springs
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Hooke's law
the extension of a spring is directly proportional to the force applied provided that the limit of proportionality is not exceeded
In Hooke's law, what quantity is usually represented by the letter “k”?
the force constant
Select the correct SI derived units of the force constant, k.
Nm-1
Identify the correct force-extension graph for a spring that obeys Hooke’s Law.
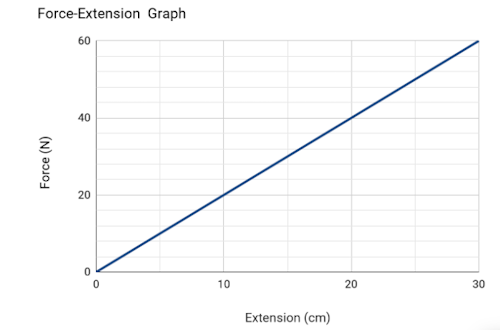
Hooke's law states that F = k Δx. If F is plotted on the vertical axis and Δx is plotted on the horizontal axis, then what is k equal to?
The gradient is equal to k
When a string is stretched, it stores the energy that it is given in the form of….
elastic potential energy
The equation for elastic potential energy is E.P.E=(0.5)FΔx. One way of interpreting the “1/2” in this equation is that it comes from the formula for the area of a triangle. Select a correct alternative interpretation.
The “1/2” appears because we need to use the average force in the equation for work done.
Consider a spring resting horizontally on a frictionless table. It gets compressed, storing elastic potential energy, and then gets released, firing the spring across the table. Select the correct statement about the energy changes after the release.
The spring loses elastic potential energy and gains kinetic energy
A compressed spring stores 0.5 J of elastic potential energy. It is resting horizontally on a frictionless table. The spring uncompresses and is fired across the table. Calculate the kinetic energy.
The table is frictionless.
∙∙ We can therefore assume that the energy transfer is 100% efficient.
∙∙ Since no energy is lost, all 0.5 J of elastic potential energy gets converted to kinetic energy.
identify the correct equation for determining the combined force constant of two parallel springs, of force constant K1 and K2
KT=K1+K2
Identify the correct equation for determining the combined force constant of two series springs, of force constant K1 and K2.
For series springs, the combined force constant is 1/KT=1/K1+1/K2
Elastic Deformation
A reversible change in the shape of an object due to a compressive or tensile force; removal of stress or force will return the object to its original shape
Plastic Deformation
An irreversible change in the shape of an object due to a compressive or tensile force; removal of the stress or force will not return the object to its original shape
Force Constant
The amount of force required to produce an extension of one metre
Extension
The difference between the length when under load and the original length
The force exerted by a stretched spring is proportional to the extension only but in the opposite direction to the displacement