NSCI 311 L6 Flashcards L6 MT1 (V)
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
What are the 3 main functions of the brainstem?
1) Acts as a conduit (tracts)
2) Houses cranial nerve nuclei (III-XII, except XI)
3) Integrates vital functions
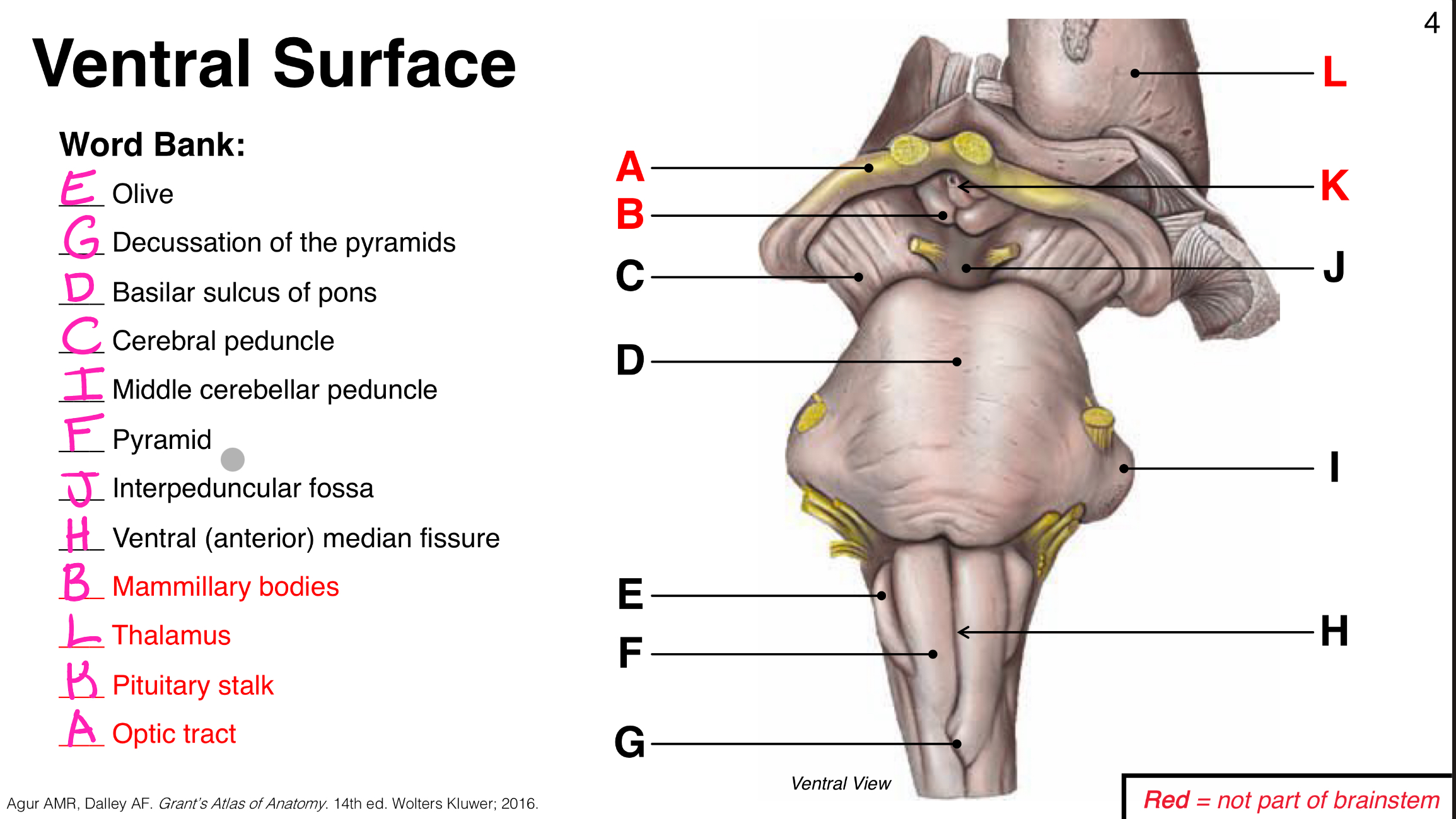
Ventral Surface Photo
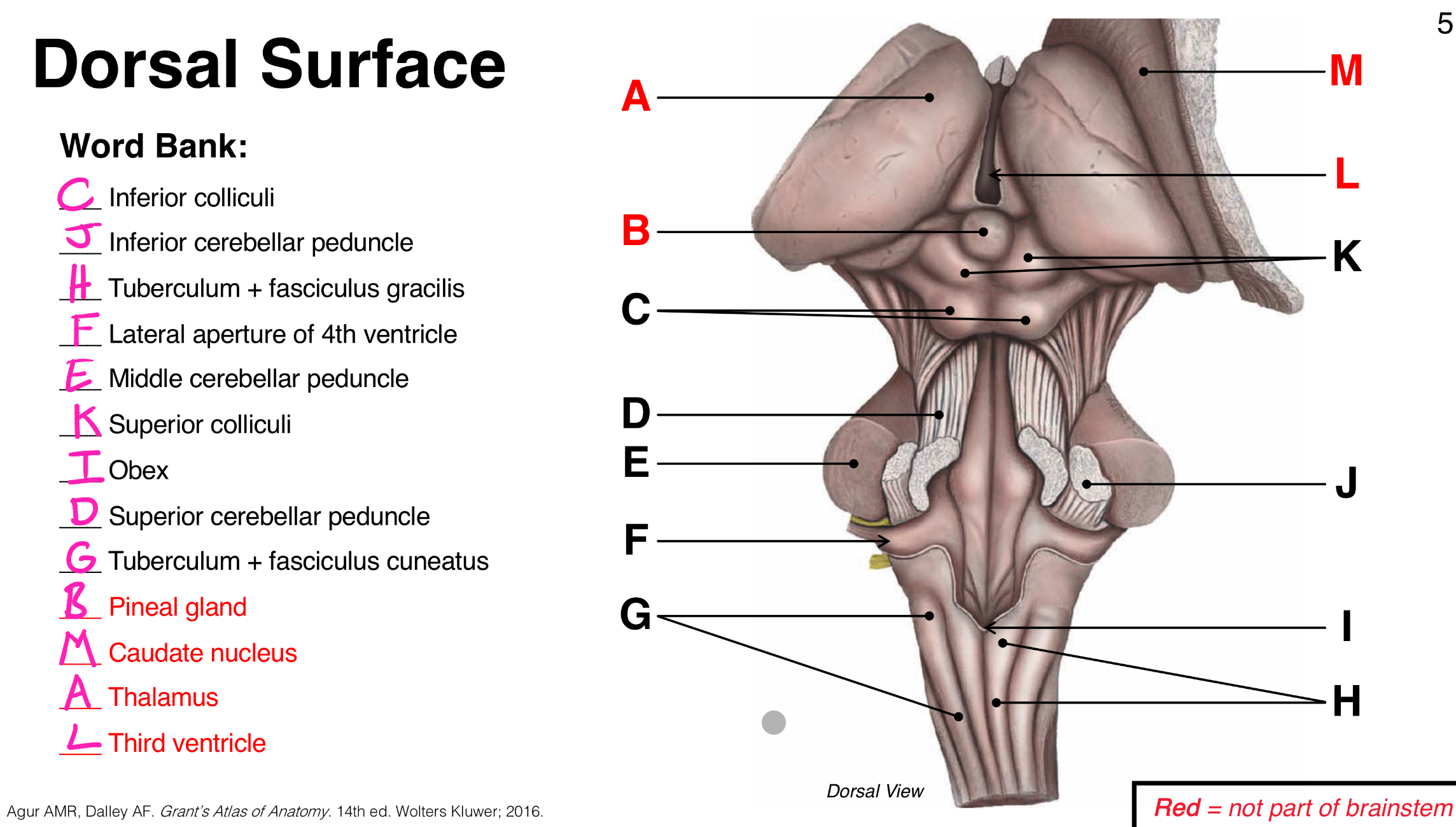
Doral Surface Photo
What are the 4 longitudinal partitions of the brainstem?
Base (ventral), Tegmentum, Ventricular System, Tectum (roof)
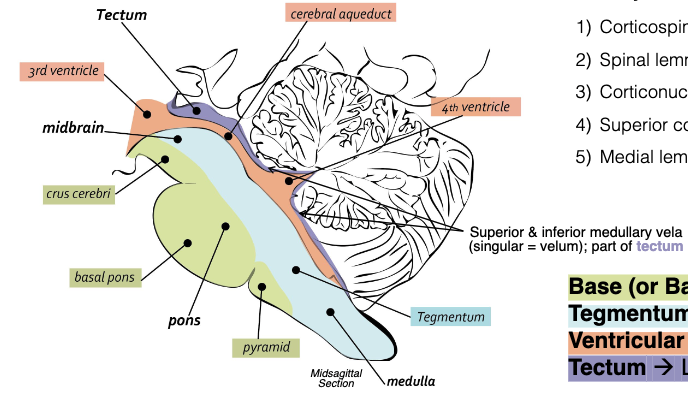
In which longitudinal partition would you find the…
1) Corticospinal fibers?
2) Spinal lemniscus?
3) Corticonuclear fibers?
4) Superior colliculi?
5) Medial lemniscus?

How many cranial nerve pairs are there?
12, numbered rostral → caudal
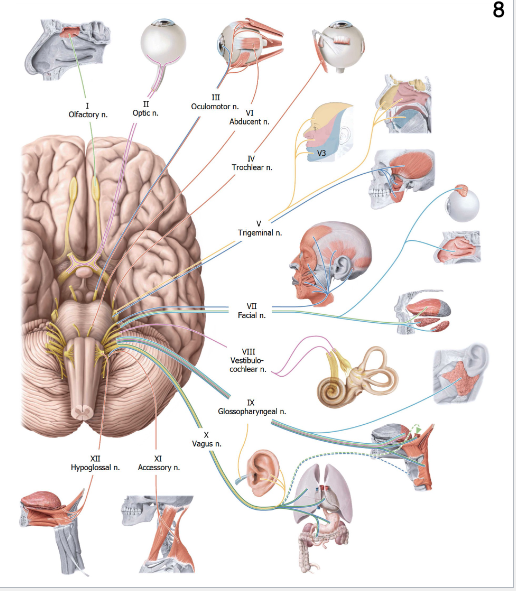
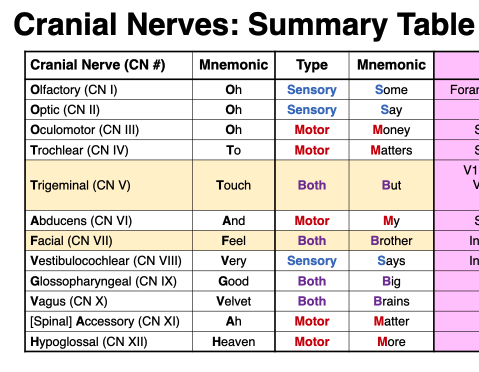
Cranial Nerve Mnemonics
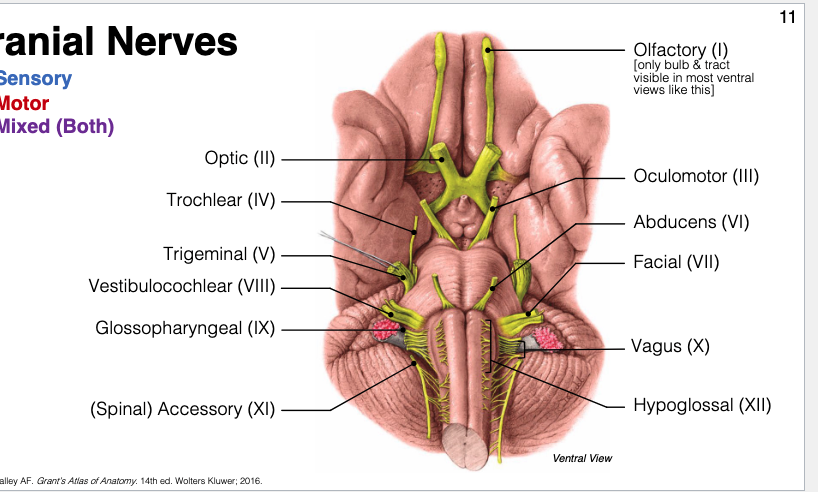
Which CNs are sensory only? Motor only? Mixed?
Sensory = I, II, VIII (O.V.O → Olfactory. Vestibulochlear. Optic)
Motor = III, IV, VI, XI, XII
Mixed = V, VII, IX, X (F.G.T.V → Facial. Glossopharyngeal. Trigeminal. Vagus)
What does SSA mean?
Special somatic afferent = Vision, hearing, balance
What does GSA mean?
General somatic afferent = Somatosensation from skin +muscles (Touch, pain, temp, proprioception etc)
What does SVA mean?
Special visceral afferent = Taste & smell
What does GVA mean?
General visceral afferent = Sensations from internal organs (e.g heart pain or gut cramps)
What does GVE mean?
General visceral efferent = Parasympathetic only (“rest & digest” + “feed & breed”) signalling to smooth muscle, glands etc
What does SVE mean?
Special visceral efferent = Motor info to branchial arch muscles (face, pharynx, larynx)
What does GSE mean?
General somatic efferent = Motor info to skeletal muscles
What are branchial arches?
Paired “outpouchings” (lil bulges) of mesoderm; also called “pharyngeal arches”
Where do somatic muscles of the head + neck originate?
Cranial somites
What are the 2 plates of a dividing neural tube?
Alar and basal plates
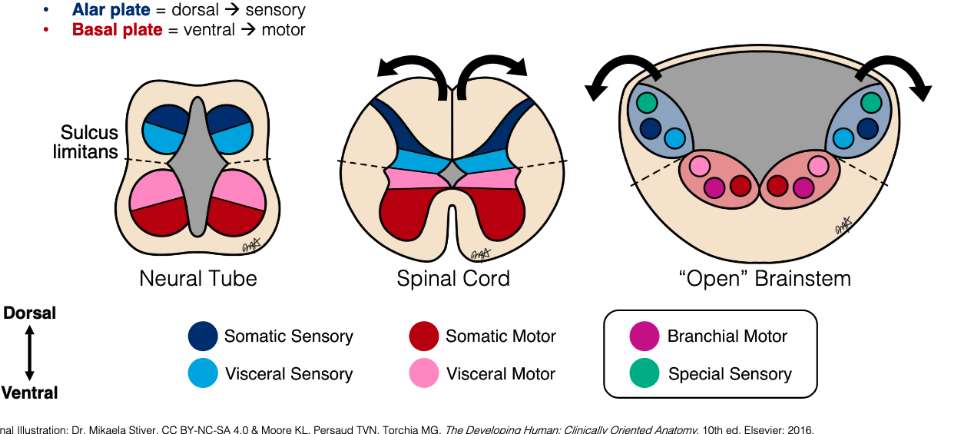
What divides alar vs basal plates?
Sulcus limitans
Alar vs Basal plate functions?
Alar = sensory (dorsal)
Basal = motor (ventral)
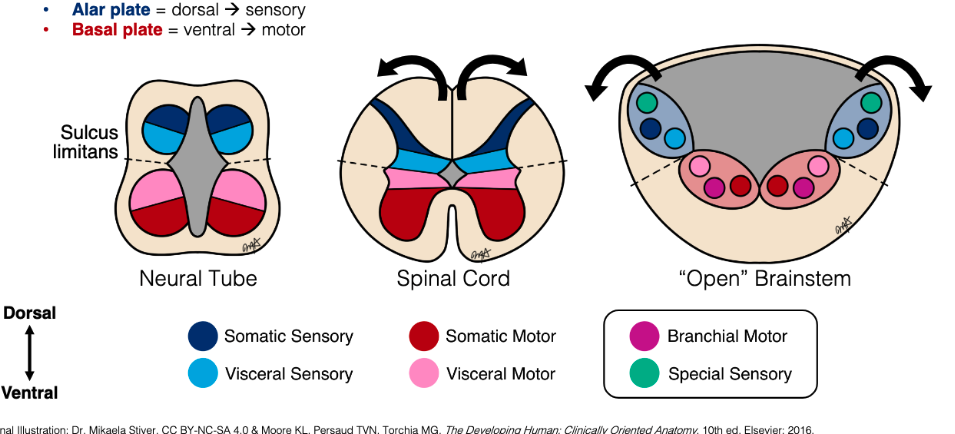
What migration pattern is shown here?
Secondary migration of branchial motor & somatic sensory nuclei
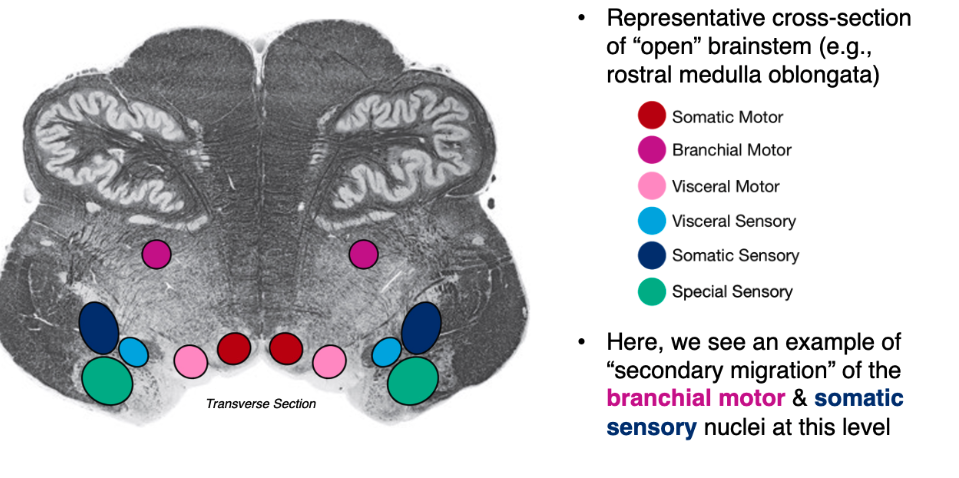
How are brainstem nuclei arranged longitudinally?
Same-modality nuclei align in (rostral-caudal) columns; not all columns at every level
SVA nuclei align with which column?
With GVA (visceral sensory)
Can one CN have multiple nuclei?
Yes—typically one nucleus per modality
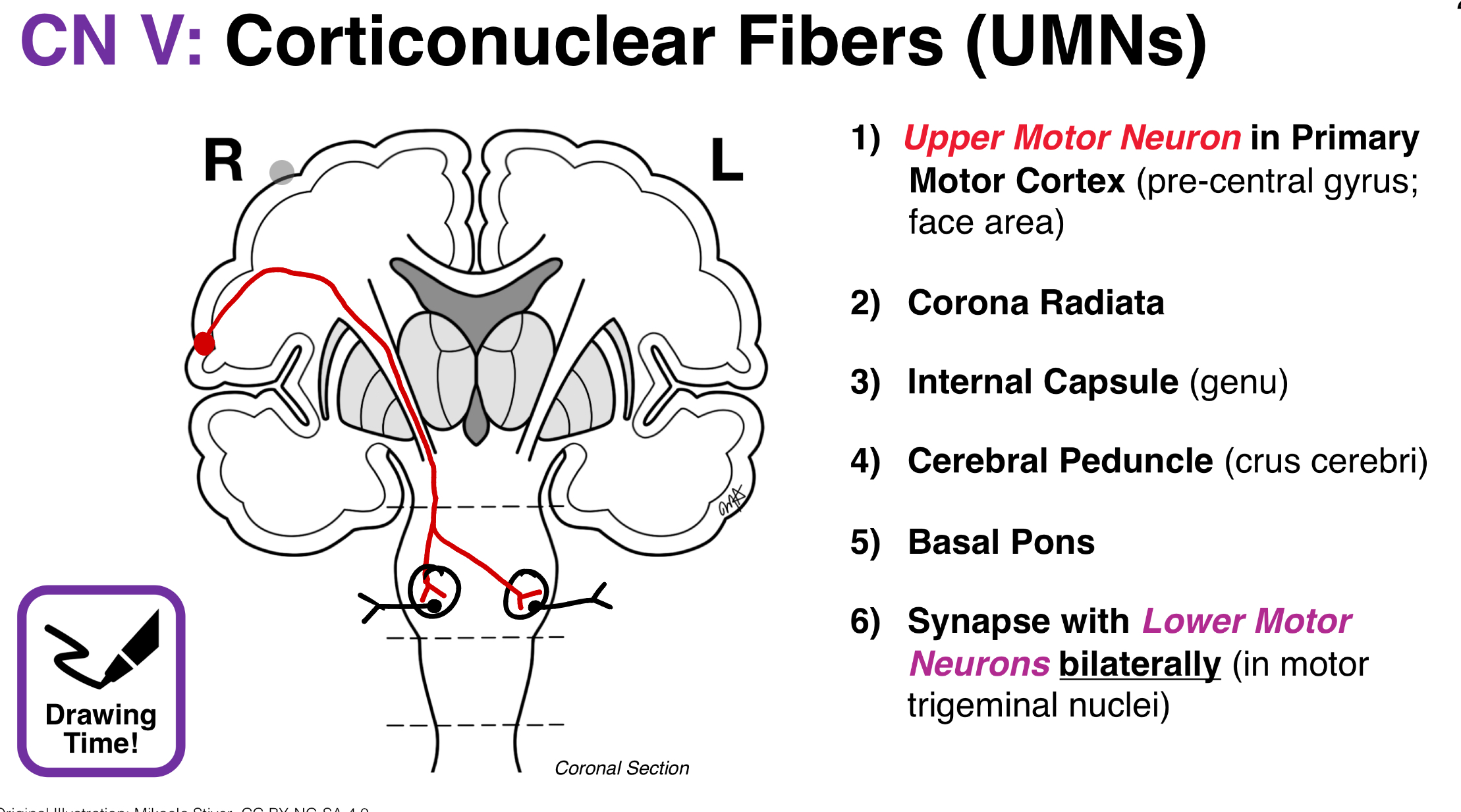
CN V (Trigeminal Nerve) type(s) & modalities?
Both sensory & motor;
Somatic sensation
Branchial motor
Parts of sensory trigeminal nerve nuclei?
3 parts:
Mesencephalic nucleus (midbrain → pons)
Chief nucleus (mid-pons)
Spinal nucleus (pons → cervical spine)
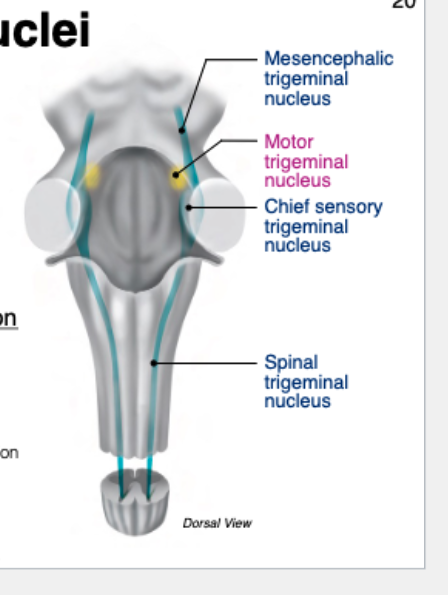
What does the spinal nucleus do?
Receives pain & temperature
Also continuous w/ the dorsal horn in the spinal cord
What does the chief sensory nucleus do?
Receives fine touch & vibration
Mesencephalic nucleus purpose?
Receives proprioception
Only nucleus w/ cell bodies of primary sensory neurons in the CNS
CN V: Corticonuclear Fibers (UMNs) Picture
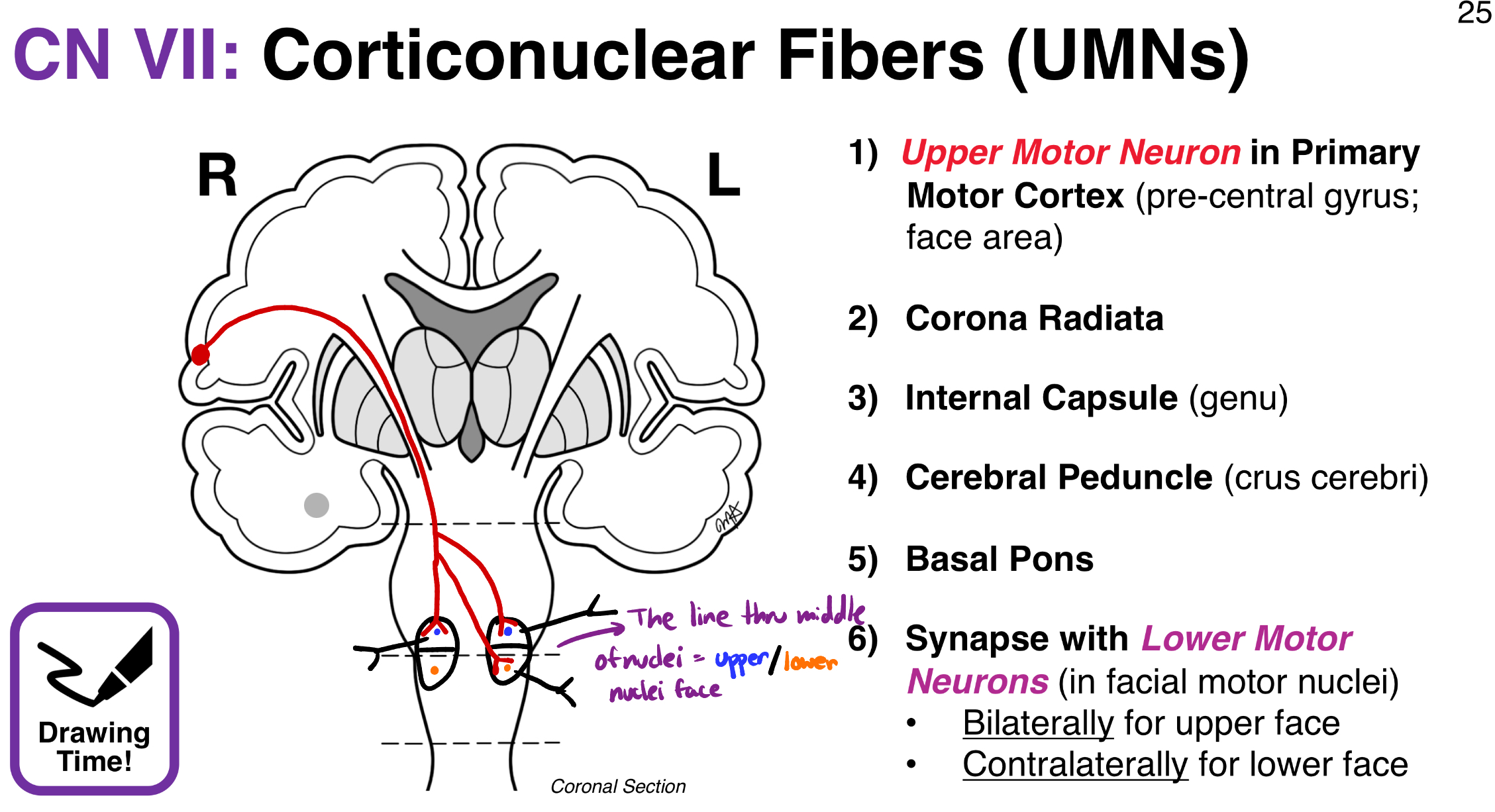
CN VII “modalities” (its sensory/motor neurons + functions)?
Both; sensory + motor
Branchial motor
Visceral motor
Special sensory (taste)
Somatic sensory
Facial motor nucleus function?
Branchial motor → muscles of facial expression
Fibers loop around abducens nucleus
Superior salivatory nucleus function?
Lacrimation (tear production)
Salivation (Saliva production)
Nucleus solitarius function?
Taste sensation
CN VII: Corticonuclear Fibers (UMNs) photo
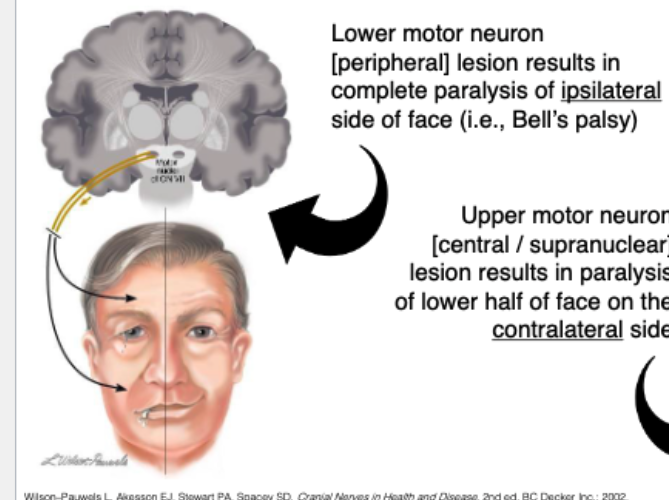
UMN (central) facial lesion causes…
Contralateral lower-face paralyis
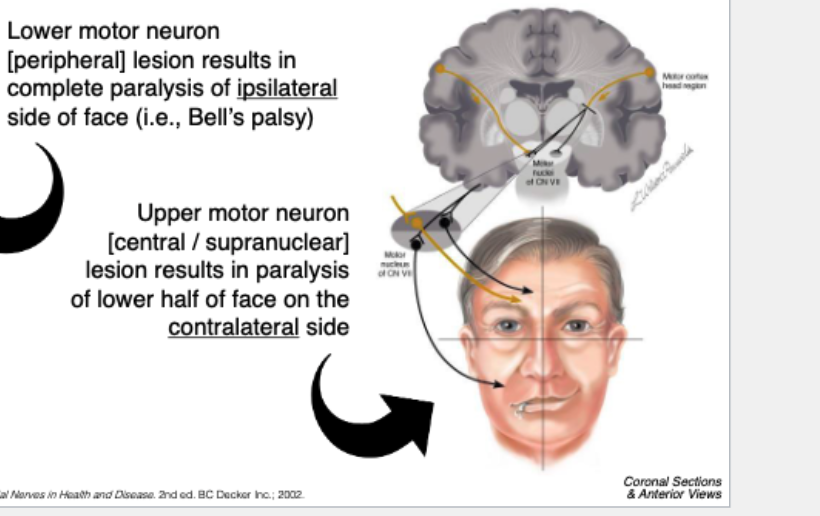
LMN (peripheral) facial lesion causes…
Entire ipsilateral side paralysis (i.e bell’s palsy)