Lymphoreticular System
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What are the major effector cells produced in the bone marrow and their functions?
Hematopoietic stem cells give rise to erythrocytes (oxygen transport), leukocytes (immune defense), and megakaryocytes/platelets (hemostasis).
What is the lymphoreticular system?
A network of lymphatic vessels, lymphoid organs, and phagocytic cells that monitor and filter body fluids, support hematopoiesis, and mediate immune responses.
Which organs are primary lymphoid organs and what do they do?
Bone marrow (B‐cell development) and thymus (T‐cell maturation).
Which organs are secondary lymphoid organs and what is their role?
Lymph nodes, spleen, liver, peripheral blood and MALT (Peyer’s patches, tonsils); they facilitate antigen presentation and lymphocyte activation.
Describe the capsule and trabeculae of a lymph node.
A fibrous collagen capsule surrounds the node; trabeculae extend inward to partition cortex and medulla.
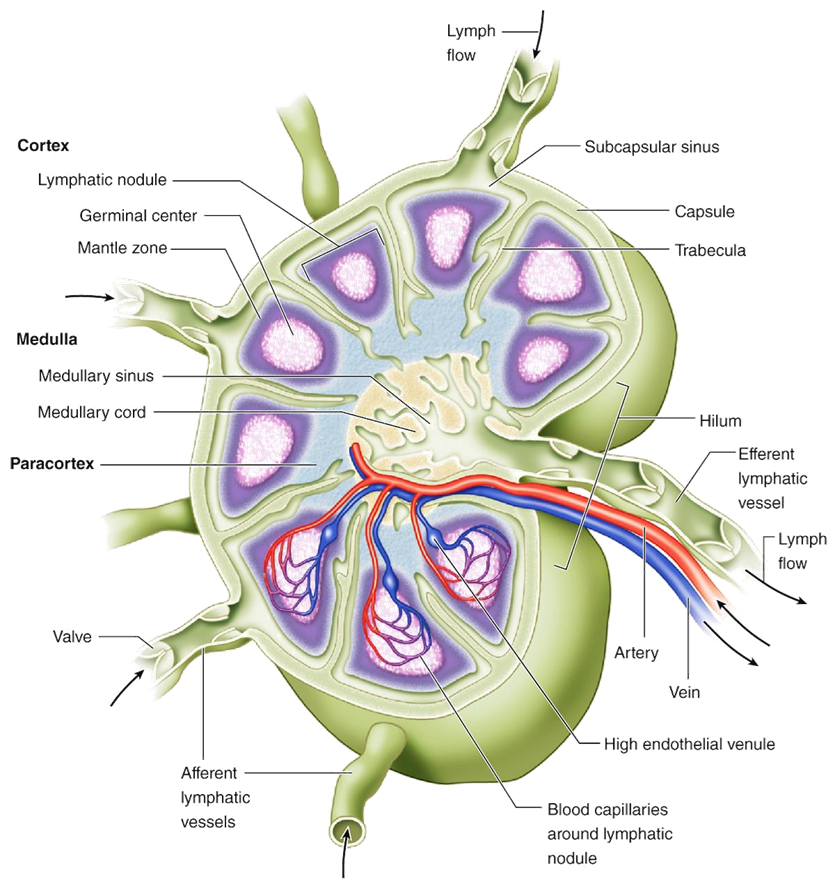
What cell types are found in the lymph node cortex?
B-cells in follicles and germinal centers; follicular dendritic cells support B-cell maturation.
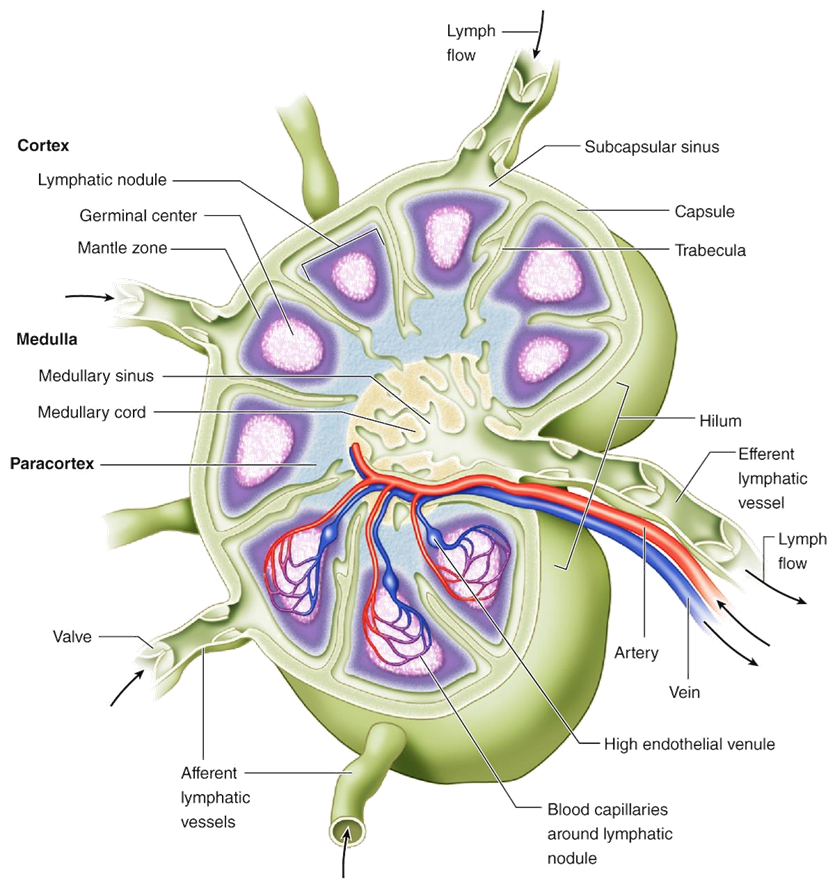
What characterizes the paracortex of a lymph node?
A T-cell zone rich in interdigitating dendritic cells and high endothelial venules for lymphocyte entry.
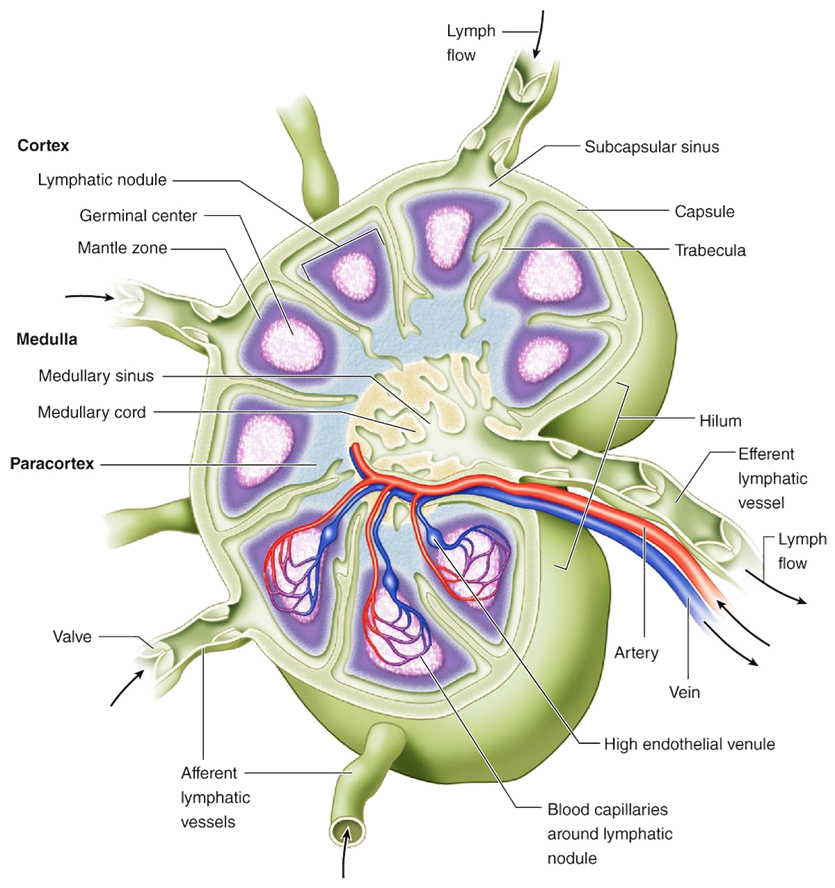
What are medullary cords and sinuses in a lymph node?
Medullary cords: lymphocytes and plasma cells; sinuses: channels lined by macrophages for lymph filtration.
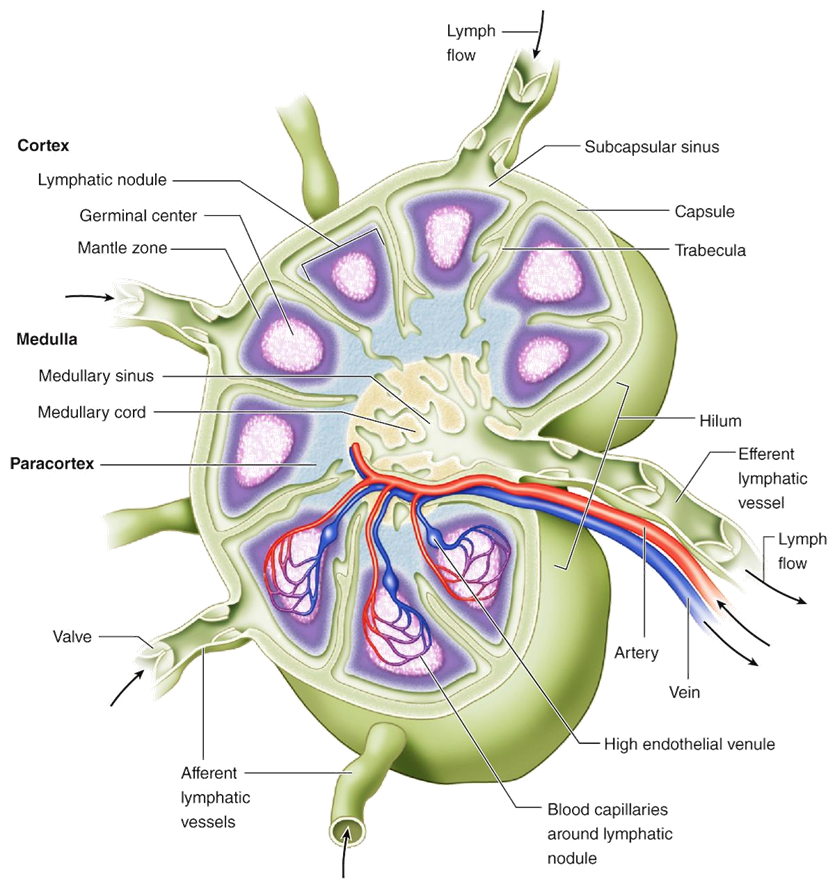
What is the significance of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT)?
Provides immune surveillance at mucosal surfaces; initiates secretory IgA responses to pathogens.
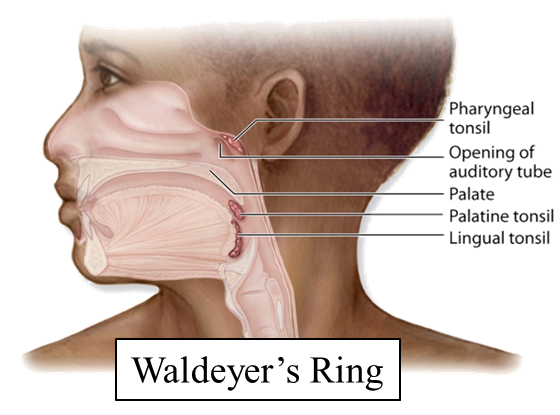
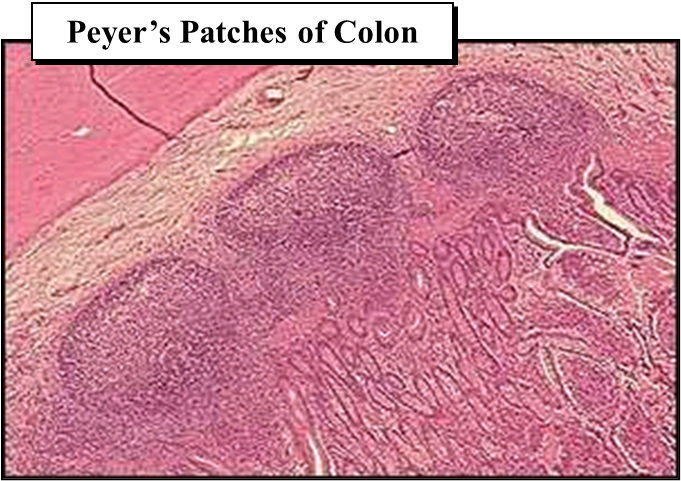
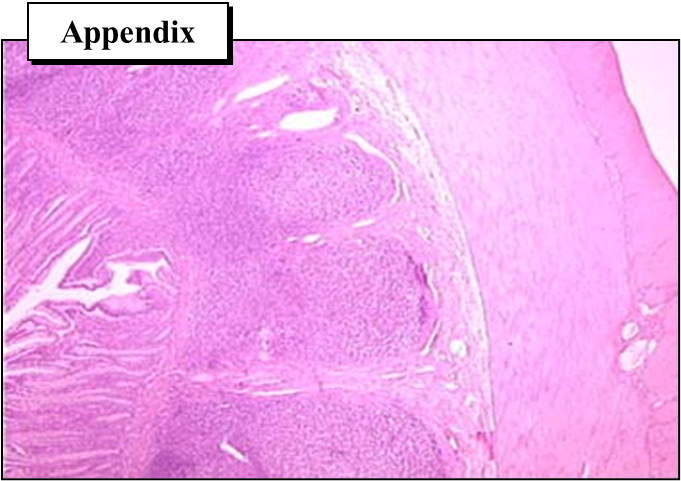
Name four examples of MALT and their locations.
Waldeyer’s ring (tonsils/adenoids), Peyer’s patches (ileum), appendix (colon), BALT (bronchial mucosa).
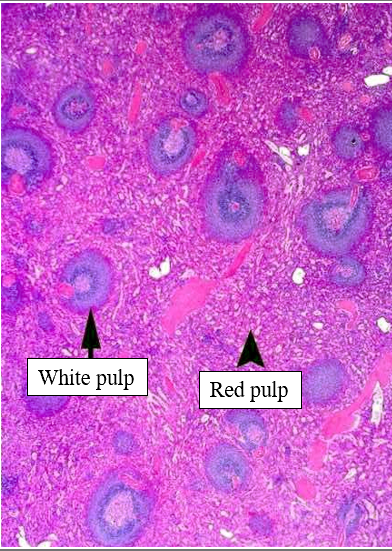
Describe the red pulp of the spleen.
Cords of Billroth with macrophages for RBC clearance; sinusoids filter blood and allow cell passage.
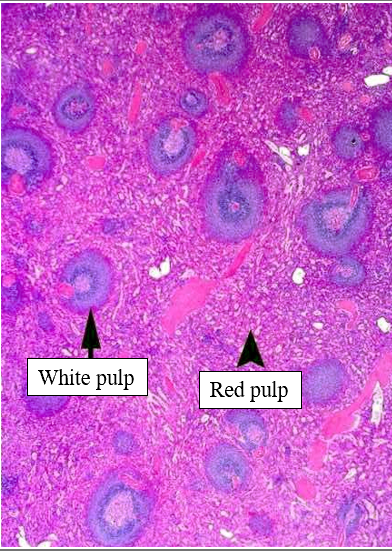

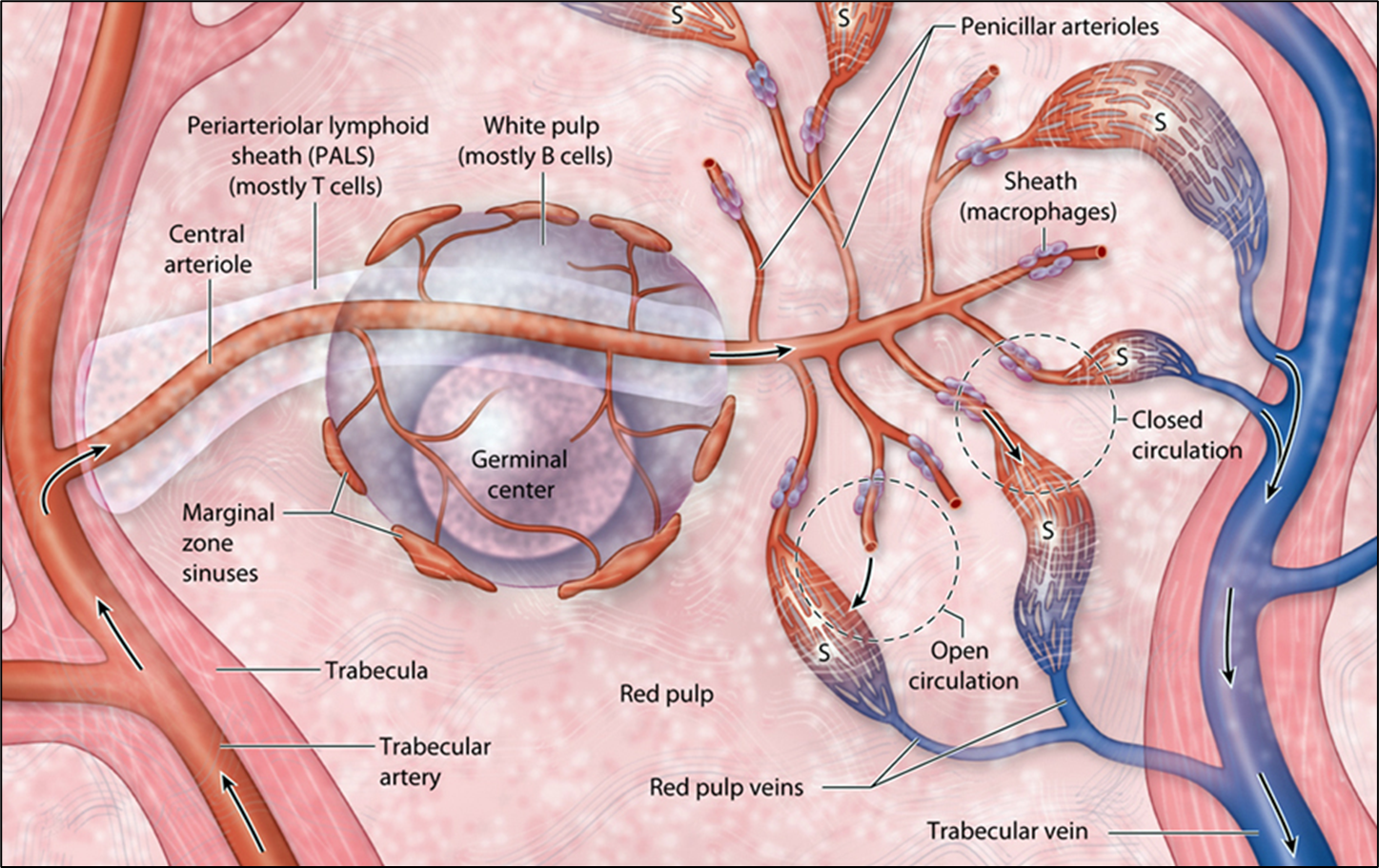
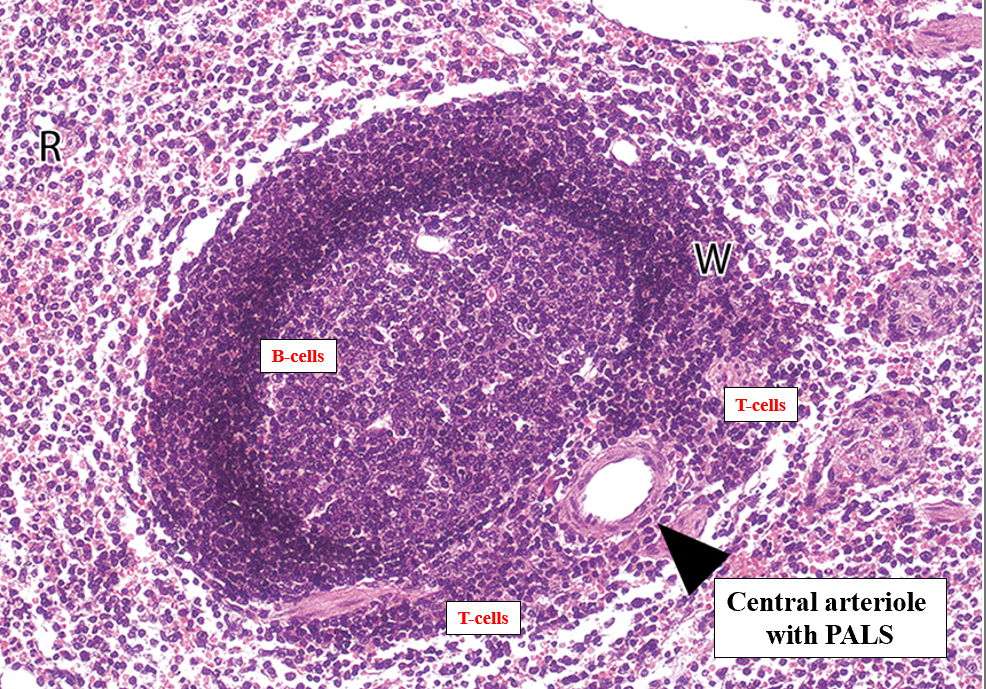
Describe the white pulp of the spleen.
Periarteriolar lymphoid sheaths (PALS) with T cells; germinal centers in follicles for B-cell responses.

How does the spleen remove aged erythrocytes?
Macrophages in red pulp phagocytose damaged RBCs; splenic sinusoids mechanically filter rigid cells.
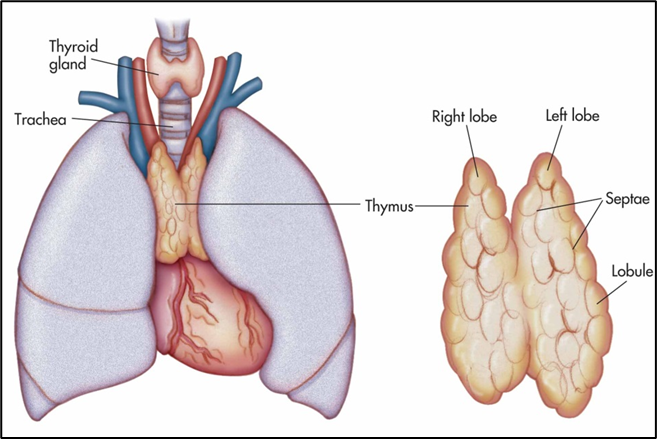
What is the form and function of the thymus?
A bilobed organ in the superior mediastinum with cortex (immature T cells) and medulla (mature T cells, Hassall corpuscles); educates and selects T lymphocytes.
What are Hassall’s corpuscles?
Eosinophilic concentric keratinized epithelial cell structures in thymic medulla, involved in regulatory T-cell development.
How do lymphatic capillaries differ from blood capillaries?
Blind-ended, larger diameter, incomplete basement membrane, endothelial flaps, one-way valves for lymph uptake.
What drives lymph flow through lymphatic vessels?
Skeletal muscle contraction, respiratory pressure changes, and intrinsic vessel smooth muscle tone. (Us moving around)
Where does lymph reenter the bloodstream?
At the venous angles: right lymphatic duct drains upper right quadrant; thoracic duct drains the rest into left venous angle.
Which thoracic structure is the main lymphatic drainage vessel?
The thoracic duct, which collects lymph from below the diaphragm, left side of thorax, head, and arm.
What role do macrophages play in lymphoid tissues?
Phagocytose pathogens and debris, present antigens to lymphocytes, secrete cytokines.
What is the function of high endothelial venules (HEVs)?
Specialized postcapillary venules in lymph nodes that allow naive lymphocytes to enter from blood.
How are B- and T-cell zones organized in secondary lymphoid organs?
B cells form follicles in cortex/follicular areas; T cells reside in paracortical zones around vessels.

What change occurs in MALT with chronic antigen exposure?
Follicle enlargement (reactive hyperplasia) and increased germinal center activity.
How does the spleen respond to systemic infection?
White pulp expands with lymphocyte proliferation and antibody production; red pulp phagocytosis increases.
Why does the thymus involute after puberty?
Decline in thymic epithelial cell function leads to replacement by adipose tissue and reduced T-cell output. (Regresses)