Breeding and Welfare of Companion Animals
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
What is the primary goal of selective breeding in companion animals?
To gain specific traits in animal individuals that meet human preferences.
How do selective breeding practices differ from natural evolution?
Selective breeding focuses on traits desired by humans, rather than traits linked to fitness or survivability in the wild.
What is the role of a 'tameness gene' in the domestication of animals?
It is involved in allowing domestication by influencing behavior traits that make animals more amenable to living with humans.
What does the concept of paedomorphism explain in companion animals?
It explains how many companion animal species can exhibit similar characteristics or appearances due to selective breeding.
What are some potential welfare consequences of selective breeding?
Welfare consequences can include perpetuation of harmful traits, inbreeding, and poor health outcomes.
What is the significance of 'survival of the fittest' in relation to domesticated species?
It is less relevant for domesticated species, as many breeds would not survive in the wild but continue to exist due to human selection.
What factors influence the traits desired in companion animals?
Traits can vary widely; some are commonly desired while others may be sought by fewer individuals.
What happens to traits that are completely removed from a species through selective breeding?
They may be lost forever, as many mutations are chance occurrences.
What are breeding programs designed to achieve?
Defined breeding objectives to produce the next generation of animals with specific traits.
What is the difference between the original goals of selective breeding and current goals?
Original goals were likely focused on utility, while current goals may prioritize aesthetics or specific behaviors.
How does selective breeding affect genetic diversity in companion animals?
It can reduce genetic diversity by favoring certain traits and discarding those that do not meet standards.
What is the impact of selective breeding on animal behavior?
Selective breeding can lead to behavioral traits that are more suited to human companionship but may not be beneficial for the animal's natural instincts.
What is meant by 'utility selection' in some companion animal species?
It refers to breeding practices that maintain traits beneficial for specific functions, such as herding or hunting in dogs.
How does the variation in companion animal species arise?
It arises from purposive selection by humans aiming to achieve specific goals in traits like size, color, and behavior.
What is a potential risk of breeding for aesthetic traits in companion animals?
It may lead to health issues or genetic mutations due to a lack of focus on the overall fitness of the animal.
What is the relationship between selective breeding and inbreeding?
Selective breeding can lead to inbreeding, which increases the risk of genetic mutations and health problems.
What are 'companion animals' often defined as?
Domesticated species that are kept for companionship rather than for utility or work.
What should be considered when evaluating current breeding practices of companion animals?
The welfare implications and whether the traits being selected for are beneficial or harmful.
Why is it important to have defined breeding objectives?
To ensure that the breeding process is systematic and aimed at achieving desired traits in the next generation.
What is the significance of discarding animals that do not meet breeding standards?
It accelerates the breeding of those that do meet the standards, shaping the genetic direction of the breed.
How do breeding practices impact the future of companion animal species?
They can determine the traits that are perpetuated or lost, affecting the species' diversity and health.
What is the purpose of keeping records of individuals in breeding programs?
To track desired genetic traits for potential parent animals.
What are the three key methods utilized in breeding strategies?
Selection for characteristics, cross-breeding to combine traits, and capturing mutations.
What is the difference between species, sub-species, and breed?
Not all species have sub-species or breeds; they represent different levels of classification.
What is tandem selection in breeding?
Focusing on one characteristic at a time before moving on to the next.
What is parallel selection in breeding?
Selecting for multiple characteristics simultaneously.
How can selecting for a single trait negatively impact animal welfare?
It may concentrate harmful genes linked to the trait or affect other health aspects.
What is cross-breeding?
Combining characteristics from two or more existing breeds to produce desirable traits.
Give an example of a cross-bred dog breed.
Cockapoo or Labradoodle.
What is hybridization in the context of breeding?
When individuals from two species reproduce to produce offspring with traits from both.
What are some examples of hybrid animals?
Liger, Tigon, Mule, Geep.
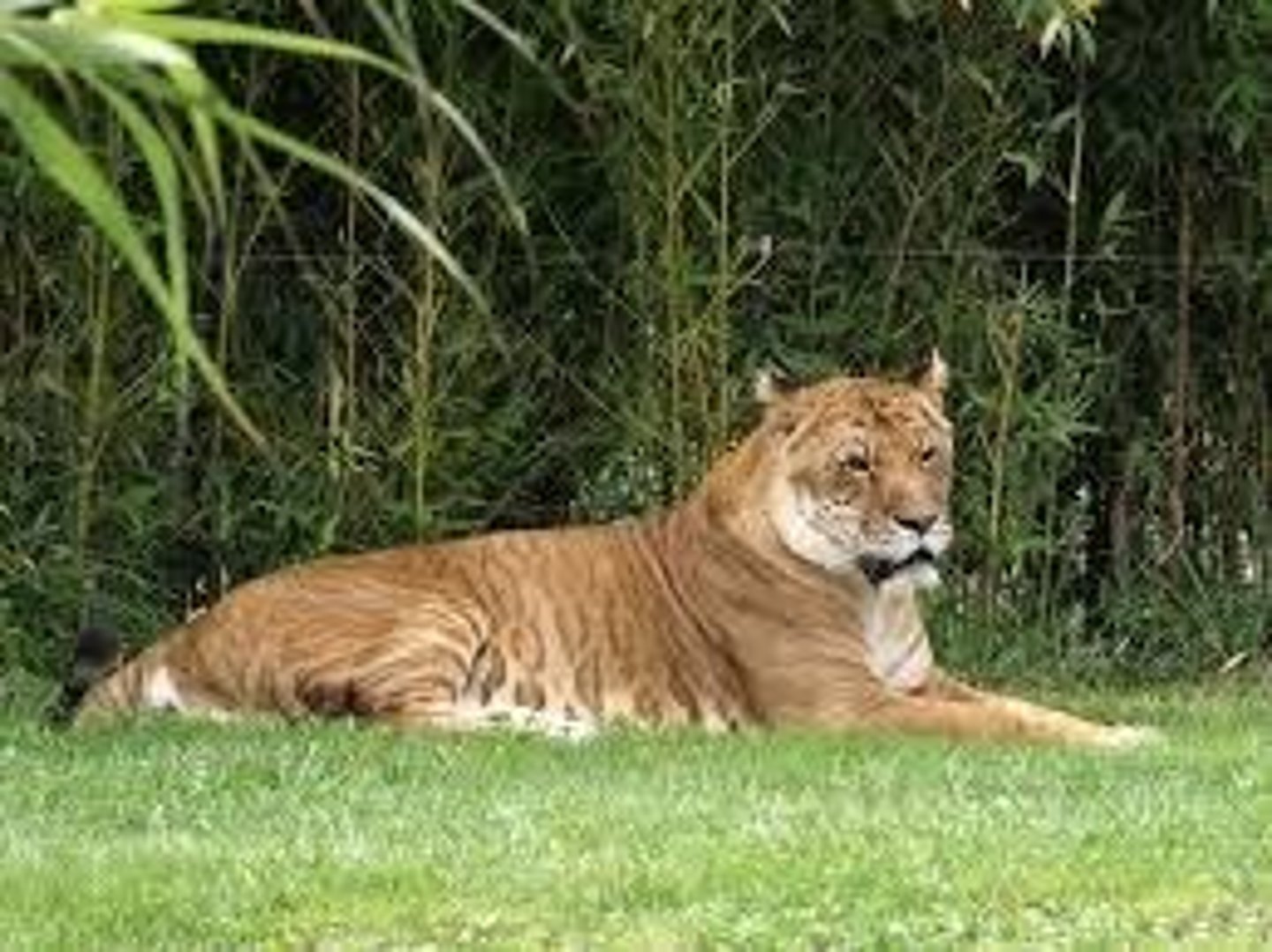

Why is hybridization not common in the wild?
Due to location and the likelihood of individuals from different species coming into contact.
What is the goal of capturing mutations in breeding?
To 'fix' desired traits in the descendant population so all future offspring carry them.
What ethical considerations arise from selective breeding?
Determining where to draw the line on welfare impacts versus desired traits.
What is the impact of focusing on aesthetic traits in breeding?
It may lead to neglecting health traits, affecting overall animal welfare.
What is the significance of scoring characteristics in breeding?
It helps prioritize traits based on their importance to the breeder.
How does cross-breeding aim to improve welfare?
By combining desirable traits from different breeds.
What is the role of the Kennel Club in cross-breeding?
Recognizing certain cross-breeds as legitimate breeds.
What is the assumption about the fertility of hybrid offspring?
Most hybrids are assumed to be infertile due to chromosomal differences.
What is the aim of a breeding program?
To evaluate and review the success of breeding efforts and determine if further generations are needed.
What can be a consequence of selecting for exaggerated traits?
It may lead to health issues, such as the example of white cats and ear tip squamous cell carcinoma.
What is the significance of capturing mutations in breeding strategies?
It allows breeders to establish and maintain desired traits in future generations.
What is the relationship between selection and animal welfare in breeding?
Selection for certain traits can negatively impact health and welfare if not balanced with health considerations.
What is a consequence of fixing mutations through inbreeding?
It generally requires mating related individuals, which can lead to issues like asymmetrical skulls and poor-quality semen, as seen in cheetahs.
What are some intentional approaches to inbreeding?
Sibling-mating, parent-offspring matings (backcrossing), and half-sibling matings.
How does the time between generations affect trait presence in offspring?
It influences how quickly a new trait is present and the number of offspring produced.
What is inbreeding depression?
It refers to the negative effects on biological fitness due to inbreeding, including loss of fertility, reduced birth weight, and increased disease risk.
What are some potential consequences of selective breeding techniques?
They can include hybridization, cross-breeding, and inbreeding, which may have both beneficial and adverse welfare consequences.
What is exaggerated morphology in animals?
It refers to alterations in structures used for communication or other functions, leading to health and behavioral challenges.
What are some examples of exaggerated morphology issues in cats and dogs?
Tail-lessness in cats, pendulous ears in dogs, and brachycephalic traits leading to health problems.
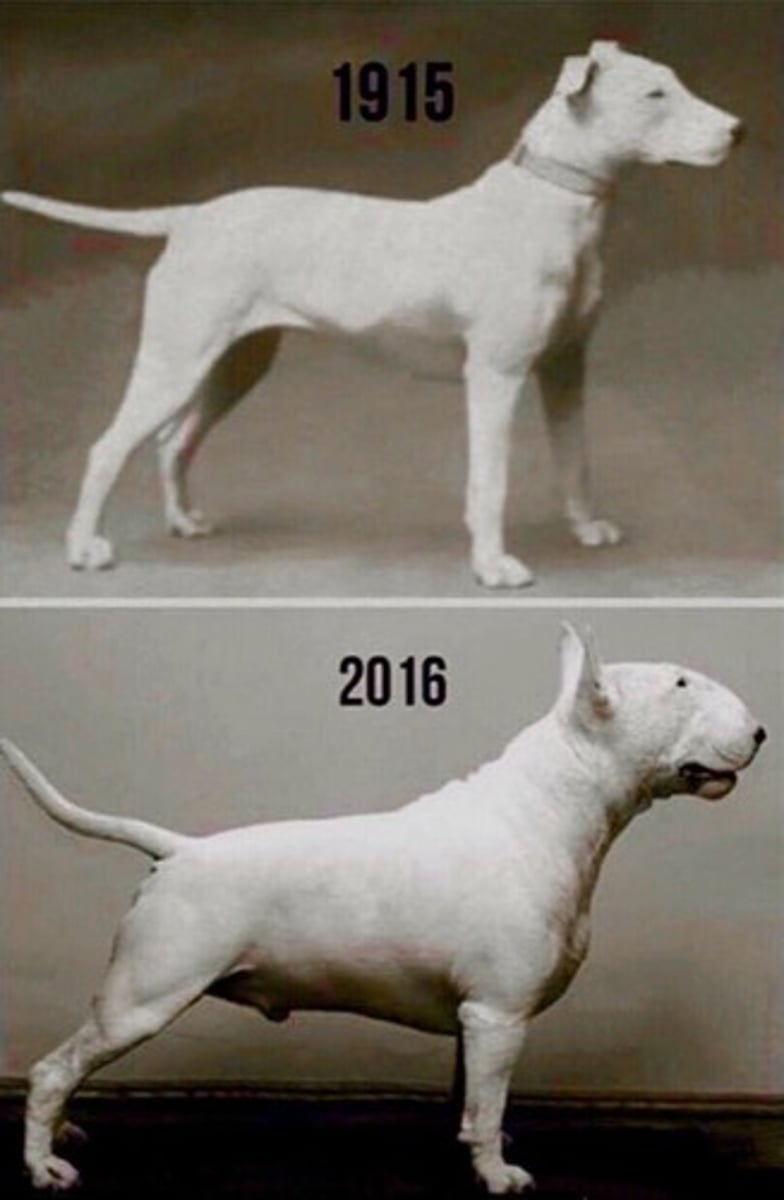

What health issues can arise from selecting for brachycephalic traits?
Labored breathing, prolapsed soft palates, and ocular problems.
What is the difference between homozygous and heterozygous alleles?
Homozygous alleles are the same, while heterozygous alleles are different.
How does genetic diversity affect survival in animal breeds?
Increased genetic diversity can enhance survival and provide more diverse responses to environmental stimuli.
What influences the genetic diversity of a breed?
The way in which a breed is developed, with breeds having a working phenotype generally showing more diversity.
What are some health challenges associated with certain coat colors in cats?
White cats with blue eyes can be deaf, and tortoiseshell cats may have health problems.
What are the implications of reduced genetic diversity in animal populations?
It can lead to increased susceptibility to diseases and reduced adaptability to environmental changes.
What is the role of inbreeding in capturing mutations?
Inbreeding can concentrate specific traits but also harmful genes, impacting overall population health.
What are some behavioral challenges associated with exaggerated morphology?
Dogs or cats may be unable to raise hackles due to long hair or other morphological changes.
What is the effect of inbreeding on litter size and birth weight?
Inbreeding can lead to reduced litter size and lower birth weight.
How can selective breeding techniques be both beneficial and harmful?
While they can enhance certain traits, they may also lead to adverse welfare consequences.
What is a common health issue in Cavalier King Charles Spaniels related to morphology?
Syringomyelia, which is associated with selection for specific eye and eyelid shapes.
What is the significance of allele diversity in a gene pair?
Greater allele diversity increases genetic diversity and survival potential in a breed.
What historical figure discussed the risks of concentrating harmful genes in populations?
Charles Darwin, in the 1800s.
What is the relationship between inbreeding and fertility?
Inbreeding can impair fertility, which is one of the effects of inbreeding depression.
What are the potential risks of frequent selective breeding practices?
They may take natural behaviors that are rare and make them common, leading to negative health outcomes.
What is the Founder Effect in genetics?
The loss of genetic variation that occurs when a new population is established from a limited number of individuals.
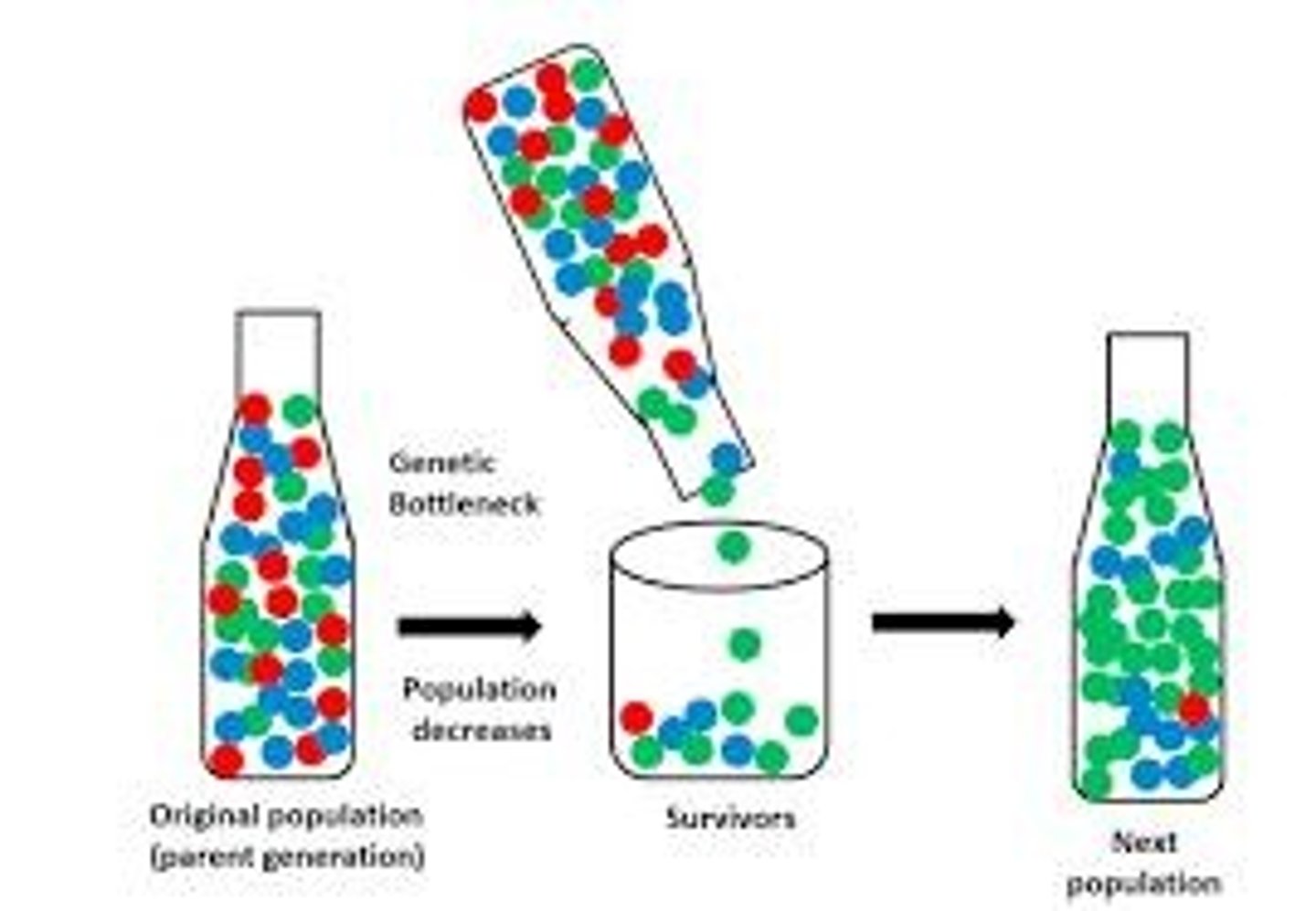
What are Population Bottlenecks?
An environmental effect that reduces the size of a population, leading to a new population built only from the original survivors.
How has selective breeding affected the health and welfare of specific breeds?
Breeds selected for specific aesthetic traits tend to have less genetic diversity, leading to health and welfare problems and increased susceptibility.
What percentage of cats in the UK and USA are pure-bred?
Only around 7%.
What has led to the creation of different cat breeds in recent history?
Their presence as status symbols and the desire to maintain wild characteristics.
What characteristics have canaries been bred for?
Color, feather structure, and song ability.
What are some breeding traits of budgerigars?
Size, color, feather mutations (circular and half circular crests), and long flight feathers.
What hybridizations have occurred in falconry birds?
Peregrine falcon x merlin falcon and peregrine falcon x saker falcon.
What historical uses have rabbits been bred for?
Initially for food since Roman times, and later for aesthetics as pets.
How many recognized breeds of rabbit existed in 1850 compared to today?
There were 10 recognized breeds in 1850; today there are over 300.
What is the most popular breed of rabbit in the UK?
The lop-eared rabbit.
What is notable about the diversity of dog breeds?
Dogs are the most diverse domesticated species, with body size, shape, and behavioral characteristics varying greatly.
What percentage of dogs in the UK and USA are pure bred?
75%.
What assumptions exist about the Syrian hamster population?
Current Syrian hamsters are believed to be descended from a single female and her twelve offspring.
What is the most common domesticated rat kept as a pet?
The fancy rat.
What is the significance of mice in domestication history?
Mice are potentially one of the earliest domesticated animals, resulting from the transition from hunting-gathering to farming.
What ethical considerations arise from selective breeding for aesthetics?
Concerns about the welfare of animals bred solely for appearance.
What are some aesthetic traits selected in companion animals?
Color, size, ear length, conformation, fur texture, and fur length.
What is the impact of selective breeding on animal welfare?
It raises questions about how far breeding will go and at what cost to the animals' welfare.
What is the relationship between feral dog populations and domesticated dogs?
Feral dogs can act differently from traditional domestic dogs and wild dog populations, representing a middle ground.
How has the breeding of birds for falconry affected their genetics?
Hybridization has combined attributes from different species.
What is a breed in the context of domesticated animals?
A group of domesticated animals with identifiable characteristics that distinguish them from others, preserved by controlled matings.