Anatomy and physiology exam 3
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
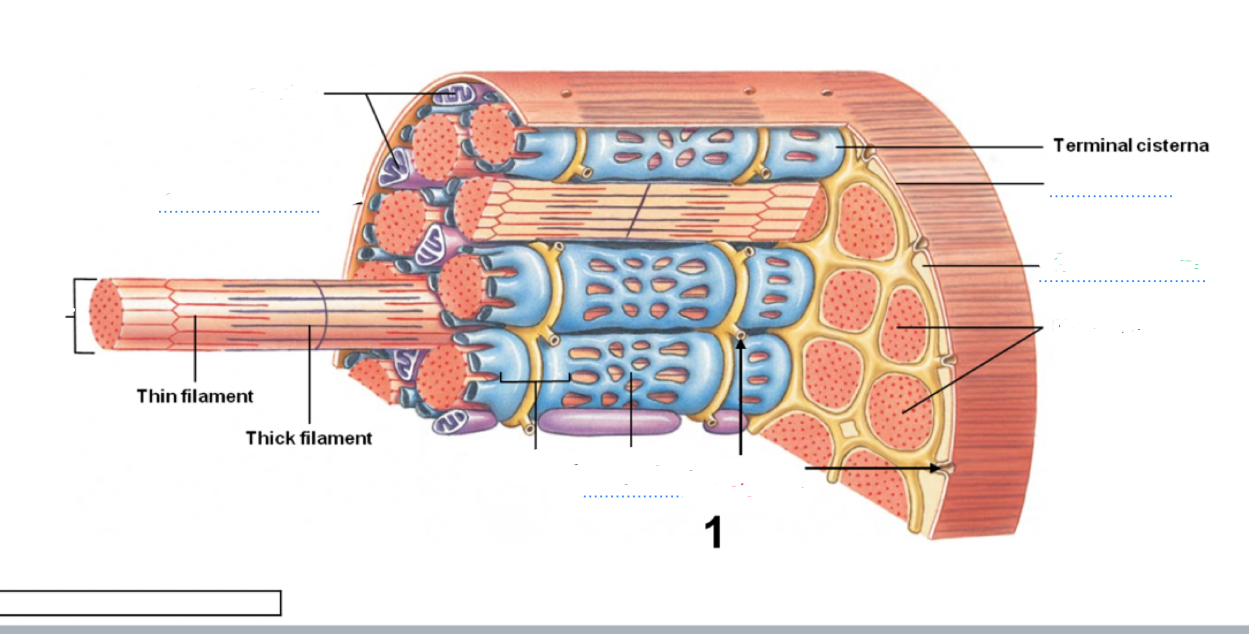
Be able to identify structures of a skeletal muscle. Where is the mitochondria,transverse tubules, sarcoplasmic reticulum, myofibril and sarcolemma located?
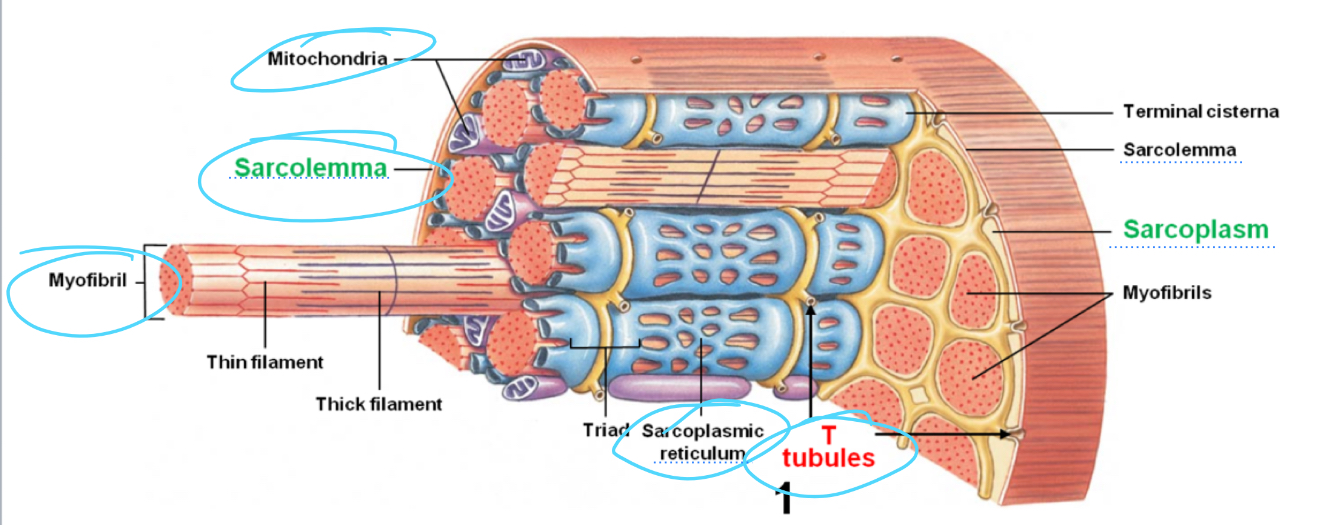
What does the Sarcoplasm reticulum Retain? What does it release to cause a muscle contraction? What causes it to release the substance?
It retains and stores calcium and is released due to a nerve impulse that reaches the fiber, causing ATP to travel along the sarcolemma then the ttub that then activate proteins linked to the calcium Channels on it, causing it to open
Lecture explanation
Cirstenae (part of sacroplasmic reticulum )concentrates and releases, calcium into sacromeresto begin muscle contractions. This is triggered by the action potential coming in from the nerve that flows through the sarcolemma in through the T tubules that released calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
What is the structure and function of the epimysium
Structure: Surrounds the muscle organ and has an exterior collagen layer connected to a deep fascia
Function: Separates muscle from surrounding tissue
Perimysium
Structure: Surrounds the muscle Fascicle
Function: Contains blood vessels and nerves that will feed and innervate myofibers
Endomysium
Structure surrounds the muscle cell(myofiber)
Function has capillaries and nerve fibers that feed and contact myofibers
Also has myosatellite cells that repair myofiber damage
sacromere
Structure: Structural units of myofibrils form stripes
Function it is the contractile unit units of muscles
sacrolemma
Structure plasma membrane of the mayo fiber
Function change in the transmembrane potential leads to contraction cycle
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Structure: membranous structure that surrounds each myofibril
Function-helps transmit AP to myofibril
Releases calcium and retain
Fascicles
Structure : muscle fiber bundles
Function contract, and make force
Myofilaments
Structure within myofibrils and part of sacromere
Function protein filament is responsible for muscle contractions/sliding filament theory
What is a thick filament?
Made of the protein myosin that are dark filaments in A band
What is a thin filament
Made of protein acting that are light filaments I band
How is action potential propagated from the surface to the interior of a muscle fiber? What is the conduit?
Skeleton muscle contracts, when stimulated by mortar neuron in neuromuscular junction, then the AP at the synthetic terminal causes acetylcholine to release into the synaptic cleft which diffuse and binds and open sodium channels that lead to the production of action potential in the sarcolemma that tracks along the t tubules to triads where it triggers the release of calcium ions from the terminal cirstenae of sarcoplasmic reticulum= construction cycles begins the conduit is the TTubules
What is the sequence for contraction of a skeletal muscle?
Neuromuscular junction, then excitation contraction coupling then Crossbridge cycle
The contraction cycle
Tropomyosin shifts leaving the active site exposed then the Cross-bridge forms and the myosin head pivots which advances power strokes(pulls the actin towards center which shorten sarcomere this is the muscle contraction), the Cross bridge detaches, and myosin reactivates
What is the primary neurotransmitter? It is released in the new
Acetycholine
What is troponin?
Troponin is a globular protein that works with tropomyosin and regulates binding affinity of tropomyosin for globular actin structure is modified by binding calcium. This bonding relaxes tropomyosin, exposing the active site on actin that works with myosin to start contractions.
Tropomyosin
is a fibrous double-stranded protein that when the muscle is at rest, it prevents actin and myosin interaction by covering up the active site of actin
Aerobic respiration
This is the primary energy source of resting, skeletal muscle. It uses fatty asses and glycogen.
Anaerobic respiration
Peak muscular activity that uses carbs, lipid Animo acids
It transforms pyruvate to lactic acid and uses glycolysis for ATP known as the Cori cycle
What is the I band?
Only actin filaments are on it. ends of sacromere marked by Z on I band
What is the H band?
Area around M line the only has thick filaments
What is the Zline?
are at the middle of the I band, defines the two ends of the sacromere
Zone of overlap
Dens and darkest area on light microscope, thick and thin, filaments overlap
M line
Is the center of the a band and middle of the sacromere
What structure gets larger during muscle contraction
The I band and the h zone gets small smaller
What do anabolic steroids do?
They stimulate contractile protein synthesis and muscle enlargement. They are similar to testosterone, but have detrimental side effects.
What is atrophy?
Muscle Shrinkage due to the lack of muscle activity which reduces muscle size tone and power
Hypertrophy
Muscle growth from strenuous physical exercise, which increases the diameter of myofibers not the number of them
hyperplasticity
Increase the number of myofibers due to hyperplasia -growth of the muscle tissue by number of muscle fiber rather than the size
You are working out with weights after a while you noticed that your muscles are becoming larger. What is the best explanation?
Muscle hypertrophy the muscle fibers diameters have increased anaerobic training Has fast fibers that fatigue quickly with strenous activity which causes hypertrophy and then improves frequent brief intense workouts
What is a sphincter?
A ring of muscle that surrounds and serves to guard or close and opening or tube an example is the anus
From the PowerPoint, it says a controls the movement of materials through the urethra and anus
Agonist
Produces the prime movement
Antagonist
Contradicts the movement caused by the agonist
Synergist
Assist the larger agonist to start motion
Difference between the agonist and the antagonist
When one contracts the other relaxes
Oblique muscles
Lies within the body wall, which compresses the underlying structures and flexes and rotates vertebral canal
Transverses
Deepest layer of abdominal muscle muscles wrapping around the trunk and assisting in core stabilization
Medialis
Towards the midline of the body
Lateralis
Away from the Midland
Rectus
Lies within the body wall, straight muscles that flex the vertebral column and oppose the erector spinae muscles
These muscles are called "rectus" because their fibers run straight along the body part they are located in and have straight parallel alignment
If you sever the tendon that attaches to the point of insertion of the biceps brachii, what action would be difficult to perform?
Elbow flexion and forearm supination
What is the kissing muscle?
Orbicularis oris
Which eye Muscles are intrinsic
Collard muscle, Iris spincter, and radio pupil dilator
What eye muscles are extrinsic
Inferior medial superior and lateral rectus along with inferior and superior oblique
What does the sternocleidomastoid do?
Flexes and rotates the neck. Not head and pull head down to either shoulder.
You look down at your shoes what eye muscle are you using?
Inferior rectus
As a surgeon, you make an incision that is parallel and lateral to the linear Albea the midline of the abdominal area. What muscle are you cutting
Rectus abdomen is
Were powerful muscle abduct the shoulder
Del toy and the supraspinatus is a helper
What are the rotator cuff muscles?
Super spinatus, subscapularis, infraspinatus, and teres minor
What muscle extend the forearm?
Triceps Breaky
What muscle Dorsiflexes the foot?
tibialis anterior
What muscles composed the quadriceps
The quadriceps femoris Has rectus femoris vagus lateralis medialis and intermedius
The biceps group
Biceps brachi brachioradialis brachialis coracobachialis
The tricep group
Triceps brachi lateral long and medial head
Anconeus
Playing trouble, your tackled heart, and have difficulty getting up trouble flexing your leg. What muscle could you have injured?
The hamstrings
Biceps femoris
Seminembranosus
Semitendinosus
Popliteus
What is the strongest jaw muscle used to elevate the mandible
Masseter