Soil (The physical environment)
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Soil fertility
The ability of soil to sustain plant growth
Features of fertile soil
Water content, soluble materials, air content, dead organic matter, pH, soil biota, soil texture
Water content (fertile soil)
Fertile soil needs good drainage so it’s not waterlogged, but has enough water for survival of soil biota
Soluble materials (fertile soil)
Fertile soil contains macro nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium all present in ionic form.
They also contain micro nutrients eg. Boron, cobalt, copper, iron, manganese and magnesium
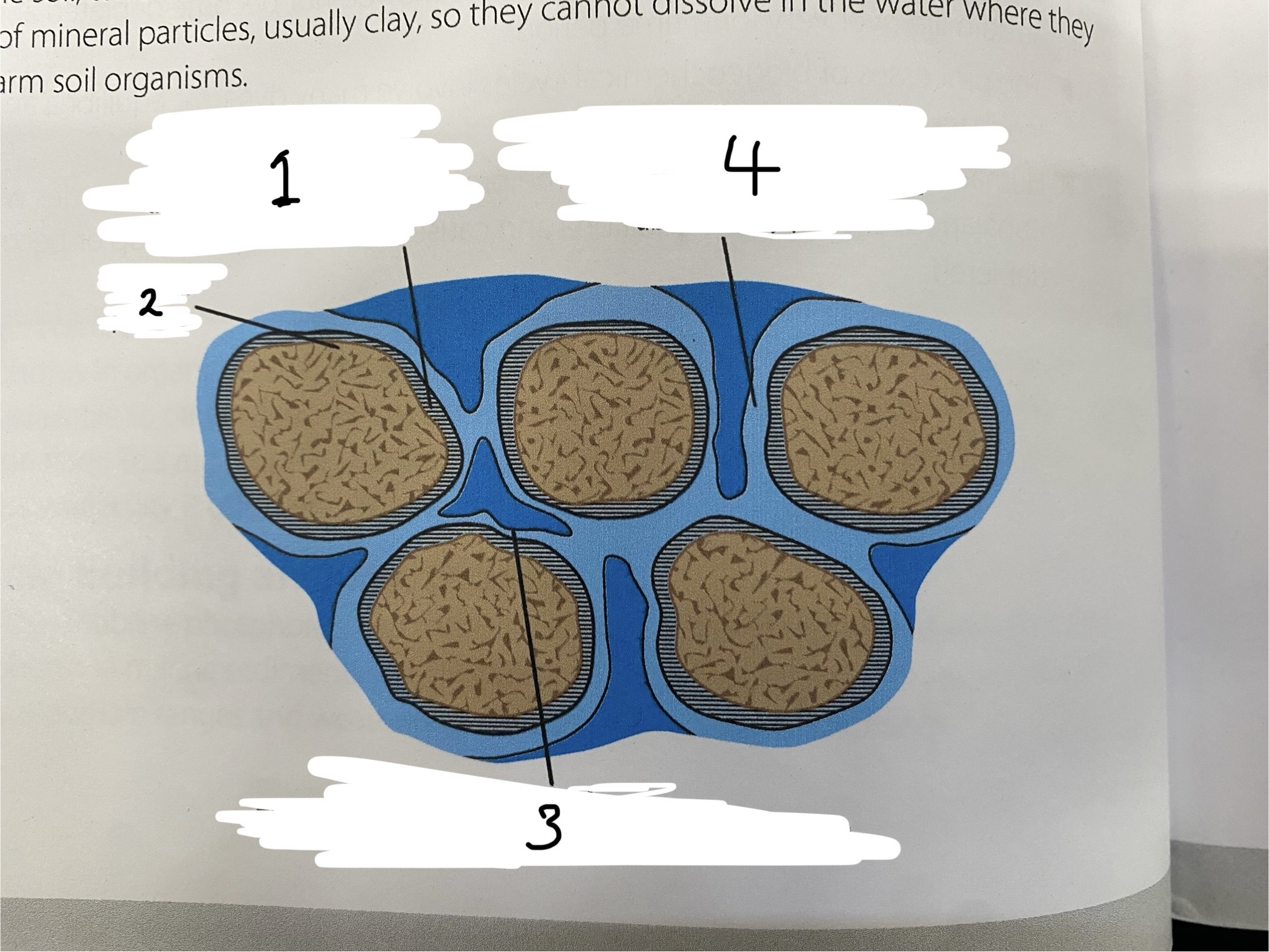
Behavioir of water between soil particles
1- Hygroscopic water held by adhesive forces on the minera particle cant be absorbed by plants
2- mineral particle
3- gravitational water, can be absorbed by plants, drains easily
4- capillary water, water held by soil particles so does not drain from the soil but can be absorbed by plants
Air content (fertile soil)
Living organisms and other processes that increase fertility are aerobic = more aerated soils are likely to be more fertile
Dead organic matter (fertile soil)
Fertile soils have high content of dead organic matter which releases plant nutrients as it decomposes Whig also increases water retention and provides food for soil biota
pH (fertile soil)
Usually on range of pH5.5-pH-7.0 which is the range of tolerance for most plants and soil biota
What is soil biota
Living organisms involved in soil processes that affect soil fertility
Soil biota (fertile soil examples)
Detritivores such as millipedes, wood lice, slugs break up dead organic matter releasing nutrients into the soil
Nitrogen fixing bacteria oxidise ammonium ions to nitrate pins then nitrate ions
Soil structure (fertile soil)
Soil particles form aggregates called peds bound together by polysaccharide gums produced by decomposition. The ped type affects soil properties and fertility
Crumb peds - small, round, produce good drainage and easy root penetration improving soil fertility
Platy peds- large, flat, reduce drainage and root penetration, produce less fertile soils
Soil depth (fertile soil)
Deeper soils are less likely to become waterlogged or to dry out rapidly
How human activities affect soil fertility
Aeration by ploughing and drainage, soil nutrient levels, irrigation, soil compaction
Aeration by ploughing and drainage (human activities-soil fertility)
Ploughing and drainage make soils more aerobic increasing nitrogen fixation nitrification and decomposition of organic matter
Soil nutrient levels (human activities-soil fertility)
Farmers increase levels by adding inorganic fertilisers, organic matter or supporting natural processes eg. Bacterial nitrogen fixation
Farming decreases levels due to soil erosion, biomass removal, inhibiting natural processes eg increased leaching of dissolved nutrients
Irrigation (human activities-soil fertility)
Increases fertility where water is a limiting factor on growth, sufficient water allows plants to keep stomata open and continue gaseous exchange
Soil compaction (human activities-soil fertility)
Excessive use of machinery/livestock causes soil compaction reducing aeration making water logging more likely
Soil texture
Is the proportions of sand silt and clay in the soil
Soil profile
Unique to an area due to climate, properties of original rocks/minerals, time, relief
Sand soil characteristics
Has large air spaces, best drainage rate, but may lead to nutrient loss
Clay soil characteristics
Smallest particles, small air spaces, prone to waterlogging, lower temperature due to high water retention impacting biota enzymes
drainage pipe systems
Installed systems in soil to prevent flooding and maintain oxygen levels for aerobic processes
Zero-tillage farming
Method of farming that avoids disrupting soil structure to maintain fertility and stable humus levels eg ploughing
Why does crop harvesting reduce fertility
Crops remove nutrients during growth and store them in their biomass
Green manure
Crops grown alongside main crops ploughed back into the soil to increase organic matter instead of being harvested
Leguminous crops
Crops containing nitrogen fixing bacteria in their root nodules deciding the need for fertiliser use
Stomata
Pores on a plants lead for gas exchange, importsnt for photosynthesis and respiration, allows water to leave the plant tissue