AROMATIC REACTIONS OF BENZENE
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
What are the ortho- para- deactivators and hence, meta-directors? Descending order
Electron withdrawing groups:
-N+R3
-NO2
-CN
-SO3H
-COCH3
-COOH
-COOCH3
-COH
Are halogens deactivators of the benzene ring?
Yes, they are deactivators because they are electron withdrawing groups however they form an additional resonance structure with adds stability to the benzene ring allow for them to be ortho- and para- directors.
What are the ortho- and para- activators of the benzene ring? (ascending order)
Electron Donating Groups (lone-pairs):
-benzene
-CH3
-NHCOCH3
-OCH3
-OH
-NH2
Clemmensen reduction reagents
Zn(Hg); amalgamated, HCl and heat
NH2NH2 (hydrazine), OH- and heat
(reduces the acyl group to a straight chain)
What can be used to reduce all reactions ?
H2 ,Pd (hydrogen in palladium) or H2,Pt (hydrogen in platinum)
For acyl groups to straight chains, deprotect amines, reduce nitro groups and deprotect ethers
Bromination reagents (state effect on the ring)
Br2 and FeBr3
OR
Br2 and AlBr3 (friedel crafts catalyst)
Bromine is ortho- and para- directing
Chlorination reagents (state effect on the ring)
Cl2 and FeCl3
OR
Cl2 and AlCl3 (friedel crafts catalyst)
Bromine is ortho- and para- directing
Nitration of Benzene (state the effect on the ring)
HNO3 and H2SO4
Deactivates the ring. Alkylation and Acylation is prevented from taking place.
What are the reagents to synthesise aniline?
1st: Nitration
Reagents: HNO3 and H2SO4
Reduce the Nitro Group
2nd: Add Fe, HCl or SnCl, HCl or H2/Pt
How to protect and deprotect the amine group of aniline?
Convert the group to an amide by adding an acyl chloride (R-CO-Cl). This amide is activating and also can act as a blocking group. (The NH2 loses an H to bind and Cl is removed)
To deprotect the amine use aqueous NaOH, H2O and heat
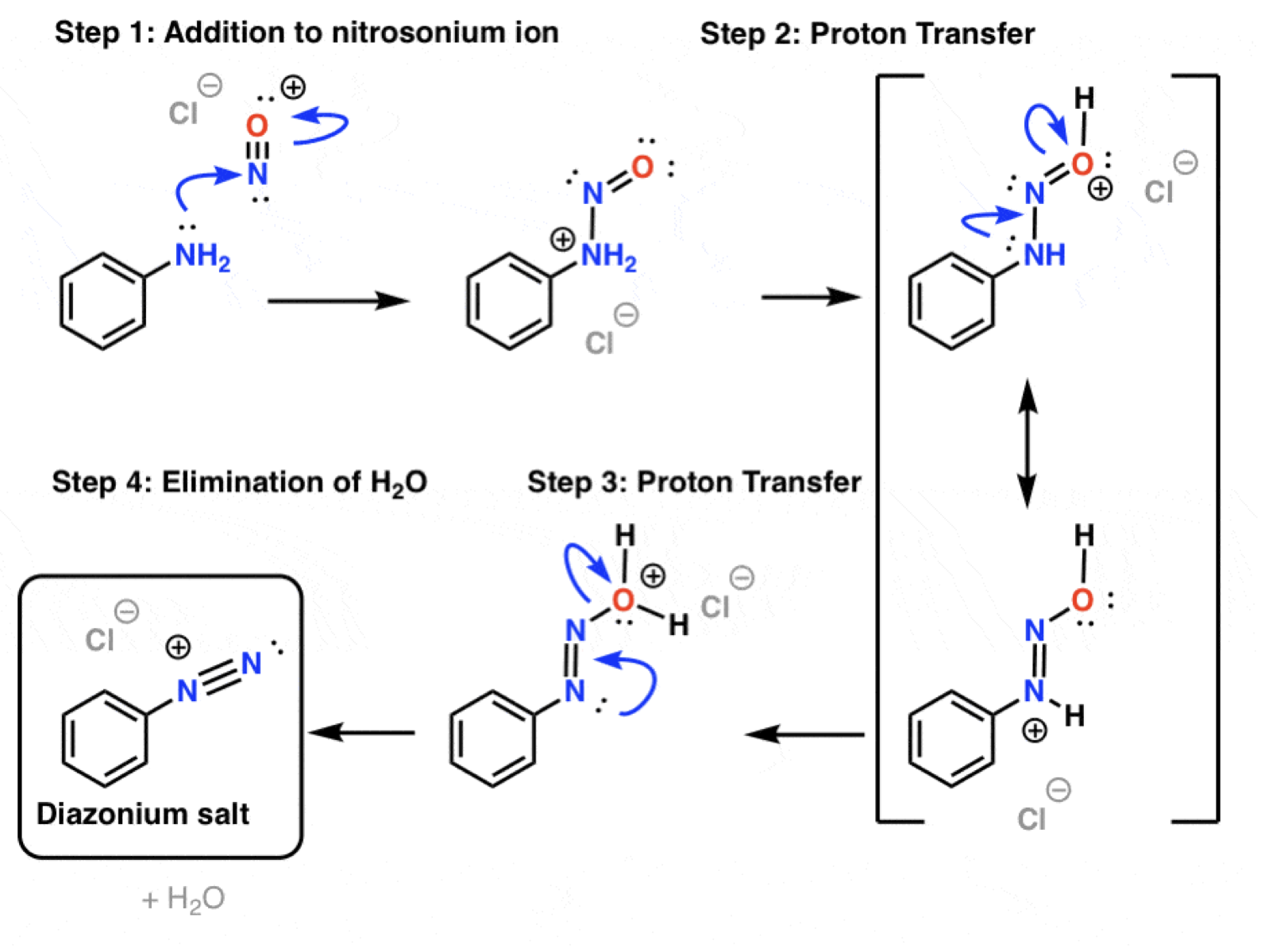
How to synthesise a aryl diazonium salt?
Use steps to synthesise aniline:
1st: Nitration
Reagents: HNO3 and H2SO4
2nd: Add Fe, HCl
To aniline
Add NaNO2 (sodium nitrite), HCl at 0oC
Remember to include counter ion (Cl-)
This group must be fully converted before any other substituent is added.
What is an azo linkage?
An azo linkage is where the diazonium salt prepared, itself can be used as an electrophile to another benzene ring. It is normally added at the para- position of the ring. If the para- position is taken it is substituted at the ortho- position.
What are the reagents to synthesise a phenol from an aryl diazonium salt?
H2SO4 or H3O+, H2O
-OH is an activating group.
What are the Sandmeyer reactions? (give the reagents and substituent added)
They utilise copper salts (CuX) and enable installation of a halogen or a cyano (CN) group on the ring.
This a way of adding nucleophiles to the benzene ring which is an electron-rich species.
Nucleophiles: -CN, Cl-, Br- will; replace the diazonium group if appropriate cuprous salt is added to the solution.
CuBr = Br
CuCl = Cl
CuI = I
CuCN = CN
Using phenol, how can this group be converted to an ether (methoxybenzene synthesis)? (protection of the phenol, because phenol can as a weak base)
To protect benzyl bromide (BnBr) and K2CO3 can be used to add on O-CH2-Ph
To convert to a standard ether
NaOH - O-
then CH3I is added
To deprotect H2 Pd/C can be used
How can phenol be used to make an ester?
Acylation using acid anhydrides (RCOOCOR) and base, or acyl chlorides (RCOCL) and base
What is another reagent when added to an aryl diazonium salt would substitute Iodine?
KI
What reagents are used to convert an aryl diazonium salt to flourobenzene?
1.HBF4
2.Heat
What can be used to convert an aryl diazonium salt to benzene?
H3PO2
What are the reagents of sulphonation?
SO3, H2SO4
- SO3H is a deactivating group and blocking group.
To remove/desulphonate H2SO4, H2O can be used.
What are the reagents for alkylation of an aromatic ring?
RCl and AlCl3
The substituent is the R group
At the benzylic carbon what reagents and substituents can be added?
NBS (N-Bromosuccinimide) + heat
Substitutes and H on the Benzylic carbon to form -CH2Br (ortho-/para- directing)
Note when performing benzylic reactions, these work best on straight chain alkyl groups
2. Na2Cr2O7, H2SO4 and H2O
Substitutes -COOH in place of the alkyl chain
What are the reagents for acylation?
R-CO-X
X = Cl/Br
and Friedel Craft Catalyst (e.g. AlCl3)
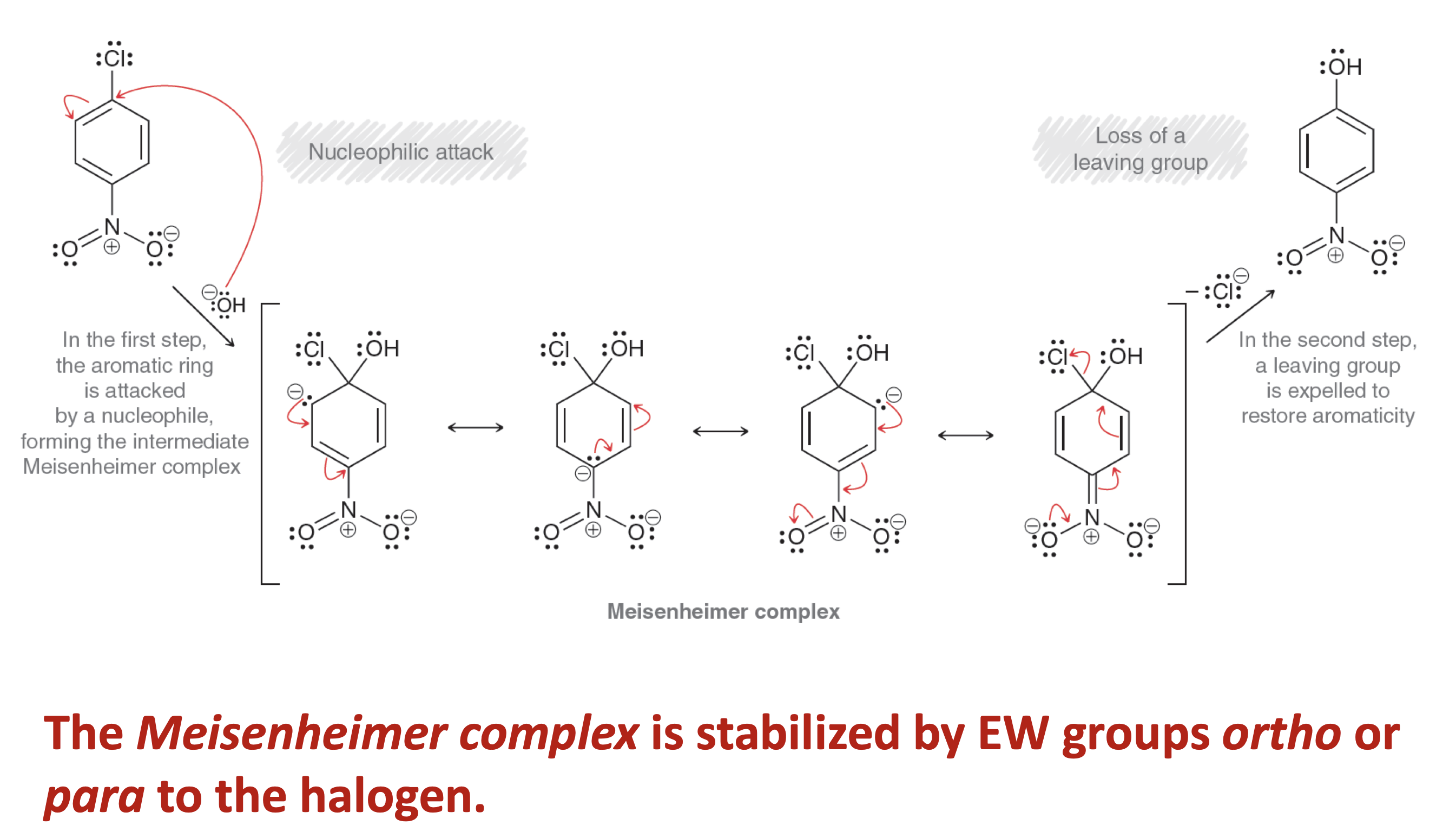
What is SnAr, Addition-Elimination
This occurs when powerful EW substituents are on the ring.
SNAr results in ipso substitution or bimolecular displacement mechanism , i.e., substitution at an atom that already had a substituent.
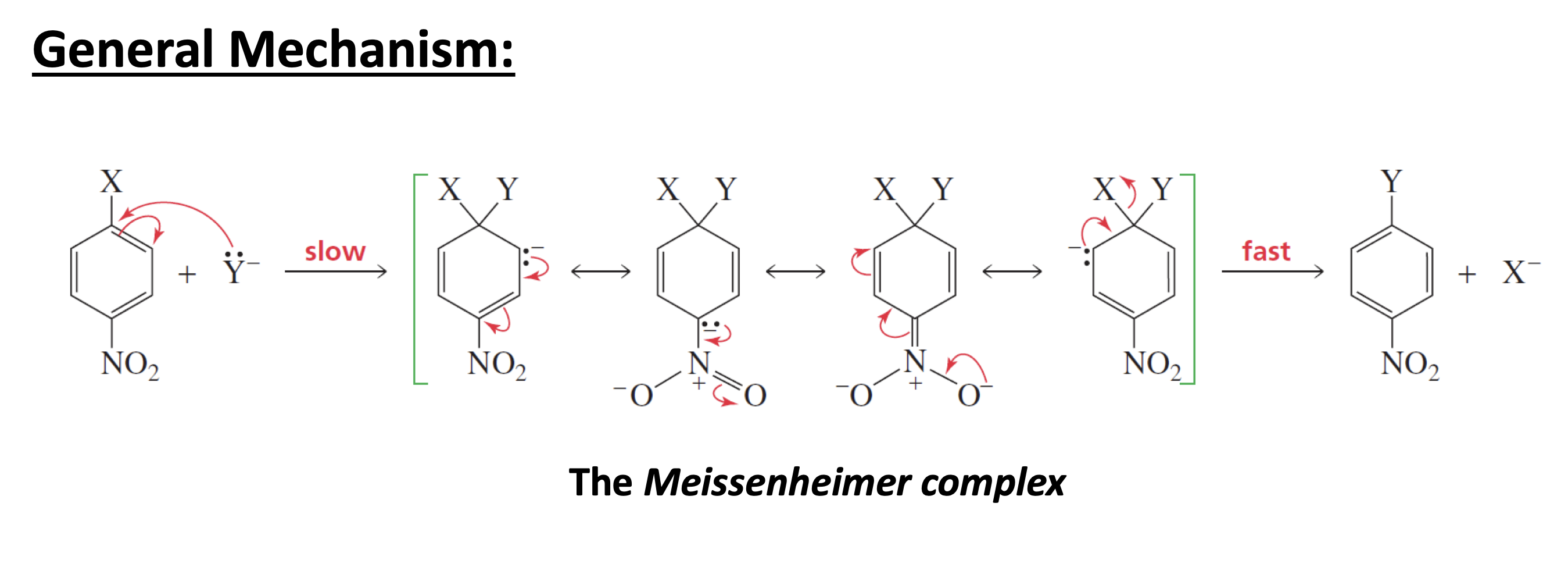
What are the considerations for SnAr, Addition-Elimination
In SNAr, the incoming nucleophile must be a stronger base than the substituent that is being replaced, because the weaker of the two bases will be the one eliminated from the
intermediate.
• The electron-withdrawing substituent must be ortho or para to the site of nucleophilic attack because the electrons of the attacking nucleophile can be delocalized onto the substituent only if the substituent is in one of those positions.
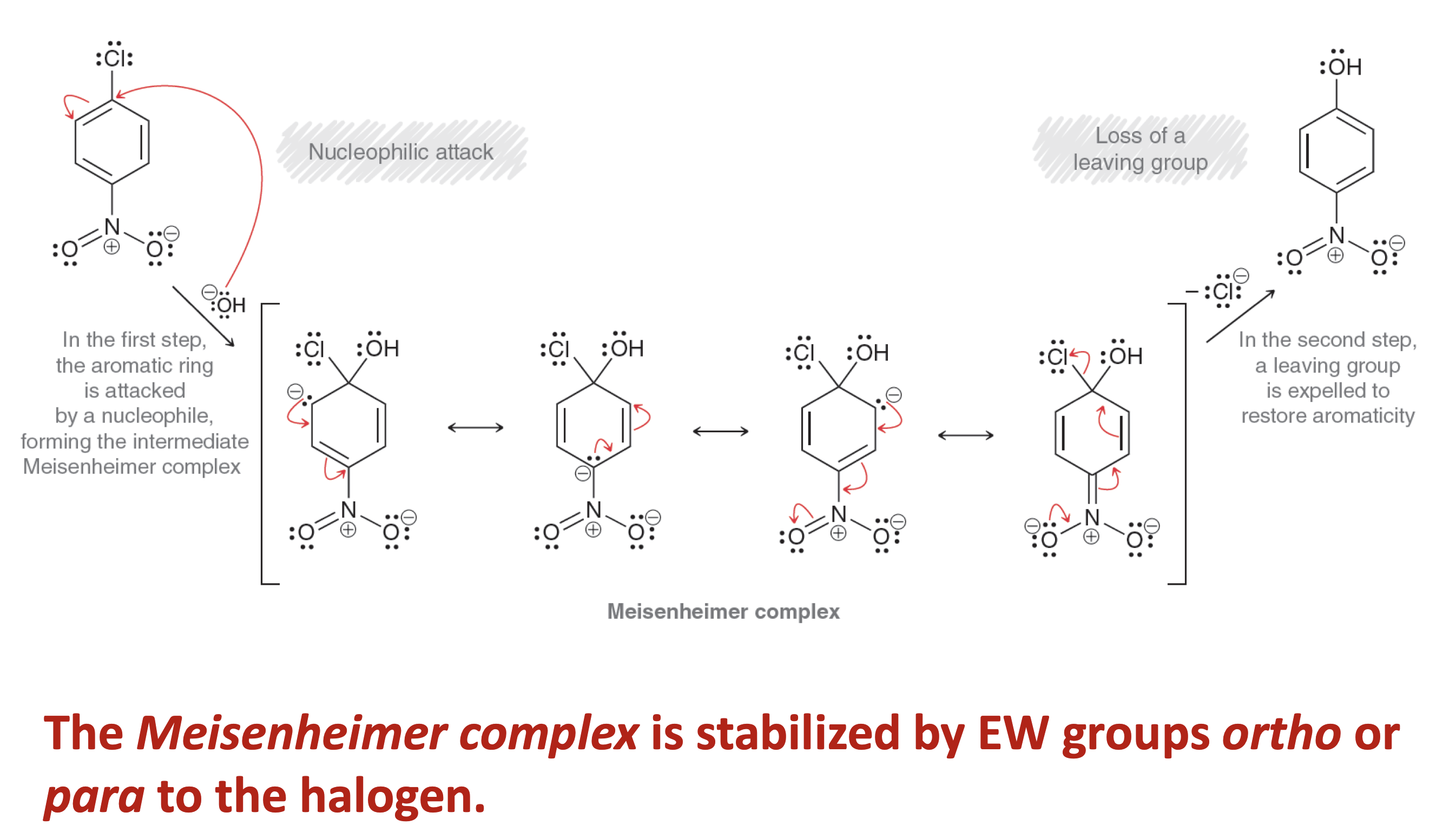
Describe the mechanism for SnAr, Addition-Elimination
What is the other type of nucleophilic aromatic substitution than addition-elimination.
Elimination-Addition
What are the two aromatic products that elimination-addition SnAr would give?
Phenol
Reagents: 1. NaOH 2. H3O+
Conditions: 3500C
Aniline
Reagents: NaNH2, NH3(l) and 2. H3O+
Explain the formation of the benzyne?
Elimination-addition involves the formation of an interesting intermediate called a benzyne.
The amide (base) abstracts an o-proton that triggers the elimination of Cl-.
The third bond in the benzyne is due to sp2 – sp2 overlap of orbitals which are perpendicular to the π- orbitals of the aromatic ring.
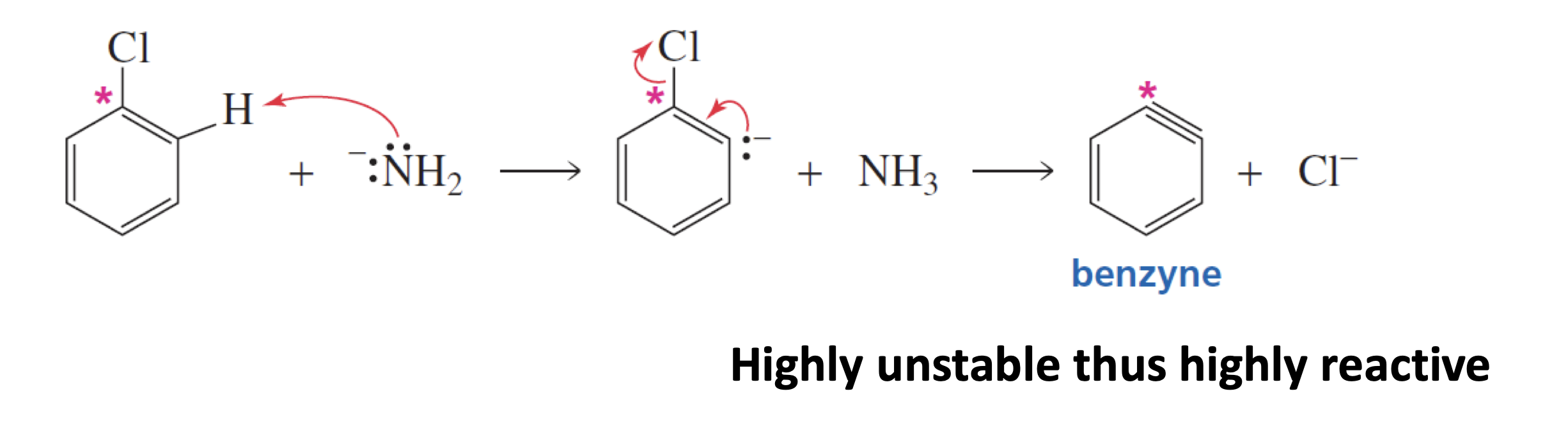
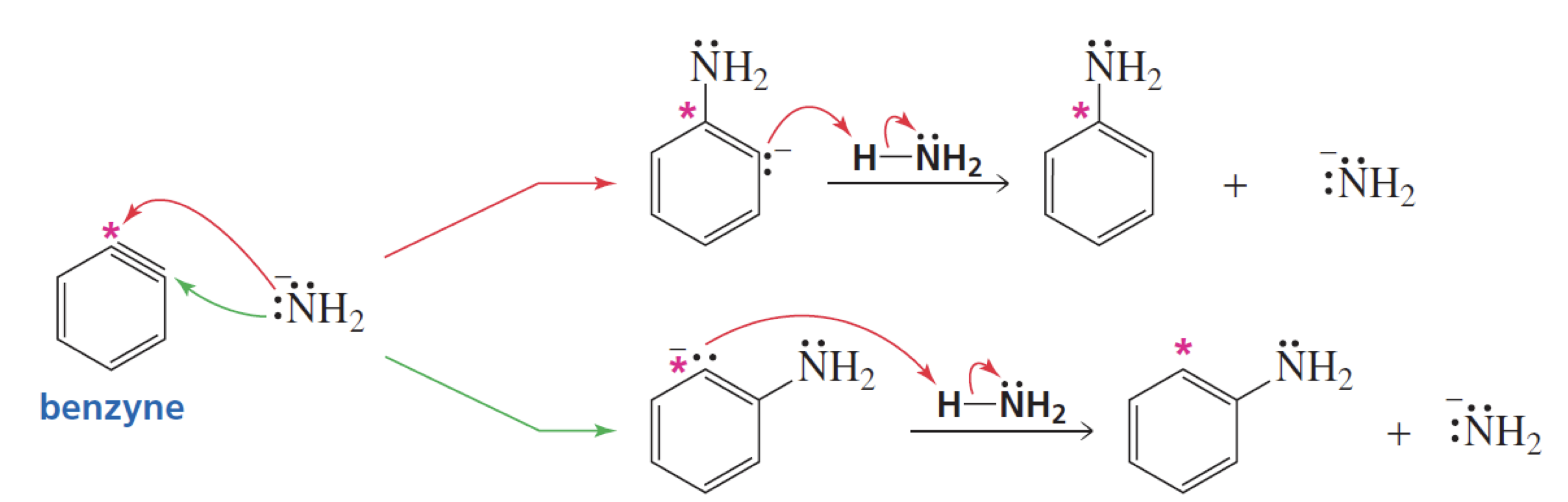
What happens after the formation of benzyne in the elimination-addition mechanism?
• The incoming nucleophile can attack either of the carbons of the “triple bond” of benzyne.
• Protonation of the resulting anion forms the substitution product.
• The overall reaction is an elimination–addition reaction: Benzyne is formed in an elimination reaction and immediately undergoes an addition
reaction.
What is the first step In the diazonium salt formation?

Explain the remainder of the diazonium salt formation after the nitrosonium ion formation