Computer Science Unit 4.4: Theory of Computation
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
What is computational thinking?
Working out how to work things out
What are the methods of problem solving?
Simulation
Enumeration
Trial and Error
Theoretical approach
Creative solution
What does decrease and conquer mean?
Involves finding a solution to a sequence of smaller, related problems until the problem is small enough to be solved directly.
What’s an example of decrease and conquer?
The binary search algorithm
What does iteration mean?
Repetition
Why is structured programming possible?
The structures are built into the programming languages
What does structured programming use to write a computer program?
Top-down analysis for problem-solving.
Modularisation for program structure and organisation.
Structured code for individual modules.
What kind of format does structured programming use?
Top-down design format
What is the program divided down into in a top down design?
Modules
Where are modules called from?
The main program
What can modules be broken down into?
Subtasks
What do the smallest of modules perform?
A single function
What is a hierarchy used to show?
The overall program structure
What are the benefits of structured programming?
Programs are more easily and quickly written
Programs are more reliable and have fewer errors
Programs take less time to test and debug
Programs are easier to maintain
What are 3 qualities of good coding practice?
Use meaningful names for variables and subroutines.
Add lots of comments to explain each module.
Each module should perform a single task.
What is modular programming most useful for?
Large and complex programs
What is an algorithm?
A sequence of steps that can be followed to complete a task and always terminates
What is an example of a problem solved by algorithms?
Sorting large amounts of data
What are 3 properties of a good algorithm?
Has clear and precisely stated steps that produce a correct output for any set of valid inputs.
Should allow for invalid inputs.
Must always terminate at some point.
What is the purpose of testing software?
The purpose of testing software is to reveal errors
What are the stages of testing?
Module testing
Program testing
System testing
What does module testing do?
Makes sure each subroutine works correctly
What does program testing do?
Makes sure each program in the system works correctly
What does system testing do?
Makes sure the whole system works as expected, and does what the original specification required
What are the 3 types of test data?
Normal (typical) data
Boundary data
Erroneous (unexpected) data
What are hand-tracing algorithms useful for?
Figuring out how an algorithm works
Finding out why an algorithm isn’t working properly
What is a trace table used for?
Used to write down the contents of each variable as it changes during execution
What is representational abstraction?
Removing unnecessary details to concentrate on what is necessary to solve the problem
What is an example of information hiding?
The London Underground Map
What is abstraction by generalisation?
Grouping common characteristics to achieve a hierarchal structure
What is an example of abstraction by generalisation?
The bridges of Konigsberg
What is problem abstraction?
Removing details until the problem is possible to solve, as it reduces to one which has already been solved
What is an example of problem abstraction?
The Four Knights Problem
What are the 4 steps of automation?
Building models of real world objects
Decide what details are relevant to the program and discard everything else.
Design algorithms to solve the problem.
Algorithm is then implemented in program code and executed.
What is an example of automation?
A financial model which calculates the likely profit from a coffee shop, based on the available data.
What is decomposition?
Breaking a problem into sub-problems, so that each sub-problem accomplishes an identifiable task
What is composition?
Combining procedures to form a compound procedure and combining data objects to form compound data objects
What is procedural abstraction?
Where you separate the values used in order to keep the actual values used in a computation separate from the overall design
What is an example of procedural abstraction?
drawTriangle("Blue",7.8,4.2)What is functional abstraction?
When you call a function to calculate a square root, or generate a random number
What is an example of functional abstraction?
x = sqrt(17)What is data abstraction?
The data relevant to solving any problem may be in the form of an abstract data structure
What is an example of data abstraction?
A stack
What is a finite state machine (FSM)?
An abstract representation of how something changes from one state to another in response to a condition or event.
What are some facts about FSMs?
The machine can only be in one state at a time.
It can change from one state to another in response to an event or condition.
Is defined by a list of its states and the conditions for each transition.
What is an example of a FSM?
A turnstile
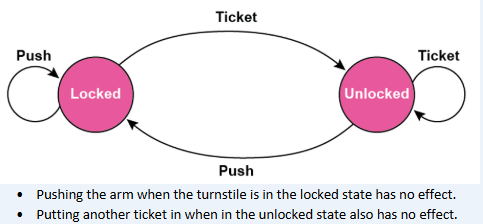
What are 2 examples of the uses of FSMs?
Robotics
Video games industry
What is Finite State Automation?
A FSM which has no output
It has a start state and a set of end or accept states.
If the automation can reach a final state, it is said to accept the input
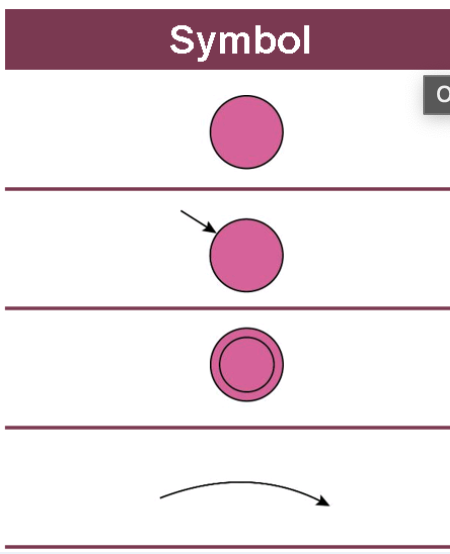
What do the symbols of a FSM mean?
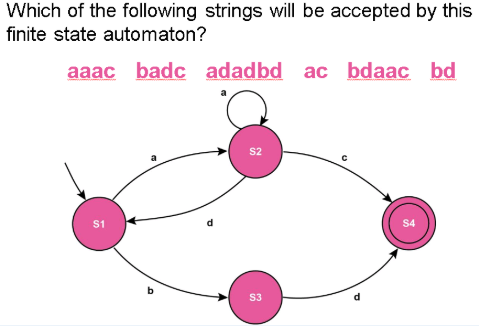
Accepted: aaac, adadbd, ac, bd
Rejected: badc, bdaacS
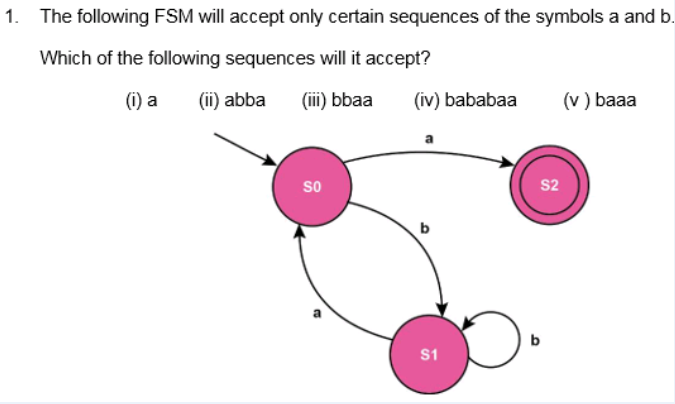
Accepted: a, bbaa, bababaa
Rejected: abba, baaa
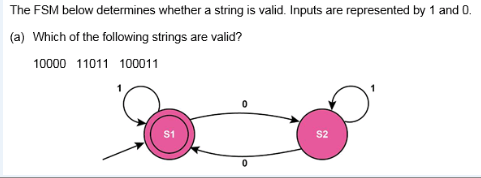
Accepted: 10000
Rejected: 1011, 100011
What are the advantages of structured programming?
Easier to understand
Quicker to write
Less likely to contain errors
What are the disadvantages of structured programming?
Takes time to convert into machine code as it’s machine-independent
The converted machine code is not the same as assembly language
What is linear search?
An algorithm that searches through an array and returns the index of the value it searches for
What is binary search?
An algorithm that searches for the presence of an item stored within an array and requires all items to be in order.