Intro to Psych Exam 3
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
Conformity
Adjusting one’s behavior(s) or beliefs to fit group norms.
Tendency to shift one’s attitudes/beliefs in the direction of the majority.
Obedience
a type of social influence where a person follows an order from another person who is usually an authority figure
Compliance
changing one's behavior at the request or direction of another person
Asch Line Study
visual task asking participants to match up lines of equal length 5-8 confederates (plants) and 1 participant involved in this study 18 trials where confederates give wrong answer 12 times on easy task
-approximately 37% of participants conforms (gives wrong answer) answering alone on this task participant answers correct 99% of time
-have a standard line and are asked which it is the same compared to lines labeled A, B, C
Normative Social influence
conformity to group norms based on fear of appearing social deviant or from fear of disapproval (endorsing wrong group answers on easy tasks)
Informational Social Influence
conformity to group norms based upon lack of information or uncertainty of correct response (2 heads better than 1)
public conformity
beliefs are not actually changed you just pretend they are
sometimes called compliance
asch study
private conformity
beliefs are actually changed
true acceptance or persuasion
sherif study
foot in the door
2 step compliance strategy designed to ask for a small request at step 1 and gain compliance, and then ask for a later larger request at step 2
(you really want them to accept your step 2 request)
Ex: he wants me to buy 4 boxes for $20 of girl scout cookies. He asks me to buy 1 box for $5 which I buy and then he asks if I will buy 4 for $20. He really wants me to buy 4 for $20
door in the face
2 step compliance strategy designed to ask for a large request at step 1 and expect rejection, then ask for a smaller request at step 2
(you really want them to accept your step 2 request)
Ex: will you buy 8 for $40? No. well what about 4 for $20? Ok fine.
that’s not all
GETS THE MOST SALES
-2 step compliance strategy designed to ask for an inflated request a step 1 and before receiving response, you throw in a bonus/ gift/ discount at step 2
(you really want them to accept your step 2 request)
Ex: you can get 3 boxes of girl scout cookies for $20. Oh wait, we are closing?! I will give you an extra box for free. I can give you 4 boxes for $20.
cognitive dissonance
Attitude change theory claiming that people enter into a state of cognitive dissonance or tension when 1) holding contradictory attitudes/ beliefs or 2) holding attitudes incongruence (not matching) with their behaviors. This tension experiences moves them to change attitudes so they align or change attitudes or behaviors so they match. (examples needed for your paper)
-attitude change and personality change strategy, you can you change religious views, political views you can change with this
Ex: you say that you are an environmentalist but you don't recycle or have a 0 carbon emissions car, you don't believe in carpooling, the person then gets motivates to change one of those to make them lineup
-you just said the opposite so which one is it/ you make them feel like a hypocrite
Ex: williams said that you will get an A or B if you read the textbook and take notes, the student says that they are not coming to class and they don't want to buy the textbook and read it, then you either take the C or you do those two things to get an A or B
Milgrams Shock Study
Stanley Milgram set up this experiment to see how far people would go to follow orders from an author figure even if it harmed people
the “teacher” (participant) was to administer a certain voltage of shocks to a “learner” in another room every time the learner got a question wrong (the learner never received nay shocks ever, milligram just wanted to see how far the teacher would go)
with every wrong question the voltage would increase from slight shock all the way up to severe shock
despite the learners cries and pleas 65% of teachers would have administered a lethal shock of 450 volts
Zimbardo’s Prison Study
Study performed at Stanford University that demonstrates how susceptible people are to social roles (how social roles shape our behaviors). Students participate in a study where some are assigned to be prisoners and some prison guards.
-you will verbally or physically assault people if you are placed in a role to do so
-24 total people participated at this experiment, 12 are assigned prison guards (glasses, uniform, and bat club) and 12 are prisoners
-the outfits give you license to be a different person/ more aggressive
-if you do not follow orders then you get solitary confinement, no food or water, or beat
-they blindfold you, put you in a cop car and take you to a place, they strip you to put on your outfit, fingerprint you, then put you in a cell
-they claimed that their was no distress but the prisoners were beat, and when they saw the videos of the experiment back they were all crying and did not know why they did that
-if you are a kind person you will become evil and hurt people
-the uniform makes you a different person
Social Roles
the expected behaviors, responsibilities, and social positions associated with a particular status or position in society, shaped by cultural norms and values
zimbardo prison experiment
Situational attribution
(external)
Describing others behaviors as due to situational factors, outside forces, social influence.
Ex: not one's fault, was driven to act by social forces
Dispositional attribution
(personal or internal)
Describing others behaviors as due to personal, genetic, or internal motivations
Ex: Jeffery Dahmer: serial killer, cooked and ate them, targeted young gay males hispanic or black, wanted a piece of them inside of him
Ex: Michael Vick: great football player that fought dogs almost until they died and he was suspended and went to jail for 2 years. He said that this is what he grew up doing and did not know it was wrong
Ex: Deer Hunters: kills deer for fun, that is gruesome if not from that tradition, give 5th grader a gun and tell them to kill it, did not go to jail
Fundamental attribution error
(blaming the victim/ damsel in distress)
Overemphasizing dispositional (personal factors) and underemphasizing (situational factors) when describing others behaviors or outcomes.
Ex: a woman goes to her car late at night and gets assaulted. People say that you were wearing provocative clothes, you shouldn't be out late at night, blaming the victim, she brought this on herself
Ex: professor is moving towards you fast, looking frantically, Is he trying to hurt you or is he trying to find something? You have to judge and prejudge
Stereotypes
Tendency to automatically associate traits/ behaviors with members of social groups and these exaggerated beliefs confirmed approximately 30% of the time
prejudice
-negative feelings/ attitudes toward someone based upon their group membership (ex. race/ ethnicity, gender, religion, sexual orientation)
-us vs them
-you are more forgiving to your group
discrimination
-systematic unequal treatment of someone based upon their group membership (ex. 1960’s = sit back bus/ movies, can't eat in restaurants)
-acting on the prejudice
racism
Prejudice + Discrimination towards others due to race
sexism
Prejudice + Discrimination towards others due to gender
social categorization
Prejudice + Discrimination towards others due to social status
in-group/ out-group bias
Group you belong to (us) and group that you are not a part of (them)
(Ex. eye color film)
(ex. Health Care -no white women are allowed to help negro men)
attraction
Degree of liking people have for one another based upon physical traits, personality traits, and similarities (values, beliefs, interests)
Proximity/ Mere Exposure effect
Tendency to become attracted to those we live and work near. (ex. co-workers/college students marry at higher than chance %)
More time you spend with someone = the more attractive they become.
(ex. Mere Exposure Effect also called “bar/club” effect: your standards are very high when you enter a bar and then your standards lower the more alcohol you drink and the longer you are with them.)
Matching hypothesis
Tendency to be more attracted to those perceived as similar to us in attractiveness. (1’s like 1’s, 7’s like 7’s but 1’s don't like 7’s)
-the social pressure is so great that the people do not want to be together anymore
-it is too much pressure so if you don't handle it then don't do it
Physical Attractiveness
-men are more focused on physical attractiveness than women
-their number of attractiveness based on external physical attributes
ex: body shape, facial features
Empathy altruism hypothesis
-2 steps
-personal distress/ feeling alarmed/ troubled by seeing someone in a pinch and then you feel empathy and a sense of compassion for the person and that empathy drives you to provide helping behavior regardless of cost or risk consideration
-you see someone in distress then feel empathy for them then you help them regardless of cost or risk
bystander intervention
-the presence of other decreases the likelihood of someone receiving help
-the more people around then the less likely a person will receive help
social exchange theory
-people run a cost / benefit analysis before providing help
-think of all the costs, danger, loss of time, the embarrassment of not providing sufficient help and then think of the reward, personal gain, personal gratification, boost in self-esteem
-takes time to do this and these cognitions are anti-altruism
-cost outweigh benefits = they will not help
-benefit outweigh cost = they will help
diffusion of responsibility
-the more people there are around the less likely you are to help because you think that someone else is closer/ more capable and will assist
Kitty Genovese
-in Queens, NY in March 1964
-she was stabbed by a hunting knife and there were 38-40 confirmed witnesses
-kitty was walking into her apartment complex where she was robbed and stabbed
-the lights flickered on and off and kitty screams for help
-15-20 people yelled leave her alone and get out of there
-the killer leaves
-no one comes down
-the killer comes back and continues to stab her and rob her
-more lights flicker on and off
-25-35 people yelled at the killer to stop and leave her alone but no one came down to help again
-the killer leave and then comes back again
-finishes robbing her and kills her
-people just screamed and left but no one actually came out to help
social facilitation
-The presence of others increases performance in easy tasks
-The presence of others decreases performance in difficult tasks
social loafing
-reducing one's personal efforts while in a group
-people in a group use less effort than they would than when they are alone
Ex: group papers
-each student will give lower effort and only use the amount of effort that they need to
-if you see someone giving a little effort then why are you going to give three times the amount of work as them for the same grade
-if there are 4 group members then each group member should be given equal parts of work to do and they each have individual accountability
deindividuation
-a temporary loss of self awareness or self restraint when someone is anonymous often leading to a behavior inconsistent to their normal values
Ex: police offices because they put on a uniform and become that person
Ex: 1976 halloween study → had mirror → take 1-2 pieces of candy
-people with masks took more candy/ people without masks took 1-2
Ex: post eagles winning the super bowl and rioting
-Why do we do things in groups that we wouldn't do on our own?
-If you could be invisible for 24 hours what would you do?
-rob a bank or stalk people
-usually people do something devious and do not do good deeds
group polarization
-The tendency for group members to lose perspective when engaged in discussions leading to polarization or one-sided views
Ex: extreme liberals clubs → holding discussions with people in your groups → you then have to present a more extreme position than what was previously presented → people lose perspective in group discussions
groupthink
-faulty decision making resulting when groups rush to decisions or make decision hastily in order to maintain group harmony or consensus
Ex: Pearl Harbor → if US airspace was invaded then we should attack → US airspace was not invaded so there was no attack needed → but the US was attacked
Sir Francis Galton
Negatives
-key historical figure in psych that believes in selective breeding
-only those extremely gifted cognitively should be the only ones having children
-low IQ folks will pass down their IQ and dumb down the culture
-stupid people having 2-4 babies and the smart people having 1 baby
-give cash incentives for high IQ folks to have kids with high IQ folks
-their children would receive free schooling for their lives
-give cash to dumb people to get sterilized to not have kids
Positive
-Created correlational research method, mz/ dz twin studies, behavioral genetics research, nature vs nurture study using correlational research
Alfred Binet
-book: IQ a Smart History of a Failed Idea
-a teacher who can get everyone to master the information by knowing where being are mentally
-K-3 only, do not label, do not take it outside of children, and do not talk about genetics
-created a placement test to see where you are strong and weak in certain areas (a special ed diagnostic test)
Lewis Terman
-created Stanford Binet IQ test
-2nd most popular IQ test
-30 points above average is gifted and talented program
-30 points below average is a disability
-Based on this test certain groups of europeans are inferior to others (not what Binet wanted)
-Iq = Mental age/ chronological age x100
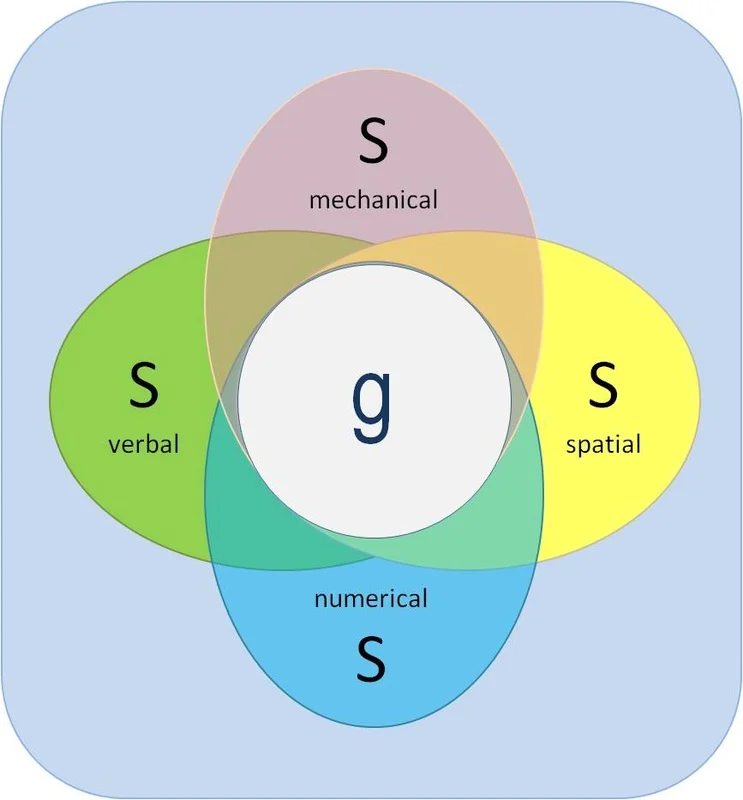
Charles Spearman
Two Factor Theory
1st factor = g
general intelligence
problem solving
2nd factor = s
specific mental abilities
verbal or meth skills
Howard Gardener
Multiple intelligences include
-musical ability
-linguistics
-logical / math
-spatial
-athletic
-memory
Excellence in one does not = excellence in others
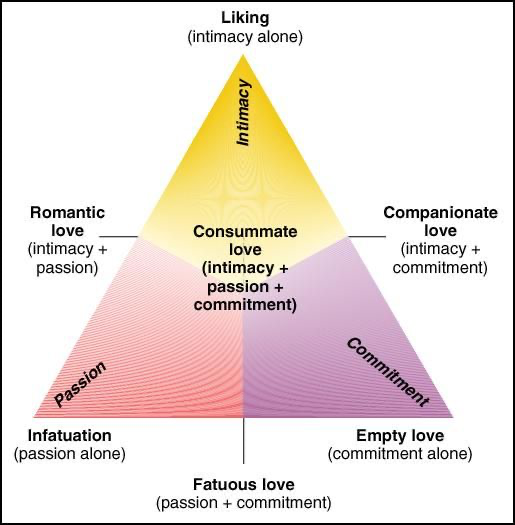
Robert Sternberg
Triangular Theory of Love
1) Intimacy (Liking)
2) Passion (Infatuation)
3) Commitment (Empty Love)
Intimacy + Passion = Romantic Love
Intimacy + Commitment =Companionate Love
Passion + Commitment = Fatuous Love
mental age
your age based off of your abilities to perform well or not on certain tasks
chronoligcial age
the numerical age your are determined by your birthday
IQ
Intelligence quotient
IQ = Mental age/ chronological age x100
emotional intelligence (EQ)
emotional quotient
the ability to understand, use, and manage your own emotions in positive ways
Eugenics Movement
-want a plan of selective breeding
-the culture is being dumbed down for stupid people having 2-4 babies and the smart people having 1 baby
-the educational, political, and health getting taking over my dumb people
Henry Goddard
-the most serious misuser of the IQ test
-Feeble-Minded Girls and Boys in Vineland, New Jersey
-held hostage and starved
-he could tell intelligence based off of facial features
-categories:
1) idiot: a 5 year old with mental age of 2
2) imbecile: a 12 year old with a mental age 3-7
3) moron: an adult with mental age of 8-12
-italians, polish, and russians scored lower because they didn't understand american ideas and did not speak english
Robert Yerkes
-Army Testing (1921)
-gave out IQ test for army soldier in ww1
-if your IQ was low you were in the front line of battle because it would kill them
-it was a way to kill 2 birds with 1 stone
-killed the italians and polish first
-in order to gain citizenship you would serve in the war but that is if you come back
Immigration Restriction Act
-had a quota of the amount of italians/ polish people that were allowed into the country
-the ret of them could not be let into the US
-they scored lower on the IQ tests because they didn't speak english and did not know US customs
test-retest IQ
respondents “learn” to answer the same questions in the first test and this affects their responses in the next test
IQ scores tend to be higher in the next test
Parallel form IQ
differing versions of tests or assessments that contain the same information, only in different order
predictive validity
the ability of a test or other measurement to predict a future outcome
concurrent validity
shows you the extent of agreement between two different measures or assessments taken at the same time
content validity
Is the test fully representative of what it aims to measure?
-must cover all relevant aspects of that concept
construct validity
Does the test measure the concept that it's intended to measure?
-must measure the one specific concept
culture/ gender bias in testing
the tendency of tests to perpetuate certain beliefs about cultures, racial stereotypes, and gender biases that are not inclusive to all learners
ex: what is a slice? a type of hit in golf
only men would really know the answer to his so this is a gender biased question
stereotype threat
a phenomenon where individuals fear confirming negative stereotypes about their social group, leading to anxiety and potentially impacting their performance, especially in academic or professional settings
IQ score mean
the average score for the entire population
100
IQ score standard deviation
15 points
If you have an IQ score of 115 you have an IQ score 1 standard deviation above the mean
IQ score placement
145+
131-145
114-130
85-115 Average
70-84
69-55
54 and below
IQ score mental retardation
Mild: 50-70
Moderate: 35-50
Severe: 20-35
Profound: 20 and below
Weschler Adult Intelligence Scale
an IQ test designed to measure intelligence and cognitive ability in adults and older adolescents
Picture Competition
Object Assembly
Block Design
Information
Digit Span
Similarities
Math
Vocabulary
Comprehension