How markets work 1.2
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
what is a market ?
where consumers and producers come into contact with each other to exchange goods and services
what is utility ?
the amount of satisfaction obtained from consuming a good/ service
what does it mean for consumers to be assumed to make rational decisions
it means consumers will allocate their income to maximise their utility and satisfaction from the goods and services they obtain
what is the equation for maximising consumer utility ?
marginal utility of good A =marginal utility of good B
price of good A = price of good B
if a consumers has £100 if he spends £20 on a T-shirt and £80 on shoes what is the marginal utility
40 units of extra utility - T-shirt
160 units of extra utility - shoes
what is rational decision making ?
where consumers allocate their expenditure on goods and services to maximise utility and producers allocate their resources to maximise profits
what does it mean for a producer to make a rational decision
firms will use their resources to maximise profits from the goods and services produced
This is involves producing at the level of output where total revenue exceeds total cost by the largest amount
demand
the quantity of a good/ service purchased at given price over at a given time period
demand curve
shows the quantity of a good or service that would be bought over a range of different price levels in a given time period
why does a demand curve slope downwards from left to right
as price falls the goods become cheaper compared to substitutes so demand increases and more can be purchased with a given level of income
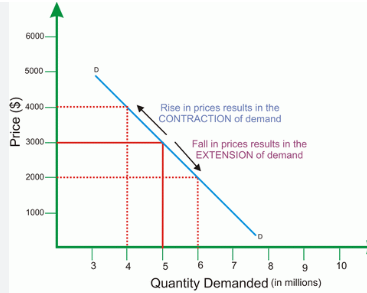
how does movement along a demand curve occur
when their is a change price
fall in price - extension demand
rise in price - contraction demand
marginal utility
the utility / satisfaction obtained from consuming one extra unit of a good/ service
diminishing marginal utility
as successive units of a good is consumed the utility/ satisfaction gained from each extra unit will fall
marginal utility x demand curve
as a someone consumes more of one good the utility x satisfaction gained from each extra units will decrease that’s why it is downward sloping
example using cereal on diminishing marginal utility
total utility from consuming a bowl of cereal will increase but at a diminishing rate until the consumer feels sick then it will drastically fall
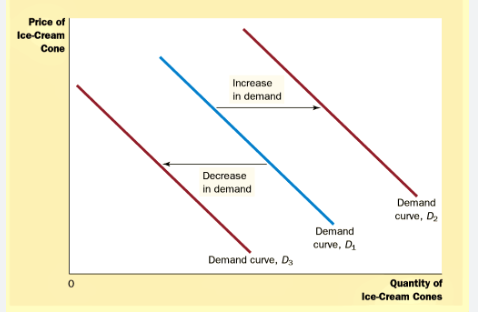
what factors could cause a shift in the demand curve (8)
rise in the price of substitute goods
change in fashion taste
increase advertising
increase in real real incomes
decrease in income tax
fall in the price of complementary goods
increase in population / change in average of population
increase in credit facilities
ped
the responsiveness in the demand of a good due to the change in its price
PED formula
percentage change in demand of good A
percentage change in the price of good A
most circumstances a minus is produced indicating that the two variables move in opposite direction
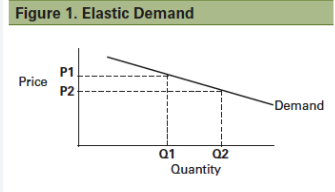
PED greater than 1
relatively price elastic
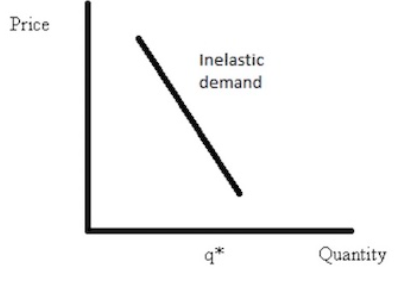
PED is less than 1
relatively price inelastic
PED=1
the good has unit elasticity
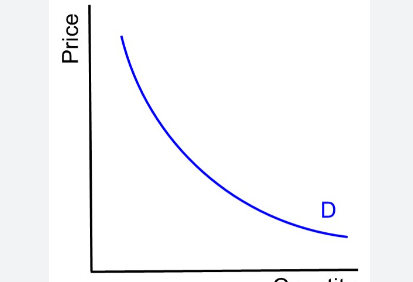
PED=0
perfectly inelastic - e.g heroin to a drug addict
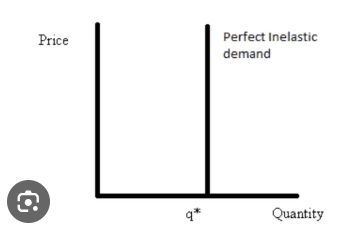
PED is infinity
perfectly elastic
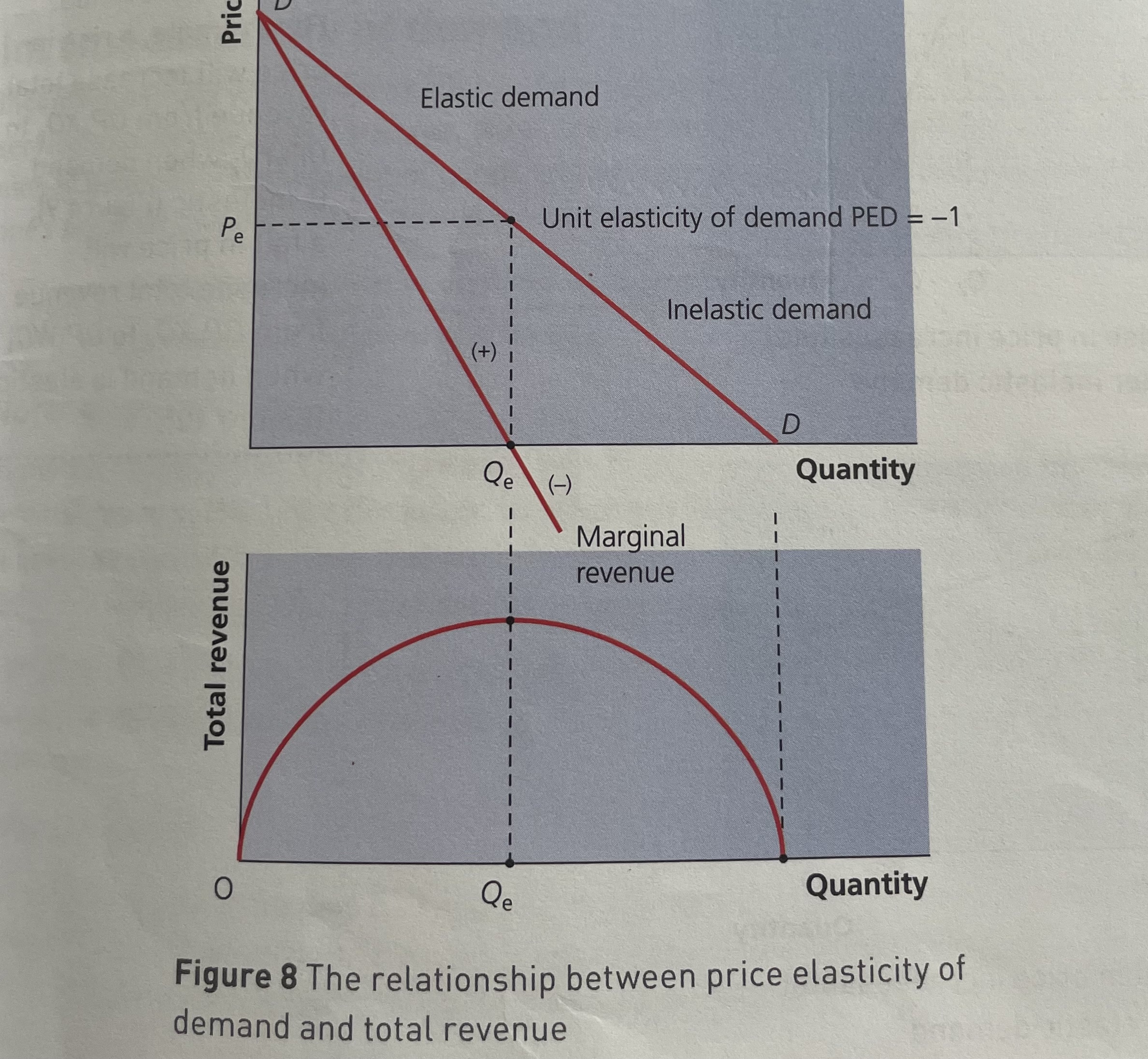
what happens to elasticity as you move along the demand curve from the top left to bottom right
elasticity falls
what does the middle of a demand curve signify
demand has unit elasticity
total revenue
the price per unit of a good multiplied by the quantity sold
how does elastic demand effect revenue when there is a cut in the price
increases revenue as it will increase total consumer spending
how does elastic demand effect revenue when there is a rise in the price ?
decrease revenue as consumers total spending will decrease as they are responsive to price
when a good is demand inelastic how will a rise in price effect revenue
it will increase revenue as consumers are not responsive to price so they are still willing to buy the product
when a good is demand inelastic how will a decrease in price effect revenue
decrease revenue for the firm wont effect consumer spending so firm looses revenue
unit price elasticity and revenue
the firms is maximising its total revnue
marginal revenue is 0
demand is unit elastic
marginal revenue is negative
demand inelastic
marginal revenue is positive
demand is elastic
how does availability of substitutes effect PED