Veterinary Immunology: Vaccine Types, Production, and Administration
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What is the primary role of vaccination in disease control?
Vaccination is the most efficient and cost-effective method of controlling infectious diseases in humans and animals.
What are the two main types of immunization procedures?
Passive Immunization and Active Immunization.
How does passive immunization provide protection?
It produces temporary immunity by transferring antibodies from a resistant to a susceptible animal, offering immediate protection that wanes over time.
What are some examples of passive immunization?
Serum containing antibodies (antisera), immune globulins, and toxoids.
What is the mechanism of active immunization?
It involves administering antigens to an animal, prompting the body to mount an immune response.
What is the advantage of active immunization?
It provides a prolonged period of protection and allows for recall and boosting of the immune response.
What is a disadvantage of active immunization?
Protection is not conferred immediately; it takes time to establish immunity.
What is the process of natural passive immunity?
Antibodies pass from mother to fetus across the placenta or through breast milk, providing immediate protection.
What is the significance of colostrum in passive immunity?
Colostrum provides antibodies to the newborn, with absorption highest immediately after birth and declining significantly after 24 hours.
What can cause failure of passive transfer?
Production failure by the dam or ingestion failure by the newborn.
What characterizes modified live vaccines?
They infect host cells and undergo viral replication, triggering a strong immune response but may carry risks of disease or persistent infection.
What are the safety concerns associated with modified live vaccines?
They may revert to a fully virulent type, spread to unvaccinated animals, or be contaminated with unwanted organisms.
What are killed vaccines and their advantages?
Killed vaccines act as exogenous antigens, are safe regarding residual virulence, and are relatively easy to store.
What is a disadvantage of killed vaccines?
They often require adjuvants to enhance effectiveness, which can cause severe inflammation or systemic toxicity.
What is the goal of inactivation in vaccine production?
To ensure killed organisms remain antigenically similar to living organisms without altering the protective antigens.
What is attenuation in vaccine production?
It is the process of reducing the virulence of living organisms so they can no longer cause disease but still remain alive.
What are the methods of attenuation?
Adapting organisms to unusual growth conditions, genetic manipulation, or growth in non-natural hosts.
What is Category I in modern vaccine technology?
Antigens generated by gene cloning, where DNA coding for an antigen is isolated and expressed in a host cell.
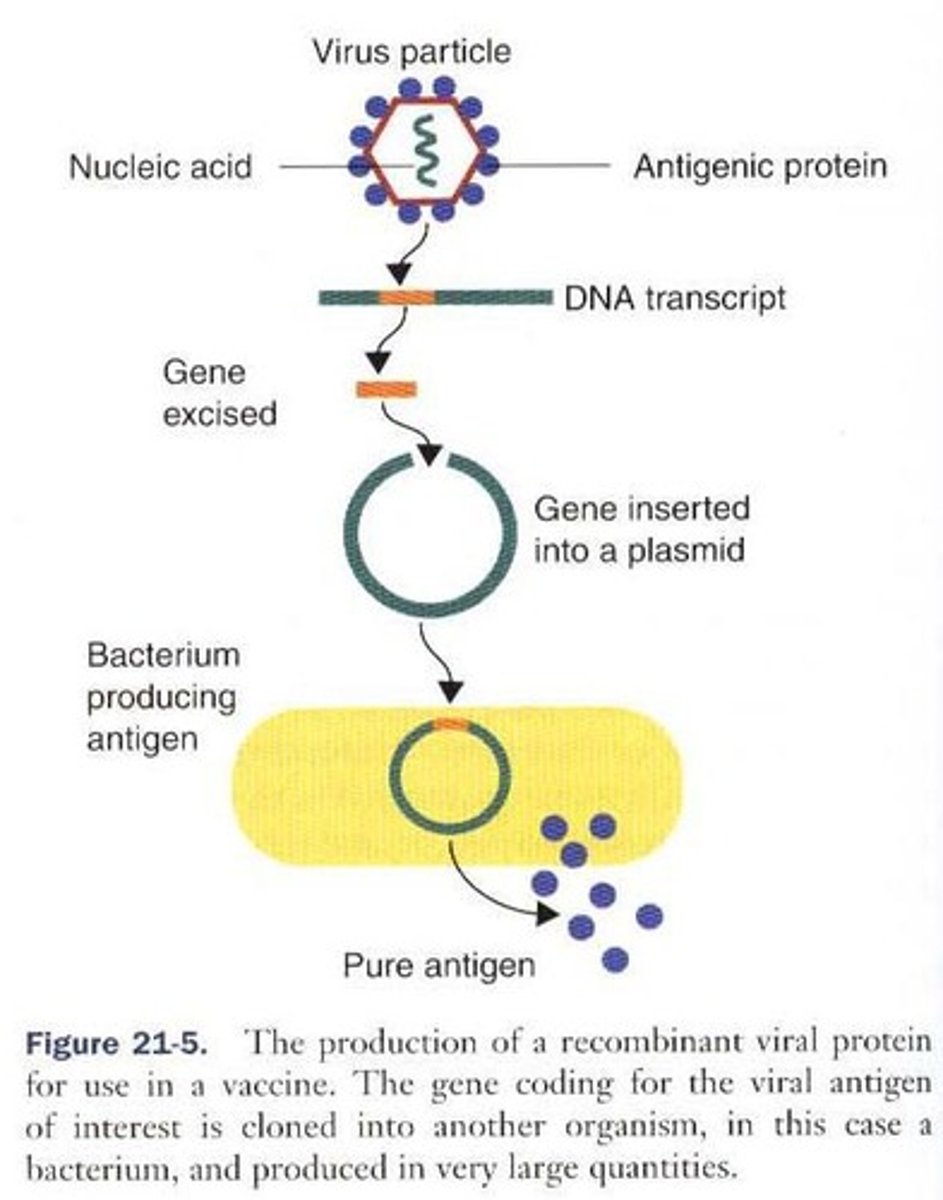
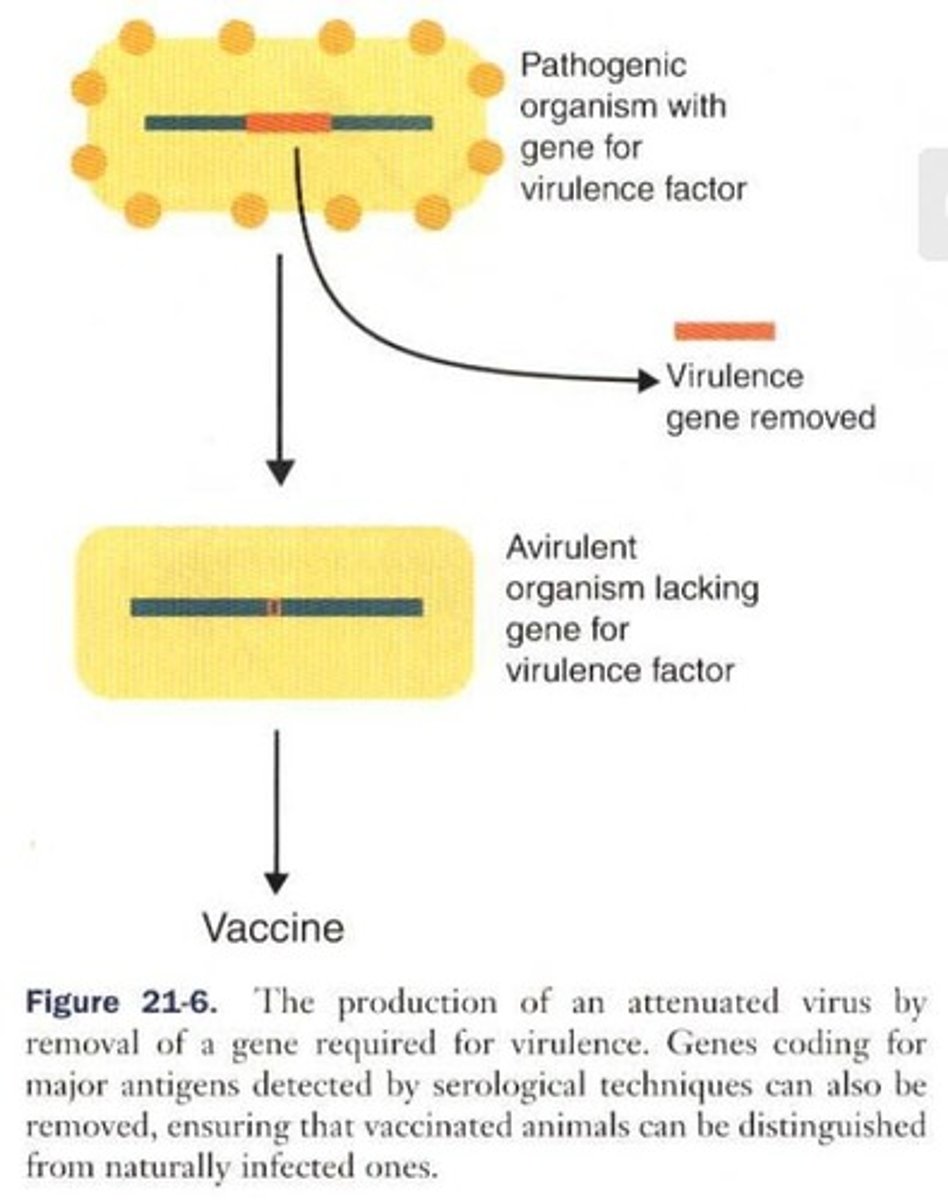
What is Category II in modern vaccine technology?
Genetically attenuated organisms, where molecular techniques irreversibly modify genes to create attenuated strains.
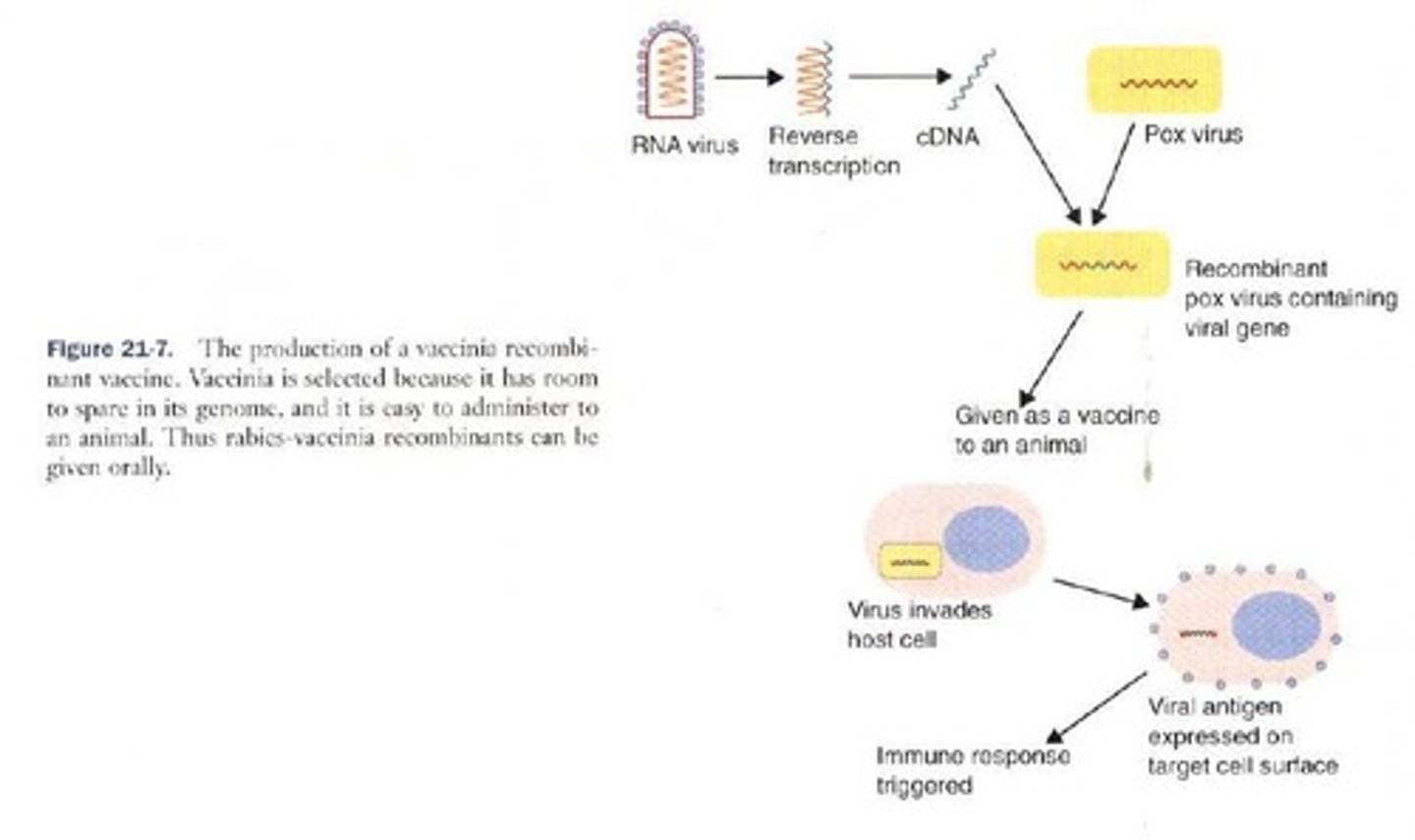
What is Category III in modern vaccine technology?
Live recombinant organisms, where genes coding for protein antigens are cloned into various organisms for vaccine development.
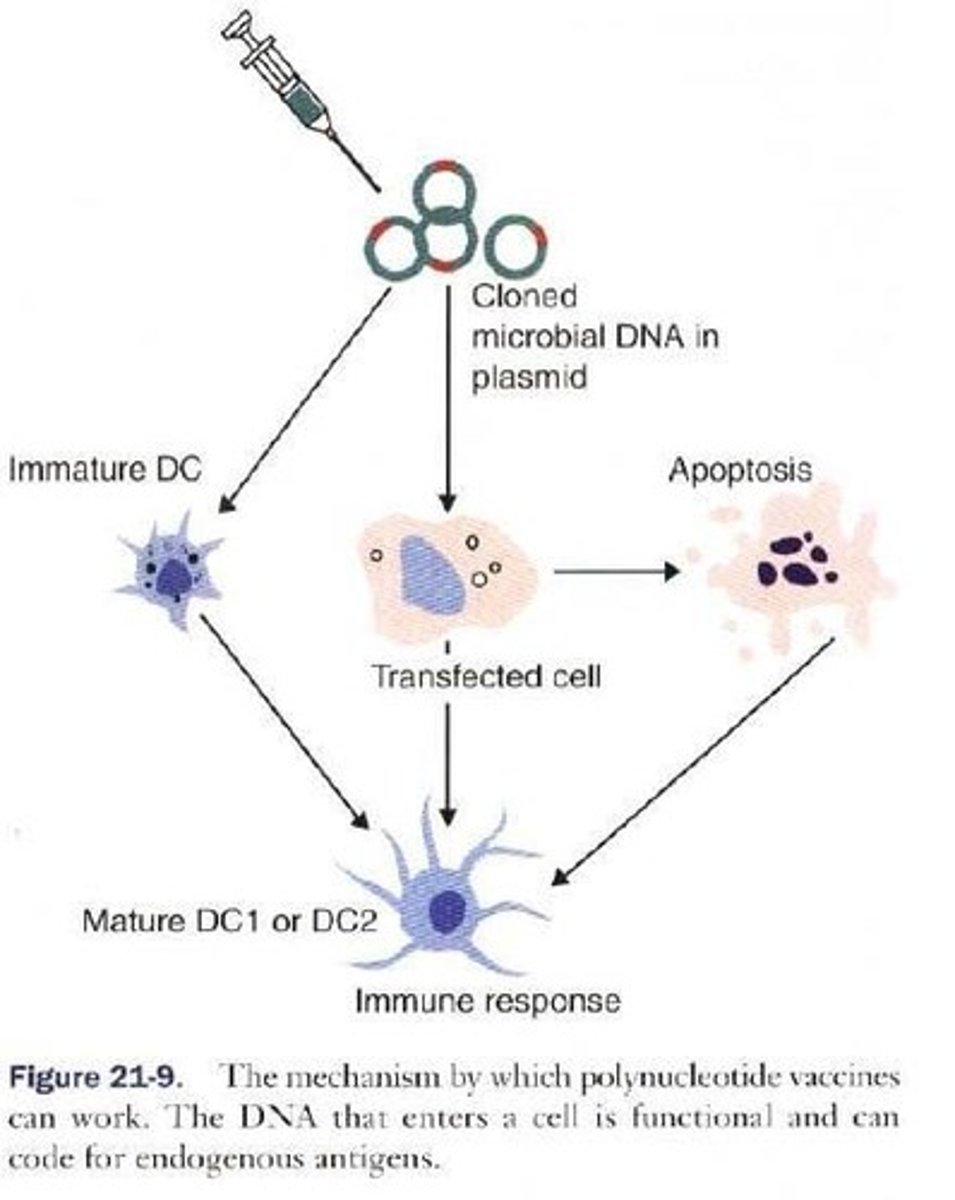
What are polynucleotide vaccines?
Vaccines that involve the injection of DNA encoding foreign antigens, which is taken up by host cells and transcribed into proteins.
What role do adjuvants play in vaccination?
Adjuvants enhance the effectiveness of vaccines, especially those containing killed organisms, and help establish long-term memory.
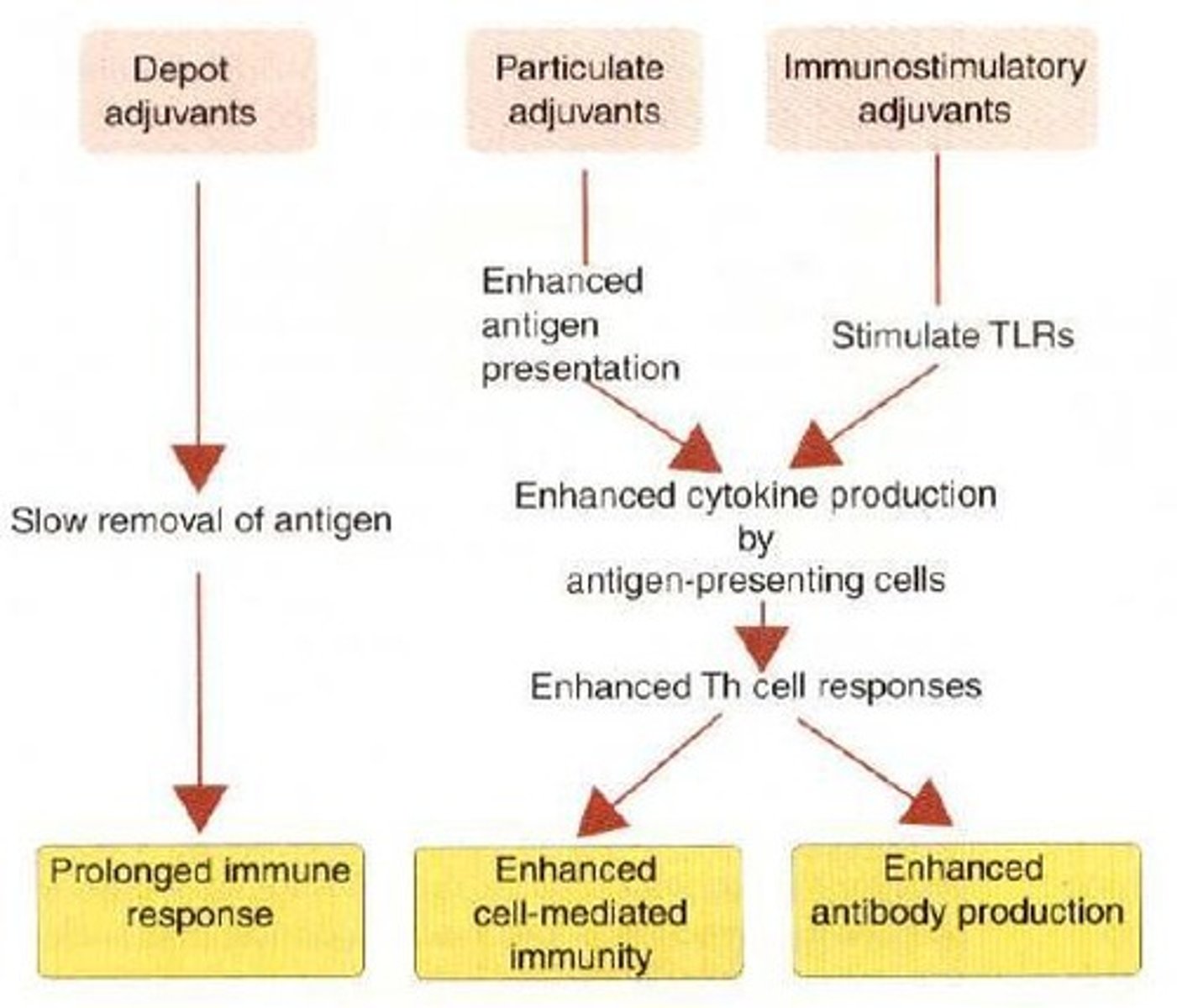
What are the three major groups of adjuvants?
Depot, particulate, and Immunostimulatory adjuvants
What is the ideal characteristic of a vaccine?
It should be cheap, stable, adaptable to mass vaccination, stimulate an immune response distinguishable from natural infection, and be free of adverse side effects.
What is the importance of understanding immune mechanisms in vaccine technology?
It allows for the optimization of immune responses and the advancement of vaccine technology.
What is the significance of reimmunization in active immunization?
It results in a secondary immune response that greatly enhances immunity.