Pathology module 4
1/186
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
187 Terms
DNA
made up of 3 billion base pairs of chemical bases
4 types of base pairs
Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine
genetic information of an organism
genome
genome broken down into pieces
chromosome
23
How many pairs of chromosomes do humans have
46
how many chromosomes do humans have
genes
segments of DNA on chromosomes
provides instructions to make proteins which make you
genes
DNA looks exactly the same in every organism on earth
true
first 22 pair of chromosomes
autosomes
last pair of chromosomes
sex chromosomes
karyotype
visual chart of chromosomes in numerical order
female sex chromosomes
XX
male sex chromosomes
XY
47
how many chromosomes do people with down syndrome have
centromere
ensures each daughter cell will have a full set of chromosomes
metacentric chromosomes
centromere is in center
submetacentric chromosomes
centromere is off-center
acrocentric chromosomes
centromere is near the end
acrocentric
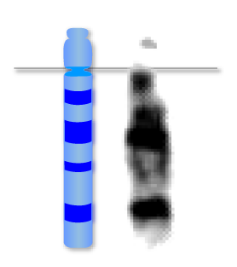
submetacentric
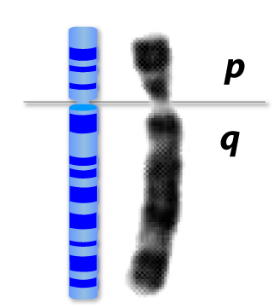
metacentric
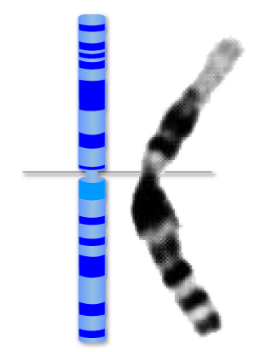
trisomy
person has 3 copies of a chromosome
human DNA is 99.9% similar to each other
true
SNPS
variations in genes are caused by
polymorphism
many forms
SNPS
one-letter difference in the gene that allows for differences in characteristics between people
single base change that occurs in less than 1% of the population
mutation
characteristic of a person caused by genetic or environmental factors
trait
different versions of a gene
allele
similar alleles
homozygous
heterozygous
different alleles
dominant allele
always shown if inherited
recessive allele
require 2 copies to show
genotype
alleles you inherit
phenotype
physical traits
eye color is influenced by 2 or more different genes
true
21,000
how many genes are in the human genome
SNPS are mutations in the genetic code that cause disease
false
genetic disorders
differences in DNA
congenital disorders
caused by something that happened or did not develop correctly
congenital
occurring at or around time of birth
congenital
stunted development from drinking alcohol, drugs, or a virus
congenital
baby getting cerebral palsy from being deprived of oxygen during delivery
DNA
long stringy stuff that sits inside of cells
errors in copying DNA may cause incorrect proteins that cause genetic disorders
true
sex linked
disorders caused by genes on the sex chromosomes
x linked
disorders caused by genes on the x chromosome
autosomal dominant
1 diseased gene is needed to get the disease
autosomal recessive
2 diseased genes are needed to get the disease
genetic disorders with x linked inheritance affect female and males differently
true
x linked
disorder caused by genes in the X chromosomes
are most X-linked disorders dominant or recessive
recessive
person has 1 diseased recessive gene
carrier
cystic fibrosis
recessive disorder on chromosome 7 that results in lungs producing thick, sticky mucus and problems with critical enzymes involved in digesting food
with this mutation on chromosome 15, fatty substance in the cell membrane is not broken down and fat builds up in the brain, killing brain tissue
tay sachs
PKU - phenylketonuria
metabolism disorder caused by chromosome 12 where they lack a specific enzyme, this causes high levels of amino acid phenylalanine to build up in the brain
mutation in chromosome 11 causing a problem with the red blood cells. The hemoglobin is abnormal and makes the cells into a C shaped instead of round. These cells cannot go smoothly through the bloodstream and get lodged in the capillaries, causing extreme pain and even blocking circulation
sickle cell anemia
cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, tay sachs, PKU
autosomal recessive disorders
achondroplasia
mutation in chromosome 4 that causes dwarfism
familial hydrocholesterolemia
mutation in chromosome 19 causing high cholesterol
polydactyly
mutation on chromosome 7 that causes more than five fingers or toes
Marfan syndrome
mutation on chromosome 15 causing you to be tall and lean with a long face, arms, and legs
Huntington’s disease
mutation on chromosome 4 that causes the letters CAG in DNA to constantly repeat, causes brain damage overtime
pedigree
record of descendant
autosomal dominant disorders have carriers
false
most common type of sex linked disorder
x linked recessive
who determines the sex of the baby
males
Duchenne muscular dystrophy
mutation in dystrophin gene caused on X chromosome which causes progressive muscle weakness and early death in boys
hemophilia
missing a clotting factor in the blood
SCID
causes decreased number of T lymphocytes
fragile x syndrome
causes changes in the FMR1 gene on the X chromosome, which makes a protein needed for brain development. Defective gene repeats letters CGC over and over.
red-green color blindness
caused by defect in the OPN1LW and OPN1MW genes on the X chromosomes. defect is found in approximately 1 out of 12 boys and 1 in 200 females
monosomy
person with 1 chromosome instead of 2
trisomy 21
down syndrome
trisomy 13 - Patau Syndrome
most die before 1 month of age and only 5-10% live past age 1
Turner Syndrome
Because of the missing extra X chromosome, people with it appear female, but the ovaries and other female characteristics do not develop normally at puberty. only affects females
cry du cat syndrome
part of the short arm chromosome is missing, making genetic material for it unavailable. Most children with this syndrome have neurological and physical problems and a shortened lifespan
proteins are made up of
amino acids
cancer
cells grow out of control
overgrowth of cells
hyperplasia
dysplasia
cells continue to divide and look abnormal in appearance
neoplasm
tumor
benign
noncancerous
lipoma
benign fatty tumor
malignant
cancerous
benign blood vessel tumor
hemangioma
meningioma
benign tumor in brain covering
benign tumor of muscle tissue
myoma
true
different cancers have different risk factors, treatments, prognosis
fibroma
benign tumor in fibrous tissue
adenoma
benign tumor in glandular tissue
metastasis
cancer breaks off and travels to a new place
carcinoma
cancer of epithelial tissue
sarcoma
cancer of connective tissue
melanoma
cancer of pigment cells
lymphoma
cancer of lymphocytes
glioblastoma
brain cancer
leukemia
cancer of white blood cells
true
cancer is named from where it originates