Pre- AP Biology | Ch. 10-17 | FINAL EXAM|
1/127
Earn XP
Description and Tags
You're cooked lil bro.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
128 Terms
P Generation
The parent generation in a genetic cross (P = parental).
F1 Generation
The first filial generation—offspring of the P generation.
F2 generation
The second filial generation—offspring of the F1 generation (grandkids of the P gen).
Alleles
Different versions of the same gene (e.g., tall vs. short for plant height)
Dominant Traits
Shows up if at least one dominant allele is present (e.g., T)
Recessive Traits
Only shows if both alleles are recessive (e.g., tt).
Probability
The likelihood that an event will occur.
Homozygous, dominant and recessive
Homozygous dominant: Two dominant alleles (TT).
Homozygous recessive: Two recessive alleles (tt).
Homozygous
Has two identical alleles for a gene. It can be homozygous dominant (TT) or homozygous recessive (tt).
Heterozygous
One dominant and one recessive allele (Tt).
Phenotype
What the organism looks like (e.g., tall or short).
Genotype
The genetic makeup (e.g., TT, Tt, or tt).
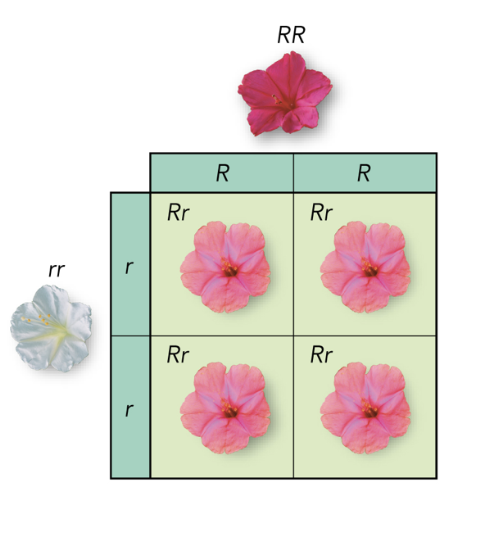
Punnett Square
A chart used to predict the possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring.
Principle (Law) of Independent Assortment
The principle stating that allele pairs separate independently during the formation of gametes, allowing for a variety of combinations in offspring. Genes for different traits separate independently during gamete formation (meiosis).
Principle (Law) of Segregation
Each parent passes only one allele for a trait to offspring (alleles separate during gamete formation).
Codominance
Both alleles show equally in the phenotype (e.g., AB blood type).

Incomplete Dominance
A blend of both alleles shows (e.g., red + white = pink flowers).
Environmental Factors and Genetics
Skin color is affected by exposure to the sun.
Heart disease and cancer can be influenced by genes and the environment.
Nutrition influences height.
Exercise influence body shape.
Sex Chromosomes
Sex chromosomes: X and Y determine biological sex (XX = female, XY = male). Pair 23 determines your gender.
Gametes
Reproductive cells (sperm and egg) with half the chromosome.
Haploid
A cell with one set of chromosomes (n), like a gamete.
Diploid
A cell with two sets of chromosomes (2n), like body cells.
Meiosis
Is the process in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half through the separation of homologous chromosomes in a diploid cell. (Has two cellular divisions)
Interphase (Meiosis)
Happens before meiosis.
The chromosomes replicate/duplicate.
Two centrosomes form, which are organelles that are used during cell division.
By the end of interphase the cell is ready to divide.
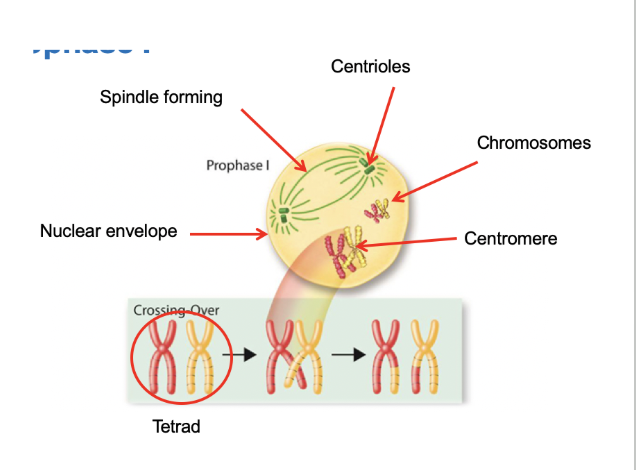
Prophase I (Meiosis)
After interphase the cell begins to divide and the chromosomes pair up.
Each replicated chromosome pairs with its corresponding homologous chromosomes.
The paring forms a tetrad, which contains four chromatids.
Crossing over may happen, which is when parts of the homologous chromosomes exchange. This leads to more variation.
The nuclear membrane breaks apart.
Spindle fibers form from the centrioles.
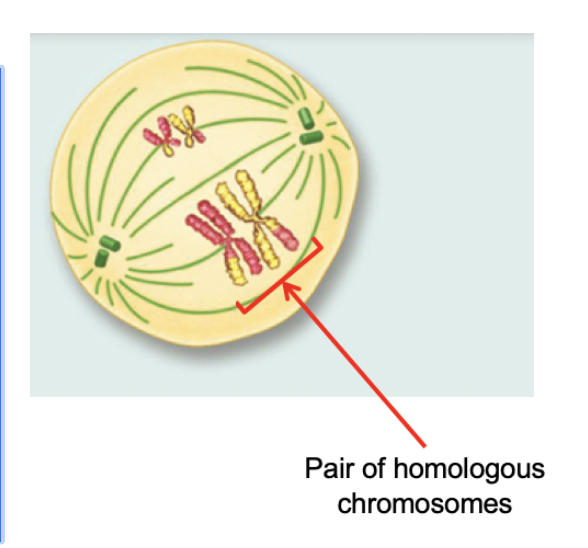
Metaphase I (Meiosis)
Paired homologous chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell.
Mitotic spindles come out of the centrosomes. They attach to each chromosome and they guide the separation of the two sets of chromosomes.
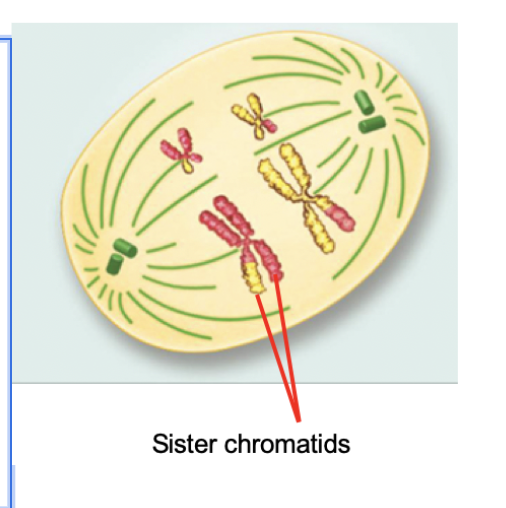
Anaphase I (Meiosis)
During anaphase I the spindle fibers pull each homologous chromosomes apart toward opposite ends of the cell.
The sister chromatids remain attached.
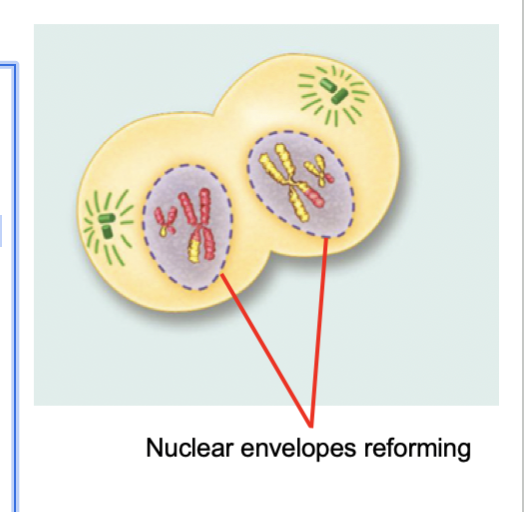
Telophase I (Meiosis)
The cell elongates.
The chromosomes have reached the opposite ends of the cell.
The nuclear membrane forms around each cluster of chromosomes.
Telophase divides the DNA.
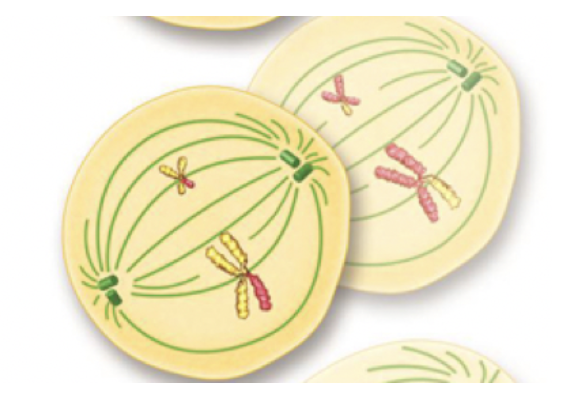
Cytokinesis (Meiosis)
Cytokinesis follows and forms two new cells.
Cytokinesis divides the cell organelles and the cytoplasm.
The mitotic spindle retract into the centrosomes.
Prophase II (Meiosis)
The chromosomes, each containing two chromatids become visible.
The chromosomes do not pair to form tetrad, because the homologous pair were separated during meiosis I.
The mitotic spindles form the centrosome.
The nuclear membrane breaks apart.

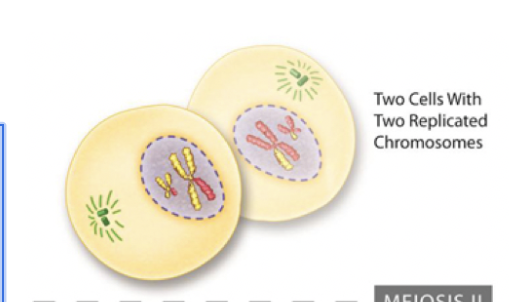
Metaphase II (Meiosis)
The chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell.
The mitotic spindle attach to the chromosomes.
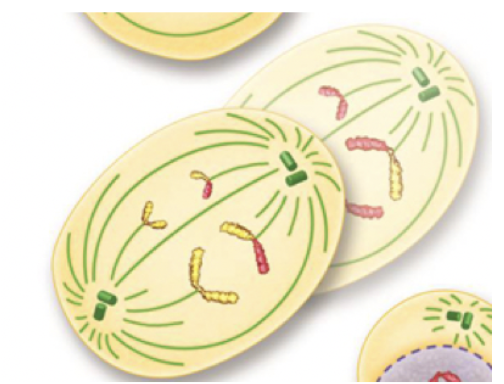
Anaphase II (Meiosis)
The paired chromatids separate as they move apart towards opposite ends of the cell.
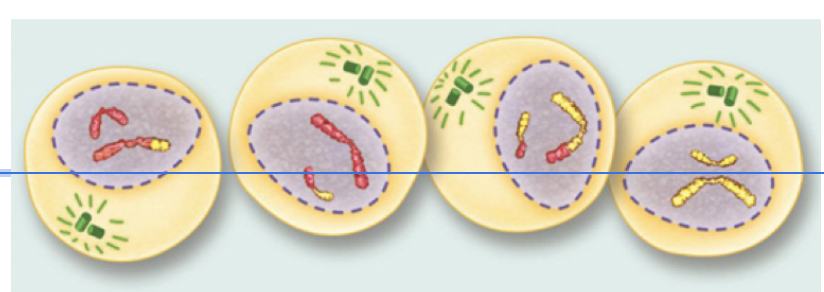
Telophase II (Meiosis)
The cell elongates.
The chromosomes move towards the poles.
A nuclear membrane forms around each set of chromosomes.
The DNA is divided.
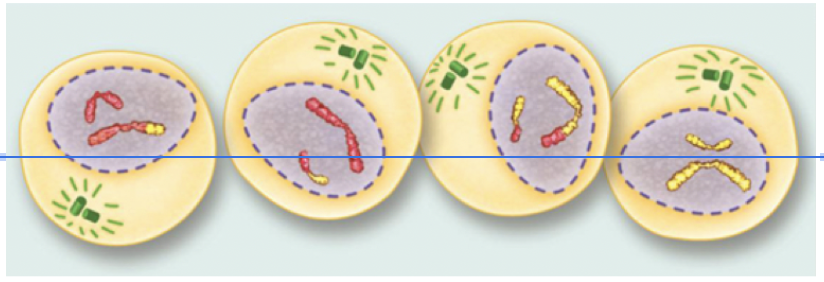
Cytokinesis II (Meiosis)
In cytokinesis the cytoplasm and the organelles divide.
The end result is four haploid daughter cells that are genetically different. They have half the number of chromosomes.
Spindle Fibers
Structures that help pull chromosomes apart during cell division.
Crossing Over
During meiosis, when parts of the homologous chromosomes exchange. This leads to more variation.
What DNA does?
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) is the molecule that stores genetic information.
It gives the instructions to make proteins and controls traits in living things.
DNA is made up of nucleotides.
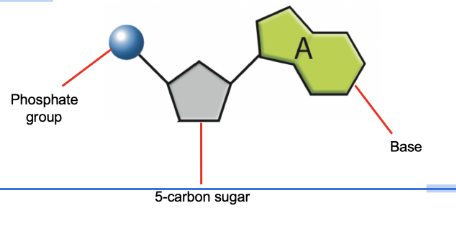
Nucleotides
Join together to form a strand of DNA.
A nucleotide is made up of three things:
A 5 carbon sugar called deoxyribose
A phosphate group
A nitrogen base (one of four)
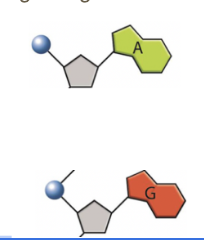
Purines
Adenine (A) and Guanine (G) are purines.
They have a double-ring structure.
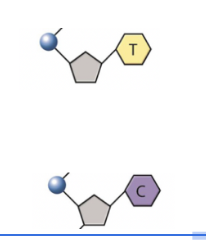
Pyrimidines
Thymine (T) and Cytosine (C) are pyrimidines.
They have a single-ring structure.
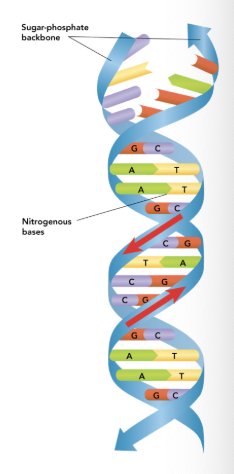
Chargaff’s Base Pairing Rules
Adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T)
Guanine (G) pairs with cytosine (C).
Rosalind Franklin
Took X-ray images of DNA.
Her photo (called Photo 51) showed that DNA had a twisted, helical shape.
Watson and Crick
Used Franklin’s data to build the first accurate model of the DNA double helix.
DNA Double Helix
Shaped like a twisted ladder.
Sides = sugar + phosphate (backbone)
Rungs = base pairs (A-T, C-G)
DNA Replication
DNA makes a copy of itself before a cell divides.
It happens during the S phase of the cell cycle.
DNA is Semiconservative
Each new DNA molecule has one old strand and one new strand.
This helps reduce mistakes.
DNA is Complementary
The strands match up by base pairing:
A ↔ T
C ↔ G
If you know one side, you can figure out the other.
Role of Enzymes in DNA Replication
Helicase: Unzips the DNA strands.
DNA polymerase: Adds new bases and proofreads them.
Ligase: Seals the DNA fragments (like glue).
Replicate a DNA Strand
If a DNA strand is:
A T G C C A
Then the complementary strand is:
T A C G G T
RNA (Ribonucleic Acid)
A single-stranded molecule that helps make proteins.
Uses uracil (U) instead of thymine (T).
RNA uses DNA instructions to direct the production of amino acids into proteins which help determine an organism’ characteristics.
Types of RNA
mRNA (messenger RNA): Carries the code from DNA to ribosomes.
rRNA (ribosomal RNA): Part of the ribosome—helps build proteins.
tRNA (transfer RNA): Brings amino acids to the ribosome during translation.
Transcription
Happens in the nucleus.
DNA is used to make mRNA.
RNA base pairing rules:
A ↔ U
T ↔ A
C ↔ G
G ↔ C
Translation
Happens in the ribosome.
mRNA code is read to build a protein (chain of amino acids).
Codons
A codon is a set of 3 mRNA bases that codes for 1 amino acid.
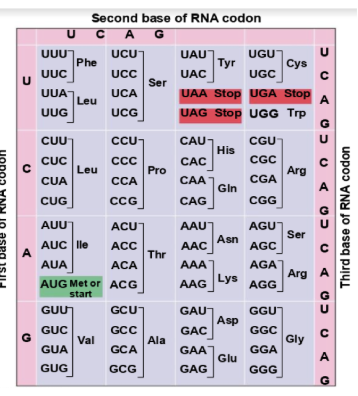
Anticodons
Found on tRNA—3 bases that pair with the codon on mRNA.
Amino Acids
The building blocks of proteins.
Brought in order by tRNA based on the mRNA code.
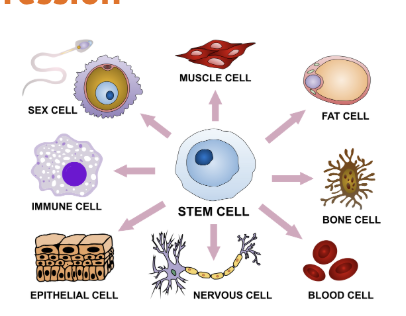
Differentiation
When cells become specialized for a specific job (e.g., muscle, skin, nerve).
Gene Mutations
Changes in DNA that affect proteins.
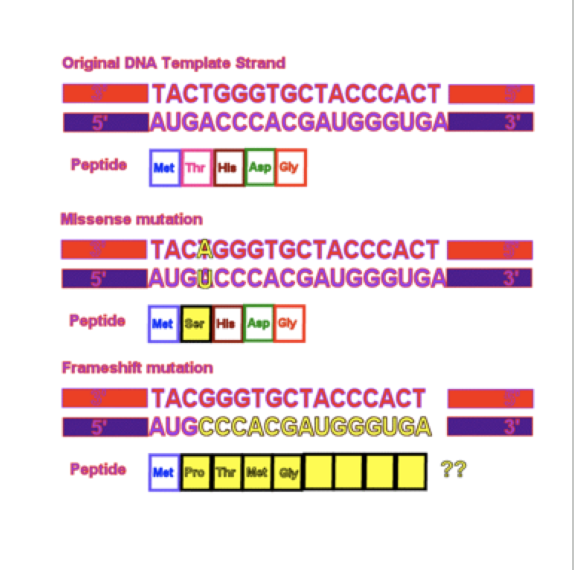
Point Mutations
Affect a single nucleotide. They involve one base changing into a different base.
Broken into 3 types Silent Mutation, Nonsense Mutation, and Missense Mutations
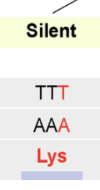
Silent Mutation
It only affects a single amino acid, and sometimes they have no effect because some amino acids are coded by different codons.
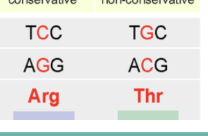
Missense mutation
Change into a different amino acid.
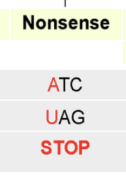
Nonsense mutations
Changes the amino acid into a stop codon and can have a serve affect because it would cause translation to stop.
Frameshift mutation
(caused by insertion or deletion)
They shift the reading frame of the genetic message. They have a greater effect because they can change every amino acid that follows the mutation.
Are mutations in which bases are inserted or removed from the DNA sequence.
Genome
Is the full set of genetic information that an organism carries in its DNA.
It includes all the genes that code for traits and all the non-coding DNA too.
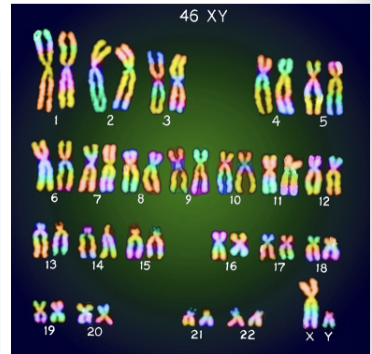
Karyotype
A picture of all the chromosomes in a cell, arranged in pairs.
Helps doctors spot chromosome disorders (like Down syndrome).
Show the complete diploid set of chromosomes that are grouped together in pairs arranged in order of decreasing size.
Chromosome Number
Humans have 46 chromosomes (or 23 pairs).
22 pairs = autosomes
1 pair = sex chromosomes (XX or XY)
Autosomes
The first 22 pairs of chromosomes that are the same in males and females.
They carry most of the genes for your body traits.
Sex Chromosomes
The 23rd pair of chromosomes.
XX = female
XY = male
They carry genes that determine biological sex and sex-linked traits.
Sex-Linked Disorders and Inheritance
Caused by genes on the X chromosome (rarely on the Y).
Examples: Color blindness, hemophilia, Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
More common in males because they only have one X (no backup copy).
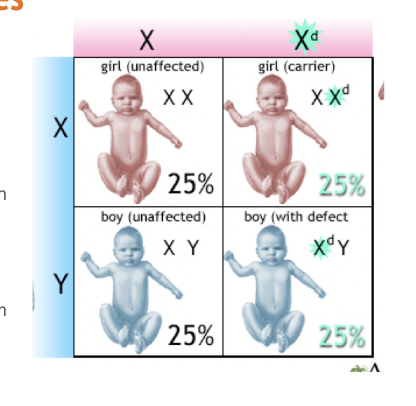
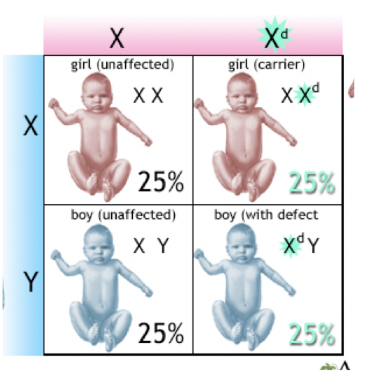
Carrier
A person (usually female) who has one normal allele and one faulty allele for a sex-linked disorder.
They don’t show symptoms, but they can pass it on to their children.
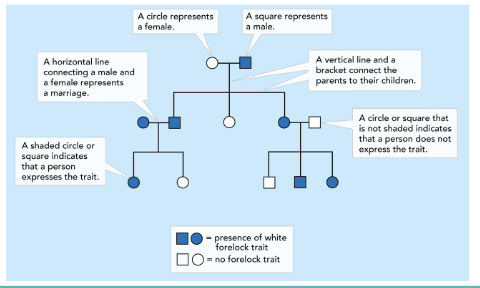
Pedigree
A family tree diagram that shows how a trait is inherited through generations.
Circles = females
Squares = males
Shaded = has the trait
Half-shaded = carrier (for recessive or sex-linked traits)
Biotechnology
Is the application of a technological process, invention or method to living organism.
Ex: selective breeding
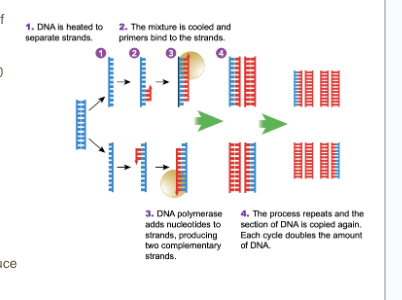
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
A method used to make many copies of DNA super fast.
Is a process used to multiple copies of specific DNA sequences when a sample contains too little DNA.
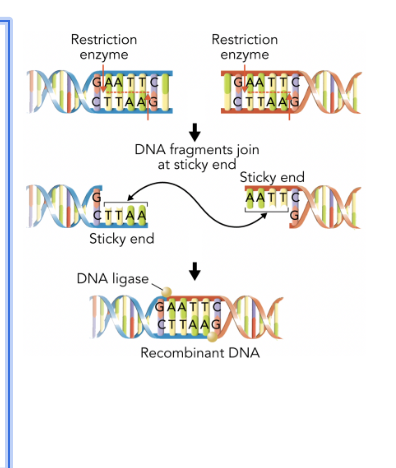
Recombinant DNA
Are DNA from different organisms that have been joined together. This technology makes it possible to change the genes of living organisms.
Transgenic Organism
Are organism that contain genes from other species.
Can be produced by inserting recombinant DNA into the genome of a host organism.
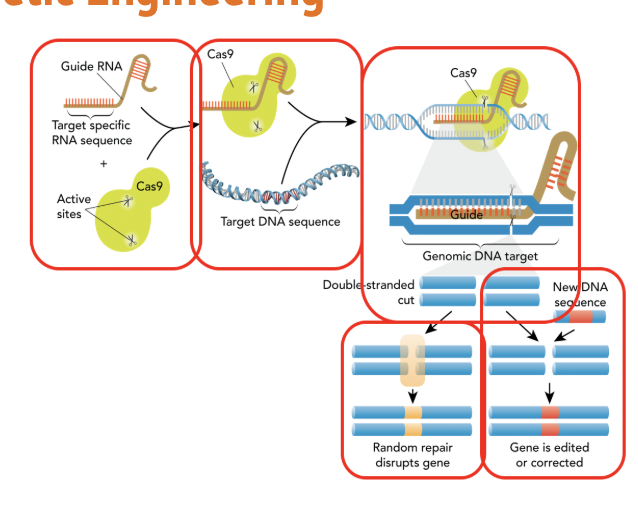
CRISPR (clustered regulatory interspersed short palindromic repeats)
Is a technology used for genetic engineering and genome editing. It changes the DNA sequence of genes.
A gene editing tool that acts like tiny scissors to cut and change DNA.
Used to fix mutations or turn genes on or off.
Clone
Genetic copy of an organism or cell.
Example: Dolly the sheep was the first cloned animal from an adult cell.
Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs)
Organisms whose DNA has been changed by humans.
Often used in crops to resist bugs or grow faster.
Organisms that have been altered using biotechnology.
Genetic Testing
Tests DNA to find mutations or risk for diseases.
Can be used before birth, during life, or even for ancestry.
Gene Therapy
A medical treatment that inserts a healthy gene into someone with a faulty one.
Still being tested for many diseases (like cystic fibrosis or certain cancers).
It changes your genes to treat a disease or disorder. It uses stem cells.
Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotic Cells
Prokaryotes: No nucleus, simple (ex: bacteria).
Eukaryotes: Have a nucleus and organelles (ex: plants, animals).
Plant Cell vs. Animal Cell
Plant Cells: Have cell wall, chloroplasts, large central vacuole.
Animal Cells: No cell wall or chloroplasts, smaller vacuoles.
Cytoplasm
The portion of the cell outside the nucleus. It's a jellylike substance that holds the organelles.
Nucleus
Contains all of the cell’s DNA and instructions for making proteins and other important molecules.
Nuclear Envelope
Is a double lipid bilayer that surrounds the nucleus in eukaryotic cells.
Nucleoid
The area in a prokaryotic cell (like bacteria) where the DNA is found.
Ribosomes
Are small particles that make proteins found throughout the cytoplasm in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.
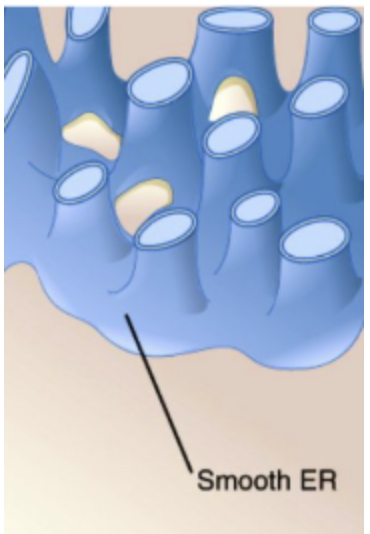
Smooth ER
Makes lipids and does not have ribosomes on the surface.
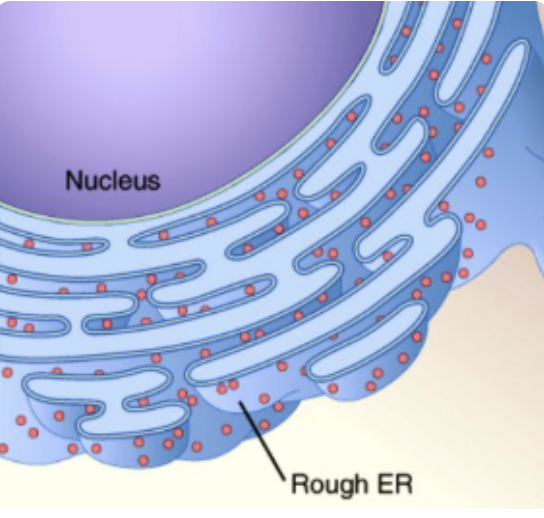
Rough ER
Makes proteins and has ribosomes on the surface.
Golgi Apparatus
Is an organelle that packages, sorts, and sends out proteins and other materials made in the cell.
Vacuoles
Store materials like water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates.
Vesicles
Store and move materials between cell organelles and to and from the cell’s surface.
Lysosomes
Are organelles that use enzymes to break down waste, old cell parts, and food inside the cell.
Chloroplast
Are found in plant cells only and they capture energy from sunlight and convert it into chemical energy during photosynthesis.
Mitochondria
Converts the chemical energy stored in food molecules into compounds that the cell can use.
Cell Wall
Supports, shape, and protects the cell.
Cell Membrane
Controls what enters and leaves the cell. It also protects and supports the cell.
Semipermeable
Is selectively permeable which means that it allows some substances to enter and other cannot enter.
Phospholipid
Main part of the membrane; has a water-loving head and water-fearing tail
Diffusion
Is the process by which particles move from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration.
