Chapter 2: Reasoning and Proofs Overview
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Conditional statement
A logical statement that has a hypothesis and a conclusion.
If-then form
A conditional statement in the form 'if p, then q'.
Hypothesis
The 'if' part of a conditional statement written in if-then form.
Conclusion
The 'then' part of a conditional statement written in if-then form.
Negation
The opposite of a statement.
Converse
The statement formed by exchanging the hypothesis and conclusion of a conditional statement.
Inverse
The statement formed by negating both the hypothesis and conclusion of a conditional statement.
Contrapositive
The statement formed by negating both the hypothesis and conclusion of the converse of a conditional statement.
Two-column proofs
A type of proof that has numbered statements and corresponding reasons that show an argument in a logical order.
Equivalent statements
Two related conditional statements that are both true or both false.
Perpendicular lines
Two lines that intersect to form a right angle.
Biconditional statement
A statement that contains the phrase 'if and only if'.
Truth table
A table that shows the truth values for a hypothesis, conclusion, and conditional statement.
Conjecture
An unproven statement that is based on observations.
Inductive reasoning
A process that includes looking for patterns and making conjectures.
Counterexample
A specific case for which a conjecture is false.
Deductive reasoning
A process that uses facts, definitions, accepted properties, and laws of logic to form a logical argument.
Theorem
A statement that can be proven.
Truth value
A value that represents whether a statement is true (T) or false (F).
Line perpendicular to a plane
A line that intersects the plane in a point and is perpendicular to every line in the plane that intersects it at that point.
Proof
A logical argument that uses deductive reasoning to show that a statement is true.
Flowchart proof
A type of proof that uses boxes and arrows to show the flow of a logical argument.
Paragraph proof
A style of proof that presents statements and reasons as sentences in a paragraph, using words to explain the logical flow of an argument.
Two Point Postulate
Through any two points, there exists exactly one line.
Line-Point Postulate
A line contains at least two points.
Line Intersection Postulate
If two lines intersect, then their intersection is exactly one point.
Three Point Postulate
Through any three noncollinear points, there exists exactly one plane.
Plane-Point Postulate
A plane contains at least three noncollinear points.
Plane-Line Postulate
If two points lie in a plane, then the line containing them lies in the plane.
Plane Intersection Postulate
If two planes intersect, then their intersection is a line.
Linear Pair Postulate
If two angles form a linear pair, then they are supplementary.
Properties of Segment Congruence
Segment congruence is reflexive, symmetric, and transitive.
Reflexive Property of Segment Congruence
For any segment AB, 𝐴𝐴𝐴𝐴 ≅ 𝐴𝐴𝐴𝐴.
Symmetric Property of Segment Congruence
If 𝐴𝐴𝐴𝐴 ≅ 𝐶𝐶𝐶𝐶, then 𝐶𝐶𝐶𝐶 ≅ 𝐴𝐴𝐴𝐴.
Transitive Property of Segment Congruence
If 𝐴𝐴𝐴𝐴 ≅ 𝐶𝐶𝐶𝐶 and 𝐶𝐶𝐶𝐶 ≅ 𝐸𝐸𝐸𝐸, then 𝐴𝐴𝐴𝐴 ≅ 𝐸𝐸𝐸𝐸.
Properties of Angle Congruence
Angle congruence is reflexive, symmetric, and transitive.
Reflexive Property of Angle Congruence
For any angle A, ∠𝐴𝐴 ≅ ∠𝐴𝐴.
Symmetric Property of Angle Congruence
If ∠𝐴𝐴 ≅ ∠𝐵𝐵, then ∠𝐵𝐵 ≅ ∠𝐴𝐴.
Transitive Property of Angle Congruence
If ∠𝐴𝐴 ≅ ∠𝐵𝐵 and ∠𝐵𝐵 ≅ ∠𝐶𝐶, then ∠𝐴𝐴 ≅ ∠𝐶𝐶.
Right Angles Congruence Theorem
All right angles are congruent.
Congruent Supplements Theorem
If two angles are supplementary to the same angle (or to congruent angles), then they are congruent.
Congruent Complements Theorem
If two angles are complementary to the same angle (or to congruent angles), then they are congruent.
Vertical Angles Congruence Theorem
Vertical angles are congruent.
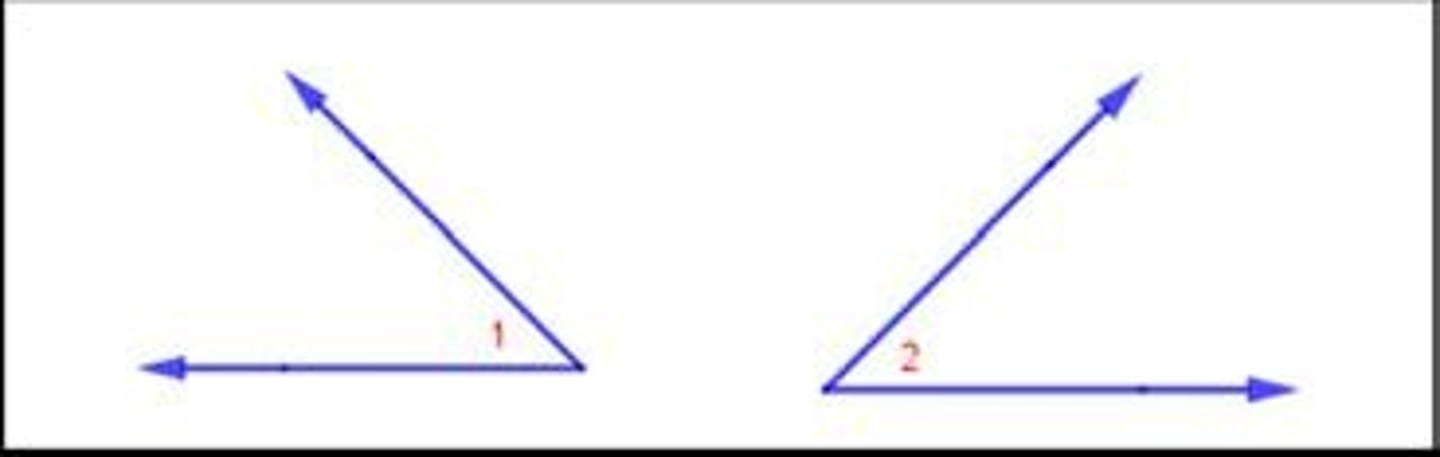
Addition Property of Equality
If a = b, then a + c = b + c.
Subtraction Property of Equality
If a = b, then a - c = b - c.
Multiplication Property of Equality
If a = b, then a∙𝑐 = 𝑏∙𝑐, 𝑐≠0.
Division Property of Equality
If a = b, then 𝑎/𝑐 = 𝑏/𝑐, c ≠0.
Substitution Property of Equality
If a = b, then a can be substituted for b (or b for a) in any equation or expression.
Distributive Property
a(b + c) = ab + ac.
Law of Detachment
If the hypothesis of a true conditional statement is true, then the conclusion is also true.
Law of Syllogism
If hypothesis p, then conclusion q. If hypothesis q, then conclusion r. If these statements are true, then this last statement is true.
Two-Column Proof
In a proof, you make one statement at a time until you reach the conclusion.
Proof of the Symmetric Property of Angle Congruence
Given: ∠1 ≅ ∠2; Prove: ∠2 ≅ ∠1.
Statements in Proofs
Statements based on facts that you know or on conclusions from deductive reasoning.
Reasons in Proofs
Definitions, postulates, or proven theorems that allow you to state the corresponding statement.
Symmetric Property of Equality
If a = b, then b = a.
Reflexive Property
For any real number a, a = a.
Transitive Property
If a = b and b = c, then a = c.
Real Numbers
Numbers that include all the rational and irrational numbers.
Segment Lengths
The distance between two points on a line segment.
Angle Measures
The measure of an angle in degrees or radians.
Reflexive Property of Congruence
For any angle ∠A, ∠A ≅ ∠A.
Symmetric Property of Congruence
If ∠A ≅ ∠B, then ∠B ≅ ∠A.
Transitive Property of Congruence
If ∠A ≅ ∠B and ∠B ≅ ∠C, then ∠A ≅ ∠C.