W3L1: Serotonin, Mood Disorders, Designer Drugs
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine = 5-HT)
mood regulator, sleep, arousal, appetite, temperature, working memory, hallucinations
serotonin: neuromodulator
influence activity of a variety of neurone throughout brain
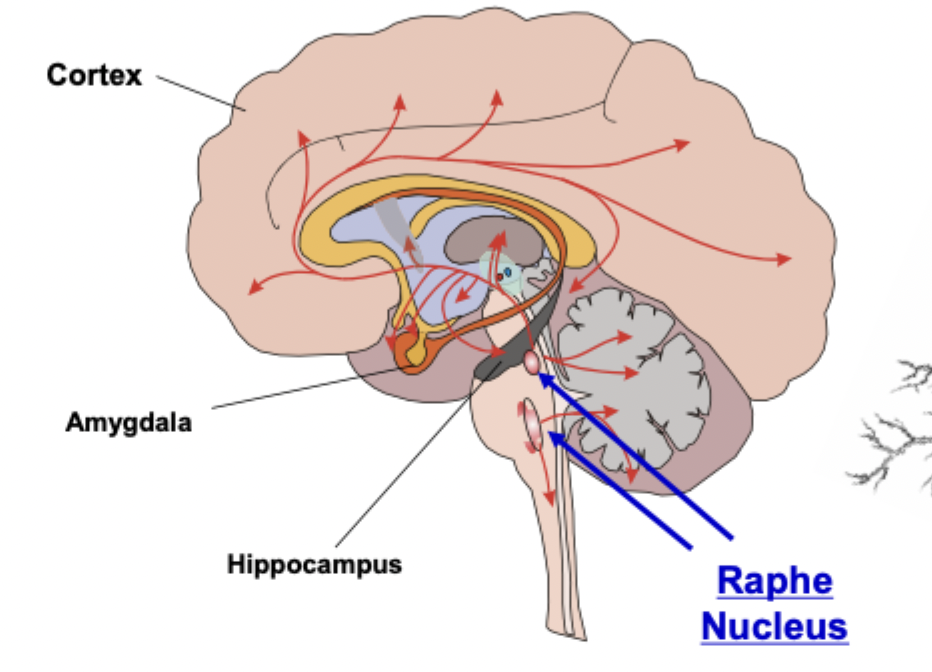
serotonin: location
raphe nucleus, cortex, amygdala, hippocampus
serotonin: receptor subtyes
has different effects depending on receptor subtypes, drugs often only activate one or a few subtypes so will be more selective then natural neuromodulator
serotonin: synthesis
caused by tryptophan synthesised into serotonin
serotonin: tryptophan
amino acid found in food - chicken, cheese, chocolate
monoamine oxidase
modulate and get rid of neuromodulators (serotonin, dopamine, noradrenaline) to shut down neurotransmitter system
serotonin is…
all about modulating (mood, sleep, appetite etc.)
serotonin: depression
some serotonergic abnormality occurring
depression: familial clustering: neighbour
16%
depression: familial clustering: sibling
30%
depression: familial clustering: identical twin
>80%
serotonin: depression: serotonergic receptors
less in depressed people (has relation to depressive symptoms)
serotonin: antidepressants (SSRI’s)
citalopram, fluoxetine, paroxetine, sertraline (similar structure to serotonin so they can attach to serotonergic receptors)
SSRI - Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors
prevents reuptake of serotonin back into presynaptic neuron
SSRIs: long latency onset theories: altered gene expression
slow changes in action of different processes within neuron (neurotransmitter synthesis and storage), changes in structure of neuron (synaptic remodelling)
SSRIs: long latency onset theories: stress response
shuts off response underlying depressive symptoms, allowing for important neural adaptations
SSRIs: long latency onset theories: increased levels of neurogenesis
birth of new brain cells change/strengthen important mood related circuits in brain
SSRIs: in clinical populations
reduces symptoms of depression
SSRIs: in healthy people
increases empathy and prosocial behaviour
serotonin: monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs)
blocks enzyme from breaking down serotonin (causes upregulation of serotonin because there’s nothing to break it down) - can lead to lethal levels of serotonin if taken too much
MDMA
key MAOI
more dopaminergic than serotonergic the drug
more addictive