B3- Organism Level Systems
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
what is in the central nervous system?
brain and spinal chord
what does a sensory neurone do?
send electrical impulses from receptors to the CNS
what do motor neurones do?
carry electrical impulses from the CNS to the effectors
what do effectors do?
they are all your muscles and glands which respond to the nervous impulses and create a response
what is the order of co-ordinating a response?
stimulus —> receptor —> sensory neurone —> CNS (+ relay neurone) —> motor neurone —> effector —> response
what is a synapse?
the connection between 2 neurons (gap in between)
how are signals transferred through synapses?
when an impulse reaches a synapse it releases chemicals which diffuse across the gap from a receptor to a neurone
this triggers a new electrical impulse which travels through the next neurone
what is a reflex arc?
when reflexes are automatic responses to the stimuli and don’t involve the brain but goes down the spinal chord so it is quicker
what does the reflex arc do?
used to quickly protect your body
what is an example of a reflex arc response?
touching a hot object and moving your hand away quickly
what is the order of a reflex arc?
stimuli —> receptor —> sensory neurone —> spinal chord —> relay neurone —> motor neurone —> effector —> response
what does a relay neurone do?
pass on electrical impulses to the motor neurone
what are hormones?
hormones are chemical messengers produced by endocrine glands
what does the endocrine system do?
produce hormones which are released directly into the blood and to the target organs which need it then the hormones bind to receptor cells on organ
where are the glands located?
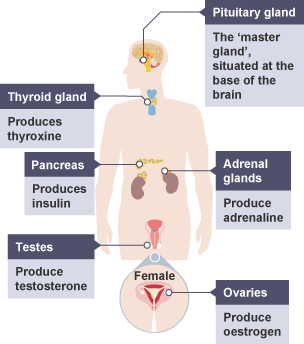

what does the pituitary gland produce?
it is the ‘master gland’ and it acts on other glands to produce hormones
also produces LH, FSH, growth hormone, ADH (water content of blood)
what does the thyroid gland produce?
thyroxine which regulates metabolism, heart rate and temp.
what does the adrenal gland produce?
adrenaline, used for fight or flight response
what does the pancreas produce?
insulin which regulates blood glucose levels
what do ovaries produce?
oestrogen and progesterone, involved in menstrual cycle
what do the testes produce?
testosterone, controls puberty and sperm production
what are the hormones in the menstrual cycle?
FSH, oestrogen, LH, progesterone
what does the FSH do?
stimulates egg to mature and stimulates ovaries to produce oestrogen
what does oestrogen do?
causes lining or wall of the uterus to grow
what does LH do?
stimulates release of an egg at day 14 (ovulation)
what does progesterone do?
maintains the lining of the uterus, when progesterone levels fall- lining breaks down
describe what happens on each day of the menstrual cycle
day 1-4= uterus lining breaks down, period
day 4-14= oestrogen causes lining of uterus thicken full of blood
day 14= ovulation- LH causes release of an egg
day 15-28= uterus wall is maintained ready for fertilized egg, if no fertilized egg cycle starts again
how does FSH work in contraceptives?
no egg will be developed or released also no oestrogen will be made so egg development will stop
how does progesterone work in contraceptives?
stimulates production of thick mucus in cervix, preventing sperm from reaching egg
are hormonal contraceptives effective?
they are 99% effective but don’t protect against STDs
what are the hormonal methods of contraception?
IUD- placed in uterus and releases progesterone- plastic or copper version doesn’t release hormones but kills sperm
contraceptive implant- implanted into the arm, released progesterone, lasts up to 3 years
contraceptive injection- releases progesterone, lasts 2-3 months
contraceptive patch- released oestrogen and progesterone, lasts up to 1 week
are non- hormonal contraceptive methods effective?
they are 98% effective as they stop sperm from meeting the egg and protect against STDs
what are the non-hormonal methods of contraception?
condoms (male and female)= protect against sperm meeting the egg
diaphragm= fits over cervix and blocks sperm from entering- unreliable has to be used with spermicide- kills sperm
sterilisation- women= cutting/tying fallopian tubes, men= sperm ducts cut/tied
sex at certain times of the month- unreliable
what does homeostasis mean?
maintaining internal body environment constant
why does the body need to control levels of water, glucose and salts?
to ensure chemicals can be transported effectively into and out of cells by osmosis and active transport
why does temperature have to remain constant?
so chemical reactions can be catalysed by enzymes and they function best at their optimum temp
what are blood sugar levels controlled by?
by the pancreas which produces insulin
what does insulin do?
causes cells to become more permeable to glucose so glucose can move from blood into the cells
also causes the liver to turn excess glucose into glycogen
what happens if blood glucose levels are too high?
insulin is secreted by pancreas to blood and this removes glucose from the blood and turns it into glycogen
what happens if blood glucose levels are too low?
glucagon is secreted by pancreas to blood which makes the liver turn glycogen back into glucose
what is metabolism?
sum of all chemical reactions that happen in an organism
what is type 1 diabetes?
it’s when little or no insulin is made so blood glucose levels are too high and it develops at young age or birth
treatments for type 1 diabetes?
insulin injections to remove glucose from blood, limit carbs and exercise more and eat healthy
what is type 2 diabetes?
insulin is still produced but the person becomes resistant to their own insulin and it develops gradually through life due to unhealthy diet
treatments of type 2 diabetes?
eating healthy, exercise and maybe medication