area where they are more concentrated → required energy
What is endocytosis?
mechanism by which particles enter cells
What are the three types of endocytosis’
Phagocytosis: “cell eating”
Pinocytosis: “cell drinking”
Receptor-mediated endocytosis: “receptors get activated when something binds with it”
What is Exocytosis?
Mechanism that moves substances out of the cell
Cytoplasm (location and function)
Location: lies internal to plasma
Function: stored nutrients, secretory products, and pigment granules
What is Cytosol
It is a jelly-like fluid in which other cellular elements are suspended and consists of water, ions, and enzymes
Ribosomes
part of the cell that makes proteins by reading instructions from RNA.
Rough Endoplasmic reticulum
ribosomes stud the external surfaces
Smooth Endoplasmic reticulum
consists of tubules in a branching network
Golgi apparatus
sorts products of rough ER and sends them to proper destination
Mitochondria
generate most of the cell’s energy; most complex organelle
Lysosomes
digest external invaders and waste
Peroxisomes
break down internal toxins and fats
Cytoskeleton
“cell skeleton” = an elaborate network of rods
What are the three different rods in a Cytoskeleton?
Microtubules: cylindrical structures made of proteins
Microfilaments: filaments of contractile protein actin
Intermediate filaments: protein fibers
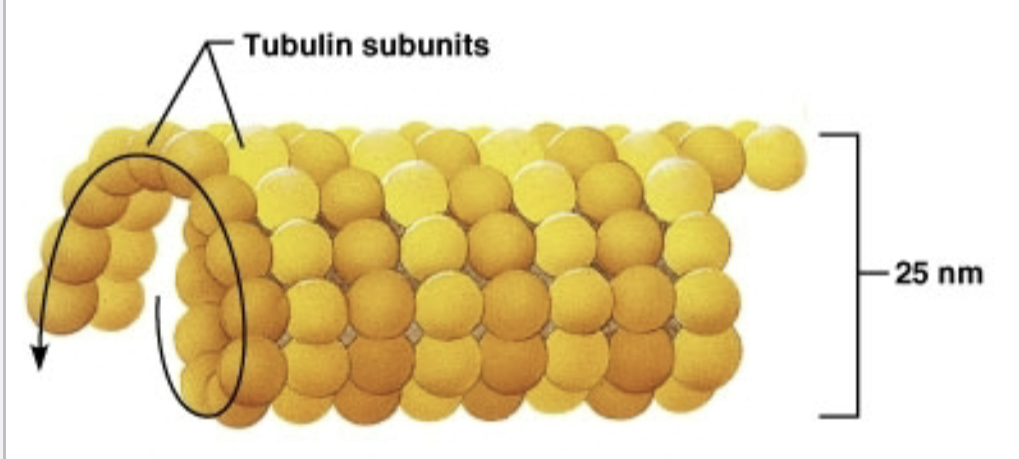
Microtubule
originate from centrosome
Microfilament
found internal to the plasma membrane of the cell

Intermediate Filament
most stable and permanent

Centrosome
composed of centrosome matrix and centrioles
Centrioles
act in forming cilia, flagella, and mitotic spindle fibers
Nucleus
control center of cell, DNA directs the cell’s activities, and nucleus is approximate 5um in diameter
Nuclear envelope
Nuclear pore allows large molecules (RNA) to be exported from the nucleus or proteins from the cytoplasm to come in
nucleolus
contains parts of several chromosomes and site of ribosome subunit manufacture
Chromosomes
highest level of organization of chromatin
Chromatin
compsed of DNA and histone proteins