Lecture 2: Social Anxiety Disorder
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What is SAD in a nutshell?
An overwhelming fear of social situations & persistent anxiety of being humiliated, criticized, and negatively evaluated
What is the common onset and prevalence rate of SAD?
Common onset: Adolescence
Prevalence rate: 5-12%
What are the behavioural symptoms of SAD?
Fear of situations in which you may be judged negatively
Avoidance of social situations
Post- analysis of performance and identification of flaws in social interactions
• Expectation of the worst possible consequences
(catastrophizing) from a negative experience during
a social situation
What are physical symptoms of social anxiety disorder?
• Blushing
• Fast heartbeat
• Trembling
• Sweating
• Upset stomach or nausea
• Trouble catching your breath
• Dizziness or lightheadedness
• Feeling that your mind has
gone blank
• Muscle tension
What is the difference between someone with SAD and someone who is an introvert?
With SAD, it gets in your way, if you’re an introvert, that is your way
What situations do people with SAD struggle with?
THE BASICS … WHAT SITUATIONS ARE “SCARY” / AVOIDED?
Interacting with unfamiliar people or
strangers
Attending parties or social gatherings
Going to work or school
Starting conversations
Making eye contact
Dating
Entering a room in which people are
already seated
Returning items to a store
Eating & even drinking in front of others
Using a public restroom
When SAD is left untreated, what are the effects?
Low self-esteem
Negative self-talk
Poor social skills
Isolation and difficult social relationships
Low academic and employment achievement
Risk of substance abuse
Risk of depression
Suicide or suicide attempts
What is the relationship between depression and SAD?
They are often comorbid, and SAD is the most common anxiety disorder for people with depression to have. SAD is a risk factor for depression. (treat SAD first) The risk of developing MD is increased 3.5 times in patients with SAD and 2 times
higher in patients with SAD compared to healthy controls
Why is the link between SAD and depression so pronounced?
Because SAD can lead to impairments in everyday life, it is easy to feel depressed if those things are not going well
What early experience factors contribute to SAD?
Certain parenting styles (overconcern with what others think, controlling, reluctant to show affection, overly cautious)
Experiences of being teased or bullied
(30-40% greater likelihood of developing SAD - genetic factors)
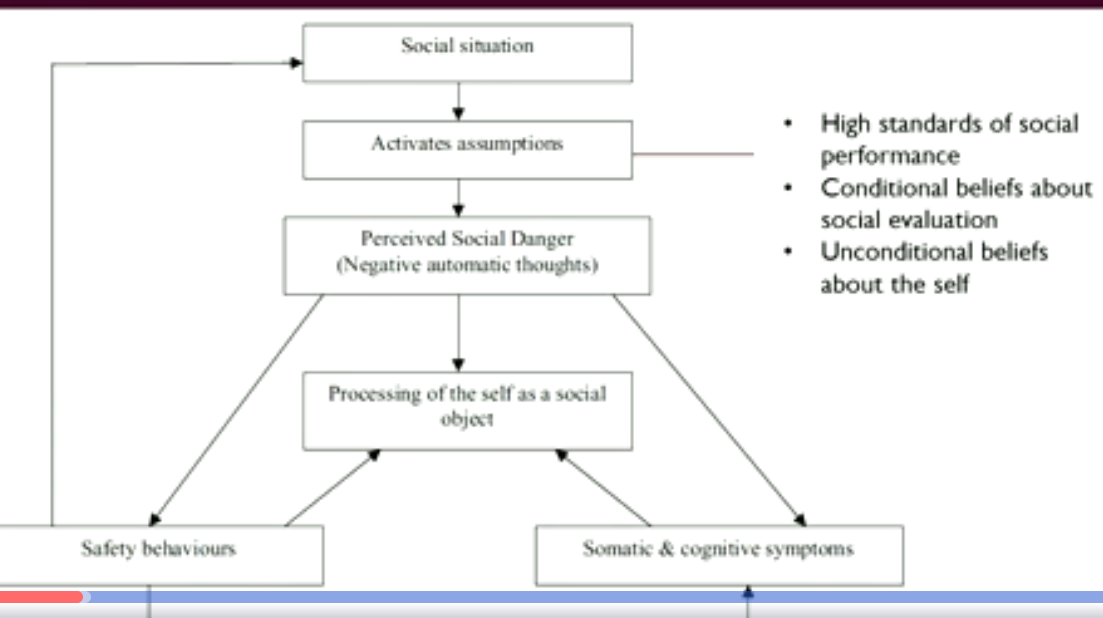
What is Clark and Well’s model of SAD?
What is the difference between Clark and Well’s and Rapee and Heimberg’s model?
R&H emphasises the importance of external threat cues
C&W see anxiety as a “closed model”
What is Rapee and Heimbergs model of SAD?
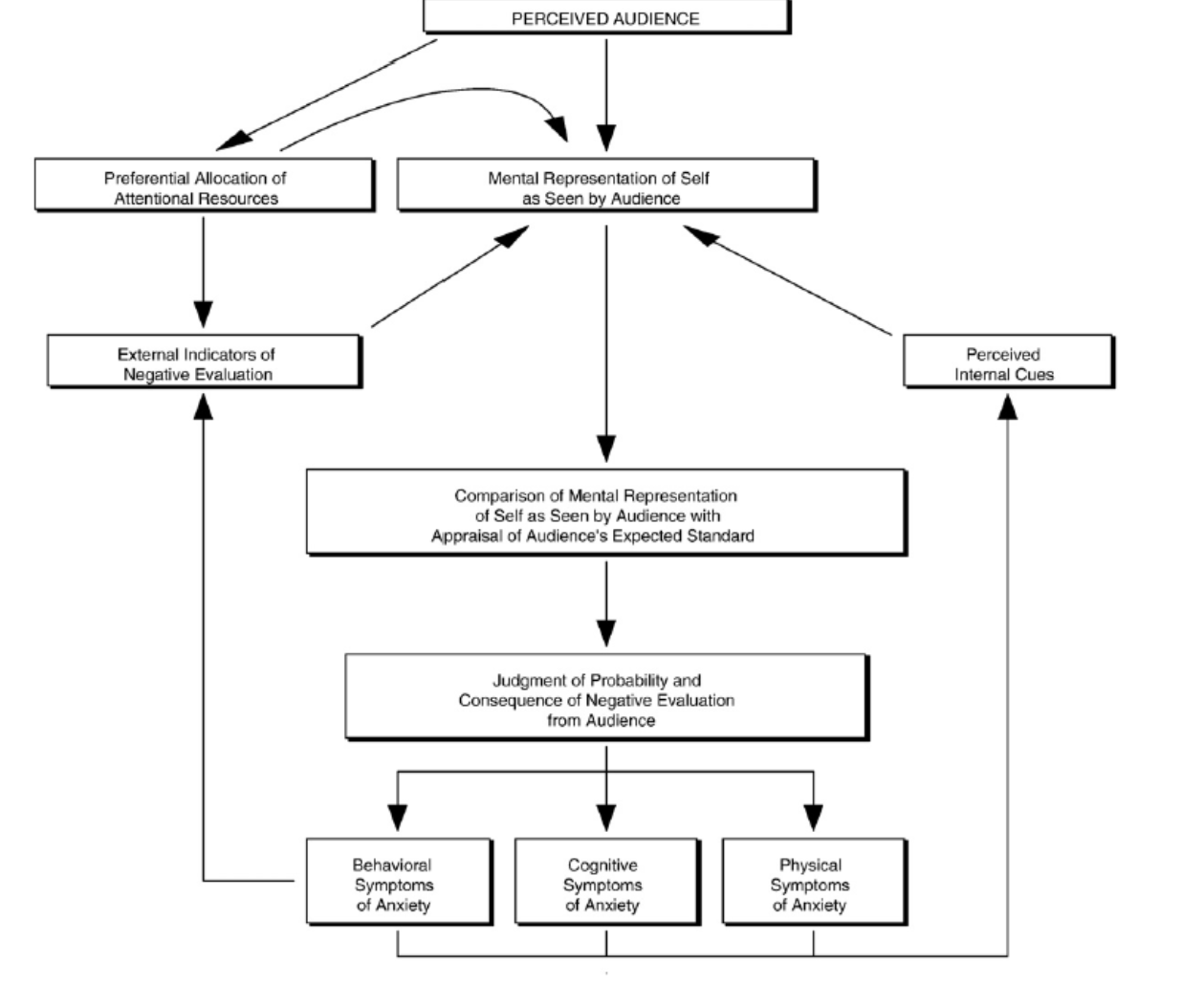
Why does attentional training help people with SAD?
Our attention is limited, so if they pay attention to the world around them consciously they will have less time to think about how they’re being evaluated
What is the emotional processing theory of exposure?
The idea that people have a “fear structure” when they encounter a dangerous stimulus. This is a good thing. However, fear structure becomes a problem when
(1) The information in the structure does not
accurately represent the world,
(2) Physical and escape/avoidance responses are
triggered by harmless stimuli,
(3) The fear responses interfere with daily
functioning,
(4) Harmless stimuli and responses are viewed as
being dangerous
In exposure, we reduce this fear association towards social stimuli by showing that the fear response will go down when repeatedly exposed
What is the problem with emotion processing theory?
Within and between-session habituation don’t predict treatment outcome sufficiently
Inhibitory learning theory
The idea that the feared association is still there, it’s just overridden by the CS- no US association when that happens repeatedly
Expectancy violation
Proving in exposure therapy that unexpected outcomes with regard to the feared stimulus occur
Design an experiment to conduct expectancy violation
What are you most afraid of? What could happen?
Under which circumstances do you think it most likely that this will
actually happen?
Think of an experiment with which you can best test your expectation.
Determine the duration and frequency that are necessary to violate your expectation.
Check the feasibility of the experiment
“Self presentation efficacy expectancy” (Leary & Atherton, 1986)
• The probability of behaving in a certain intended manner in order to convey an intended impression.
• The more positive the beliefs or expectancies are, the less social anxiety one will experience and vice versa