The working memory model - Baddeley & Hitch
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Why was the WMM created?
The MSM provides us with an oversimplified representation of human memory.
The WMM focuses on STM /' ‘working memory’
Baddeley and Hitch felt that STM was not just one store, but was made from different stores.
What is an issue with the WMM?
Focusing on STM makes it reductionist as there is other memory stores like LTM.
How is the WMM supported?
Supported by KF because as he couldn’t remember verbal things but he could remember visual things.
What is the basic understanding of the WMM?
All information that comes through the sensory store is kept here for a period of time and ‘worked on’ before it is either lost or transferred somewhere else.
We rely on this store for many functions such as remembering phone numbers, lists, mental calculations and reasoning.
A diagram of the WMM.
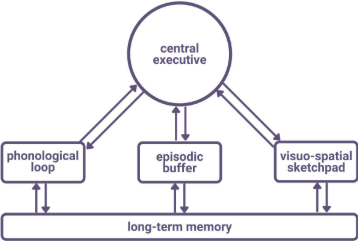
What are the 4 stores in the WMM?
The central exe3cutive.
Visuospatial sketchpad (inner eye)
Phonological loop
Episodic buffer
What is the central executives function?
It drives the whole system and allocates data to the sub-systems - central part of working memory.
Its function is to direct attention to particular tasks.
Determines how the other parts of the model are used, and has the capacity to focus, divide and switch attention.
Very limited capacity.
It also deals with cognitive tasks such as mental arithmetic and problem solving.
What is the function of the visuospatial sketchpad (inner eye)
Slave system.
Used to manipulate verbal and spatial information.
Stores and processes information in visual or spatial form.
The visuospatial sketchpad is used for navigation.
It can deal with information directly through images or information from LTM.
Used when you have to plan a spatial task - e.g. getting from one place to another.
What is the visuospatial sketchpad split into, and what do they do?
Visual cache - Stores information about form and colour.
Inner scribe - Deals with spatial information and movement.
What is the phonological loops function?
Slave system.
Deals with spoken and written material.
Limited capacity
Sub-divided into:
the phonological store which holds information in a speech based form.
And the articulatory process which allows us to repeat verbal information in a loop.
What are the phonological store and articulatory process used for?
The phonological store - Holds words you hear (difficulty when words sound the same.)
The articulatory process - Used for words that are seen and heard (difficulty when the words are long.)
These words are silently repeated (looped) which is a form of maintenance rehearsal.
What is the function of the episodic buffer?
This was added by Baddeley in 2000.
He felt that the model needed a more general store.
Because the slave systems deal with specific types of information - there is nowhere to hold both visual and auditory information.
The episodic buffer is multi-modal - it is not limited to one sense like the other two slave systems.
Its job sems to be to ‘bind’ memories together, weaving visual memories and phonological memories into single episodes.
Which then get stored in episodic LTM.